
West African craton
Encyclopedia
The West African craton is one of the five large masses, or cratons, of the Precambrian
basement rock
of Africa
that make up the African Plate
, the others being the Kalahari craton
, Congo craton
, Saharan Metacraton
and Tanzania craton. These land masses came together in the late Precambrian and early Palaeozoic eras to form the African continent. At one time, volcanic action around the rim of the craton may have contributed to a major global warming event.
cratons fused: Leo-Man-Ghana, Taoudeni and Reguibat. The first two docked around 2,100 Ma (million years ago), and the Reguibat craton docked with the craton around 2,000 Ma. The roots of the combined craton extend to a depth of over 300 km in the sub-continental lithospheric mantle.
The West African craton stretches from the Little Atlas mountains of Morocco
to the Gulf of Guinea
, and is bounded by mobile belts of much younger rocks to the north, east and west. The oldest rocks were metamorphosed
2,900-2,500 million years ago. In the Sahara
they are mostly covered by more recent sediments from the Phanerozoic
eon. Further south, younger volcanic and sedimentary rocks outcrop in Ghana
, Ivory Coast, and Sierra Leone
, surrounded by even younger sediments laid down in the Precambrian
era.
The West African craton underlies the modern countries of Morocco
, Algeria
, Mauritania
, Senegal
, The Gambia
, Guinea Bissau, Guinea
, Mali
, Burkina Faso
, Sierra Leone
, Liberia
, Côte d'Ivoire
, Ghana
, Togo
and Benin
.
, consisting of the crust
and the rigid uppermost part of the mantle solidified. The lithosphere rides on the asthenosphere
, which is also solid but can flow like a liquid on geological time scales. The lithosphere is broken up into tectonic plates
, which slowly move in relation to one another at speeds of 50–100 mm annually, colliding, combining into continents, splitting and drifting apart to form new continental configurations.
It is difficult to reconstruct the early wanderings of the West African craton, but around 1,100 million years ago it seems to have been one of the cratons that came together to form Rodinia
, a supercontinent
. At that time, the Congo craton lay to the west of the Amazonia craton, and the West African craton lay to the south of them (rotated about 180o, they retain this relative configuration.)
Around 750 million years ago Rodinia rifted apart into three continents: Proto-Laurasia, the Congo craton
and Proto-Gondwana. The West African craton may then have combined with other cratons to form Pannotia
, a hypothetical supercontinent
that existed from the Pan-African orogeny
about 600 million years ago to the end of the Precambrian
about 540 million years ago. Later it became part of Gondwana
, and later still part of Pangaea
, the supercontinent
that existed during the Paleozoic
and Mesozoic
eras about 250 million years ago, before North and South America separated from Eurasia and Africa and the continents started to drift towards their current configuration.
 Proponents of the Snowball Earth
Proponents of the Snowball Earth
theory claim that around 530 million years ago the Earth was going through an extremely cold period. The oceans were frozen to great depths, and their snow covering reflected the heat from the sun through cloudless skies. Only simple forms of life could survive in locations such as deep oceanic hydrothermal vents. At the end of this period the edges of the West African craton became highly active, throwing up a ring of volcanoes. The thermal activity was caused by excessive mantle
heat that had built up below the craton, insulated by the lithosphere
. The volcanic eruptions created a greenhouse effect
on massive scale, melting the ice and releasing CO2 into the atmosphere. The climate quickly switched to one much warmer than today, resulting in the Cambrian explosion
of life forms.
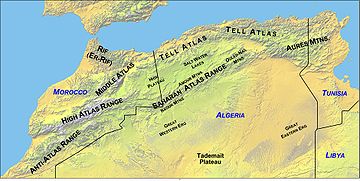
The Little Atlas range formed about 300 million years ago when Euramerica
and Gondwana
ground against one another during the Alleghenian orogeny
, a process that also formed the Appalachians in present-day North America
. More recently, in the Tertiary period from 65 million to about 1.8 million year ago, the mountain chains that today compose the Atlas Mountains
were lifted up as Europe and Africa collided at the southern end of the Iberian peninsula
. Erosion has reduced the Little Atlas range so that it is today lower than the High Atlas
range to the north.
apart from the areas near the Atlantic or Gulf of Guinea. However, below the surface there are ancient sedimentary basins such as the Taoudeni basin
that may contain large reserves of oil and gas.
