
Ringing artifacts
Encyclopedia
In signal processing
, particularly digital image processing
, ringing artifacts are artifacts
that appear as spurious signals near sharp transitions in a signal. Visually, they appear as bands or "ghosts" near edges; audibly, they appear as "echos" near transients, particularly sounds from percussion instrument
s; most noticeable are the pre-echo
s. As with other artifacts, their minimization is a criterion in filter design
.
 The main cause of ringing artifacts is due to a signal being bandlimited
The main cause of ringing artifacts is due to a signal being bandlimited
(specifically, not having high frequencies) or passed through a low-pass filter
; this is the frequency domain
description.
In terms of the time domain
, the cause of this type of ringing is the ripples in the sinc function, which is the impulse response
(time domain representation) of a perfect low-pass filter. Mathematically, this is called the Gibbs phenomenon
.
One may distinguish overshoot
(and undershoot), which occurs when transitions are accentuated – the output is higher than the input – from ringing, where after an overshoot, the signal overcorrects and is now below the target value; these phenomena often occur together, and are thus often conflated and jointly referred to as "ringing".
The term "ringing" is most often used for ripples in the time domain, though it is also sometimes used for frequency domain effects:
windowing a filter in the time domain by a rectangular function causes ripples in the frequency domain for the same reason as a brick-wall low pass filter (rectangular function in the frequency domain) causes ripples in the time domain, in each case the Fourier transform of the rectangular function being the sinc function.
There are related artifacts caused by other frequency domain
effects,
and similar artifacts due to unrelated causes.
.svg.png) By definition, ringing occurs when a non-oscillating input yields an oscillating output: formally, when an input signal which is monotonic
By definition, ringing occurs when a non-oscillating input yields an oscillating output: formally, when an input signal which is monotonic
on an interval has output response which is not monotonic. This occurs most severely when the impulse response
or step response
of a filter
has oscillations – less formally, if for a spike input, respectively a step input (a sharp transition), the output has bumps. Ringing most commonly refers to step ringing, and that will be the focus.
Ringing is closely related to overshoot
and undershoot, which is when the output takes on values higher than the maximum (respectively, lower than the minimum) input value: one can have one without the other, but in important cases, such as a low-pass filter
, one first has overshoot, then the response bounces back below the steady-state level, causing the first ring, and then oscillates back and forth above and below the steady-state level. Thus overshoot is the first step of the phenomenon, while ringing is the second and subsequent steps. Due to this close connection, the terms are often conflated, with "ringing" referring to both the initial overshoot and the subsequent rings.
If one has a linear time invariant (LTI) filter, then one can understand the filter and ringing in terms of the impulse response (the time domain view), or in terms of its Fourier transform, the frequency response
(the frequency domain view). Ringing is a time domain artifact, and in filter design
is traded off with desired frequency domain characteristics: the desired frequency response may cause ringing, while reducing or eliminating ringing may worsen the frequency response.
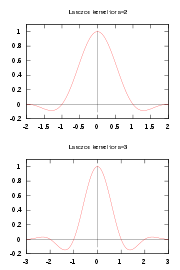
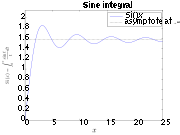 The central example, and often what is meant by "ringing artifacts", is the ideal (brick-wall) low-pass filter
The central example, and often what is meant by "ringing artifacts", is the ideal (brick-wall) low-pass filter
, the sinc filter
. This has an oscillatory impulse response function, as illustrated above, and the step response – its integral, the Sine integral – thus also features oscillations, as illustrated at right.
These ringing artifacts are not results of imperfect implementation or windowing: the ideal low-pass filter, while possessing the desired frequency response, necessarily causes ringing artifacts in the time domain.
Turning to step response,
the step response is the integral of the impulse response
; formally, the value of the step response at time a is the integral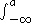 of the impulse response. Thus values of the step response can be understood in terms of tail integrals of the impulse response.
of the impulse response. Thus values of the step response can be understood in terms of tail integrals of the impulse response.
Assume that the overall integral of the impulse response is 1, so it sends constant input to the same constant as output – otherwise the filter has gain
, and scaling by gain gives an integral of 1.
The impulse response may have many negative lobes, and thus many oscillations, each yielding a ring, though these decay for practical filters, and thus one generally only sees a few rings, with the first generally being most pronounced.
Note that if the impulse response has small negative lobes and larger positive lobes, then it will exhibit ringing but not undershoot or overshoot: the tail integral will always be between 0 and 1, but will oscillate down at each negative lobe. However, in the sinc filter, the lobes monotonically decrease in magnitude and alternate in sign, as in the alternating harmonic series, and thus tail integrals alternate in sign as well, so it exhibits overshoot as well as ringing.
Conversely, if the impulse response is always nonnegative, so it has no negative lobes – the function is a probability distribution
– then the step response will exhibit neither ringing nor overshoot or undershoot – it will be a monotonic function growing from 0 to 1, like a cumulative distribution function
. Thus the basic solution from the time domain perspective is to use filters with nonnegative impulse response.
, as discussed below.
and many audio compression codecs (in the form of pre-echo
), as discussed in the examples.
In the time domain, the cause is an impulse response that oscillates, assuming negative values. This can be resolved by using a filter whose impulse response is non-negative and does not oscillate, but shares desired traits. For example, for a low-pass filter, the Gaussian filter
is non-negative and non-oscillatory, hence causes no ringing. However, it is not as good as a low-pass filter: it rolls off in the passband, and leaks in the stopband: in image terms, a Gaussian filter "blurs" the signal, which reflects the attenuation of desired higher frequency signals in the passband.
