Western Hindi languages
Encyclopedia
Hindi
(in the broad sense) is a subset of the Indo-Aryan language family
in the northern plains of India, bounded on the northwest and west by Punjabi, Sindhi
, Gujarati
and Marathi
; on the east by Maithili
and Bengali
; and on the north by Nepali
. As defined by the 1991 Indian census, Hindi covers a number of Central, East-Central, Eastern, and Northern Zone languages, including the Bihari languages
excepting Maithili
, the Rajasthani languages, and the Pahari languages
excepting Dogri
and Nepali
. However, they do not form a natural clade, as which varieties are considered Hindi, and which not, are determined by social convention rather than by anything intrinsic. Moreover, according to linguists like George Abraham Grierson
, Rajasthani language
is a distinct language and not a dialect of Hindi. Today Sahitya Akademi
, National Academy of Letters and University Grants Commission
recognize it as a distinct language. The Central Zone languages, or Hindi proper
, are conventionally divided into Western
and Eastern Hindi.
"Hindi" in the narrow sense of Standard Hindi is a standardized
register
of one of the Central Zone dialects variously called Khari boli, Hindustani
, Hindawi, or Urdu
.
of Bihar
, Chhattisgarh
, Delhi
, Haryana
, Himachal Pradesh
, Jharkhand
, Madhya Pradesh
, Rajasthan
, Uttar Pradesh
and Uttarakhand
.
Distinctive non-standard varieties of Hindi are spoken in large, urban area
s outside of the Hindi belt. Most notable of these are those spoken in Mumbai
, Kolkata
, and Hyderabad. Overseas forms of Hindi are found in Fiji
, Guyana
, Mauritius
, Suriname
, and Trinidad and Tobago
. Recent immigration to the West – Europe
, USA, etc. – has resulted in the establishment of Hindi-speaking communities there as well.
According to the 2001 Indian census, 258 million people in India (25% of the population) regarded their native language
to be "Hindi". The government, however, counted 422 million Hindi speakers (41% of the population) by including people who identified their language as Awadhi, Bagheli, Bhojpuri (Bihari), Bundeli, Chhattisgarhi, Garhwali, Harauti, Haryanvi, Khortha (Khotta), Kumauni, Lamani (Lambadi), Magadhi (Bihari), Malvi, Marwari, Mewari, Nimadi, Pahari, Rajasthani, and Sadan (Sadri), as well as numerous other languages with fewer than 2 million self-indentified speakers. Note that these figures do not count 52 million Indians who considered their mother tongue to be "Urdu". The numbers are also not directly comparable to the table above; for example, while independent estimates in 2001 counted 37 million speakers of Awadhi, in the 2001 census only 2½ million of these identified their language as "Awadhi" rather than as "Hindi".
Hindi
Standard Hindi, or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi, also known as Manak Hindi , High Hindi, Nagari Hindi, and Literary Hindi, is a standardized and sanskritized register of the Hindustani language derived from the Khariboli dialect of Delhi...
(in the broad sense) is a subset of the Indo-Aryan language family
Indo-Aryan languages
The Indo-Aryan languages constitutes a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages, itself a branch of the Indo-European language family...
in the northern plains of India, bounded on the northwest and west by Punjabi, Sindhi
Sindhi language
Sindhi is the language of the Sindh region of Pakistan that is spoken by the Sindhi people. In India, it is among 22 constitutionally recognized languages, where Sindhis are a sizeable minority. It is spoken by 53,410,910 people in Pakistan, according to the national government's Statistics Division...
, Gujarati
Gujarati language
Gujarati is an Indo-Aryan language, and part of the greater Indo-European language family. It is derived from a language called Old Gujarati which is the ancestor language of the modern Gujarati and Rajasthani languages...
and Marathi
Marathi language
Marathi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Marathi people of western and central India. It is the official language of the state of Maharashtra. There are over 68 million fluent speakers worldwide. Marathi has the fourth largest number of native speakers in India and is the fifteenth most...
; on the east by Maithili
Maithili language
Maithili language is spoken in the eastern region of India and South-eastern region of Nepal. The native speakers of Maithili reside in Bihar, Jharkhand,parts of West Bengal and South-east Nepal...
and Bengali
Bengali language
Bengali or Bangla is an eastern Indo-Aryan language. It is native to the region of eastern South Asia known as Bengal, which comprises present day Bangladesh, the Indian state of West Bengal, and parts of the Indian states of Tripura and Assam. It is written with the Bengali script...