, the Birimian
sequence of metasediments and metavolcanics found in Lower Proterozoic rocks of Ghana, Guinea, Mali, Burkina Faso, Côte d'Ivoire, and Liberia is important as a source of major gold deposits.
Precambrian
The Precambrian is the name which describes the large span of time in Earth's history before the current Phanerozoic Eon, and is a Supereon divided into several eons of the geologic time scale...
basement rock
Basement Rock
Basement or Basement Rock music was a sub-genre coined in 2006 in an article by music magazine TGR. This was first in relation to the existence of underground record label Criminal Records but more for the independent bands they represent. The roots of the sub-genre are noted to be as far back as...
of Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
that make up the African Plate
African Plate
The African Plate is a tectonic plate which includes the continent of Africa, as well as oceanic crust which lies between the continent and various surrounding ocean ridges.-Boundaries:...
, the others being the Kalahari craton
Kalahari craton
The Kalahari craton is a craton, an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere with thick crust and deep lithospheric roots extending up to a few hundred kilometers into the Earth's mantle, that occupies a large portion of South Africa and consists of the Kaapvaal, the Zimbabwe craton, the...
, Congo craton
Congo craton
The Congo craton, covered by the Palaeozoic-to-recent Congo basin, is an ancient Precambrian craton that with four others makes up the modern continent of Africa. These cratons were formed between about 3.6 and 2.0 billion years ago and have been tectonically stable since that time...
, Saharan Metacraton
Saharan Metacraton
The Saharan Metacraton is a term used by some geologists to describe a large area of continental crust in the north-central part of Africa. Where a craton is an old and stable part of the lithosphere, the term "metacraton" is used to describe a craton that has been remobilized during an orogenic...
and Tanzania craton. These land masses came together in the late Precambrian and early Palaeozoic eras to form the African continent. At one time, volcanic action around the rim of the craton may have contributed to a major global warming event.
Location and composition
The craton appears to have formed when three ArcheanArchean
The Archean , also spelled Archeozoic or Archæozoic) is a geologic eon before the Paleoproterozoic Era of the Proterozoic Eon, before 2.5 Ga ago. Instead of being based on stratigraphy, this date is defined chronometrically...
cratons fused: Leo-Man-Ghana, Taoudeni and Reguibat. The first two docked around 2,100 Ma (million years ago), and the Reguibat craton docked with the craton around 2,000 Ma. The roots of the combined craton extend to a depth of over 300 km in the sub-continental lithospheric mantle.
The West African craton stretches from the Little Atlas mountains of Morocco
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
to the Gulf of Guinea
Gulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean between Cape Lopez in Gabon, north and west to Cape Palmas in Liberia. The intersection of the Equator and Prime Meridian is in the gulf....
, and is bounded by mobile belts of much younger rocks to the north, east and west. The oldest rocks were metamorphosed
Metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rock is the transformation of an existing rock type, the protolith, in a process called metamorphism, which means "change in form". The protolith is subjected to heat and pressure causing profound physical and/or chemical change...
2,900-2,500 million years ago. In the Sahara
Sahara
The Sahara is the world's second largest desert, after Antarctica. At over , it covers most of Northern Africa, making it almost as large as Europe or the United States. The Sahara stretches from the Red Sea, including parts of the Mediterranean coasts, to the outskirts of the Atlantic Ocean...
they are mostly covered by more recent sediments from the Phanerozoic
Phanerozoic
The Phanerozoic Eon is the current eon in the geologic timescale, and the one during which abundant animal life has existed. It covers roughly 542 million years and goes back to the time when diverse hard-shelled animals first appeared...
eon. Further south, younger volcanic and sedimentary rocks outcrop in Ghana
Ghana
Ghana , officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country located in West Africa. It is bordered by Côte d'Ivoire to the west, Burkina Faso to the north, Togo to the east, and the Gulf of Guinea to the south...
, Ivory Coast, and Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone , officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Guinea to the north and east, Liberia to the southeast, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west and southwest. Sierra Leone covers a total area of and has an estimated population between 5.4 and 6.4...
, surrounded by even younger sediments laid down in the Precambrian
Precambrian
The Precambrian is the name which describes the large span of time in Earth's history before the current Phanerozoic Eon, and is a Supereon divided into several eons of the geologic time scale...
era.