A general solution is to use a window function
on the sinc filter, which cuts off or reduces the negative lobes: these respectively eliminate and reduce overshoot and ringing. Note that truncating some but not all of the lobes eliminates the ringing beyond that point, but does not reduce the amplitude of the ringing that is not truncated (because this is determined by the size of the lobe), and increases the magnitude of the overshoot if the last non-cut lobe is negative, since the magnitude of the overshoot is the integral of the tail, which is no longer canceled by positive lobes.
Further, in practical implementations one at least truncates sinc, otherwise one must use infinitely many data points (or rather, all points of the signal) to compute every point of the output – truncation corresponds to a rectangular window, and makes the filter practically implementable, but the frequency response is no longer perfect.
In fact, if one takes a brick wall low-pass filter (sinc in time domain, rectangular in frequency domain) and truncates it (multiplies with a rectangular function in the time domain), this convolves the frequency domain with sinc (Fourier transform of the rectangular function) and causes ringing in the frequency domain, which is referred to as ripple. In symbols,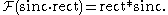 The frequency ringing in the stopband is also referred to as side lobe
The frequency ringing in the stopband is also referred to as side lobe
s. Flat response in the passband is desirable, so one windows with functions whose Fourier transform has fewer oscillations, so the frequency domain behavior is better.
Multiplication in the time domain corresponds to convolution in the frequency domain, so multiplying a filter by a window function corresponds to convolving the Fourier transform of the original filter by the Fourier transform of the window, which has a smoothing effect – thus windowing in the time domain corresponds to smoothing in the frequency domain, and reduces or eliminates overshoot and ringing.
In the frequency domain
, the cause can be interpreted as due to the sharp (brick-wall) cut-off, and ringing reduced by using a filter with smoother roll-off. This is the case for the Gaussian filter, whose magnitude Bode plot
is a downward opening parabola (quadratic roll-off), as its Fourier transform is again a Gaussian, hence (up to scale)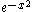 – taking logarithms yields
– taking logarithms yields 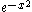
In electronic filter
s, the trade-off between frequency domain response and time domain ringing artifacts is well-illustrated by the Butterworth filter
: the frequency response of a Butterworth filter slopes down linearly on the log scale, with a first-order filter having slope of −6 dB
per octave
, a second-order filter –12 dB per octave, and an nth order filter having slope of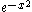 dB per octave – in the limit, this approaches a brick-wall filter. Thus, among these the, first-order filter rolls off slowest, and hence exhibits the fewest time domain artifacts, but leaks the most in the stopband, while as order increases, the leakage decreases, but artifacts increase.
dB per octave – in the limit, this approaches a brick-wall filter. Thus, among these the, first-order filter rolls off slowest, and hence exhibits the fewest time domain artifacts, but leaks the most in the stopband, while as order increases, the leakage decreases, but artifacts increase.
 While ringing artifacts are generally considered undesirable, the initial overshoot (haloing) at transitions increases acutance
While ringing artifacts are generally considered undesirable, the initial overshoot (haloing) at transitions increases acutance
(apparent sharpness) by increasing the derivative across the transition, and thus can be considered as an enhancement.
.svg.png)
Another artifact is overshoot
(and undershoot), which manifests itself not as rings, but as an increased jump at the transition. It is related to ringing, and often occurs in combination with it.
Overshoot and undershoot are caused by a negative tail – in the sinc, the integral from the first zero to infinity, including the first negative lobe. While ringing is caused by a following positive tail – in sinc, the integral from the second zero to infinity, including the first non-central positive lobe.
Thus overshoot is necessary for ringing, but can occur separately: for example, the 2-lobed Lanczos filter has only a single negative lobe on each side, with no following positive lobe, and thus exhibits overshoot but no ringing, while the 3-lobed Lanczos filter exhibits both overshoot and ringing, though the windowing reduces this compared to the sinc filter or the truncated sinc filter.
Similarly, the convolution kernel used in bicubic interpolation
is similar to a 2-lobe windowed sinc, taking on negative values, and thus produces overshoot artifacts, which appear as halos at transitions.
.
If the signal is bounded, for instance an 8-bit or 16-bit integer, this overshoot and undershoot can exceed the range of permissible values, thus causing clipping.
Strictly speaking, the clipping is caused by the combination of overshoot and limited numerical accuracy, but it is closely associated with ringing, and often occurs in combination with it.
Clipping can also occur for unrelated reasons, from a signal simply exceeding the range of a channel.
 In signal processing and related fields, the general phenomenon of time domain oscillation is called ringing
In signal processing and related fields, the general phenomenon of time domain oscillation is called ringing
, while frequency domain oscillations are generally called ripple, though generally not "rippling".
A key source of ripple in digital signal processing is the use of window function
s: if one takes an infinite impulse response
(IIR) filter, such as the sinc filter, and windows it to make it have finite impulse response
, as in the window design method, then the frequency response of the resulting filter is the convolution of the frequency response of the IIR filter with the frequency response of the window function. Notably, the frequency response of the rectangular filter is the sinc function (the rectangular function and the sinc function are Fourier dual
to each other), and thus truncation of a filter in the time domain corresponds to multiplication by the rectangular filter, thus convolution by the sinc filter in the frequency domain, causing ripple. In symbols, the frequency response of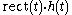 is
is 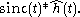 In particular, truncating the sinc function itself yields
In particular, truncating the sinc function itself yields 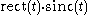 in the time domain, and
in the time domain, and 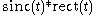 in the frequency domain, so just as low-pass filtering (truncating in the frequency domain) causes ringing in the time domain, truncating in the time domain (windowing by a rectangular filter) causes ripple in the frequency domain.
in the frequency domain, so just as low-pass filtering (truncating in the frequency domain) causes ringing in the time domain, truncating in the time domain (windowing by a rectangular filter) causes ripple in the frequency domain.