; and on the north by Nepali
Nepali language
Nepali or Nepalese is a language in the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family.It is the official language and de facto lingua franca of Nepal and is also spoken in Bhutan, parts of India and parts of Myanmar...
. As defined by the 1991 Indian census, Hindi covers a number of Central, East-Central, Eastern, and Northern Zone languages, including the Bihari languages
Bihari languages
Bihari is a name given to the western group of Eastern Indic languages, spoken in Bihar and neighboring states in India. Angika, Bajjika, Bhojpuri, Magahi, and Maithili are spoken in Nepal as well. The Angika, Bajjika, Bhojpuri, Magahi and Maithili speaking population form more than 21% of Nepalese...
excepting Maithili
Maithili language
Maithili language is spoken in the eastern region of India and South-eastern region of Nepal. The native speakers of Maithili reside in Bihar, Jharkhand,parts of West Bengal and South-east Nepal...
, the Rajasthani languages, and the Pahari languages
Pahari languages
The Pahari languages are a geographic group of Indic languages spoken in the lower ranges of the Himalayas, from Nepal in the east to the Indian states of Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh and Jammu and Kashmir in the west.-Classification:The Pahari languages fall into three groups:*Eastern, consisting...
excepting Dogri
Dogri language
Dogri is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by about five million people in Pakistan and India, chiefly in the Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir, but also in northern Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, other parts of Jammu and Kashmir, and elsewhere. Dogri speakers are called Dogras, and the Dogri-speaking...
and Nepali
Nepali language
Nepali or Nepalese is a language in the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family.It is the official language and de facto lingua franca of Nepal and is also spoken in Bhutan, parts of India and parts of Myanmar...
. However, they do not form a natural clade, as which varieties are considered Hindi, and which not, are determined by social convention rather than by anything intrinsic. Moreover, according to linguists like George Abraham Grierson
George Abraham Grierson
Sir George Abraham Grierson OM KCIE was born to a prominent Dublin family in 1851. His father and grandfather, both also named George, were well-known printers and publishers.-Biography:Educated at St...
, Rajasthani language
Rajasthani language
Rajasthani Rajasthani Rajasthani (Devanagari: , Perso-Arabic: is a language of the Indo-Aryan languages family. It is spoken by 50 million people in Rajasthan and other states of India and in some areas of Pakistan. The number of speakers may be up to 80 million worldwide...
is a distinct language and not a dialect of Hindi. Today Sahitya Akademi
Sahitya Akademi
The Sahitya Akademi ', India's National Academy of Letters, is an organisation dedicated to the promotion of literature in the languages of India...
, National Academy of Letters and University Grants Commission
University Grants Commission (India)
The University Grants Commission of India is a statutory organisation set up by Union government in 1956, for the coordination, determination and maintenance of standards of university education. It provides recognition for universities in India, and provides funds for government-recognised...
recognize it as a distinct language. The Central Zone languages, or Hindi proper
Hindi languages
The Hindi languages, also known as Madhya and the Central Zone of the Indo-Aryan languages, is a subset of the varieties of Hindi spoken across northern India that descend from the Madhya prakrits, and includes the official languages of India and Pakistan, Hindi and Urdu...
, are conventionally divided into Western
Western Hindi
Western Hindi is a group of Hindi dialects that evolved out of the Apabhramsa form of Shaurseni prakrit. According to G. A. Grierson it comprises such varieties as Haryanvi or Bangaru , Brajbhakha , Bundeli Western Hindi is a group of Hindi dialects that evolved out of the Apabhramsa form of...
and Eastern Hindi.
"Hindi" in the narrow sense of Standard Hindi is a standardized
Standard language
A standard language is a language variety used by a group of people in their public discourse. Alternatively, varieties become standard by undergoing a process of standardization, during which it is organized for description in grammars and dictionaries and encoded in such reference works...
register
Register (linguistics)
In linguistics, a register is a variety of a language used for a particular purpose or in a particular social setting. For example, when speaking in a formal setting an English speaker may be more likely to adhere more closely to prescribed grammar, pronounce words ending in -ing with a velar nasal...
of one of the Central Zone dialects variously called Khari boli, Hindustani
Hindustani language
Hindi-Urdu is an Indo-Aryan language and the lingua franca of North India and Pakistan. It is also known as Hindustani , and historically, as Hindavi or Rekhta...