The West African craton underlies the modern countries of Morocco
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
, Algeria
Algeria
Algeria , officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria , also formally referred to as the Democratic and Popular Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of Northwest Africa with Algiers as its capital.In terms of land area, it is the largest country in Africa and the Arab...
, Mauritania
Mauritania
Mauritania is a country in the Maghreb and West Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean in the west, by Western Sahara in the north, by Algeria in the northeast, by Mali in the east and southeast, and by Senegal in the southwest...
, Senegal
Senegal
Senegal , officially the Republic of Senegal , is a country in western Africa. It owes its name to the Sénégal River that borders it to the east and north...
, The Gambia
The Gambia
The Republic of The Gambia, commonly referred to as The Gambia, or Gambia , is a country in West Africa. Gambia is the smallest country on mainland Africa, surrounded by Senegal except for a short coastline on the Atlantic Ocean in the west....
, Guinea Bissau, Guinea
Guinea
Guinea , officially the Republic of Guinea , is a country in West Africa. Formerly known as French Guinea , it is today sometimes called Guinea-Conakry to distinguish it from its neighbour Guinea-Bissau. Guinea is divided into eight administrative regions and subdivided into thirty-three prefectures...
, Mali
Mali
Mali , officially the Republic of Mali , is a landlocked country in Western Africa. Mali borders Algeria on the north, Niger on the east, Burkina Faso and the Côte d'Ivoire on the south, Guinea on the south-west, and Senegal and Mauritania on the west. Its size is just over 1,240,000 km² with...
, Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso – also known by its short-form name Burkina – is a landlocked country in west Africa. It is surrounded by six countries: Mali to the north, Niger to the east, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and Côte d'Ivoire to the southwest.Its size is with an estimated...
, Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone , officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Guinea to the north and east, Liberia to the southeast, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west and southwest. Sierra Leone covers a total area of and has an estimated population between 5.4 and 6.4...
, Liberia
Liberia
Liberia , officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Sierra Leone on the west, Guinea on the north and Côte d'Ivoire on the east. Liberia's coastline is composed of mostly mangrove forests while the more sparsely populated inland consists of forests that open...
, Côte d'Ivoire
Côte d'Ivoire
The Republic of Côte d'Ivoire or Ivory Coast is a country in West Africa. It has an area of , and borders the countries Liberia, Guinea, Mali, Burkina Faso and Ghana; its southern boundary is along the Gulf of Guinea. The country's population was 15,366,672 in 1998 and was estimated to be...
, Ghana
Ghana
Ghana , officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country located in West Africa. It is bordered by Côte d'Ivoire to the west, Burkina Faso to the north, Togo to the east, and the Gulf of Guinea to the south...
, Togo
Togo
Togo, officially the Togolese Republic , is a country in West Africa bordered by Ghana to the west, Benin to the east and Burkina Faso to the north. It extends south to the Gulf of Guinea, on which the capital Lomé is located. Togo covers an area of approximately with a population of approximately...
and Benin
Benin
Benin , officially the Republic of Benin, is a country in West Africa. It borders Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east and Burkina Faso and Niger to the north. Its small southern coastline on the Bight of Benin is where a majority of the population is located...
.
Wanderings
The Earth formed about 4.6 billion years ago. As it cooled the lithosphereLithosphere
The lithosphere is the rigid outermost shell of a rocky planet. On Earth, it comprises the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of thousands of years or greater.- Earth's lithosphere :...
, consisting of the crust
Crust (geology)
In geology, the crust is the outermost solid shell of a rocky planet or natural satellite, which is chemically distinct from the underlying mantle...
and the rigid uppermost part of the mantle solidified. The lithosphere rides on the asthenosphere
Asthenosphere
The asthenosphere is the highly viscous, mechanically weak and ductilely-deforming region of the upper mantle of the Earth...
, which is also solid but can flow like a liquid on geological time scales. The lithosphere is broken up into tectonic plates
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that describes the large scale motions of Earth's lithosphere...
, which slowly move in relation to one another at speeds of 50–100 mm annually, colliding, combining into continents, splitting and drifting apart to form new continental configurations.
