
New Siberian Islands
Encyclopedia
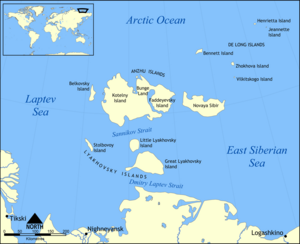

Archipelago
An archipelago , sometimes called an island group, is a chain or cluster of islands. The word archipelago is derived from the Greek ἄρχι- – arkhi- and πέλαγος – pélagos through the Italian arcipelago...
, located to the North of the East Siberian coast between the Laptev Sea
Laptev Sea
The Laptev Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, the Taimyr Peninsula, Severnaya Zemlya and the New Siberian Islands. Its northern boundary passes from the Arctic Cape to a point with co-ordinates of 79°N and 139°E, and ends at the Anisiy...
and the East Siberian Sea
East Siberian Sea
The East Siberian Sea is a marginal sea in the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the Arctic Cape to the north, the coast of Siberia to the south, the New Siberian Islands to the west and Cape Billings, close to Chukotka, and Wrangel Island to the east...
north of the Sakha (Yakutia) Republic.
The New Siberian Islands proper, or Anzhu Islands
Anzhu Islands
The Anzhu Islands or Anjou Islands are a geographical subgroup of the New Siberian Islands archipelago. They are located between the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea in the Russian Arctic. The total area of the islands is approx...
, covering a land area of about 29,000 km², consist of
- Kotelny Island (о. Коте́льный) 11,700 km² and
- Faddeyevsky Island (о. Фадде́евский) 5,300 km²
- Both linked by Bunge LandBunge LandBunge Land or Zemlya Bunge is a huge empty and almost barren intermediate zone. It is located between Kotelny and Faddeyevsky, which, unlike Bunge Land, could be described as proper islands. Sandy and flat, its area is 6,200 km²...
(земля́ Бу́нге) 6,200 km² (occasionally submerged by sea). Very close to Bunge Land's northwestern coast there are two islands: Zheleznyakov Island (Ostrov Zheleznyakova), right off the NW cape and, east of it, Matar Island (Ostrov Matar). Both islands are about 5 km in length.
- Nanosnyy Island 76.283°N 140.416°E is a small island located due north off the northern bay formed by Kotelny and Bunge. It is C-shaped and only 4 km in length, but its importance lies in the fact that it is the northernmost island of the New Siberian group.
- Novaya Sibir (о. Но́вая Сиби́рь) 6,200 km²
- Belkovsky IslandBelkovsky IslandBelkovsky Island is the westernmost island of the Anzhu Islands subgroup of the New Siberian Islands archipelago in the Laptev Sea. The strait between Belkovsky Island and neighboring Kotelny Island is known as the Zarya Strait, after Eduard Toll's Zarya...
(о. Бельковский) 500 km²
To the south and nearer to the Siberia
Siberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
n mainland lie the Lyakhovskiye Islands (6,095 km²):
- Great Lyakhovsky Island (о. Большо́й Ля́ховский) 4,600 km²
- Little Lyakhovsky Island (о. Ма́лый Ля́ховский) 1,325 km²
- Stolbovoy IslandStolbovoy IslandStolbovoy Island is a long and narrow island off the southwest side of the New Siberian archipelago in the eastern part of the Laptev Sea. It is located 184 km away from the Siberian coast and 100 km southwest of Kotelny Island, being thus quite detached from the New Siberian island...
(о. Столбово́й) 170 km² - Semyonovsky IslandSemyonovsky IslandSemyonovsky Island was an island in the southwest part of the New Siberian Islands in the eastern part of the Laptev Sea. Before its destruction, it was at 4 km2, one of the smallest islands in the archipelago...
(о. Семёновский) 0 km² (now submerged)
The small De Long Islands
De Long Islands
The De Long Islands are an uninhabited archipelago often included as part of the New Siberian Islands, lying north east of Novaya Sibir. This archipelago consists of Jeannette Island, Henrietta Island, Bennett Island, Vilkitsky Island and Zhokhov Island. These five islands have a total area of...
