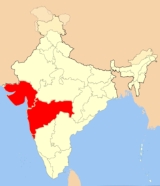
West India
Encyclopedia
West India or the Western region of India
consists of the states
of Goa, Gujarat and Maharashtra
, along with the Union Territories of Daman and Diu and Dadra and Nagar Haveli. It is highly industrialized, with a large urban population. Most of Western India was part of the Maratha Empire
before colonization by the British. The regions became part of India upon independence, and took their current form after the States Reorganization Act of 1956. The states are roughly bounded by the Thar Desert
in the northwest, the Vindhya Range
in the north and the Arabian Sea
in the west. A major portion of Western India shares the Deccan Plateau
with South India
. Before the partition of India, Sindh
and Balochistan
were also included in this region.
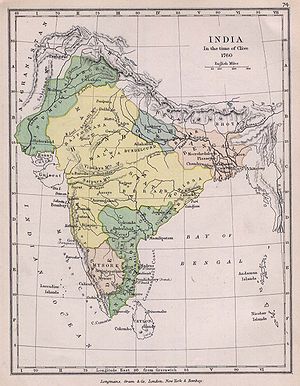 (For detailed history please read the respective articles of the three western states: Maharashtra, Goa, Gujarat)
(For detailed history please read the respective articles of the three western states: Maharashtra, Goa, Gujarat)
Parts of Gujarat were the site of Indus Valley Civilization
. Sites have been uncovered in Gujarat at Lothal
, Surkotada
, and around Ghaggar river in Rajasthan
. The Western Indian region was ruled by the Maurya Kingdom, Gurjars, Rajputs, Satavahanas, Western Satraps, Indo Greeks etc. in the ancients times. During the medieval age, the region came under Persian
influence and also under Mughal
rule. Later, the Maratha Empire
which arose in western Maharashtra came to dominate a major portion of the Indian sub-continent. However its defeat by the British in the Anglo-Maratha
wars left most of India under colonial rule. The region then experienced great upheavals during the struggle for Indian Independence. Gandhi's Dandi March took place in Gujarat. The region became part of independent India in 1947, and the present state boundaries were drawn based on linguistic considerations in 1956.
 The region consists of the predominantly arid to semi-arid region of Saurashtra and Kutch in the North. The region South of that of Cambay and Southern Gujarat makes the northern semi arid region and the southern humid region submerge, though this region itself being the humid to sub humid. The Western Ghats
The region consists of the predominantly arid to semi-arid region of Saurashtra and Kutch in the North. The region South of that of Cambay and Southern Gujarat makes the northern semi arid region and the southern humid region submerge, though this region itself being the humid to sub humid. The Western Ghats
and Konkan
lie along the coast of Maharashtra and Goa. The Deccan plains of the Vidarbha
, Marathwada
in central and eastern Maharashtra define the rest of the region. The vegetation varies from tropical rainforests along the Konkan coast to thorny bushes and shrubs in northern Gujarat. The rivers in this region are the Narmada
, Tapti, Godavari, Zuari, Mandovi, Krishna
, Ghaggar, Chambal
and many other smaller tributaries of other rivers.
and northern Konkan
regions experience cooler winters with minimum temperatures hovering around 12 °C. Interior Maharashtra experiences hot summers
with maximum temperatures averaging 40°C and mild winters
with minimum temperatures
averaging about 10°C. Gujarat also has a warm climate with hot summers and cool winters.
 The majority follow Hinduism
The majority follow Hinduism
and there are significant minority who follow Islam
and smaller number who follow Buddhism
and Christianity
. There are also a few indigenous Jews called the Bene Israel
who speak Marathi
. The Parsees who settled in Gujarat made Mumbai and Surat
their home. Significant percentages of Jains
and Buddhists can be found too. Most Christians live in the state of Goa.
Overall, 83.66 % of the population is Hindu
, 10.12 % Muslim
, 4 % Buddhist with Christians in Goa and Maharashtra making up the majority of the remainder. Marathi, with about 73 million speakers is the most widely spoken language, followed by Gujarati
with about 46 million speakers and Konkani
2.5 million speakers, all of which are Indo-Aryan languages
. As in other parts of India, a high level of multilingualism
is seen with English and Hindi being spoken as additional languages in urban areas.