It is difficult to reconstruct the early wanderings of the West African craton, but around 1,100 million years ago it seems to have been one of the cratons that came together to form Rodinia
Rodinia
In geology, Rodinia is the name of a supercontinent, a continent which contained most or all of Earth's landmass. According to plate tectonic reconstructions, Rodinia existed between 1.1 billion and 750 million years ago, in the Neoproterozoic era...
, a supercontinent
Supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is a landmass comprising more than one continental core, or craton. The assembly of cratons and accreted terranes that form Eurasia qualifies as a supercontinent today.-History:...
. At that time, the Congo craton lay to the west of the Amazonia craton, and the West African craton lay to the south of them (rotated about 180o, they retain this relative configuration.)
Around 750 million years ago Rodinia rifted apart into three continents: Proto-Laurasia, the Congo craton
Congo craton
The Congo craton, covered by the Palaeozoic-to-recent Congo basin, is an ancient Precambrian craton that with four others makes up the modern continent of Africa. These cratons were formed between about 3.6 and 2.0 billion years ago and have been tectonically stable since that time...
and Proto-Gondwana. The West African craton may then have combined with other cratons to form Pannotia
Pannotia
Pannotia, first described by Ian W. D. Dalziel in 1997, is a hypothetical supercontinent that existed from the Pan-African orogeny about six hundred million years ago to the end of the Precambrian about five hundred and fifty million years ago. It is also known as the Vendian supercontinent...
, a hypothetical supercontinent
Supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is a landmass comprising more than one continental core, or craton. The assembly of cratons and accreted terranes that form Eurasia qualifies as a supercontinent today.-History:...
that existed from the Pan-African orogeny
Pan-African orogeny
The Pan-African orogeny was a series of major Neoproterozoic orogenic events which related to the formation of the supercontinents Gondwana and Pannotia about 600 million years ago....
about 600 million years ago to the end of the Precambrian
Precambrian
The Precambrian is the name which describes the large span of time in Earth's history before the current Phanerozoic Eon, and is a Supereon divided into several eons of the geologic time scale...
about 540 million years ago. Later it became part of Gondwana
Gondwana
In paleogeography, Gondwana , originally Gondwanaland, was the southernmost of two supercontinents that later became parts of the Pangaea supercontinent. It existed from approximately 510 to 180 million years ago . Gondwana is believed to have sutured between ca. 570 and 510 Mya,...
, and later still part of Pangaea
Pangaea
Pangaea, Pangæa, or Pangea is hypothesized as a supercontinent that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras about 250 million years ago, before the component continents were separated into their current configuration....
, the supercontinent
Supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is a landmass comprising more than one continental core, or craton. The assembly of cratons and accreted terranes that form Eurasia qualifies as a supercontinent today.-History:...
that existed during the Paleozoic
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic eon, spanning from roughly...
and Mesozoic
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic era is an interval of geological time from about 250 million years ago to about 65 million years ago. It is often referred to as the age of reptiles because reptiles, namely dinosaurs, were the dominant terrestrial and marine vertebrates of the time...
eras about 250 million years ago, before North and South America separated from Eurasia and Africa and the continents started to drift towards their current configuration.
Snowball Earth

Snowball Earth
The Snowball Earth hypothesis posits that the Earth's surface became entirely or nearly entirely frozen at least once, some time earlier than 650 Ma . Proponents of the hypothesis argue that it best explains sedimentary deposits generally regarded as of glacial origin at tropical...
theory claim that around 530 million years ago the Earth was going through an extremely cold period. The oceans were frozen to great depths, and their snow covering reflected the heat from the sun through cloudless skies. Only simple forms of life could survive in locations such as deep oceanic hydrothermal vents. At the end of this period the edges of the West African craton became highly active, throwing up a ring of volcanoes. The thermal activity was caused by excessive mantle
Mantle (geology)
The mantle is a part of a terrestrial planet or other rocky body large enough to have differentiation by density. The interior of the Earth, similar to the other terrestrial planets, is chemically divided into layers. The mantle is a highly viscous layer between the crust and the outer core....
heat that had built up below the craton, insulated by the lithosphere
Lithosphere
The lithosphere is the rigid outermost shell of a rocky planet. On Earth, it comprises the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of thousands of years or greater.- Earth's lithosphere :...