(228 km²) lie to the north-east of Novaya Sibir. These islands are usually not considered as part of the New Siberian group:
- Jeannette IslandJeannette IslandJeannette Island is the easternmost island of the De Long Islands archipelago in the East Siberian Sea. It is the second smallest island of the De Long group, being only 2 km in length. It has an area of approximately . The highest peak of the island is...
(о. Жанне́тты) - Henrietta IslandHenrietta IslandHenrietta Island is the northernmost island of the De Long archipelago in the East Siberian Sea. 40% of the island is covered with glaciers. Henrietta is roughly circular in shape and its diameter is about 6 km...
(о. Генрие́тты) - Bennett IslandBennett IslandBennett Island is the largest of the islands of the De Long group in the northern part of the East Siberian Sea. The area of this island is approximately 150 km² ...
(о. Бе́ннетта) - Vilkitsky Island (о. Вильки́цкого)
- Zhokhov IslandZhokhov IslandZhokhov Island is an island in the East Siberian Sea, situated 128 km north east of Novaya Sibir Island, the easternmost of the New Siberian Islands. Zhokhov Island belongs to the De Long group. It has an area of 77 km². The highest point of the island is 123 m...
(о. Жо́хова)
The new Siberian Islands are low-lying. Their highest point is Mt. Malakatyn-Tas on Kotelny island with an elevation of 374 m.
The New Siberian Islands were once major hills within the Great Arctic Plain that once formed northern part of Late Pleistocene “Beringia” between Siberia and Alaska during the Last Glacial Maximum
Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum refers to a period in the Earth's climate history when ice sheets were at their maximum extension, between 26,500 and 19,000–20,000 years ago, marking the peak of the last glacial period. During this time, vast ice sheets covered much of North America, northern Europe and...
(Late Weichselian Epoch). These islands are what remains of about 1.6 million square kilometers of the formerly subaerial Great Arctic Plain that now lies submerged below parts of the Arctic Ocean
Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean, located in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Arctic north polar region, is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceanic divisions...
, East Siberian Sea
East Siberian Sea
The East Siberian Sea is a marginal sea in the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the Arctic Cape to the north, the coast of Siberia to the south, the New Siberian Islands to the west and Cape Billings, close to Chukotka, and Wrangel Island to the east...
, and Laptev Sea
Laptev Sea
The Laptev Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, the Taimyr Peninsula, Severnaya Zemlya and the New Siberian Islands. Its northern boundary passes from the Arctic Cape to a point with co-ordinates of 79°N and 139°E, and ends at the Anisiy...
. At this plain's greatest extent, sea level was 100–120 m below modern sea level and the coastline was located 700-1000 kilometers north of its current position. This plain was neither extensively glaciated during the Late Pleistocene nor the Last Glacial Maximum because it lay in the rain shadow
Rain shadow
A rain shadow is a dry area on the lee side of a mountainous area. The mountains block the passage of rain-producing weather systems, casting a "shadow" of dryness behind them. As shown by the diagram to the right, the warm moist air is "pulled" by the prevailing winds over a mountain...
of the Northern European ice sheet. During the frigid polar climate of the Last Glacial Maximum, 17,000 to 24,000 BP, small passive ice caps formed on the adjacent De Long Islands
De Long Islands
The De Long Islands are an uninhabited archipelago often included as part of the New Siberian Islands, lying north east of Novaya Sibir. This archipelago consists of Jeannette Island, Henrietta Island, Bennett Island, Vilkitsky Island and Zhokhov Island. These five islands have a total area of...
. Fragments of these ice caps are preserved on Jeannette
Jeannette Island
Jeannette Island is the easternmost island of the De Long Islands archipelago in the East Siberian Sea. It is the second smallest island of the De Long group, being only 2 km in length. It has an area of approximately . The highest peak of the island is...
