
Roll-off
Encyclopedia
Roll-off is a term commonly used to describe the steepness of a transmission function
with frequency
, particularly in electrical network analysis
, and most especially in connection with filter circuits
in the transition between a passband
and a stopband
. It is most typically applied to the insertion loss
of the network, but can in principle be applied to any relevant function of frequency, and any technology, not just electronics. It is usual to measure roll-off as a function of logarithmic
frequency, consequently, the units of roll-off are either decibel
s per decade
(dB/decade), where a decade is a 10-times increase in frequency, or decibels per octave
(dB/8ve), where an octave is 2-times increase in frequency.
The concept of roll-off stems from the fact that in many networks roll-off tends towards a constant gradient at frequencies well away from the cut-off point of the frequency curve. Roll-off enables the cut-off performance of such a filter network to be reduced to a single number. Note that roll-off can occur with decreasing frequency as well as increasing frequency, depending on the bandform of the filter being considered: for instance a low-pass filter
will roll-off with increasing frequency, but a high-pass filter
or the lower stopband
of a band-pass filter
will roll-off with decreasing frequency. For brevity, this article describes only low-pass filters. This is to be taken in the spirit of prototype filter
s; the same principles may be applied to high-pass filters by interchanging phrases such as "above cut-off frequency" and "below cut-off frequency".
will have a roll-off of 20 dB/decade. This is approximately equal (to within normal engineering required accuracy) to 6 dB/8ve and is the more usual description given for this roll-off. This can be shown to be so by considering the voltage transfer function
, A, of the RC network:
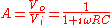
Frequency scaling this to ωc=1/RC=1 and forming the power ratio gives,
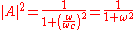
In decibels this becomes,

or expressed as a loss,
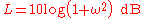
At frequencies well above ω=1, this simplifies to,
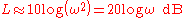
Roll-off is given by,
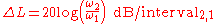
For a decade this is;

and for an octave,
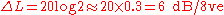
is used) there is no interaction between the stages. In that circumstance, for n identical first-order sections in cascade, the voltage transfer function of the complete network is given by;
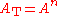
consequently, the total roll-off is given by,
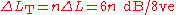
A similar effect can be achieved in the digital domain
by repeatedly applying the same filtering algorithm to the signal.
The calculation of transfer function becomes somewhat more complicated when the sections are not all identical, or when the popular ladder topology construction is used to realise the filter. In a ladder filter each section of the filter has an effect on its immediate neighbours and a lesser effect on more remote sections so the response is not a simple An even when all the sections are identical. For some filter classes, such as the Butterworth filter
, the insertion loss is still monotonically
increasing with frequency and quickly asymptotically
converges to a roll-off of 6n dB/8ve, but in others, such as the Chebyshev
or elliptic filter
the roll-off near the cut-off frequency is much faster and elsewhere the response is anything but monotonic. Nevertheless, all filter classes eventually converge to a roll-off of 6n dB/8ve theoretically at some arbitrarily high frequency, but in many applications this will occur in a frequency band of no interest to the application and parasitic effects
may well start to dominate long before this happens.
: here the need is not so much for a high roll-off but that the roll-offs of the high frequency and low-frequency sections are symmetrical and complementary. An interesting need for high roll-off arises in EEG
machines. Here the filters mostly make do with a basic 6 dB/8ve roll-off, however, some instruments provide a switchable 35 Hz filter at the high frequency end with a faster roll-off to help filter out noise generated by muscle activity.
Transmission function
Transmission function can refer to*transfer function*propagation constant...
with frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
, particularly in electrical network analysis
Network analysis (electrical circuits)
A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are a number of different techniques for achieving this...
, and most especially in connection with filter circuits
Filter (signal processing)
In signal processing, a filter is a device or process that removes from a signal some unwanted component or feature. Filtering is a class of signal processing, the defining feature of filters being the complete or partial suppression of some aspect of the signal...
in the transition between a passband
Passband
A passband is the range of frequencies or wavelengths that can pass through a filter without being attenuated.A bandpass filtered signal , is known as a bandpass signal, as opposed to a baseband signal....
and a stopband
Stopband
A stopband is a band of frequencies, between specified limits, through which a circuit, such as a filter or telephone circuit, does not allow signals to pass, or the attenuation is above the required stopband attenuation level...