 JPEG
JPEG
compression can introduce ringing artifacts at sharp transitions, which are particularly visible in text.
This is a due to loss of high frequency components, as in step response ringing.
JPEG uses 8×8 blocks, on which the discrete cosine transform
(DCT) is performed. The DCT is a Fourier-related transform, and ringing occurs because of loss of high frequency components or loss of precision in high frequency components.
They can also occur at the edge of an image: since JPEG splits images into 8×8 blocks, if an image is not an integer number of blocks, the edge cannot easily be encoded, and solutions such as filling with a black border create a sharp transition in the source, hence ringing artifacts in the encoded image.
Ringing also occurs in the wavelet
-based JPEG 2000
.
JPEG and JPEG 2000 have other artifacts, as illustrated above, such as blocking ("jaggies
") and edge busyness ("mosquito noise"), though these are due to specifics of the formats, and are not ringing as discussed here.
Some illustrations:

In audio signal processing
, ringing causes echoes to occur before and after transients, such as the impulsive sound from percussion instrument
s, such as cymbal
s (this is impulse ringing). The echo after the transient is not heard, because it is masked by the
transient, an effect called temporal masking
. Thus only the echo before the transient is heard, and the phenomenon is called pre-echo
.
This phenomenon occurs as a compression artifact
in audio compression algorithms that use Fourier-related transforms, such as MP3
, AAC
, and Vorbis
.
, which aims to increase edges, may cause ringing phenomena, particularly under repeated application, such as by a DVD player followed by a television. This may be done by high-pass filtering, rather than low-pass filtering.
 Many special functions
Many special functions
exhibit oscillatory decay, and thus convolving with such a function yields ringing in the output; one may consider these ringing, or restrict the term to unintended artifacts in frequency domain signal processing.
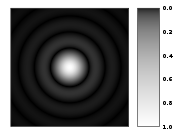
Fraunhofer diffraction
yields the Airy disk as point spread function
, which has a ringing pattern.
.svg.png) The Bessel function
The Bessel function
of the first kind,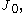 which is related to the Airy function
which is related to the Airy function
, exhibits such decay.
 In cameras, a combination of defocus and spherical aberration
In cameras, a combination of defocus and spherical aberration
can yield ring patterns.
is a form of television interference
where an image in repeated, though this is not ringing; it can be interpreted as convolution with a function which is 1 at the origin and ε (the intensity of the ghost) at some distance, which is formally similar to the above functions.
 In photography, lens flare
In photography, lens flare
is a defect where various circles can appear around highlights, and with ghosts throughout a photo, due to undesired light, such as reflection and scattering off elements in the lens.
 Visual illusions can occur at transitions, as in Mach bands
Visual illusions can occur at transitions, as in Mach bands
, which exhibit a similar undershoot/overshoot to the Gibbs phenomenon.
Signal processing
Signal processing is an area of systems engineering, electrical engineering and applied mathematics that deals with operations on or analysis of signals, in either discrete or continuous time...
, particularly digital image processing
Digital image processing
Digital image processing is the use of computer algorithms to perform image processing on digital images. As a subcategory or field of digital signal processing, digital image processing has many advantages over analog image processing...
, ringing artifacts are artifacts
Artifact (error)
In natural science and signal processing, an artifact is any error in the perception or representation of any visual or aural information introduced by the involved equipment or technique....
that appear as spurious signals near sharp transitions in a signal. Visually, they appear as bands or "ghosts" near edges; audibly, they appear as "echos" near transients, particularly sounds from percussion instrument
Percussion instrument
A percussion instrument is any object which produces a sound when hit with an implement or when it is shaken, rubbed, scraped, or otherwise acted upon in a way that sets the object into vibration...
s; most noticeable are the pre-echo
Pre-echo
Pre-echo is a digital audio compression artifact where a sound is heard before it occurs . It is most noticeable in impulsive sounds from percussion instruments such as castanets or cymbals....
s. As with other artifacts, their minimization is a criterion in filter design
Filter design
Filter design is the process of designing a filter , often a linear shift-invariant filter, that satisfies a set of requirements, some of which are contradictory...
.
Introduction

Bandlimited
Bandlimiting is the limiting of a deterministic or stochastic signal's Fourier transform or power spectral density to zero above a certain finite frequency...
(specifically, not having high frequencies) or passed through a low-pass filter
Low-pass filter
A low-pass filter is an electronic filter that passes low-frequency signals but attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The actual amount of attenuation for each frequency varies from filter to filter. It is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble cut filter...
; this is the frequency domain
Frequency domain
In electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, frequency domain is a term used to describe the domain for analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency, rather than time....
description.
In terms of the time domain
Time domain
Time domain is a term used to describe the analysis of mathematical functions, physical signals or time series of economic or environmental data, with respect to time. In the time domain, the signal or function's value is known for all real numbers, for the case of continuous time, or at various...
, the cause of this type of ringing is the ripples in the sinc function, which is the impulse response
Impulse response
In signal processing, the impulse response, or impulse response function , of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an impulse. More generally, an impulse response refers to the reaction of any dynamic system in response to some external change...
(time domain representation) of a perfect low-pass filter. Mathematically, this is called the Gibbs phenomenon
Gibbs phenomenon
In mathematics, the Gibbs phenomenon, named after the American physicist J. Willard Gibbs, is the peculiar manner in which the Fourier series of a piecewise continuously differentiable periodic function behaves at a jump discontinuity: the nth partial sum of the Fourier series has large...