, Henrietta
Henrietta Island
Henrietta Island is the northernmost island of the De Long archipelago in the East Siberian Sea. 40% of the island is covered with glaciers. Henrietta is roughly circular in shape and its diameter is about 6 km...
, and Bennett Island
Bennett Island
Bennett Island is the largest of the islands of the De Long group in the northern part of the East Siberian Sea. The area of this island is approximately 150 km² ...
s. Traces of former small slope and cirque glaciers in the form of buried ground ice deposits are preserved on Zhokhov Island
Zhokhov Island
Zhokhov Island is an island in the East Siberian Sea, situated 128 km north east of Novaya Sibir Island, the easternmost of the New Siberian Islands. Zhokhov Island belongs to the De Long group. It has an area of 77 km². The highest point of the island is 123 m...
. The Great Arctic Plain was submerged, except for the New Siberian and other isolated islands, within a relatively short time span of 7,000 years during the Early-Middle Holocene
Holocene
The Holocene is a geological epoch which began at the end of the Pleistocene and continues to the present. The Holocene is part of the Quaternary period. Its name comes from the Greek words and , meaning "entirely recent"...
.
Geology
As noted by Digby and numerous later publications, this archipelago consists of a mixture of folded and faulted sedimentary and igneous rockIgneous rock
Igneous rock is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic rock. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava...
s ranging in age from Precambrian
Precambrian
The Precambrian is the name which describes the large span of time in Earth's history before the current Phanerozoic Eon, and is a Supereon divided into several eons of the geologic time scale...
to Pliocene
Pliocene
The Pliocene Epoch is the period in the geologic timescale that extends from 5.332 million to 2.588 million years before present. It is the second and youngest epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Miocene Epoch and is followed by the Pleistocene Epoch...
. The Lyakhovsky Islands consist of a folded and faulted assemblage of Precambrian metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rock is the transformation of an existing rock type, the protolith, in a process called metamorphism, which means "change in form". The protolith is subjected to heat and pressure causing profound physical and/or chemical change...
s; upper Paleozoic
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic eon, spanning from roughly...
to Triassic
Triassic
The Triassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about 250 to 200 Mya . As the first period of the Mesozoic Era, the Triassic follows the Permian and is followed by the Jurassic. Both the start and end of the Triassic are marked by major extinction events...
sandstone
Sandstone
Sandstone is a sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized minerals or rock grains.Most sandstone is composed of quartz and/or feldspar because these are the most common minerals in the Earth's crust. Like sand, sandstone may be any colour, but the most common colours are tan, brown, yellow,...
s and shale
Shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock composed of mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals and tiny fragments of other minerals, especially quartz and calcite. The ratio of clay to other minerals is variable. Shale is characterized by breaks along thin laminae or parallel layering...
s; Jurassic
Jurassic
The Jurassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about Mya to Mya, that is, from the end of the Triassic to the beginning of the Cretaceous. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic era, also known as the age of reptiles. The start of the period is marked by...
to lower Cretaceous
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
turbidite
Turbidite
Turbidite geological formations have their origins in turbidity current deposits, which are deposits from a form of underwater avalanche that are responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean.-The ideal turbidite sequence:...
s; Cretaceous granite
Granite
Granite is a common and widely occurring type of intrusive, felsic, igneous rock. Granite usually has a medium- to coarse-grained texture. Occasionally some individual crystals are larger than the groundmass, in which case the texture is known as porphyritic. A granitic rock with a porphyritic...
s; and ophiolites. The Anzhu Islands consist of a highly faulted and folded assemblage of Ordovician
Ordovician
The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six of the Paleozoic Era, and covers the time between 488.3±1.7 to 443.7±1.5 million years ago . It follows the Cambrian Period and is followed by the Silurian Period...
to Devonian
Devonian
The Devonian is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic Era spanning from the end of the Silurian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya , to the beginning of the Carboniferous Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya...