. The volcanic eruptions created a greenhouse effect
Greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect is a process by which thermal radiation from a planetary surface is absorbed by atmospheric greenhouse gases, and is re-radiated in all directions. Since part of this re-radiation is back towards the surface, energy is transferred to the surface and the lower atmosphere...
on massive scale, melting the ice and releasing CO2 into the atmosphere. The climate quickly switched to one much warmer than today, resulting in the Cambrian explosion
Cambrian explosion
The Cambrian explosion or Cambrian radiation was the relatively rapid appearance, around , of most major phyla, as demonstrated in the fossil record, accompanied by major diversification of other organisms, including animals, phytoplankton, and calcimicrobes...
of life forms.
Features
During its wanderings, at different times covered by ice sheets, forests, marshes or arid desert, the surface of the West African craton has been heavily eroded by ice, water and wind. In most places the original rocks are buried far below more recent volcanic and sedimentary deposits. The visible features are usually of comparatively recent origin.Little Atlas Range and Atlas Mountains

The Little Atlas range formed about 300 million years ago when Euramerica
Euramerica
Euramerica was a minor supercontinent created in the Devonian as the result of a collision between the Laurentian, Baltica, and Avalonia cratons .300 million years ago in the Late Carboniferous tropical rainforests lay over the equator of Euramerica...
and Gondwana
Gondwana
In paleogeography, Gondwana , originally Gondwanaland, was the southernmost of two supercontinents that later became parts of the Pangaea supercontinent. It existed from approximately 510 to 180 million years ago . Gondwana is believed to have sutured between ca. 570 and 510 Mya,...
ground against one another during the Alleghenian orogeny
Alleghenian orogeny
The Alleghenian orogeny or Appalachian orogeny is one of the geological mountain-forming events that formed the Appalachian Mountains and Allegheny Mountains. The term and spelling Alleghany orogeny was originally proposed by H.P. Woodward in 1957....
, a process that also formed the Appalachians in present-day North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
. More recently, in the Tertiary period from 65 million to about 1.8 million year ago, the mountain chains that today compose the Atlas Mountains
Atlas Mountains
The Atlas Mountains is a mountain range across a northern stretch of Africa extending about through Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia. The highest peak is Toubkal, with an elevation of in southwestern Morocco. The Atlas ranges separate the Mediterranean and Atlantic coastlines from the Sahara Desert...
were lifted up as Europe and Africa collided at the southern end of the Iberian peninsula
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
. Erosion has reduced the Little Atlas range so that it is today lower than the High Atlas
High Atlas
High Atlas, also called the Grand Atlas Mountains is a mountain range in central Morocco in Northern Africa.The High Atlas rises in the west at the Atlantic Ocean and stretches in an eastern direction to the Moroccan-Algerian border. At the Atlantic and to the southwest the range drops abruptly...
range to the north.
Saharan Basins
South of the mountains, the West African craton is relatively flat, mostly desert or dry savannaSavanna
A savanna, or savannah, is a grassland ecosystem characterized by the trees being sufficiently small or widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to support an unbroken herbaceous layer consisting primarily of C4 grasses.Some...
apart from the areas near the Atlantic or Gulf of Guinea. However, below the surface there are ancient sedimentary basins such as the Taoudeni basin
Taoudeni basin
The Taoudeni Basin is a major geological formation in West Africa named after the Taoudenni village in northern Mali. It covers large parts of the West African craton in Mauritania and Mali. It is of considerable interest due to its possible reserves of oil....
that may contain large reserves of oil and gas.
Southern region
The southern region of the West African craton is interrupted by the remains of weathered volcanoes that are younger than the craton itself. Overlaying the Man ShieldMan Shield
The Man Shield or Leo-Man shield or craton is a geological area in the southeast of the West African craton, in part overlaid by gold-bearing Birimian formations....
, the Birimian
Birimian
The Birimian rocks are major sources of gold and diamonds that extend through Ghana, the Ivory Coast, Guinea, Mali and Burkina Faso. They are named after the Birim River, one of the main tributaries of the Pra River in Ghana and the country's most important diamond-producing area...
sequence of metasediments and metavolcanics found in Lower Proterozoic rocks of Ghana, Guinea, Mali, Burkina Faso, Côte d'Ivoire, and Liberia is important as a source of major gold deposits.