.
One may distinguish overshoot
Overshoot (signal)
In signal processing, control theory, electronics, and mathematics, overshoot is when a signal or function exceeds its target. It arises especially in the step response of bandlimited systems such as low-pass filters...
(and undershoot), which occurs when transitions are accentuated – the output is higher than the input – from ringing, where after an overshoot, the signal overcorrects and is now below the target value; these phenomena often occur together, and are thus often conflated and jointly referred to as "ringing".
The term "ringing" is most often used for ripples in the time domain, though it is also sometimes used for frequency domain effects:
windowing a filter in the time domain by a rectangular function causes ripples in the frequency domain for the same reason as a brick-wall low pass filter (rectangular function in the frequency domain) causes ripples in the time domain, in each case the Fourier transform of the rectangular function being the sinc function.
There are related artifacts caused by other frequency domain
Frequency domain
In electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, frequency domain is a term used to describe the domain for analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency, rather than time....
effects,
and similar artifacts due to unrelated causes.
Description
.svg.png)
Monotonic function
In mathematics, a monotonic function is a function that preserves the given order. This concept first arose in calculus, and was later generalized to the more abstract setting of order theory....
on an interval has output response which is not monotonic. This occurs most severely when the impulse response
Impulse response
In signal processing, the impulse response, or impulse response function , of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an impulse. More generally, an impulse response refers to the reaction of any dynamic system in response to some external change...
or step response
Step response
The step response of a system in a given initial state consists of the time evolution of its outputs when its control inputs are Heaviside step functions. In electronic engineering and control theory, step response is the time behaviour of the outputs of a general system when its inputs change from...
of a filter
Filter (signal processing)
In signal processing, a filter is a device or process that removes from a signal some unwanted component or feature. Filtering is a class of signal processing, the defining feature of filters being the complete or partial suppression of some aspect of the signal...
has oscillations – less formally, if for a spike input, respectively a step input (a sharp transition), the output has bumps. Ringing most commonly refers to step ringing, and that will be the focus.
Ringing is closely related to overshoot
Overshoot (signal)
In signal processing, control theory, electronics, and mathematics, overshoot is when a signal or function exceeds its target. It arises especially in the step response of bandlimited systems such as low-pass filters...
and undershoot, which is when the output takes on values higher than the maximum (respectively, lower than the minimum) input value: one can have one without the other, but in important cases, such as a low-pass filter
Low-pass filter
A low-pass filter is an electronic filter that passes low-frequency signals but attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The actual amount of attenuation for each frequency varies from filter to filter. It is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble cut filter...
, one first has overshoot, then the response bounces back below the steady-state level, causing the first ring, and then oscillates back and forth above and below the steady-state level. Thus overshoot is the first step of the phenomenon, while ringing is the second and subsequent steps. Due to this close connection, the terms are often conflated, with "ringing" referring to both the initial overshoot and the subsequent rings.
If one has a linear time invariant (LTI) filter, then one can understand the filter and ringing in terms of the impulse response (the time domain view), or in terms of its Fourier transform, the frequency response
Frequency response
Frequency response is the quantitative measure of the output spectrum of a system or device in response to a stimulus, and is used to characterize the dynamics of the system. It is a measure of magnitude and phase of the output as a function of frequency, in comparison to the input...
(the frequency domain view). Ringing is a time domain artifact, and in filter design
Filter design
Filter design is the process of designing a filter , often a linear shift-invariant filter, that satisfies a set of requirements, some of which are contradictory...
is traded off with desired frequency domain characteristics: the desired frequency response may cause ringing, while reducing or eliminating ringing may worsen the frequency response.
sinc filter

Low-pass filter
A low-pass filter is an electronic filter that passes low-frequency signals but attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The actual amount of attenuation for each frequency varies from filter to filter. It is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble cut filter...
, the sinc filter
Sinc filter
In signal processing, a sinc filter is an idealized filter that removes all frequency components above a given bandwidth, leaves the low frequencies alone, and has linear phase...
. This has an oscillatory impulse response function, as illustrated above, and the step response – its integral, the Sine integral – thus also features oscillations, as illustrated at right.
These ringing artifacts are not results of imperfect implementation or windowing: the ideal low-pass filter, while possessing the desired frequency response, necessarily causes ringing artifacts in the time domain.
Time domain
In terms of impulse response, the correspondence between these artifacts and the behavior of the function is as follows:- impulse undershoot is equivalent to the impulse response having negative values,
- impulse ringing (ringing near a point) is precisely equivalent to the impulse response having oscillations, which is equivalent to the derivative of the impulse response alternating between negative and positive values,
- and there is no notion of impulse overshoot, as the unit impulse is assumed to have infinite height (and integral 1 – a Dirac delta functionDirac delta functionThe Dirac delta function, or δ function, is a generalized function depending on a real parameter such that it is zero for all values of the parameter except when the parameter is zero, and its integral over the parameter from −∞ to ∞ is equal to one. It was introduced by theoretical...
), and thus cannot be overshot.
Turning to step response,
the step response is the integral of the impulse response
Impulse response
In signal processing, the impulse response, or impulse response function , of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an impulse. More generally, an impulse response refers to the reaction of any dynamic system in response to some external change...
