
Pi (letter)
Encyclopedia
Pi is the sixteenth letter of the Greek alphabet
, representing [p]. In the system of Greek numerals
it has a value of 80. Letters that arose from pi include Cyrillic
Pe
(П, п), Coptic
pi , and Gothic
pairthra .
The upper-case letter Π is used as a symbol for:
The lower-case letter π is used as a symbol for:
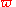 or ϖ) is a glyph
or ϖ) is a glyph
variant of lower case pi sometimes used in technical contexts as though it were a lower-case omega
with a macron
, though historically it is simply a cursive
form of pi, with its legs bent inward to meet. It is used as a symbol for:
The various forms of pi are present in Unicode
as:.
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
, representing [p]. In the system of Greek numerals
Greek numerals
Greek numerals are a system of representing numbers using letters of the Greek alphabet. They are also known by the names Ionian numerals, Milesian numerals , Alexandrian numerals, or alphabetic numerals...
it has a value of 80. Letters that arose from pi include Cyrillic
Cyrillic alphabet
The Cyrillic script or azbuka is an alphabetic writing system developed in the First Bulgarian Empire during the 10th century AD at the Preslav Literary School...
Pe
Pe (Cyrillic)
Pe is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It commonly represents the voiceless bilabial plosive , like the pronunciation of ⟨p⟩ in "pack".-History:...
(П, п), Coptic
Coptic alphabet
The Coptic alphabet is the script used for writing the Coptic language. The repertoire of glyphs is based on the Greek alphabet augmented by letters borrowed from the Demotic and is the first alphabetic script used for the Egyptian language...
pi , and Gothic
Gothic alphabet
The Gothic alphabet is an alphabet for writing the Gothic language, created in the 4th century by Ulfilas for the purpose of translating the Christian Bible....
pairthra .
The upper-case letter Π is used as a symbol for:
- The productProduct (mathematics)In mathematics, a product is the result of multiplying, or an expression that identifies factors to be multiplied. The order in which real or complex numbers are multiplied has no bearing on the product; this is known as the commutative law of multiplication...
operator in mathematics, indicated with capital pi notation ∏ (in analogy to the use of the capital SigmaSigmaSigma is the eighteenth letter of the Greek alphabet, and carries the 'S' sound. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 200. When used at the end of a word, and the word is not all upper case, the final form is used, e.g...
Σ as summationSummationSummation is the operation of adding a sequence of numbers; the result is their sum or total. If numbers are added sequentially from left to right, any intermediate result is a partial sum, prefix sum, or running total of the summation. The numbers to be summed may be integers, rational numbers,...
symbol). - In textual criticismTextual criticismTextual criticism is a branch of literary criticism that is concerned with the identification and removal of transcription errors in the texts of manuscripts...
, Codex Petropolitanus, a 9th century, uncialUncialUncial is a majuscule script commonly used from the 3rd to 8th centuries AD by Latin and Greek scribes. Uncial letters are written in either Greek, Latin, or Gothic.-Development:...
codexCodexA codex is a book in the format used for modern books, with multiple quires or gatherings typically bound together and given a cover.Developed by the Romans from wooden writing tablets, its gradual replacement...
of the GospelGospelA gospel is an account, often written, that describes the life of Jesus of Nazareth. In a more general sense the term "gospel" may refer to the good news message of the New Testament. It is primarily used in reference to the four canonical gospels of Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John...
s, now located in St. Petersburg, Russia. - In legal shorthand, it represents a plaintiffPlaintiffA plaintiff , also known as a claimant or complainant, is the term used in some jurisdictions for the party who initiates a lawsuit before a court...
.
The lower-case letter π is used as a symbol for:
- The mathematical transcendentalTranscendental numberIn mathematics, a transcendental number is a number that is not algebraic—that is, it is not a root of a non-constant polynomial equation with rational coefficients. The most prominent examples of transcendental numbers are π and e...
(and thus irrationalIrrational numberIn mathematics, an irrational number is any real number that cannot be expressed as a ratio a/b, where a and b are integers, with b non-zero, and is therefore not a rational number....
) constant πPi' is a mathematical constant that is the ratio of any circle's circumference to its diameter. is approximately equal to 3.14. Many formulae in mathematics, science, and engineering involve , which makes it one of the most important mathematical constants...
≈ 3.14159…, the ratio of a circleCircleA circle is a simple shape of Euclidean geometry consisting of those points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point, the centre. The distance between any of the points and the centre is called the radius....
's circumferenceCircumferenceThe circumference is the distance around a closed curve. Circumference is a special perimeter.-Circumference of a circle:The circumference of a circle is the length around it....
to its diameterDiameterIn geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints are on the circle. The diameters are the longest chords of the circle...
in Euclidean geometryEuclidean geometryEuclidean geometry is a mathematical system attributed to the Alexandrian Greek mathematician Euclid, which he described in his textbook on geometry: the Elements. Euclid's method consists in assuming a small set of intuitively appealing axioms, and deducing many other propositions from these...
. The letter "π" is the first letter of the Greek words "περιφέρεια" 'periphery' and "περίμετρος" 'perimeter', i.e. the circumference. - The prime-counting function in mathematics.