 The average literacy rate of West India is around 76%, higher than the national average of 70.5%. The population density
The average literacy rate of West India is around 76%, higher than the national average of 70.5%. The population density
is around 290 per square km. The average fertility rate is about 2.2, while the average household size is about 4.7.
 The states of Maharashtra, Goa and Gujarat are varied and distinct. 450 years of brutal Portuguese
The states of Maharashtra, Goa and Gujarat are varied and distinct. 450 years of brutal Portuguese
rule has influenced Goa a lot. The architecture of Goa is a unique blend of Indian and Portuguese
cultures. Goa is also well known for its beaches, temples and churches.
Maharashtrian culture derives from the ancient Indo-Aryan
Vedic
culture influenced deeply by the Maratha Empire and British
colonial rule. Maharashtrians
take great pride in the Maratha Empire
, and many places in Maharashtra are named after the founder of the Empire, Shivaji. Marathi literature
and cinema
are popular in the state as well as across India.
Gujarati culture includes both Hindu and Islamic influence. It has also been influenced by the Parsis, who migrated to Gujarat from Iran
about a 1000 years ago. Recently events like Rann Utsav, International Kite Festival and Global Garba festivals have been started to showcase its culture internationally. Mumbai and Goa
are renowned for their nightlifes. Bollywood
has had a huge impact on the lifestyle and culture of this part of India as Bollywood
is situated in Mumbai.

 The cuisine of Western India is diverse. Maharashtrian cuisine
The cuisine of Western India is diverse. Maharashtrian cuisine
is diverse and ranges from bland to fiery hot. Pohay
, Shrikhand
, Pav Bhaji
, Vada Pav
are good examples of Maharashtrian cuisine
. Goan cuisine
is dominated by the use of rice, coconut, seafood, Kokum, cashew-nuts.With its distinct spices and medium of cooking as coconut oil, both vegetarian as well as non-vegetarian cuisine is equally popular.
Gujarati cuisine
is almost exclusively vegetarian. Gujarat is one of three states in India, with prohibition on alcohol, along with Mizoram
and Manipur
. In contrast, Maharashtra has some of the best vineyard
s in India
, with Nashik and Sangli
districts being the country's biggest grape-producing districts.
of the country. More than 85% of the households have access to electricity with about 55% owning a television. Agriculture
employs most people in the region, while services have largest share in the total GDP.
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
consists of the states
States and territories of India
India is a federal union of states comprising twenty-eight states and seven union territories. The states and territories are further subdivided into districts and so on.-List of states and territories:...
of Goa, Gujarat and Maharashtra
Maharashtra
Maharashtra is a state located in India. It is the second most populous after Uttar Pradesh and third largest state by area in India...
, along with the Union Territories of Daman and Diu and Dadra and Nagar Haveli. It is highly industrialized, with a large urban population. Most of Western India was part of the Maratha Empire
Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire or the Maratha Confederacy was an Indian imperial power that existed from 1674 to 1818. At its peak, the empire covered much of South Asia, encompassing a territory of over 2.8 million km²....
before colonization by the British. The regions became part of India upon independence, and took their current form after the States Reorganization Act of 1956. The states are roughly bounded by the Thar Desert
Thar Desert
The Thar Desert |Punjab]] province. The Cholistan Desert adjoins the Thar desert spreading into Pakistani Punjab province.-Location and description:...
in the northwest, the Vindhya Range
Vindhya Range
The Vindhya Range is a range of older rounded mountains and hills in the west-central Indian subcontinent, which geographically separates the Indian subcontinent into northern India and Southern India.- Introduction :...
in the north and the Arabian Sea
Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea is a region of the Indian Ocean bounded on the east by India, on the north by Pakistan and Iran, on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, on the south, approximately, by a line between Cape Guardafui in northeastern Somalia and Kanyakumari in India...
in the west. A major portion of Western India shares the Deccan Plateau
Deccan Plateau
The Deccan Plateau is a large plateau in India, making up the majority of the southern part of the country. It rises a hundred meters high in the north, rising further to more than a kilometers high in the south, forming a raised triangle nested within the familiar downward-pointing triangle of...
with South India
South India
South India is the area encompassing India's states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu as well as the union territories of Lakshadweep and Pondicherry, occupying 19.31% of India's area...