, Hindawi, or Urdu
Urdu
Urdu is a register of the Hindustani language that is identified with Muslims in South Asia. It belongs to the Indo-European family. Urdu is the national language and lingua franca of Pakistan. It is also widely spoken in some regions of India, where it is one of the 22 scheduled languages and an...
.
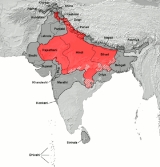
Demographics
The Hindi languages predominate in the Indian states and union territoriesStates and territories of India
India is a federal union of states comprising twenty-eight states and seven union territories. The states and territories are further subdivided into districts and so on.-List of states and territories:...
of Bihar
Bihar
Bihar is a state in eastern India. It is the 12th largest state in terms of geographical size at and 3rd largest by population. Almost 58% of Biharis are below the age of 25, which is the highest proportion in India....
, Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh is a state in Central India, formed when the 16 Chhattisgarhi-speaking South-Eastern districts of Madhya Pradesh gained separate statehood on 1 November 2000....
, Delhi
Delhi
Delhi , officially National Capital Territory of Delhi , is the largest metropolis by area and the second-largest by population in India, next to Mumbai. It is the eighth largest metropolis in the world by population with 16,753,265 inhabitants in the Territory at the 2011 Census...
, Haryana
Haryana
Haryana is a state in India. Historically, it has been a part of the Kuru region in North India. The name Haryana is found mentioned in the 12th century AD by the apabhramsha writer Vibudh Shridhar . It is bordered by Punjab and Himachal Pradesh to the north, and by Rajasthan to the west and south...
, Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh is a state in Northern India. It is spread over , and is bordered by the Indian states of Jammu and Kashmir on the north, Punjab on the west and south-west, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh on the south, Uttarakhand on the south-east and by the Tibet Autonomous Region on the east...
, Jharkhand
Jharkhand
Jharkhand is a state in eastern India. It was carved out of the southern part of Bihar on 15 November 2000. Jharkhand shares its border with the states of Bihar to the north, Uttar Pradesh and Chhattisgarh to the west, Orissa to the south, and West Bengal to the east...
, Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh , often called the Heart of India, is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal and Indore is the largest city....
, Rajasthan
Rajasthan
Rājasthān the land of Rajasthanis, , is the largest state of the Republic of India by area. It is located in the northwest of India. It encompasses most of the area of the large, inhospitable Great Indian Desert , which has an edge paralleling the Sutlej-Indus river valley along its border with...
, Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh abbreviation U.P. , is a state located in the northern part of India. With a population of over 200 million people, it is India's most populous state, as well as the world's most populous sub-national entity...
and Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand , formerly Uttaranchal, is a state in the northern part of India. It is often referred to as the Land of Gods due to the many holy Hindu temples and cities found throughout the state, some of which are among Hinduism's most spiritual and auspicious places of pilgrimage and worship...
.
Distinctive non-standard varieties of Hindi are spoken in large, urban area
Urban area
An urban area is characterized by higher population density and vast human features in comparison to areas surrounding it. Urban areas may be cities, towns or conurbations, but the term is not commonly extended to rural settlements such as villages and hamlets.Urban areas are created and further...
s outside of the Hindi belt. Most notable of these are those spoken in Mumbai
Mumbai
Mumbai , formerly known as Bombay in English, is the capital of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the most populous city in India, and the fourth most populous city in the world, with a total metropolitan area population of approximately 20.5 million...
, Kolkata
Kolkata
Kolkata , formerly known as Calcutta, is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal. Located on the east bank of the Hooghly River, it was the commercial capital of East India...
, and Hyderabad. Overseas forms of Hindi are found in Fiji
Fiji
Fiji , officially the Republic of Fiji , is an island nation in Melanesia in the South Pacific Ocean about northeast of New Zealand's North Island...
, Guyana
Guyana
Guyana , officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, previously the colony of British Guiana, is a sovereign state on the northern coast of South America that is culturally part of the Anglophone Caribbean. Guyana was a former colony of the Dutch and of the British...
