
Samogitia
Encyclopedia
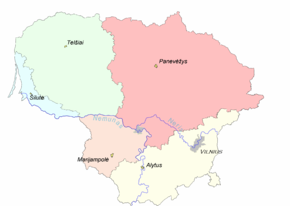
Regions of Lithuania
Lithuania can be divided into historical and cultural regions . The exact borders are not fully clear, as the regions are not official political or administrative units. They are delimited by culture, such as country traditions, traditional lifestyle, songs, tales, etc. To some extent regions...
. It is located in northwestern Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
. Its largest city is Šiauliai
Šiauliai
Šiauliai , is the fourth largest city in Lithuania, with a population of 133,900. It is the capital of Šiauliai County. Unofficially, the city is the capital of Northern Lithuania.-Names:...
/Šiaulē. The region has a long and distinct cultural history, reflected in the existence of the Samogitian dialect. Its status as a dialect rather than as an ISO-recognized language was challenged in 2009. (In 2010 Samogitian was assigned an ISO 639-3 code, "sgs". http://www.sil.org/iso639-3/documentation.asp?id=sgs)
Etymology and alternate names
Old Russian sources mentioned the region as Žomaiti; this gave rise to its Polish form, Żmudź, and to the Middle High GermanMiddle High German
Middle High German , abbreviated MHG , is the term used for the period in the history of the German language between 1050 and 1350. It is preceded by Old High German and followed by Early New High German...
Samaythen, which was Latinized as Samogitia. The region is also known in English as Lower Lithuania, Žemaitija, or, in reference to its Yiddish
Yiddish language
Yiddish is a High German language of Ashkenazi Jewish origin, spoken throughout the world. It developed as a fusion of German dialects with Hebrew, Aramaic, Slavic languages and traces of Romance languages...
name, Zamet.
Geography
The region is located in northwestern LithuaniaLithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
in the territories of Palanga city municipality, Rietavas municipality
Rietavas municipality
Rietavas municipality is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania....
, Tauragė district municipality
Taurage district municipality
Tauragė district municipality is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania....
, Šilalė district municipality
Šilale district municipality
Šilalė district municipality is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania....
, Skuodas district municipality, Jurbarkas district municipality
Jurbarkas district municipality
Jurbarkas district municipality is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania....
, Mažeikiai district municipality
Mažeikiai district municipality
Mažeikiai district municipality is in north-west Lithuania, on the Venta River . The administrative center of Mažeikiai district is the town of Mažeikiai...
, Kretinga district municipality
Kretinga district municipality
Kretinga district municipality is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania....
, Plungė district municipality
Plunge district municipality
Plungė district municipality is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania.-Tourism and pilgrimage:Major tourist attraction is Lake Plateliai and nearby town Plateliai...
, Telšiai district municipality
Telšiai district municipality
Telšiai district municipality is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania, containing the city of Telšiai.-References:...
, Akmenė district municipality
Akmene district municipality
Akmenė district municipality is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania. It lies in the northwest of the country, with administrative centre in Naujoji Akmene and borders Latvia in the north, Joniškis district municipality in the east, Šiauliai district municipality in the southeast, Telšiai...
, Kelmė district municipality
Kelme district municipality
Kelmė district municipality is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania, located in western part of Lithuania....
, Šiauliai district municipality
Šiauliai district municipality
-References:...
, Raseiniai district municipality
Raseiniai district municipality
-References:...
, eastern parts of Klaipėda district municipality
Klaipeda district municipality
Klaipėda district municipality is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania.- Elderships :There are 11 elderships in Klaipėda district municipality:*Agluonėnai eldership*Dauparai-Kvietiniai eldership...
and Šilutė district municipality
Šilute district municipality
Šilutė district municipality is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania. It is known for spring floods when ice on Neman River starts melting. This is the only municipality in Lithuania that gets flooded on regular basis....
, western part of Joniškis district municipality
Joniškis district municipality
Joniškis district municipality is a territorial unit of Lithuania with a population of about 30,000. The administrative center of the municipality is the town of Joniškis.-References:...