. Before the partition of India, Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
and Balochistan
Balochistan (Pakistan)
Balochistan is one of the four provinces or federating units of Pakistan. With an area of 134,051 mi2 or , it is the largest province of Pakistan, constituting approximately 44% of the total land mass of Pakistan. According to the 1998 population census, Balochistan had a population of...
were also included in this region.
History

Parts of Gujarat were the site of Indus Valley Civilization
Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilization was a Bronze Age civilization that was located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, consisting of what is now mainly modern-day Pakistan and northwest India...
. Sites have been uncovered in Gujarat at Lothal
Lothal
Lothal is one of the most prominent cities of the ancient Indus valley civilization. Located in Bhāl region of the modern state of Gujarāt and dating from 2400 BCE. Discovered in 1954, Lothal was excavated from February 13, 1955 to May 19, 1960 by the Archaeological Survey of India...
, Surkotada
Surkotada
Surkotada is an archeological site located in India. It contains horse remains dated to ca. 2000 BCE .-Location and environment:The site at Surkotada is located 160 km north-east of Bhuj, in the district of Kutch, Gujarat. The ancient mound stands surrounded by an undulating rising ground...
, and around Ghaggar river in Rajasthan
Rajasthan
Rājasthān the land of Rajasthanis, , is the largest state of the Republic of India by area. It is located in the northwest of India. It encompasses most of the area of the large, inhospitable Great Indian Desert , which has an edge paralleling the Sutlej-Indus river valley along its border with...
. The Western Indian region was ruled by the Maurya Kingdom, Gurjars, Rajputs, Satavahanas, Western Satraps, Indo Greeks etc. in the ancients times. During the medieval age, the region came under Persian
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
influence and also under Mughal
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
rule. Later, the Maratha Empire
Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire or the Maratha Confederacy was an Indian imperial power that existed from 1674 to 1818. At its peak, the empire covered much of South Asia, encompassing a territory of over 2.8 million km²....
which arose in western Maharashtra came to dominate a major portion of the Indian sub-continent. However its defeat by the British in the Anglo-Maratha
Third Anglo-Maratha War
The Third Anglo-Maratha War was the final and decisive conflict between the British East India Company and the Maratha Empire in India. The war left the Company in control of most of India. It began with an invasion of Maratha territory by 110,400 British East India Company troops, the largest...
wars left most of India under colonial rule. The region then experienced great upheavals during the struggle for Indian Independence. Gandhi's Dandi March took place in Gujarat. The region became part of independent India in 1947, and the present state boundaries were drawn based on linguistic considerations in 1956.
Geography

Western Ghats
The Western Ghats, Western Ghauts or the Sahyādri is a mountain range along the western side of India. It runs north to south along the western edge of the Deccan Plateau, and separates the plateau from a narrow coastal plain along the Arabian Sea. The Western Ghats block rainfall to the Deccan...
and Konkan
Konkan
The Konkan also called the Konkan Coast or Karavali is a rugged section of the western coastline of India from Raigad to Mangalore...
lie along the coast of Maharashtra and Goa. The Deccan plains of the Vidarbha
Vidarbha
Vidarbha is the eastern region of Maharashtra state made up of Nagpur Division and Amravati Division. Its former name is Berar . It occupies 31.6% of total area and holds 21.3% of total population of Maharashtra...
, Marathwada
Marathwada
The name Marathwada identifies one of the five regions in Maharashtra state of India. The region coincides with the Aurangabad Division.-Historical highlights:...
in central and eastern Maharashtra define the rest of the region. The vegetation varies from tropical rainforests along the Konkan coast to thorny bushes and shrubs in northern Gujarat. The rivers in this region are the Narmada
Narmada River
The Narmada , also called Rewa is a river in central India and the fifth largest river in the Indian subcontinent. It is the third largest river that completely flows within India after Ganges and Godavari...