- Homotopy groupHomotopy groupIn mathematics, homotopy groups are used in algebraic topology to classify topological spaces. The first and simplest homotopy group is the fundamental group, which records information about loops in a space...
s in algebraic topology. - Dimensionless parameters constructed using the Buckingham π theorem of dimensional analysisDimensional analysisIn physics and all science, dimensional analysis is a tool to find or check relations among physical quantities by using their dimensions. The dimension of a physical quantity is the combination of the basic physical dimensions which describe it; for example, speed has the dimension length per...
. - The osmotic pressureOsmotic pressureOsmotic pressure is the pressure which needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of water across a semipermeable membrane....
in chemistry. π=MRT - The elementary particleElementary particleIn particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a particle not known to have substructure; that is, it is not known to be made up of smaller particles. If an elementary particle truly has no substructure, then it is one of the basic building blocks of the universe from which...
called the pi meson or pionPionIn particle physics, a pion is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Pions are the lightest mesons and they play an important role in explaining the low-energy properties of the strong nuclear force....
. - Economic profitProfit (economics)In economics, the term profit has two related but distinct meanings. Normal profit represents the total opportunity costs of a venture to an entrepreneur or investor, whilst economic profit In economics, the term profit has two related but distinct meanings. Normal profit represents the total...
in microeconomics. - InflationInflationIn economics, inflation is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation also reflects an erosion in the purchasing power of money – a...
rate in macroeconomics. - A type of chemical bondChemical bondA chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electromagnetic force attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction...
in which the P-orbitals overlap, called a pi bondPi bondIn chemistry, pi bonds are covalent chemical bonds where two lobes of one involved atomic orbital overlap two lobes of the other involved atomic orbital...
. - The natural projection on the tangent bundleTangent bundleIn differential geometry, the tangent bundle of a differentiable manifold M is the disjoint unionThe disjoint union assures that for any two points x1 and x2 of manifold M the tangent spaces T1 and T2 have no common vector...
on a manifold. - The unary operation of projection in relational algebraRelational algebraRelational algebra, an offshoot of first-order logic , deals with a set of finitary relations that is closed under certain operators. These operators operate on one or more relations to yield a relation...
.
Variant pi
Variant pi or "pomega" ( or ϖ) is a glyph
or ϖ) is a glyphGlyph
A glyph is an element of writing: an individual mark on a written medium that contributes to the meaning of what is written. A glyph is made up of one or more graphemes....
variant of lower case pi sometimes used in technical contexts as though it were a lower-case omega
Omega
Omega is the 24th and last letter of the Greek alphabet. In the Greek numeric system, it has a value of 800. The word literally means "great O" , as opposed to omicron, which means "little O"...
with a macron
Macron
A macron, from the Greek , meaning "long", is a diacritic placed above a vowel . It was originally used to mark a long or heavy syllable in Greco-Roman metrics, but now marks a long vowel...
, though historically it is simply a cursive
Cursive
Cursive, also known as joined-up writing, joint writing, or running writing, is any style of handwriting in which the symbols of the language are written in a simplified and/or flowing manner, generally for the purpose of making writing easier or faster...
form of pi, with its legs bent inward to meet. It is used as a symbol for:
- Angular frequencyAngular frequencyIn physics, angular frequency ω is a scalar measure of rotation rate. Angular frequency is the magnitude of the vector quantity angular velocity...
of a waveOcean surface waveIn fluid dynamics, wind waves or, more precisely, wind-generated waves are surface waves that occur on the free surface of oceans, seas, lakes, rivers, and canals or even on small puddles and ponds. They usually result from the wind blowing over a vast enough stretch of fluid surface. Waves in the...
, in fluid dynamicsFluid dynamicsIn physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
(angular frequency is usually represented by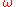 but this may be confused with vorticity in a fluid dynamics context).
but this may be confused with vorticity in a fluid dynamics context). - Longitude of pericenterLongitude of the periapsisIn astrodynamics, the longitude of the periapsis of an orbiting body is the longitude at which the periapsis would occur if the body's inclination were zero. For motion of a planet around the sun, this position could be called longitude of perihelion...
, in celestial mechanicsCelestial mechanicsCelestial mechanics is the branch of astronomy that deals with the motions of celestial objects. The field applies principles of physics, historically classical mechanics, to astronomical objects such as stars and planets to produce ephemeris data. Orbital mechanics is a subfield which focuses on...
. - Comoving distanceComoving distanceIn standard cosmology, comoving distance and proper distance are two closely related distance measures used by cosmologists to define distances between objects...
in cosmology.
The various forms of pi are present in Unicode
Unicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
as:.
See also
- П, п - Pe (Cyrillic)Pe (Cyrillic)Pe is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It commonly represents the voiceless bilabial plosive , like the pronunciation of ⟨p⟩ in "pack".-History:...
- Р, р - Er (Cyrillic)Er (Cyrillic)Er is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It commonly represents the alveolar trill , like the "rolled" sound in the Scottish pronunciation of ⟨r⟩ in "curd".-History:...
- P, p - Pe (Latin)PP is the sixteenth letter of the basic modern Latin alphabet.-Usage:In English and most other European languages, P is a voiceless bilabial plosive. Both initial and final Ps can be combined with many other discrete consonants in English words...
- Greek letters used in mathematics, science, and engineering#Ππ (pi)