, Mauritius
Mauritius
Mauritius , officially the Republic of Mauritius is an island nation off the southeast coast of the African continent in the southwest Indian Ocean, about east of Madagascar...
, Suriname
Suriname
Suriname , officially the Republic of Suriname , is a country in northern South America. It borders French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west, Brazil to the south, and on the north by the Atlantic Ocean. Suriname was a former colony of the British and of the Dutch, and was previously known as...
, and Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago is an archipelagic state in the southern Caribbean, lying just off the coast of northeastern Venezuela and south of Grenada in the Lesser Antilles...
. Recent immigration to the West – Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, USA, etc. – has resulted in the establishment of Hindi-speaking communities there as well.
Number of speakers
Population data from the 16th (2009) edition of Ethnologue is as follows, counting languages with two million or more speakers:- Central zone (Hindi proper)
- Western HindiWestern HindiWestern Hindi is a group of Hindi dialects that evolved out of the Apabhramsa form of Shaurseni prakrit. According to G. A. Grierson it comprises such varieties as Haryanvi or Bangaru , Brajbhakha , Bundeli Western Hindi is a group of Hindi dialects that evolved out of the Apabhramsa form of...
(West Central zone)- 240 M Hindi-Urdu (HindustaniHindustani languageHindi-Urdu is an Indo-Aryan language and the lingua franca of North India and Pakistan. It is also known as Hindustani , and historically, as Hindavi or Rekhta...
, KhariboliKhariboliKhariboli , also Khari Boli, Khadiboli, Khadi Boli or simply Khari, is a Western Hindi dialect spoken mainly in the rural surroundings of Delhi, the northern areas of Western Uttar Pradesh and the southern areas of Uttarakhand in India...
, numbers out of date) - 13 M Haryanvi (numbers out of date)
- 10 M Kanauji
- 240 M Hindi-Urdu (Hindustani
- Eastern Hindi (East Central zone)
- 38 M AwadhiAwadhi languageAwadhi is an Indo-Aryan language, part of the Hindi-Urdu continuum. It is spoken chiefly in the Awadh region of Uttar Pradesh, although its speakers are also found in Madhya Pradesh, Delhi and Nepal. Furthermore, the Fiji Hindi dialect spoken by Indo-Fijians is considered a variant of Awadhi,...
- 18 M ChhattisgarhiChhattisgarhi languageChhattisgarhi is the official language in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh and has approximately 17.5 million speakers. It is an East Central Indo-Iranian language with heavy presence of vocabulary and linguistic features from Munda and Dravidian languages...
- 8 M BagheliBagheliBagheli is a language of the Baghelkhand region of central India. It is often considered to be a dialect of Hindi language, and is classified such by the Indian Census Report ....
- 38 M Awadhi
- Western Hindi
- RajasthaniRajasthani languageRajasthani Rajasthani Rajasthani (Devanagari: , Perso-Arabic: is a language of the Indo-Aryan languages family. It is spoken by 50 million people in Rajasthan and other states of India and in some areas of Pakistan. The number of speakers may be up to 80 million worldwide...
(part of Western Zone, which also includes GujaratiGujarati languageGujarati is an Indo-Aryan language, and part of the greater Indo-European language family. It is derived from a language called Old Gujarati which is the ancestor language of the modern Gujarati and Rajasthani languages...
and BhiliBhili languageBhili is a Western Indo-Aryan language spoken in west-central India, in the region east of Ahmedabad. Other names for the language include Bhagoria and Bhilboli; varieties are Wagdi and Garasia. Bhili is a member of the Bhil language family, which is related to Gujarati and the Rajasthani language...
) Today Sahitya AkademiSahitya AkademiThe Sahitya Akademi ', India's National Academy of Letters, is an organisation dedicated to the promotion of literature in the languages of India...