, Tapti, Godavari, Zuari, Mandovi, Krishna
Krishna
Krishna is a central figure of Hinduism and is traditionally attributed the authorship of the Bhagavad Gita. He is the supreme Being and considered in some monotheistic traditions as an Avatar of Vishnu...
, Ghaggar, Chambal
Chambal Division
Chambal Division is an administrative geographical unit of Madhya Pradesh state of India. Morena is the administrative headquarters of the division. Currently , the division consists of the three districts of Morena, Bhind and Sheopur....
and many other smaller tributaries of other rivers.
Climate
The climate varies between tropical wet, tropical wet and dry, and semi arid. The coastal regions experience little seasonal variations although the temperatures range between 20°C to 38°C. MumbaiMumbai
Mumbai , formerly known as Bombay in English, is the capital of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the most populous city in India, and the fourth most populous city in the world, with a total metropolitan area population of approximately 20.5 million...
and northern Konkan
Konkan
The Konkan also called the Konkan Coast or Karavali is a rugged section of the western coastline of India from Raigad to Mangalore...
regions experience cooler winters with minimum temperatures hovering around 12 °C. Interior Maharashtra experiences hot summers
Summer
Summer is the warmest of the four temperate seasons, between spring and autumn. At the summer solstice, the days are longest and the nights are shortest, with day-length decreasing as the season progresses after the solstice...
with maximum temperatures averaging 40°C and mild winters
Winter
Winter is the coldest season of the year in temperate climates, between autumn and spring. At the winter solstice, the days are shortest and the nights are longest, with days lengthening as the season progresses after the solstice.-Meteorology:...
with minimum temperatures
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
averaging about 10°C. Gujarat also has a warm climate with hot summers and cool winters.
Demographics

Hinduism
Hinduism is the predominant and indigenous religious tradition of the Indian Subcontinent. Hinduism is known to its followers as , amongst many other expressions...
and there are significant minority who follow Islam
Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
and smaller number who follow Buddhism
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
and Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
. There are also a few indigenous Jews called the Bene Israel
Bene Israel
The Bene Israel are a group of Jews who migrated in the 19th century from villages in the Konkan area to the nearby Indian cities, primarily Mumbai, but also to Pune, and Ahmedabad. Prior to these waves of emigrations and to this day, the Bene Israel formed the largest sector of the subcontinent's...
who speak Marathi
Marathi language
Marathi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Marathi people of western and central India. It is the official language of the state of Maharashtra. There are over 68 million fluent speakers worldwide. Marathi has the fourth largest number of native speakers in India and is the fifteenth most...
. The Parsees who settled in Gujarat made Mumbai and Surat
Surat
Surat , also known as Suryapur, is the commercial capital city of the Indian state of Gujarat. Surat is India's Eighth most populous city and Ninth-most populous urban agglomeration. It is also administrative capital of Surat district and one of the fastest growing cities in India. The city proper...
their home. Significant percentages of Jains
Jainism
Jainism is an Indian religion that prescribes a path of non-violence towards all living beings. Its philosophy and practice emphasize the necessity of self-effort to move the soul towards divine consciousness and liberation. Any soul that has conquered its own inner enemies and achieved the state...
and Buddhists can be found too. Most Christians live in the state of Goa.
Overall, 83.66 % of the population is Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
, 10.12 % Muslim
Muslim
A Muslim, also spelled Moslem, is an adherent of Islam, a monotheistic, Abrahamic religion based on the Quran, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God as revealed to prophet Muhammad. "Muslim" is the Arabic term for "submitter" .Muslims believe that God is one and incomparable...
, 4 % Buddhist with Christians in Goa and Maharashtra making up the majority of the remainder. Marathi, with about 73 million speakers is the most widely spoken language, followed by Gujarati
Gujarati language
Gujarati is an Indo-Aryan language, and part of the greater Indo-European language family. It is derived from a language called Old Gujarati which is the ancestor language of the modern Gujarati and Rajasthani languages...
with about 46 million speakers and Konkani
Konkani language
KonkaniKonkani is a name given to a group of several cognate dialects spoken along the narrow strip of land called Konkan, on the west coast of India. This is, however, somewhat an over-generalisation. Geographically, Konkan is defined roughly as the area between the river Damanganga to the north...