; formally, the value of the step response at time a is the integral
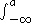 of the impulse response. Thus values of the step response can be understood in terms of tail integrals of the impulse response.
of the impulse response. Thus values of the step response can be understood in terms of tail integrals of the impulse response.Assume that the overall integral of the impulse response is 1, so it sends constant input to the same constant as output – otherwise the filter has gain
Gain
In electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a circuit to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output. It is usually defined as the mean ratio of the signal output of a system to the signal input of the same system. It may also be defined on a logarithmic scale,...
, and scaling by gain gives an integral of 1.
- Step undershoot is equivalent to a tail integral being negative, in which case the magnitude of the undershoot is the value of the tail integral.
- Step overshoot is equivalent to a tail integral being greater than 1, in which case the magnitude of the overshoot is the amount by which the tail integral exceeds 1 – or equivalently the value of the tail in the other direction,
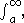 since these add up to 1.
since these add up to 1. - Step ringing is equivalent to tail integrals alternating between increasing and decreasing – taking derivatives, this is equivalent to the impulse response alternating between positive and negative values. Regions where an impulse response are below or above the x-axis (formally, regions between zeros) are called lobes, and the magnitude of an oscillation (from peak to trough) equals the integral of the corresponding lobe.
The impulse response may have many negative lobes, and thus many oscillations, each yielding a ring, though these decay for practical filters, and thus one generally only sees a few rings, with the first generally being most pronounced.
Note that if the impulse response has small negative lobes and larger positive lobes, then it will exhibit ringing but not undershoot or overshoot: the tail integral will always be between 0 and 1, but will oscillate down at each negative lobe. However, in the sinc filter, the lobes monotonically decrease in magnitude and alternate in sign, as in the alternating harmonic series, and thus tail integrals alternate in sign as well, so it exhibits overshoot as well as ringing.
Conversely, if the impulse response is always nonnegative, so it has no negative lobes – the function is a probability distribution
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
– then the step response will exhibit neither ringing nor overshoot or undershoot – it will be a monotonic function growing from 0 to 1, like a cumulative distribution function
Cumulative distribution function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function , or just distribution function, describes the probability that a real-valued random variable X with a given probability distribution will be found at a value less than or equal to x. Intuitively, it is the "area so far"...
. Thus the basic solution from the time domain perspective is to use filters with nonnegative impulse response.
Frequency domain
The frequency domain perspective is that ringing is caused by the sharp cut-off in the rectangular passband in the frequency domain, and thus is reduced by smoother roll-offRoll-off
Roll-off is a term commonly used to describe the steepness of a transmission function with frequency, particularly in electrical network analysis, and most especially in connection with filter circuits in the transition between a passband and a stopband...
, as discussed below.
Solutions
Solutions depend on the parameters of the problem: if the cause is a low-pass filter, one may choose a different filter design, which reduces artifacts at the expense of worse frequency domain performance. On the other hand, if the cause is a band-limited signal, as in JPEG, one cannot simply replace a filter, and ringing artifacts may prove hard to fix – they are present in JPEG 2000JPEG 2000
JPEG 2000 is an image compression standard and coding system. It was created by the Joint Photographic Experts Group committee in 2000 with the intention of superseding their original discrete cosine transform-based JPEG standard with a newly designed, wavelet-based method...
and many audio compression codecs (in the form of pre-echo
Pre-echo
Pre-echo is a digital audio compression artifact where a sound is heard before it occurs . It is most noticeable in impulsive sounds from percussion instruments such as castanets or cymbals....
), as discussed in the examples.
Low-pass filter
If the cause is the use of a brick-wall low-pass filter, one may replace the filter with one that reduces the time domain artifacts, at the cost of frequency domain performance. This can be analyzed from the time domain or frequency domain perspective.In the time domain, the cause is an impulse response that oscillates, assuming negative values. This can be resolved by using a filter whose impulse response is non-negative and does not oscillate, but shares desired traits. For example, for a low-pass filter, the Gaussian filter
Gaussian filter
In electronics and signal processing, a Gaussian filter is a filter whose impulse response is a Gaussian function. Gaussian filters are designed to give no overshoot to a step function input while minimizing the rise and fall time. This behavior is closely connected to the fact that the Gaussian...
is non-negative and non-oscillatory, hence causes no ringing. However, it is not as good as a low-pass filter: it rolls off in the passband, and leaks in the stopband: in image terms, a Gaussian filter "blurs" the signal, which reflects the attenuation of desired higher frequency signals in the passband.
A general solution is to use a window function
Window function
In signal processing, a window function is a mathematical function that is zero-valued outside of some chosen interval. For instance, a function that is constant inside the interval and zero elsewhere is called a rectangular window, which describes the shape of its graphical representation...
on the sinc filter, which cuts off or reduces the negative lobes: these respectively eliminate and reduce overshoot and ringing. Note that truncating some but not all of the lobes eliminates the ringing beyond that point, but does not reduce the amplitude of the ringing that is not truncated (because this is determined by the size of the lobe), and increases the magnitude of the overshoot if the last non-cut lobe is negative, since the magnitude of the overshoot is the integral of the tail, which is no longer canceled by positive lobes.
Further, in practical implementations one at least truncates sinc, otherwise one must use infinitely many data points (or rather, all points of the signal) to compute every point of the output – truncation corresponds to a rectangular window, and makes the filter practically implementable, but the frequency response is no longer perfect.
In fact, if one takes a brick wall low-pass filter (sinc in time domain, rectangular in frequency domain) and truncates it (multiplies with a rectangular function in the time domain), this convolves the frequency domain with sinc (Fourier transform of the rectangular function) and causes ringing in the frequency domain, which is referred to as ripple. In symbols,
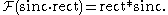 The frequency ringing in the stopband is also referred to as side lobe
The frequency ringing in the stopband is also referred to as side lobeSide lobe
In antenna engineering, side lobes or sidelobes are the lobes of the far field radiation pattern that are not the main lobe....
s. Flat response in the passband is desirable, so one windows with functions whose Fourier transform has fewer oscillations, so the frequency domain behavior is better.