, National Academy of Letters and University Grants CommissionUniversity Grants Commission (India)The University Grants Commission of India is a statutory organisation set up by Union government in 1956, for the coordination, determination and maintenance of standards of university education. It provides recognition for universities in India, and provides funds for government-recognised...
recognize RajasthaniRajasthani languageRajasthani Rajasthani Rajasthani (Devanagari: , Perso-Arabic: is a language of the Indo-Aryan languages family. It is spoken by 50 million people in Rajasthan and other states of India and in some areas of Pakistan. The number of speakers may be up to 80 million worldwide...
as a distinct language.- 31 M Marwari-MerwariMarwari languageThe Marwari language , also variously Marvari, Marwadi, Marvadi), is spoken in the Indian state of Rajasthan. Marwari is also found in the neighboring state of Gujarat and Haryana and in Eastern Pakistan...
- 10 M MalviMalvi languageMalvi is the language of the Malva region of India, with sixteen million speakers. Nimadi, spoken in the Nimar region of Madhya Pradesh and in Rajasthan, is its closest relative...
- 6 M LambadiLambadi languageLambadi is a Rajasthani language spoken by nomadic Banjara people across India.The language is known by various other names, including Lamani, Lamadi, Lambani, Labhani, Lambara, Lavani, Lemadi, Lumadale, Labhani Muka and variants, Banjara, Banjari, Bangala, Banjori, Banjuri, Brinjari, Vanjari,...
- 5 M HarautiHarauti languageThe Harauti language is a dialect of Rajasthani language of Indo-Aryan language family. It is spoken in historical Hadoti region: Kota, Baran, Bundi and Jhalawar districts of Rajasthan and its adjacent areas of Madhya Pradesh....
- 3 M Godwari
- 2 M BagriBagri languageBagri is a dialect of Rajasthani language of the Indo-Aryan family. It is spoken by about five million speakers in Hanumangarh and Sriganganagar districts of Rajasthan, Sirsa and Hissar districts of Haryana, Firozepur and Muktsar districts of Punjab of India and Bahawalpur and Bahawalnagar areas...
- 31 M Marwari-Merwari
- Bihari languagesBihari languagesBihari is a name given to the western group of Eastern Indic languages, spoken in Bihar and neighboring states in India. Angika, Bajjika, Bhojpuri, Magahi, and Maithili are spoken in Nepal as well. The Angika, Bajjika, Bhojpuri, Magahi and Maithili speaking population form more than 21% of Nepalese...
apart from MaithiliMaithili languageMaithili language is spoken in the eastern region of India and South-eastern region of Nepal. The native speakers of Maithili reside in Bihar, Jharkhand,parts of West Bengal and South-east Nepal...
(part of Eastern zone, which also includes BengaliBengali languageBengali or Bangla is an eastern Indo-Aryan language. It is native to the region of eastern South Asia known as Bengal, which comprises present day Bangladesh, the Indian state of West Bengal, and parts of the Indian states of Tripura and Assam. It is written with the Bengali script...
and OriyaOriya languageOriya , officially Odia from November, 2011, is an Indian language, belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family. It is mainly spoken in the Indian states of Orissa and West Bengal...
)- 39 M: BhojpuriBhojpuri languageBhojpuri is a language spoken in parts of north-central and eastern India. It is spoken in the western part of state of Bihar, the northwestern part of Jharkhand, and the Purvanchal region of Uttar Pradesh , as well as adjoining parts of the Nepal Terai. Bhojpuri is also spoken in Guyana,...
(the Hindi of SurinameSurinameSuriname , officially the Republic of Suriname , is a country in northern South America. It borders French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west, Brazil to the south, and on the north by the Atlantic Ocean. Suriname was a former colony of the British and of the Dutch, and was previously known as...
and MauritiusMauritiusMauritius , officially the Republic of Mauritius is an island nation off the southeast coast of the African continent in the southwest Indian Ocean, about east of Madagascar...
) - 13 M: Magadhi
- 2 M: SadriSadri languageSadri is a branch of Prakrit language and is regarded as a sister language of Oriya, Bengali and Angika. It is spoken in the Indian states of Jharkhand, Orissa and the north of West Bengal, and in Bangladesh....
- 39 M: Bhojpuri
- Central Pahari (part of Northern zone, which also includes NepaliNepali languageNepali or Nepalese is a language in the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family.It is the official language and de facto lingua franca of Nepal and is also spoken in Bhutan, parts of India and parts of Myanmar...