2.5 million speakers, all of which are Indo-Aryan languages
Indo-Aryan languages
The Indo-Aryan languages constitutes a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages, itself a branch of the Indo-European language family...
. As in other parts of India, a high level of multilingualism
Multilingualism
Multilingualism is the act of using, or promoting the use of, multiple languages, either by an individual speaker or by a community of speakers. Multilingual speakers outnumber monolingual speakers in the world's population. Multilingualism is becoming a social phenomenon governed by the needs of...
is seen with English and Hindi being spoken as additional languages in urban areas.

Population density
Population density is a measurement of population per unit area or unit volume. It is frequently applied to living organisms, and particularly to humans...
is around 290 per square km. The average fertility rate is about 2.2, while the average household size is about 4.7.
Culture

Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire , also known as the Portuguese Overseas Empire or the Portuguese Colonial Empire , was the first global empire in history...
rule has influenced Goa a lot. The architecture of Goa is a unique blend of Indian and Portuguese
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
cultures. Goa is also well known for its beaches, temples and churches.
Maharashtrian culture derives from the ancient Indo-Aryan
Indo-Aryans
Indo-Aryan is an ethno-linguistic term referring to the wide collection of peoples united as native speakers of the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-Iranian family of Indo-European languages...
Vedic
Vedic
Vedic may refer to:* the Vedas, the oldest preserved Indic texts** Vedic Sanskrit, the language of these texts** Vedic period, during which these texts were produced** Vedic pantheon of gods mentioned in Vedas/vedic period...
culture influenced deeply by the Maratha Empire and British
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
colonial rule. Maharashtrians
Marathi people
The Marathi people or Maharashtrians are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group, that inhabit the Maharashtra region and state of western India. Their language Marathi is part of the southern group of Indo-Aryan languages...
take great pride in the Maratha Empire
Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire or the Maratha Confederacy was an Indian imperial power that existed from 1674 to 1818. At its peak, the empire covered much of South Asia, encompassing a territory of over 2.8 million km²....
, and many places in Maharashtra are named after the founder of the Empire, Shivaji. Marathi literature
Marathi literature
Marathi literature is the body of literature of Marathi, a Sanskrit-derived language spoken mainly in the Indian state of Maharashtra and written in the Devanagari script.-Early Marathi Literature :...
and cinema
Marathi cinema
Marathi cinema refers to films produced in the Marathi language in the state of Maharashtra, India. It is the oldest and pioneer film industry in India...
are popular in the state as well as across India.
Gujarati culture includes both Hindu and Islamic influence. It has also been influenced by the Parsis, who migrated to Gujarat from Iran
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
about a 1000 years ago. Recently events like Rann Utsav, International Kite Festival and Global Garba festivals have been started to showcase its culture internationally. Mumbai and Goa
Goa
Goa , a former Portuguese colony, is India's smallest state by area and the fourth smallest by population. Located in South West India in the region known as the Konkan, it is bounded by the state of Maharashtra to the north, and by Karnataka to the east and south, while the Arabian Sea forms its...
are renowned for their nightlifes. Bollywood
Bollywood
Bollywood is the informal term popularly used for the Hindi-language film industry based in Mumbai , Maharashtra, India. The term is often incorrectly used to refer to the whole of Indian cinema; it is only a part of the total Indian film industry, which includes other production centers producing...
has had a huge impact on the lifestyle and culture of this part of India as Bollywood
Bollywood
Bollywood is the informal term popularly used for the Hindi-language film industry based in Mumbai , Maharashtra, India. The term is often incorrectly used to refer to the whole of Indian cinema; it is only a part of the total Indian film industry, which includes other production centers producing...
is situated in Mumbai.