limestone
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed largely of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Many limestones are composed from skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral or foraminifera....
s, dolomite
Dolomite
Dolomite is a carbonate mineral composed of calcium magnesium carbonate CaMg2. The term is also used to describe the sedimentary carbonate rock dolostone....
s, sandstones, shales, volcanoclastic strata, and igneous rocks; upper Paleozoic to Triassic sandstones and shales; Jurassic to lower Cretaceous turbidites; and upper Cretaceous to Pliocene sandstones and shales. The De Long Islands consist of early Paleozoic, middle Paleozoic, Cretaceous, and Neogene sedimentary and igneous, mostly basalt
Basalt
Basalt is a common extrusive volcanic rock. It is usually grey to black and fine-grained due to rapid cooling of lava at the surface of a planet. It may be porphyritic containing larger crystals in a fine matrix, or vesicular, or frothy scoria. Unweathered basalt is black or grey...
, rocks. These sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous rocks are mantled by loose Pleistocene
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
and Holocene
Holocene
The Holocene is a geological epoch which began at the end of the Pleistocene and continues to the present. The Holocene is part of the Quaternary period. Its name comes from the Greek words and , meaning "entirely recent"...
sediment
Sediment
Sediment is naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of fluids such as wind, water, or ice, and/or by the force of gravity acting on the particle itself....
s that range in thickness from a fraction of a meter to about 35 meters (115 ft).
Digby also noted that some early papers published about the New Siberian Islands incorrectly describe them, often along with other Arctic islands, i.e. Wrangel Island
Wrangel Island
Wrangel Island is an island in the Arctic Ocean, between the Chukchi Sea and East Siberian Sea. Wrangel Island lies astride the 180° meridian. The International Date Line is displaced eastwards at this latitude to avoid the island as well as the Chukchi Peninsula on the Russian mainland...
, as being made either up almost entirely of mammoth bones and tusks or of ice, sand, and the bones of mammoths and other extinct megafauna. Some of these papers were written by persons, i.e. Reverend D. G. Whitney, who had never visited the New Siberian Islands and relied upon anecdotes of traders and travelers and local folklore for their descriptions of them, and other articles were written by explorers and ivory hunters untrained in either geology or other sciences. Such statements have been shown to be fictional in nature by detailed studies of the geology of the New Siberian Islands by professional geologists, paleontologists, and other scientists including Dr. Andreev and others, Dr. Dorofeev and others, Dr. Kos’ko and Dr. Trufanov, Dr. Makeye and others, Dr. Meyer and others, and Dr. Romanovsky.
Ivory Deposits
As noted by Baron Eduard V. TollEduard Toll
Eduard Gustav von Toll was a Baltic German geologist and Arctic explorer in Russian service. Often referred to as Baron von Toll or as Eduard v. Toll, in Russia he is known as Eduard Vasiliyevich Toll . Eduard Toll was born on and he died in 1902 in an unknown location in the Arctic Ocean)...
in his account of the New Siberian Islands, sizable and economically significant accumulations of fossil
Fossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
ivory
Ivory
Ivory is a term for dentine, which constitutes the bulk of the teeth and tusks of animals, when used as a material for art or manufacturing. Ivory has been important since ancient times for making a range of items, from ivory carvings to false teeth, fans, dominoes, joint tubes, piano keys and...
occur within them. The ivory, along with mammoth
Mammoth
A mammoth is any species of the extinct genus Mammuthus. These proboscideans are members of Elephantidae, the family of elephants and mammoths, and close relatives of modern elephants. They were often equipped with long curved tusks and, in northern species, a covering of long hair...
and other bones are in found in recent beaches, drainage areas, river terraces and river beds. The New Siberian Islands are unique in the burial and preservation of fossil ivory “...in such a wonderful state of preservation that the tusks so found cannot be distinguished from the very best and purest ivory.” The abundant bones, even skeletons, of mammoth, rhinoceros, musk-ox, and other megafauna
Megafauna
In terrestrial zoology, megafauna are "giant", "very large" or "large" animals. The most common thresholds used are or...
along with the mammoth ivory found in these islands are preserved by permafrost, in which they are encased. The permafrost periodically developed in Late Pleistocene loess
Loess
Loess is an aeolian sediment formed by the accumulation of wind-blown silt, typically in the 20–50 micrometre size range, twenty percent or less clay and the balance equal parts sand and silt that are loosely cemented by calcium carbonate...