Multiplication in the time domain corresponds to convolution in the frequency domain, so multiplying a filter by a window function corresponds to convolving the Fourier transform of the original filter by the Fourier transform of the window, which has a smoothing effect – thus windowing in the time domain corresponds to smoothing in the frequency domain, and reduces or eliminates overshoot and ringing.
In the frequency domain
Frequency domain
In electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, frequency domain is a term used to describe the domain for analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency, rather than time....
, the cause can be interpreted as due to the sharp (brick-wall) cut-off, and ringing reduced by using a filter with smoother roll-off. This is the case for the Gaussian filter, whose magnitude Bode plot
Bode plot
A Bode plot is a graph of the transfer function of a linear, time-invariant system versus frequency, plotted with a log-frequency axis, to show the system's frequency response...
is a downward opening parabola (quadratic roll-off), as its Fourier transform is again a Gaussian, hence (up to scale)
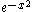 – taking logarithms yields
– taking logarithms yields 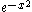
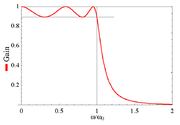
In electronic filter
Electronic filter
Electronic filters are electronic circuits which perform signal processing functions, specifically to remove unwanted frequency components from the signal, to enhance wanted ones, or both...
s, the trade-off between frequency domain response and time domain ringing artifacts is well-illustrated by the Butterworth filter
Butterworth filter
The Butterworth filter is a type of signal processing filter designed to have as flat a frequency response as possible in the passband so that it is also termed a maximally flat magnitude filter...
: the frequency response of a Butterworth filter slopes down linearly on the log scale, with a first-order filter having slope of −6 dB
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
per octave
Octave
In music, an octave is the interval between one musical pitch and another with half or double its frequency. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been referred to as the "basic miracle of music", the use of which is "common in most musical systems"...
, a second-order filter –12 dB per octave, and an nth order filter having slope of
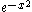 dB per octave – in the limit, this approaches a brick-wall filter. Thus, among these the, first-order filter rolls off slowest, and hence exhibits the fewest time domain artifacts, but leaks the most in the stopband, while as order increases, the leakage decreases, but artifacts increase.
dB per octave – in the limit, this approaches a brick-wall filter. Thus, among these the, first-order filter rolls off slowest, and hence exhibits the fewest time domain artifacts, but leaks the most in the stopband, while as order increases, the leakage decreases, but artifacts increase.Benefits
Acutance
In photography, acutance is the edge contrast of an image. Acutance is related to the amplitude of the derivative of brightness with respect to space...
(apparent sharpness) by increasing the derivative across the transition, and thus can be considered as an enhancement.
Overshoot
.svg.png)

Another artifact is overshoot
Overshoot (signal)
In signal processing, control theory, electronics, and mathematics, overshoot is when a signal or function exceeds its target. It arises especially in the step response of bandlimited systems such as low-pass filters...
(and undershoot), which manifests itself not as rings, but as an increased jump at the transition. It is related to ringing, and often occurs in combination with it.
Overshoot and undershoot are caused by a negative tail – in the sinc, the integral from the first zero to infinity, including the first negative lobe. While ringing is caused by a following positive tail – in sinc, the integral from the second zero to infinity, including the first non-central positive lobe.
Thus overshoot is necessary for ringing, but can occur separately: for example, the 2-lobed Lanczos filter has only a single negative lobe on each side, with no following positive lobe, and thus exhibits overshoot but no ringing, while the 3-lobed Lanczos filter exhibits both overshoot and ringing, though the windowing reduces this compared to the sinc filter or the truncated sinc filter.
Similarly, the convolution kernel used in bicubic interpolation
Bicubic interpolation
In mathematics, bicubic interpolation is an extension of cubic interpolation for interpolating data points on a two dimensional regular grid. The interpolated surface is smoother than corresponding surfaces obtained by bilinear interpolation or nearest-neighbor interpolation...
is similar to a 2-lobe windowed sinc, taking on negative values, and thus produces overshoot artifacts, which appear as halos at transitions.
Clipping
Following from overshoot and undershoot is clippingClipping (audio)
Clipping is a form of waveform distortion that occurs when an amplifier is overdriven and attempts to deliver an output voltage or current beyond its maximum capability...
.
If the signal is bounded, for instance an 8-bit or 16-bit integer, this overshoot and undershoot can exceed the range of permissible values, thus causing clipping.
Strictly speaking, the clipping is caused by the combination of overshoot and limited numerical accuracy, but it is closely associated with ringing, and often occurs in combination with it.
Clipping can also occur for unrelated reasons, from a signal simply exceeding the range of a channel.
Ringing and ripple

Ringing (signal)
In electronics, signal processing, and video, ringing is unwanted oscillation of a signal, particularly in the step response...
, while frequency domain oscillations are generally called ripple, though generally not "rippling".
A key source of ripple in digital signal processing is the use of window function
Window function
In signal processing, a window function is a mathematical function that is zero-valued outside of some chosen interval. For instance, a function that is constant inside the interval and zero elsewhere is called a rectangular window, which describes the shape of its graphical representation...
s: if one takes an infinite impulse response
Infinite impulse response
Infinite impulse response is a property of signal processing systems. Systems with this property are known as IIR systems or, when dealing with filter systems, as IIR filters. IIR systems have an impulse response function that is non-zero over an infinite length of time...