, also the Šiauliai city municipality. The largest city is Šiauliai
Šiauliai
Šiauliai , is the fourth largest city in Lithuania, with a population of 133,900. It is the capital of Šiauliai County. Unofficially, the city is the capital of Northern Lithuania.-Names:...
, or Klaipėda
Klaipeda
Klaipėda is a city in Lithuania situated at the mouth of the Nemunas River where it flows into the Baltic Sea. It is the third largest city in Lithuania and the capital of Klaipėda County....
if the latter is considered in the region. Telšiai
Telšiai
Telšiai , is a city in Lithuania with about 35,000 inhabitants. It is the capital of Telšiai County and Samogitia region, and it is located on Lake Mastis.-Names:...
is the capital, although Medininkai (now Varniai
Varniai
Varniai , is a city in the Telšiai County, western Lithuania. In the Middle Ages the city was known as Medininkai. It was established in the 14th century, on the bank of the Varnelė River, near an important Samogitian castle. It was the center of Samogitian Catholic church: after the baptism of...
) was once the capital of the Eldership of Samogitia
Eldership of Samogitia
The Duchy of Samogitia had been the administrative unit of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania from 1422 . Between 1422 to 1441 it was known as the Eldership of Samogitia...
. The largest cities (those with over 20,000 inhabitants) are (Samogitian
Samogitian language
Samogitian is a dialect of the Lithuanian language spoken mostly in Samogitia . Attempts have been made to standardize it...
name, if different, is provided after slash):
- ŠiauliaiŠiauliaiŠiauliai , is the fourth largest city in Lithuania, with a population of 133,900. It is the capital of Šiauliai County. Unofficially, the city is the capital of Northern Lithuania.-Names:...
/Šiaulē (133,883 inhabitants) - MažeikiaiMažeikiaiMažeikiai is a city in the north-western Lithuania, on the Venta River. It has a population of around 45,300, making it the eighth largest city in Lithuania. The city is the administrative center of Mažeikiai district municipality in Telšiai County. It is the largest city that does not have its...
/Mažeikē (42,675 inhabitants) - TelšiaiTelšiaiTelšiai , is a city in Lithuania with about 35,000 inhabitants. It is the capital of Telšiai County and Samogitia region, and it is located on Lake Mastis.-Names:...
/Telšē (31,460 inhabitants) - considered capital - TauragėTaurageTauragė is an industrial city in Lithuania, and the capital of Tauragė County. In 2011, its population was 26,444. Tauragė is situated on the Jūra River, close to the border with the Kaliningrad Oblast, and not far from the Baltic Sea coast....
/ Tauragie (29,124 inhabitants) - PlungėPlungePlungė is a city in Lithuania with 23,246 inhabitants. It has a crab stick factory which exports to many countries in Europe.Before World War II, Plunge had a large Jewish population.- History :...
(23,436 inhabitants) - KretingaKretingaKretinga is a city in the Klaipėda County, Lithuania. It is the capital of the Kretinga district municipality. It is located east of the popular Baltic Sea resort town of Palanga, and about north of Lithuania's 3rd largest city and principal seaport, Klaipėda.The population was listed as 21,423...
(21,423 inhabitants) - SkuodasSkuodasSkuodas is a city located in Klaipeda County, in northwestern Lithuania, on the border with Latvia. The Bartuva river flows through the town....
/ Skouds (7 314 inhabitants)
Demographics and language
The people of Samogitia speak SamogitianSamogitian language
Samogitian is a dialect of the Lithuanian language spoken mostly in Samogitia . Attempts have been made to standardize it...
, a dialect
Dialect
The term dialect is used in two distinct ways, even by linguists. One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a characteristic of a particular group of the language's speakers. The term is applied most often to regional speech patterns, but a dialect may also be defined by other factors,...
of Lithuanian
Lithuanian language
Lithuanian is the official state language of Lithuania and is recognized as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 2.96 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 170,000 abroad. Lithuanian is a Baltic language, closely related to Latvian, although they...
that was previously considered one of 3 main dialects (modern linguists have determined that it is one of two dialects, the other being Aukštaitian, and that both of these dialects have 3 subdialects each). Samogitian has northern and southern subdialects (which are further subdivided). A western subdialect once existed in the Klaipėda region
Klaipeda Region
The Klaipėda Region or Memel Territory was defined by the Treaty of Versailles in 1920 when it was put under the administration of the Council of Ambassadors...