. It is most typically applied to the insertion loss
Insertion loss
In telecommunications, insertion loss is the loss of signal power resulting from the insertion of a device in a transmission line or optical fiber and is usually expressed in decibels ....
of the network, but can in principle be applied to any relevant function of frequency, and any technology, not just electronics. It is usual to measure roll-off as a function of logarithmic
Logarithmic scale
A logarithmic scale is a scale of measurement using the logarithm of a physical quantity instead of the quantity itself.A simple example is a chart whose vertical axis increments are labeled 1, 10, 100, 1000, instead of 1, 2, 3, 4...
frequency, consequently, the units of roll-off are either decibel
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
s per decade
Decade (log scale)
One decade is a factor of 10 difference between two numbers measured on a logarithmic scale. It is especially useful when referring to frequencies and when describing frequency response of electronic systems, such as audio amplifiers and filters.-Calculations:The factor-of-ten in a decade can be...
(dB/decade), where a decade is a 10-times increase in frequency, or decibels per octave
Octave (electronics)
In electronics, an octave is a doubling or halving of a frequency. The term is derived from the musical octave which similarly describes such frequency ratios, but the prefix octa-, denoting eight, has no significance in physics...
(dB/8ve), where an octave is 2-times increase in frequency.
The concept of roll-off stems from the fact that in many networks roll-off tends towards a constant gradient at frequencies well away from the cut-off point of the frequency curve. Roll-off enables the cut-off performance of such a filter network to be reduced to a single number. Note that roll-off can occur with decreasing frequency as well as increasing frequency, depending on the bandform of the filter being considered: for instance a low-pass filter
Low-pass filter
A low-pass filter is an electronic filter that passes low-frequency signals but attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The actual amount of attenuation for each frequency varies from filter to filter. It is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble cut filter...
will roll-off with increasing frequency, but a high-pass filter
High-pass filter
A high-pass filter is a device that passes high frequencies and attenuates frequencies lower than its cutoff frequency. A high-pass filter is usually modeled as a linear time-invariant system...
or the lower stopband
Stopband
A stopband is a band of frequencies, between specified limits, through which a circuit, such as a filter or telephone circuit, does not allow signals to pass, or the attenuation is above the required stopband attenuation level...
of a band-pass filter
Band-pass filter
A band-pass filter is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects frequencies outside that range.Optical band-pass filters are of common usage....
will roll-off with decreasing frequency. For brevity, this article describes only low-pass filters. This is to be taken in the spirit of prototype filter
Prototype filter
Prototype filters are electronic filter designs that are used as a template to produce a modified filter design for a particular application. They are an example of a nondimensionalised design from which the desired filter can be scaled or transformed. They are most often seen in regards to...
s; the same principles may be applied to high-pass filters by interchanging phrases such as "above cut-off frequency" and "below cut-off frequency".
First order roll-off
A simple first order network such as a RC circuitRC circuit
A resistor–capacitor circuit ', or RC filter or RC network, is an electric circuit composed of resistors and capacitors driven by a voltage or current source...
will have a roll-off of 20 dB/decade. This is approximately equal (to within normal engineering required accuracy) to 6 dB/8ve and is the more usual description given for this roll-off. This can be shown to be so by considering the voltage transfer function
Transfer function
A transfer function is a mathematical representation, in terms of spatial or temporal frequency, of the relation between the input and output of a linear time-invariant system. With optical imaging devices, for example, it is the Fourier transform of the point spread function i.e...