Cuisine


Maharashtrian cuisine
Maharashtrian cuisine is cuisine of the Marathi people, those from the state of Maharashtra in India. Maharashtrian cuisine covers a range from being mild to very spicy dishes. Wheat, rice, jowar, bajri, vegetables, lentils and fruit form important components of Maharashtrian diet...
is diverse and ranges from bland to fiery hot. Pohay
Pohay
Pohay or Pohe is an Indian fast food prepared in Maharashtra.Its origins are unknown. Northern variants of this dish tend to be sweet, while Maharashtrian pohay tends to be spicy. It is also often served with an extremely spicy curry, locally called 'tarri'. Pohay with tarri is a relished snack in...
, Shrikhand
Shrikhand
Shrikhand is an Indian sweet dish made of strained yogurt. It is one of the main desserts in Gujarati cuisine and Maharashtrian cuisine. It is also served with Gujarati thali sometimes as a sweet dish. Preparation of this dish is very simple but it takes some time to process yogurt properly.The...
, Pav Bhaji
Pav bhaji
Pav Bhaji is a fast food dish that originated in Marathi cuisine, and is native to Maharashtra and is popular in most metropolitan areas in India, particularly in Pune. Pav in Marathi means a small loaf of bread. The word has been derived from Portuguese pão . Bhaji in Marathi means vegetable dish...
, Vada Pav
Vada pav
Vada pav , sometimes spelled wada pav, is a popular vegetarian fast food dish native to the Indian state of Maharashtra. It consists of a batata vada sandwiched between 2 slices of a pav. The compound word batata vada refers in Marathi to a vada made out of batata, the latter referring to a potato...
are good examples of Maharashtrian cuisine
Maharashtrian cuisine
Maharashtrian cuisine is cuisine of the Marathi people, those from the state of Maharashtra in India. Maharashtrian cuisine covers a range from being mild to very spicy dishes. Wheat, rice, jowar, bajri, vegetables, lentils and fruit form important components of Maharashtrian diet...
. Goan cuisine
Goan cuisine
Goan cuisine consists of regional foods popular in Goa, located along India's west coast along the Arabian Sea. Seafood, coconut milk, rice and paste are main ingredients of Goan delicacies. The area is located in a tropical climate, and spices and flavors are intense. Use of Kokum is another...
is dominated by the use of rice, coconut, seafood, Kokum, cashew-nuts.With its distinct spices and medium of cooking as coconut oil, both vegetarian as well as non-vegetarian cuisine is equally popular.
Gujarati cuisine
Gujarati cuisine
Gujarati cuisine refers to the cuisine of the Gujaratis from India, who are predominant in western India. It is primarily a vegetarian cuisine, despite having an extensive coastline for sea food, due influence of Jain vegetarianism and traditional Hinduism...
is almost exclusively vegetarian. Gujarat is one of three states in India, with prohibition on alcohol, along with Mizoram
Mizoram
Mizoram is one of the Seven Sister States in North Eastern India, sharing borders with the states of Tripura, Assam, Manipur and with the neighbouring countries of Bangladesh and Burma. Mizoram became the 23rd state of India on 20 February 1987. Its capital is Aizawl. Mizoram is located in the...
and Manipur
Manipur
Manipur is a state in northeastern India, with the city of Imphal as its capital. Manipur is bounded by the Indian states of Nagaland to the north, Mizoram to the south and Assam to the west; it also borders Burma to the east. It covers an area of...
. In contrast, Maharashtra has some of the best vineyard
Vineyard
A vineyard is a plantation of grape-bearing vines, grown mainly for winemaking, but also raisins, table grapes and non-alcoholic grape juice...
s in India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, with Nashik and Sangli
Sangli
Sangli is a city in the state of Maharashtra of India. Sangli is known as the Turmeric city for its vast production of Turmeric. Sangli is situated on the banks of river Krishna and is the largest market place for Turmeric in Asia and houses many sugar factories, which it is also noted for...
districts being the country's biggest grape-producing districts.
Economy
The region generates 20.34% of the national GDP of the country, with an annual growth rate of 14.5% as of 2006. The states generate about 23 % of the tax revenuesStates of India by tax revenues
This is a list of States of India by projected own tax revenues of their governments for the year 2010–15 by the Thirteenth Finance Commission with figures in crore of Indian Rupees...
of the country. More than 85% of the households have access to electricity with about 55% owning a television. Agriculture
Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
employs most people in the region, while services have largest share in the total GDP.