(IIR) filter, such as the sinc filter, and windows it to make it have finite impulse response
Finite impulse response
A finite impulse response filter is a type of a signal processing filter whose impulse response is of finite duration, because it settles to zero in finite time. This is in contrast to infinite impulse response filters, which have internal feedback and may continue to respond indefinitely...
, as in the window design method, then the frequency response of the resulting filter is the convolution of the frequency response of the IIR filter with the frequency response of the window function. Notably, the frequency response of the rectangular filter is the sinc function (the rectangular function and the sinc function are Fourier dual
Conjugate variables
Conjugate variables are pairs of variables mathematically defined in such a way that they become Fourier transform duals of one-another, or more generally are related through Pontryagin duality. The duality relations lead naturally to an uncertainty in physics called the Heisenberg uncertainty...
to each other), and thus truncation of a filter in the time domain corresponds to multiplication by the rectangular filter, thus convolution by the sinc filter in the frequency domain, causing ripple. In symbols, the frequency response of
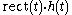 is
is 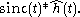 In particular, truncating the sinc function itself yields
In particular, truncating the sinc function itself yields 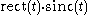 in the time domain, and
in the time domain, and 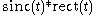 in the frequency domain, so just as low-pass filtering (truncating in the frequency domain) causes ringing in the time domain, truncating in the time domain (windowing by a rectangular filter) causes ripple in the frequency domain.
in the frequency domain, so just as low-pass filtering (truncating in the frequency domain) causes ringing in the time domain, truncating in the time domain (windowing by a rectangular filter) causes ripple in the frequency domain.JPEG

JPEG
In computing, JPEG . The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality. JPEG typically achieves 10:1 compression with little perceptible loss in image quality....
compression can introduce ringing artifacts at sharp transitions, which are particularly visible in text.
This is a due to loss of high frequency components, as in step response ringing.
JPEG uses 8×8 blocks, on which the discrete cosine transform
Discrete cosine transform
A discrete cosine transform expresses a sequence of finitely many data points in terms of a sum of cosine functions oscillating at different frequencies. DCTs are important to numerous applications in science and engineering, from lossy compression of audio and images A discrete cosine transform...
(DCT) is performed. The DCT is a Fourier-related transform, and ringing occurs because of loss of high frequency components or loss of precision in high frequency components.
They can also occur at the edge of an image: since JPEG splits images into 8×8 blocks, if an image is not an integer number of blocks, the edge cannot easily be encoded, and solutions such as filling with a black border create a sharp transition in the source, hence ringing artifacts in the encoded image.
Ringing also occurs in the wavelet
Wavelet
A wavelet is a wave-like oscillation with an amplitude that starts out at zero, increases, and then decreases back to zero. It can typically be visualized as a "brief oscillation" like one might see recorded by a seismograph or heart monitor. Generally, wavelets are purposefully crafted to have...
-based JPEG 2000
JPEG 2000
JPEG 2000 is an image compression standard and coding system. It was created by the Joint Photographic Experts Group committee in 2000 with the intention of superseding their original discrete cosine transform-based JPEG standard with a newly designed, wavelet-based method...
.
JPEG and JPEG 2000 have other artifacts, as illustrated above, such as blocking ("jaggies
Jaggies
"Jaggies" is the informal name for artifacts in raster images, most frequently from aliasing, which in turn is often caused by non-linear mixing effects producing high-frequency components and/or missing or poor anti-aliasing filtering prior to sampling....
") and edge busyness ("mosquito noise"), though these are due to specifics of the formats, and are not ringing as discussed here.
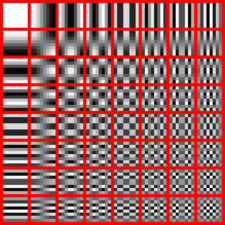
Some illustrations:
- Baseline JPEG and JPEG2000 Artifacts Illustrated
Image Lossless Compression Lossy Compression Original 

Processed by
Canny edge detector,
highlighting artifacts.
Pre-echo

In audio signal processing
Audio signal processing
Audio signal processing, sometimes referred to as audio processing, is the intentional alteration of auditory signals, or sound. As audio signals may be electronically represented in either digital or analog format, signal processing may occur in either domain...
, ringing causes echoes to occur before and after transients, such as the impulsive sound from percussion instrument
Percussion instrument
A percussion instrument is any object which produces a sound when hit with an implement or when it is shaken, rubbed, scraped, or otherwise acted upon in a way that sets the object into vibration...
s, such as cymbal
Cymbal
Cymbals are a common percussion instrument. Cymbals consist of thin, normally round plates of various alloys; see cymbal making for a discussion of their manufacture. The greater majority of cymbals are of indefinite pitch, although small disc-shaped cymbals based on ancient designs sound a...
s (this is impulse ringing). The echo after the transient is not heard, because it is masked by the
transient, an effect called temporal masking
Temporal masking
Temporal masking or "non-simultaneous masking" occurs when a sudden stimulus sound makes inaudible other sounds which are present immediately preceding or following the stimulus...
. Thus only the echo before the transient is heard, and the phenomenon is called pre-echo
Pre-echo
Pre-echo is a digital audio compression artifact where a sound is heard before it occurs . It is most noticeable in impulsive sounds from percussion instruments such as castanets or cymbals....
.
This phenomenon occurs as a compression artifact
Compression artifact
A compression artifact is a noticeable distortion of media caused by the application of lossy data compression....
in audio compression algorithms that use Fourier-related transforms, such as MP3
MP3
MPEG-1 or MPEG-2 Audio Layer III, more commonly referred to as MP3, is a patented digital audio encoding format using a form of lossy data compression...