, A, of the RC network:
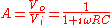
Frequency scaling this to ωc=1/RC=1 and forming the power ratio gives,
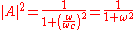
In decibels this becomes,

or expressed as a loss,
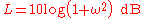
At frequencies well above ω=1, this simplifies to,
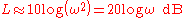
Roll-off is given by,
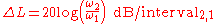
For a decade this is;

and for an octave,
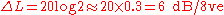
Higher order networks
A higher order network can be constructed by cascading first-order sections together. If a unity gain buffer amplifier is placed between each section (or some other active topologyActive filter
An active filter is a type of analog electronic filter that uses an amplifier stage. Amplifiers included in a filter design can be used to improve the performance, stability and predictability of a filter. An amplifier prevents the impedance of source or load stages from affecting the...
is used) there is no interaction between the stages. In that circumstance, for n identical first-order sections in cascade, the voltage transfer function of the complete network is given by;
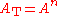
consequently, the total roll-off is given by,
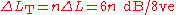
A similar effect can be achieved in the digital domain
Digital filter
In electronics, computer science and mathematics, a digital filter is a system that performs mathematical operations on a sampled, discrete-time signal to reduce or enhance certain aspects of that signal. This is in contrast to the other major type of electronic filter, the analog filter, which is...
by repeatedly applying the same filtering algorithm to the signal.
The calculation of transfer function becomes somewhat more complicated when the sections are not all identical, or when the popular ladder topology construction is used to realise the filter. In a ladder filter each section of the filter has an effect on its immediate neighbours and a lesser effect on more remote sections so the response is not a simple An even when all the sections are identical. For some filter classes, such as the Butterworth filter
Butterworth filter
The Butterworth filter is a type of signal processing filter designed to have as flat a frequency response as possible in the passband so that it is also termed a maximally flat magnitude filter...
, the insertion loss is still monotonically
Monotonic function
In mathematics, a monotonic function is a function that preserves the given order. This concept first arose in calculus, and was later generalized to the more abstract setting of order theory....
increasing with frequency and quickly asymptotically
Asymptote
In analytic geometry, an asymptote of a curve is a line such that the distance between the curve and the line approaches zero as they tend to infinity. Some sources include the requirement that the curve may not cross the line infinitely often, but this is unusual for modern authors...
converges to a roll-off of 6n dB/8ve, but in others, such as the Chebyshev
Chebyshev filter
Chebyshev filters are analog or digital filters having a steeper roll-off and more passband ripple or stopband ripple than Butterworth filters...
or elliptic filter
Elliptic filter
An elliptic filter is a signal processing filter with equalized ripple behavior in both the passband and the stopband...
the roll-off near the cut-off frequency is much faster and elsewhere the response is anything but monotonic. Nevertheless, all filter classes eventually converge to a roll-off of 6n dB/8ve theoretically at some arbitrarily high frequency, but in many applications this will occur in a frequency band of no interest to the application and parasitic effects
Parasitic capacitance
In electrical circuits, parasitic capacitance, stray capacitance or, when relevant, self-capacitance , is an unavoidable and usually unwanted capacitance that exists between the parts of an electronic component or circuit simply because of their proximity to each other...
may well start to dominate long before this happens.
Applications
Filters with a high roll-off were first developed to prevent crosstalk between adjacent channels on telephone FDM systems. Roll-off is also significant on audio loudspeaker crossover filtersAudio crossover
Audio crossovers are a class of electronic filter used in audio applications. Most individual loudspeaker drivers are incapable of covering the entire audio spectrum from low frequencies to high frequencies with acceptable relative volume and lack of distortion so most hi-fi speaker systems use a...
: here the need is not so much for a high roll-off but that the roll-offs of the high frequency and low-frequency sections are symmetrical and complementary. An interesting need for high roll-off arises in EEG
EEG
EEG commonly refers to electroencephalography, a measurement of the electrical activity of the brain.EEG may also refer to:* Emperor Entertainment Group, a Hong Kong-based entertainment company...
machines. Here the filters mostly make do with a basic 6 dB/8ve roll-off, however, some instruments provide a switchable 35 Hz filter at the high frequency end with a faster roll-off to help filter out noise generated by muscle activity.