)- 3 M GarhwaliGarhwaliThe Garhwali language is a Central Pahari language belonging to the Northern Zone of Indo-Aryan languages. It is primarily spoken by the Garhwali people who are from the north-western Garhwal Division of the northern Indian state of Uttarakhand in the Indian Himalayas.The Central Pahari...
- 3 M Kumaoni (numbers out of date)
- 3 M Garhwali
- Western Pahari apart from DogriDogri languageDogri is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by about five million people in Pakistan and India, chiefly in the Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir, but also in northern Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, other parts of Jammu and Kashmir, and elsewhere. Dogri speakers are called Dogras, and the Dogri-speaking...
(part of Northwestern zone, which also includes Panjabi)- 2 M Pahari
- 2M KangriKangri languageKangri is a dialect spoken in northern India, predominantly in the Kangra district of Himachal Pradesh, by the people of the Kangra Valley. It is an Indo-Aryan dialect, related to Dogri and classified as one of the Western Pahari group of languages, with deep vocabulary impact from Punjabi, which...
According to the 2001 Indian census, 258 million people in India (25% of the population) regarded their native language
First language
A first language is the language a person has learned from birth or within the critical period, or that a person speaks the best and so is often the basis for sociolinguistic identity...
to be "Hindi". The government, however, counted 422 million Hindi speakers (41% of the population) by including people who identified their language as Awadhi, Bagheli, Bhojpuri (Bihari), Bundeli, Chhattisgarhi, Garhwali, Harauti, Haryanvi, Khortha (Khotta), Kumauni, Lamani (Lambadi), Magadhi (Bihari), Malvi, Marwari, Mewari, Nimadi, Pahari, Rajasthani, and Sadan (Sadri), as well as numerous other languages with fewer than 2 million self-indentified speakers. Note that these figures do not count 52 million Indians who considered their mother tongue to be "Urdu". The numbers are also not directly comparable to the table above; for example, while independent estimates in 2001 counted 37 million speakers of Awadhi, in the 2001 census only 2½ million of these identified their language as "Awadhi" rather than as "Hindi".
Outside the Indian subcontinent
Much of the Hindi spoken outside of the subcontinent is quite distinct from the India-Pakistan standard language. In addition, the language of Muslims is commonly called "Hindi" or "Hindustani" rather than "Urdu".- Mauritian Hindi, spoken in MauritiusMauritiusMauritius , officially the Republic of Mauritius is an island nation off the southeast coast of the African continent in the southwest Indian Ocean, about east of Madagascar...
, based on Bhojpuri and influenced by French. - Sarnami, a form of Bhojpuri with Awadhi influence spoken by SurinameSurinameSuriname , officially the Republic of Suriname , is a country in northern South America. It borders French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west, Brazil to the south, and on the north by the Atlantic Ocean. Suriname was a former colony of the British and of the Dutch, and was previously known as...
rs of Indian descent. - Fiji HindiFiji HindiFiji Hindi, also known as Fijian Hindi or Fijian Hindustani, is the language spoken by most Fijian citizens of Indian descent. It is derived mainly from the Awadhi and Bhojpuri varieties of Hindi. It has also borrowed a large number of words from Fijian and English. The relation between Fiji Hindi...
, derived form of Awadhi, Bhojpuri and including many English and native FijianFijian languageFijian is an Austronesian language of the Malayo-Polynesian family spoken in Fiji. It has 450,000 first-language speakers, which is less than half the population of Fiji, but another 200,000 speak it as a second language...
words, is spoken by FijiFijiFiji , officially the Republic of Fiji , is an island nation in Melanesia in the South Pacific Ocean about northeast of New Zealand's North Island...
ans of Indian descent. - Trinidad Hindi, based on Bhojpuri, and spoken in Trinidad and TobagoTrinidad and TobagoTrinidad and Tobago officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago is an archipelagic state in the southern Caribbean, lying just off the coast of northeastern Venezuela and south of Grenada in the Lesser Antilles...
by people of Indian descent. - South African Hindi, based on Bhojpuri, and spoken in South AfricaSouth AfricaThe Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
by people of Indian descent.
See also
- History of Hindi
- Languages of IndiaLanguages of IndiaThe languages of India belong to several language families, the major ones being the Indo-European languages—Indo-Aryan and the Dravidian languages...
and Official languages of India - List of Indian languages by total speakers
- List of Central Indo-Aryan languages