, but it became extinct after World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
after its inhabitants fled the region, as a result of being expelled or persecuted by the Soviet authorities (since the 16th or even 15th century the Samogitian
Samogitian
Samogitian can refer to:* Anything pertaining to Samogitia , the Lowlands of Lithuania* Samogitian dialect, a dialect of the Lithuanian language, sometimes regarded as a Baltic language...
s of the Klaipėda region called themselves "Lietuvininkai", and since the end of 19th century they called themselves "Prūsai"; after World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
the territory of the western subdialect was resettled mainly by northern and southern Samogitians, and by other Lithuanians also). Samogitian has a broken tone like the Latvian
Latvian language
Latvian is the official state language of Latvia. It is also sometimes referred to as Lettish. There are about 1.4 million native Latvian speakers in Latvia and about 150,000 abroad. The Latvian language has a relatively large number of non-native speakers, atypical for a small language...
and Danish
Danish language
Danish is a North Germanic language spoken by around six million people, principally in the country of Denmark. It is also spoken by 50,000 Germans of Danish ethnicity in the northern parts of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, where it holds the status of minority language...
languages. Samogitians
Samogitians
Samogitians are a part of the Lithuanian ethnicity inhabiting the region of Samogitia in Lithuania. Many speak the Samogitian dialect of the Lithuanian language.-History:...
are closely related with Curonians
Curonians
The Curonians or Kurs were a Baltic tribe living on the shores of the Baltic sea in what are now the western parts of Latvia and Lithuania from the 5th to the 16th centuries, when they merged with other Baltic tribes. They gave their name to the region of Courland , and they spoke the Old...
and Prussians they share similar language and culture.
Samogitia is one of the most ethnically homogenous regions of the country, with an ethnic Lithuanian population exceeding 99.5% in some districts; in the 1st part of 19th century it was a major center of Lithuanian culture (Samogitians traditionally tended to oppose any anti-Lithuanian restrictions). The region is predominantly Roman Catholic, although there are significant Lutheran minorities in the south.
The use of the Samogitian dialect is decreasing as more people tend to use standard Lithuanian, although there have been some minor attempts by local councils, especially in Telšiai
Telšiai
Telšiai , is a city in Lithuania with about 35,000 inhabitants. It is the capital of Telšiai County and Samogitia region, and it is located on Lake Mastis.-Names:...
, to write certain roadside information in Samogitian as well some schools teach children Samogitian
Samogitian
Samogitian can refer to:* Anything pertaining to Samogitia , the Lowlands of Lithuania* Samogitian dialect, a dialect of the Lithuanian language, sometimes regarded as a Baltic language...
language in schools.
History
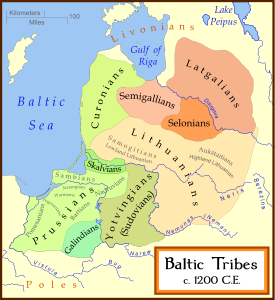
The very term "Samogitians" (Žemaičiai in Lithuanian) is a Latinized form of the ancient Lithuanian name for the region's lowlanders, who dwelt in Central Lithuania's lowlands. The original subethnic Samogitia, i.e. the Central Lithuania's flat burial grounds culture, was formed as early as the 5th-6th centuries, whereas the Western part of historical Samogitia became ethnically Lithuanian between the 13th-16th centuries, – before that time it was inhabited by southern Semigallians
Semigallians
Semigallians were the Baltic tribe that lived in the southcentral part of contemporary Latvia and northern Lithuania...
and southern Curonians
Curonians
The Curonians or Kurs were a Baltic tribe living on the shores of the Baltic sea in what are now the western parts of Latvia and Lithuania from the 5th to the 16th centuries, when they merged with other Baltic tribes. They gave their name to the region of Courland , and they spoke the Old...