, solifluction
Solifluction
In geology, solifluction, also known as soil fluction, is a type of mass wasting where waterlogged sediment moves slowly downslope, over impermeable material. It occurs in periglacial environments where melting during the warm season leads to water saturation in the thawed surface material ,...
, pond
Pond
A pond is a body of standing water, either natural or man-made, that is usually smaller than a lake. A wide variety of man-made bodies of water are classified as ponds, including water gardens, water features and koi ponds; all designed for aesthetic ornamentation as landscape or architectural...
, and stream
Stream
A stream is a body of water with a current, confined within a bed and stream banks. Depending on its locale or certain characteristics, a stream may be referred to as a branch, brook, beck, burn, creek, "crick", gill , kill, lick, rill, river, syke, bayou, rivulet, streamage, wash, run or...
sediment
Sediment
Sediment is naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of fluids such as wind, water, or ice, and/or by the force of gravity acting on the particle itself....
s as they accumulated. The radiocarbon dating of bones, ivory, and plants; optically stimulated luminescence dating of enclosing sediments; and uranium-thorium dating
Uranium-thorium dating
Uranium-thorium dating, also called thorium-230 dating, uranium-series disequilibrium dating or uranium-series dating, is a radiometric dating technique commonly used to determine the age of calcium carbonate materials such as speleothem or coral...
of associated peats demonstrate that the bones and ivory, which are found within some of the New Siberian Islands, accumulated over a period of some 200,000 years. Radiocarbon dates obtained from the collagen
Collagen
Collagen is a group of naturally occurring proteins found in animals, especially in the flesh and connective tissues of mammals. It is the main component of connective tissue, and is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up about 25% to 35% of the whole-body protein content...
of 87 mammoth tusks and bones collected from Faddeevsky, Kotelniy, and New Siberia
New Siberia
New Siberia is the easternmost of the Anzhu Islands, the northern subgroup of the New Siberian Islands lying between the Laptev Sea and East Siberian Sea. Its area of approximately 6,200 km² places it just outside the 100 largest islands in the world. New Siberia Island is low lying, rising...
islands ranged from 9470±40 BP (C14) to greater than 50,000 BP (C14). Their "wonderful state of preservation" is the result of them having been frozen in permafrost since their burial.
Climate
The climateClimate
Climate encompasses the statistics of temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, rainfall, atmospheric particle count and other meteorological elemental measurements in a given region over long periods...
is arctic
Arctic
The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost...
and severe. Snow cover is present for 9 months of the year.
- Average temperatureTemperatureTemperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
in January: −28°C to −31°C - Temperature in July: At the coasts icy Arctic water lets the temperatures stay relatively low. Average maximum temperatures from +8°C to +11°C and average minimum temperatures from -3°C to +1°C. In the interior of the islands the average maximum temperatures in July are +16°C to +19°C and average minimum temperatures +3°C to +6°C.
- PrecipitationPrecipitation (meteorology)In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation...
: up to 132 mm a year
Permafrost
Permafrost
In geology, permafrost, cryotic soil or permafrost soil is soil at or below the freezing point of water for two or more years. Ice is not always present, as may be in the case of nonporous bedrock, but it frequently occurs and it may be in amounts exceeding the potential hydraulic saturation of...
and underground ice are very common. The surface of the islands is covered with Arctic tundra
Tundra
In physical geography, tundra is a biome where the tree growth is hindered by low temperatures and short growing seasons. The term tundra comes through Russian тундра from the Kildin Sami word tūndâr "uplands," "treeless mountain tract." There are three types of tundra: Arctic tundra, alpine...
vegetation
Vegetation
Vegetation is a general term for the plant life of a region; it refers to the ground cover provided by plants. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular taxa, life forms, structure, spatial extent, or any other specific botanical or geographic characteristics. It is broader...
and numerous lakes.