, AAC
Advanced Audio Coding
Advanced Audio Coding is a standardized, lossy compression and encoding scheme for digital audio. Designed to be the successor of the MP3 format, AAC generally achieves better sound quality than MP3 at similar bit rates....
, and Vorbis
Vorbis
Vorbis is a free software / open source project headed by the Xiph.Org Foundation . The project produces an audio format specification and software implementation for lossy audio compression...
.
Similar phenomena
Other phenomena have similar symptoms to ringing, but are otherwise distinct in their causes.Edge enhancement
Edge enhancementEdge enhancement
Edge enhancement is an image processing filter that enhances the edge contrast of an image or video in an attempt to improve its acutance ....
, which aims to increase edges, may cause ringing phenomena, particularly under repeated application, such as by a DVD player followed by a television. This may be done by high-pass filtering, rather than low-pass filtering.
Special functions

Special functions
Special functions are particular mathematical functions which have more or less established names and notations due to their importance in mathematical analysis, functional analysis, physics, or other applications....
exhibit oscillatory decay, and thus convolving with such a function yields ringing in the output; one may consider these ringing, or restrict the term to unintended artifacts in frequency domain signal processing.
Fraunhofer diffraction
Fraunhofer diffraction
In optics, the Fraunhofer diffraction equation is used to model the diffraction of waves when the diffraction pattern is viewed at a long distance from the diffracting object, and also when it is viewed at the focal plane of an imaging lens....
yields the Airy disk as point spread function
Point spread function
The point spread function describes the response of an imaging system to a point source or point object. A more general term for the PSF is a system's impulse response, the PSF being the impulse response of a focused optical system. The PSF in many contexts can be thought of as the extended blob...
, which has a ringing pattern.
.svg.png)
Bessel function
In mathematics, Bessel functions, first defined by the mathematician Daniel Bernoulli and generalized by Friedrich Bessel, are canonical solutions y of Bessel's differential equation:...
of the first kind,
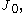 which is related to the Airy function
which is related to the Airy functionAiry function
In the physical sciences, the Airy function Ai is a special function named after the British astronomer George Biddell Airy...
, exhibits such decay.

Spherical aberration
thumb|right|Spherical aberration. A perfect lens focuses all incoming rays to a point on the [[Optical axis|optic axis]]. A real lens with spherical surfaces suffers from spherical aberration: it focuses rays more tightly if they enter it far from the optic axis than if they enter closer to the...
can yield ring patterns.
Interference
GhostingGhosting (television)
In television, a ghost is a replica of the transmitted image, offset in position, that is super-imposed on top of the main image on an analogue broadcast.-Common causes:Common causes of ghosts are:...
is a form of television interference
Television interference
Television interference is a particular case of electromagnetic interference which affects television reception. Many natural and man-made phenomena can disrupt the reception of television signals...
where an image in repeated, though this is not ringing; it can be interpreted as convolution with a function which is 1 at the origin and ε (the intensity of the ghost) at some distance, which is formally similar to the above functions.
Lens flare

Lens flare
Lens flare is the light scattered in lens systems through generally unwanted image formation mechanisms, such as internal reflection and scattering from material inhomogeneities in the lens. These mechanisms differ from the intended image formation mechanism that depends on refraction of the image...
is a defect where various circles can appear around highlights, and with ghosts throughout a photo, due to undesired light, such as reflection and scattering off elements in the lens.
Visual illusions

Mach bands
Mach bands is an optical illusion named after the physicist Ernst Mach. The illusion consists of light or dark stripes that are perceived next to the boundary between two regions of an image that have different lightness gradients .-Explanation:The Mach bands effect is due to the spatial...
, which exhibit a similar undershoot/overshoot to the Gibbs phenomenon.
See also
- Artifact (error)Artifact (error)In natural science and signal processing, an artifact is any error in the perception or representation of any visual or aural information introduced by the involved equipment or technique....
- Digital artifactDigital artifactA digital artifact is any undesired alteration in data introduced in a digital process by an involved technique and/or technology.-Possible causes:...
- sinc filterSinc filterIn signal processing, a sinc filter is an idealized filter that removes all frequency components above a given bandwidth, leaves the low frequencies alone, and has linear phase...
- Brick-wall filter
- Chromatic aberrationChromatic aberrationIn optics, chromatic aberration is a type of distortion in which there is a failure of a lens to focus all colors to the same convergence point. It occurs because lenses have a different refractive index for different wavelengths of light...
- Ghosting (television)Ghosting (television)In television, a ghost is a replica of the transmitted image, offset in position, that is super-imposed on top of the main image on an analogue broadcast.-Common causes:Common causes of ghosts are:...
- Gibbs phenomenonGibbs phenomenonIn mathematics, the Gibbs phenomenon, named after the American physicist J. Willard Gibbs, is the peculiar manner in which the Fourier series of a piecewise continuously differentiable periodic function behaves at a jump discontinuity: the nth partial sum of the Fourier series has large...
- Low-pass filterLow-pass filterA low-pass filter is an electronic filter that passes low-frequency signals but attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The actual amount of attenuation for each frequency varies from filter to filter. It is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble cut filter...
- Pre-echoPre-echoPre-echo is a digital audio compression artifact where a sound is heard before it occurs . It is most noticeable in impulsive sounds from percussion instruments such as castanets or cymbals....
- Purple fringingPurple fringingIn photography, and particularly in digital photography, purple fringing is the term for an out-of-focus purple or magenta "ghost" image on a photograph...