. The primal eastern boundary of historical Samogitia was the Šventoji River
Šventoji River
The Šventoji River is the longest river that flows entirely within Lithuania and the largest tributary of the Neris River. It originates from the Lake Samanis in the Gražutė Regional Park and flows into Neris near Jonava. The longest tributary of the Šventoji is the Širvinta River.The Šventoji...
(a tributary of the Neris River), and from the end of the 13th century (approximately about that time the Lithuanian ruler Vytenis
Vytenis
Vytenis was the Grand Duke of Lithuania from c. 1295 to c. 1316. He became the first of the Gediminid dynasty to rule for a considerable amount of time. In the early 14th century his reputation outshone that of Gediminas, who is regarded by modern historians as one of the greatest Lithuanian rulers...
had expanded the territory of his domain in Aukštaitija
Aukštaitija
Aukštaitija is the name of one of five ethnographic regions of Lithuania. The name comes from the relatively high elevation of the region, particularly the eastern parts.-Geography:...
at the expense of Samogitia) it ran along the Nevėžis River
Nevežis River
Nevėžis River is the sixth longest river in Lithuania and one of the main tributaries of the Neman River. Its length is , and it flows only within the geographical confines of Lithuania. It is the second longest river in Lithuania, after the Šventoji River, that flows exclusively within its borders...
.
Due to the fact, that in 13-16th centuries the Teutonic order and the Livonian order
Livonian Brothers of the Sword
The Livonian Brothers of the Sword were a military order founded by Bishop Albert of Riga in 1202. Pope Innocent III sanctioned the establishment in 1204. The membership of the order comprised German "warrior monks"...
bordered Samogitia, it was always threatened by their expansionist aims. As such, Samogitian territory was offered to these Orders, or exchanged in peace treaties, a number of times. Lithuania would regain Samogitia back again in subsequent conflicts.
For more than two hundred years, Samogitia played a central role in Lithuania’s wars against the crusading order of the Teutonic Knights (Knights of the Cross and Knights of the Sword). Invasions started in Lithuania in 1229. Combined military forces undertook numerous campaigns against Samogitians and Aukstaitians. Saule (1236), Skuodas (1239), Durbe (1260), Lievarde (1261) are just a few of the battles that took place. Since Samogitia was the last pagan region in Europe left to be invaded and christened, Teutonic order set their sights on this last mission. Between 1345 and 1382, the Knights of the Cross attacked from Prussia some 70 times, while the Livonian Knights of the Sword made 30 military forays. Year after year fortresses were attacked, farms and crops were put to the torch, women and children enslaved and men killed. Despite all their effort, Samogitians managed to defend their lands until 1410 decisive battle of Grunwald
Battle of Grunwald
The Battle of Grunwald or 1st Battle of Tannenberg was fought on 15 July 1410, during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respectively by King Jogaila and Grand Duke Vytautas , decisively defeated the Teutonic Knights, led...
, where united Polish-Lithuanian forces defeated Teutonic order and ended their crusading era.
In the 15th century, Samogitia was the last region in Europe to be converted to Christianity. During the 15-18th centuries, it was known as the Duchy
Eldership of Samogitia
The Duchy of Samogitia had been the administrative unit of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania from 1422 . Between 1422 to 1441 it was known as the Eldership of Samogitia...
or Eldership of Samogitia
Eldership of Samogitia
The Duchy of Samogitia had been the administrative unit of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania from 1422 . Between 1422 to 1441 it was known as the Eldership of Samogitia...
, which included some territories of what is now considered Aukštaitija
Aukštaitija
Aukštaitija is the name of one of five ethnographic regions of Lithuania. The name comes from the relatively high elevation of the region, particularly the eastern parts.-Geography:...
and Suvalkija
Suvalkija
Suvalkija or Sudovia is the smallest of the five cultural regions of Lithuania. Its unofficial capital is Marijampolė. People from Suvalkija are called suvalkiečiai or suvalkietis . It is located south of the Neman River, in the former territory of Vilkaviškis bishopric...
as well. The Duchy, or the Eldership of Samogitia was an administrative unit similar to a voivodeship
Voivodeship
Voivodship is a term denoting the position of, or more commonly the area administered by, a voivod. Voivodeships have existed since medieval times in Poland, Romania, Hungary, Lithuania, Latvia, Russia and Serbia....
in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state from the 12th /13th century until 1569 and then as a constituent part of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1791 when Constitution of May 3, 1791 abolished it in favor of unitary state. It was founded by the Lithuanians, one of the polytheistic...