The ocean surrounding the islands is covered with ice most of the year. During warm years, the ocean briefly opens for navigation July through October. During cold years, islands may remain ice-locked through the summer.
Polar night conditions are present November through February, and, conversely, the Sun remains above the horizon continuously during summer months.
History
The first news about the existence of the New Siberian Islands was brought by a CossackCossack
Cossacks are a group of predominantly East Slavic people who originally were members of democratic, semi-military communities in what is today Ukraine and Southern Russia inhabiting sparsely populated areas and islands in the lower Dnieper and Don basins and who played an important role in the...
Yakov Permyakov
Yakov Permyakov
Yakov Permyakov was a Russian seafarer, explorer, merchant, and Cossack.In 1710, while sailing from the Lena River to the Kolyma River, Permyakov observed the silhouette of two unknown island groups in the sea...
in the beginning of the 18th century. In 1712, a Cossack unit led by M. Vagin reached the Great Lyakhovsky Island
Great Lyakhovsky Island
Bolshoy Lyakhovsky Island , or Great Lyakhovsky, is the largest of the Lyakhovsky Islands belonging to the New Siberian Islands archipelago between the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea in northern Russia...
. At the beginning of the 19th century, the islands were further explored by Yakov Sannikov
Yakov Sannikov
Yakov Sannikov was a Russian merchant and explorer of the New Siberian Islands.In 1800, Sannikov discovered and charted Stolbovoy Island, and in 1805 Faddeyevsky Island. In 1809-1810, he took part in the expedition led by Matvei Gedenschtrom. In 1810, Sannikov crossed the island of New Siberia...
, Matvei Gedenschtrom
Matvei Gedenschtrom
Matvei Matveyevich Gedenschtrom was a Russian explorer of Northern Siberia, writer, and public servant.Matvei Gedenschtrom attended University of Tartu. He did not finish his studies and left his alma mater in favor of work at Tallinn customs. Soon, however, he was arrested in connection with a...
and others.
In 1809-1810 Yakov Sannikov
Yakov Sannikov
Yakov Sannikov was a Russian merchant and explorer of the New Siberian Islands.In 1800, Sannikov discovered and charted Stolbovoy Island, and in 1805 Faddeyevsky Island. In 1809-1810, he took part in the expedition led by Matvei Gedenschtrom. In 1810, Sannikov crossed the island of New Siberia...
and Matvei Gedenschtrom
Matvei Gedenschtrom
Matvei Matveyevich Gedenschtrom was a Russian explorer of Northern Siberia, writer, and public servant.Matvei Gedenschtrom attended University of Tartu. He did not finish his studies and left his alma mater in favor of work at Tallinn customs. Soon, however, he was arrested in connection with a...
went to The New Siberian Islands on a cartographic expedition. Yakov Sannikov reported the sighting of a "new land" north of Kotelny in 1811. This became the myth of Zemlya Sannikova or "Sannikov Land
Sannikov Land
Sannikov Land was a phantom island in the Arctic Ocean. Its supposed existence became something of a myth in 19th-century Russia.Yakov Sannikov and Matvei Gedenschtrom claimed to have seen it during their 1809-1810 cartographic expedition to the New Siberian Islands...
".
In 1886 Baron Eduard von Toll
Eduard Toll
Eduard Gustav von Toll was a Baltic German geologist and Arctic explorer in Russian service. Often referred to as Baron von Toll or as Eduard v. Toll, in Russia he is known as Eduard Vasiliyevich Toll . Eduard Toll was born on and he died in 1902 in an unknown location in the Arctic Ocean)...
, during his first visit to the New Siberian Islands thought that he had seen an unknown land north of Kotelny Island. He guessed that this was the so-called "Zemlya Sannikova".
Polar explorer and scientist Baron Eduard V. Toll
Eduard Toll
Eduard Gustav von Toll was a Baltic German geologist and Arctic explorer in Russian service. Often referred to as Baron von Toll or as Eduard v. Toll, in Russia he is known as Eduard Vasiliyevich Toll . Eduard Toll was born on and he died in 1902 in an unknown location in the Arctic Ocean)...
paid a further visit to this island group in the spring of 1892, accompanied only by one Cossack and three natives. He traveled over the ice in sledges drawn by dogs and reached the south coast of Great Lyakhovsky Island
Great Lyakhovsky Island
Bolshoy Lyakhovsky Island , or Great Lyakhovsky, is the largest of the Lyakhovsky Islands belonging to the New Siberian Islands archipelago between the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea in northern Russia...
. Along the southern coast of this island, Von Toll (1985), in one of his more important and interesting discoveries, found well preserved bones, ivory, peat, wood, and even a tree within 40 meter (130 feet) high sea cliffs that exposes Late Pleistocene sediments that are cemented by permafrost
Permafrost
In geology, permafrost, cryotic soil or permafrost soil is soil at or below the freezing point of water for two or more years. Ice is not always present, as may be in the case of nonporous bedrock, but it frequently occurs and it may be in amounts exceeding the potential hydraulic saturation of...
; have accumulated over the last 200,000 years; and overlie a Pliocene paleosol
Paleosol
In the geosciences, paleosol can have two meanings. The first meaning, common in geology and paleontology, refers to a former soil preserved by burial underneath either sediments or volcanic deposits , which in the case of older deposits have lithified into rock...
. These strata are described in greater detail in the Great Lyakhovsky Island
Great Lyakhovsky Island
Bolshoy Lyakhovsky Island , or Great Lyakhovsky, is the largest of the Lyakhovsky Islands belonging to the New Siberian Islands archipelago between the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea in northern Russia...
page.
Further reading
- Alfred Wegner institute (AWI) Publications, Berichte zur Polar- und Meeresforschung (Reports on polar and marine research) - free, downloadable research reports on the biology, geology, oceanography, hydrology, paleontology, paleoclimatology, fauna, flora, soils, cryology, and so forth of the New Siberian Islands, Laptev Sea, and other parts of the Arctic Circle.
- Andreev, A.A., and D.M. Peteet, 1999, Climate and Diet of Mammoths in the East Siberian Arctic . Science Briefs (August 1999). Goddard Institute for Space Studies, New York, New York. Last visited July 12, 2008.
- Babinski, E.T., nd, A Frozen Ninety Foot Tall Plum Tree. examination of reports of a 90-foot fossil plum tree being found in Great Lyakhovsky Island of the New Siberian Islands.
- Basilyan, A., and P.A. Nikolskiy, 2002, Quaternary Deposits of New Siberia Island (Russian Arctic). 32nd Annual Arctic Workshop Abstracts, March 14–16, 2002, INSTAAR, University of Colorado at Boulder.
- Espinoza, E.O., and M.-J. Mann, 1993, The history and significance of the Schreger Pattern in Proboscidean ivory chracterization. Journal for the American Institute for Conservation. vol. 32, no. 3, Article 3, pp. 241–248.
- Kuznetsova, T.V., L.D. Sulerzhitsky, Ch. Siegert, 2001, New data on the “Mammoth” fauna of the Laptev Shelf Land (East Siberian Arctic), 144 KB PDF file, The World of Elephants - International Congress, Rome 2001. Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche, Centro di Studio per il Quaternario e l'Evoluzione Ambientale, Università di Roma, Roma, Italy.
External links
- New Siberian Islands - aerial photographs of these islands.
- Location of Nanosnyy