.
After the partitions
Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland or Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth took place in the second half of the 18th century and ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland for 123 years...
of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Samogitia was incorporated into the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
along with the rest of Lithuania.
Samogitia was the main source of the Lithuanian cultural revival in the 19th century, and was a focal point for the smuggling of books
Knygnešiai
Book smugglers were people who transported Lithuanian language books printed in the Latin alphabet into Lithuanian-speaking areas of the Russian Empire, defying a ban on such materials in force from 1866 to 1904...
printed in the banned Lithuanian language.
After World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
, the region became a part of the newly re-established Lithuanian State. The Samogitians resisted the Bolsheviks, the Bermontians, and the Poles in 1919–1920, only to be occupied by the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
in 1940, as a result of the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact
Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, named after the Soviet foreign minister Vyacheslav Molotov and the German foreign minister Joachim von Ribbentrop, was an agreement officially titled the Treaty of Non-Aggression between Germany and the Soviet Union and signed in Moscow in the late hours of 23 August 1939...
.
In 1945, the Soviets denied the existence of the Lithuania Minor
Lithuania Minor
Lithuania Minor or Prussian Lithuania is a historical ethnographic region of Prussia, later East Prussia in Germany, where Prussian Lithuanians or Lietuvininkai lived. Lithuania Minor enclosed the northern part of this province and got its name due to the territory's substantial...
ethnographic region due to political concerns, declaring the Klaipėda region a part of Samogitia.
Tourism
Samogitia has a huge potential for tourism development, due to its natural beauty, culturalCulture
Culture is a term that has many different inter-related meanings. For example, in 1952, Alfred Kroeber and Clyde Kluckhohn compiled a list of 164 definitions of "culture" in Culture: A Critical Review of Concepts and Definitions...
and historical heritage
Industrial heritage
Industrial heritage is an aspect of cultural heritage dealing specifically with the buildings and artifacts of industry which are inherited from past generations, maintained in the present and bestowed for the benefit of future generations, often forming a significant attraction for tourism.The...
. Samogitia is attractive for many local and international tourists. Most popular tourist destinations are Palanga
Palanga
Palanga and beautiful sand dunes. Officially Palanga has the status of a city municipality and includes Šventoji, Nemirseta, Būtingė and other settlements, which are considered as part of the city of Palanga.-Legend:...
, Kretinga
Kretinga
Kretinga is a city in the Klaipėda County, Lithuania. It is the capital of the Kretinga district municipality. It is located east of the popular Baltic Sea resort town of Palanga, and about north of Lithuania's 3rd largest city and principal seaport, Klaipėda.The population was listed as 21,423...
and Žemaičių Kalvarija
Žemaiciu Kalvarija
Žemaičių Kalvarija is a small town in Plungė district municipality, Lithuania. It is known as a major site for Catholic pilgrimage....
. The majority of tourists come from Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
, Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
, Belarus
Belarus
Belarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,...
, Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
, Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
, Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
and Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
.
Palanga
Palanga
Palanga and beautiful sand dunes. Officially Palanga has the status of a city municipality and includes Šventoji, Nemirseta, Būtingė and other settlements, which are considered as part of the city of Palanga.-Legend:...
is popular tourist destination among tourists from the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
and Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
.
Žemaičių Kalvarija
Žemaiciu Kalvarija
Žemaičių Kalvarija is a small town in Plungė district municipality, Lithuania. It is known as a major site for Catholic pilgrimage....
(or New Jerusalem as it used to be called) is very popular among pilgrims from all around the World, due to its annual The Great Žemaičių Kalvarija Church Festival (usually in June or July).
Politics
Samogitia historically was an autonomous region in the Grand Duchy of LithuaniaGrand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state from the 12th /13th century until 1569 and then as a constituent part of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1791 when Constitution of May 3, 1791 abolished it in favor of unitary state. It was founded by the Lithuanians, one of the polytheistic...
, although it lost this status once Lithuania was annexed by the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
following the Third Partition of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1795 as a part of the Vilna Governorate
Vilna Governorate
The Vilna Governorate or Government of Vilna was a governorate of the Russian Empire created after the Third Partition of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1795...
. In 1843, the region was incorporated into the Kovno Governorate
Kovno Governorate
The Kovno Governorate or Government of Kovno was a governorate of the Russian Empire. Its capital was Kovno . It was formed on 18 December 1842 by tsar Nicholas I from the western part of the Vilna Governorate, and the order was carried out on 1 July 1843. It used to be a part of Northwestern Krai...
, with a minor part of it being attached to the Courland Governorate
Courland Governorate
Courland Governorate, also known as the Province of Courland, Governorate of Kurland , and Government of Courland , was one of the Baltic governorates of the Russian Empire, that is now part of the Republic of Latvia....
. Since then the region has not had a separate political status, although there have been some plans to administratively reform Lithuania into the traditional ethnocentric regions.
Currently Samogitia is represented by the Samogitian cultural society, a group interested in preserving Samogitian culture and language, and the Žemaitijos parlamentas (literally Parliament of Samogitia), which concerns itself with regional autonomy based on historical claims. These claims often include the Klaipėda region
Klaipeda Region
The Klaipėda Region or Memel Territory was defined by the Treaty of Versailles in 1920 when it was put under the administration of the Council of Ambassadors...
in the interwar and would claim Klaipėda
Klaipeda
Klaipėda is a city in Lithuania situated at the mouth of the Nemunas River where it flows into the Baltic Sea. It is the third largest city in Lithuania and the capital of Klaipėda County....
rather than Telšiai
Telšiai
Telšiai , is a city in Lithuania with about 35,000 inhabitants. It is the capital of Telšiai County and Samogitia region, and it is located on Lake Mastis.-Names:...
as the capital. The same group, led by Justinas Burba and having a small membership, has also published the controversial newspaper Žemaitijos parlamentas, which raised the idea that the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
should repay Samogitia for its defense of Europe against the Mongols
Mongols
Mongols ) are a Central-East Asian ethnic group that lives mainly in the countries of Mongolia, China, and Russia. In China, ethnic Mongols can be found mainly in the central north region of China such as Inner Mongolia...
.

Symbols
The coat of armsCoat of arms
A coat of arms is a unique heraldic design on a shield or escutcheon or on a surcoat or tabard used to cover and protect armour and to identify the wearer. Thus the term is often stated as "coat-armour", because it was anciently displayed on the front of a coat of cloth...
depicts a black bear with silver claws and collar on a red shield topped with a crown.
The flag of Samogitia depicts the coat of arms on a white background. It is a non-rectangular flag ending in two triangles, rather than the rectangular
Rectangle
In Euclidean plane geometry, a rectangle is any quadrilateral with four right angles. The term "oblong" is occasionally used to refer to a non-square rectangle...
flag typically used. The only official non-rectangular flags are those of Nepal
Flag of Nepal
The national flag of Nepal is the world's only national flag that is non-quadrilateral in shape. The flag is a simplified combination of two single pennons, the vexillological word for a pennant. Its crimson red is the colour of the rhododendron, the country's national flower. Red is also the sign...
and of Ohio
Flag of Ohio
The flag of the state of Ohio was adopted in 1902 and designed by John Eisemann, for the 1901 Pan-American Exposition.-Design:The large blue triangle represents Ohio's hills and valleys, and the stripes represent roads and waterways...
, USA.
Both symbols are assumed to have been in use for centuries, especially the coat of arms (differing claims assert it was first used in the 14th or 16th centuries). The symbols were used by the Eldership of Samogitia
Eldership of Samogitia
The Duchy of Samogitia had been the administrative unit of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania from 1422 . Between 1422 to 1441 it was known as the Eldership of Samogitia...
. These are the oldest symbols of the Lithuanian ethnographic regions.
Because Samogitia does not correspond to any current administrative division of Lithuania, these symbols are not officially used. However, they might come back into use if Lithuania undergoes administrative reform in the future.
On 21 July 1994 these symbols were recognized by the government of the Lithuanian Republic.

