
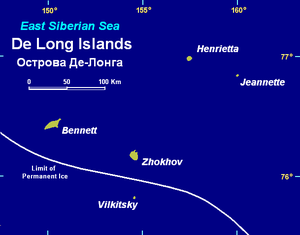
De Long Islands
Encyclopedia
Archipelago
An archipelago , sometimes called an island group, is a chain or cluster of islands. The word archipelago is derived from the Greek ἄρχι- – arkhi- and πέλαγος – pélagos through the Italian arcipelago...
often included as part of the New Siberian Islands
New Siberian Islands
The New Siberian Islands are an archipelago, located to the North of the East Siberian coast between the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea north of the Sakha Republic....
, lying north east of Novaya Sibir. This archipelago consists of Jeannette Island
Jeannette Island
Jeannette Island is the easternmost island of the De Long Islands archipelago in the East Siberian Sea. It is the second smallest island of the De Long group, being only 2 km in length. It has an area of approximately . The highest peak of the island is...
, Henrietta Island
Henrietta Island
Henrietta Island is the northernmost island of the De Long archipelago in the East Siberian Sea. 40% of the island is covered with glaciers. Henrietta is roughly circular in shape and its diameter is about 6 km...
, Bennett Island
Bennett Island
Bennett Island is the largest of the islands of the De Long group in the northern part of the East Siberian Sea. The area of this island is approximately 150 km² ...
, Vilkitsky Island and Zhokhov Island
Zhokhov Island
Zhokhov Island is an island in the East Siberian Sea, situated 128 km north east of Novaya Sibir Island, the easternmost of the New Siberian Islands. Zhokhov Island belongs to the De Long group. It has an area of 77 km². The highest point of the island is 123 m...
. These five islands have a total area of 228 km². At 75 km², Bennett (Bennetta in Russian) Island is the largest island. These islands lie around 77°N, are partially covered by glacier
Glacier
A glacier is a large persistent body of ice that forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. At least 0.1 km² in area and 50 m thick, but often much larger, a glacier slowly deforms and flows due to stresses induced by its weight...
s, and rise to peaks. In 1996, the total area of these islands covered by ice caps and glaciers was 80.6 km². This island group belongs to the Sakha (Yakutia) Republic administrative division of Russia.
The De Long Islands were once major hills within the Great Arctic Plain that once formed the northern part of Late Pleistocene “Beringia” between Siberia and Alaska during the Last Glacial Maximum
Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum refers to a period in the Earth's climate history when ice sheets were at their maximum extension, between 26,500 and 19,000–20,000 years ago, marking the peak of the last glacial period. During this time, vast ice sheets covered much of North America, northern Europe and...
(Late Weichselian Epoch). These islands are what remains of about 1.6 million square kilometers of the formally subaerial Great Arctic Plain that now lies submerged below the Arctic Ocean
Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean, located in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Arctic north polar region, is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceanic divisions...
and East Siberian Sea
East Siberian Sea
The East Siberian Sea is a marginal sea in the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the Arctic Cape to the north, the coast of Siberia to the south, the New Siberian Islands to the west and Cape Billings, close to Chukotka, and Wrangel Island to the east...
. At this plain's greatest extent during the Last Glacial Maximum, sea level was 100-120 m below modern sea level and the coastline was located 700-1000 kilometers north of its current position. This plain was neither extensively glaciated during the Late Pleistocene nor during the Last Glacial Maximum because it lay in the rain shadow
Rain shadow
A rain shadow is a dry area on the lee side of a mountainous area. The mountains block the passage of rain-producing weather systems, casting a "shadow" of dryness behind them. As shown by the diagram to the right, the warm moist air is "pulled" by the prevailing winds over a mountain...
of the Northern European ice sheet. The Great Arctic Plain was submerged, except for the New Siberian and other isolated islands, within a relatively short time span of 7,000 years during the Early-Middle Holocene.
During the extremely frigid polar climate of the Last Glacial Maximum (Late Weichselian Epoch), 17,000 to 24,000 BP, small passive ice caps did form on the De Long Islands. Fragments of these ice caps are preserved on Jeannette, Henrietta, and Bennett Islands. Traces of former Late Weichselian slope and cirque
Cirque
Cirque may refer to:* Cirque, a geological formation* Makhtesh, an erosional landform found in the Negev desert of Israel and Sinai of Egypt*Cirque , an album by Biosphere* Cirque Corporation, a company that makes touchpads...
glacier
Glacier
A glacier is a large persistent body of ice that forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. At least 0.1 km² in area and 50 m thick, but often much larger, a glacier slowly deforms and flows due to stresses induced by its weight...
s in the form of buried ground ice deposits are preserved on Zhokhov Island.
Geology
Early PaleozoicPaleozoic
The Paleozoic era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic eon, spanning from roughly...
, Middle Paleozoic, Cretaceous
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
, and Neogene
Neogene
The Neogene is a geologic period and system in the International Commission on Stratigraphy Geologic Timescale starting 23.03 ± 0.05 million years ago and ending 2.588 million years ago...
rocks have been mapped within the De Long Islands. The Early Paleozoic rocks are Cambrian
Cambrian
The Cambrian is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, lasting from Mya ; it is succeeded by the Ordovician. Its subdivisions, and indeed its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for Wales, where Britain's...
and Ordovician
Ordovician
The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six of the Paleozoic Era, and covers the time between 488.3±1.7 to 443.7±1.5 million years ago . It follows the Cambrian Period and is followed by the Silurian Period...
sedimentary rocks interbedded with minor amounts of limestone
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed largely of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Many limestones are composed from skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral or foraminifera....
. The Middle Paleozoic rocks consist of predominately folded
Fold (geology)
The term fold is used in geology when one or a stack of originally flat and planar surfaces, such as sedimentary strata, are bent or curved as a result of permanent deformation. Synsedimentary folds are those due to slumping of sedimentary material before it is lithified. Folds in rocks vary in...
and faulted basalt
Basalt
Basalt is a common extrusive volcanic rock. It is usually grey to black and fine-grained due to rapid cooling of lava at the surface of a planet. It may be porphyritic containing larger crystals in a fine matrix, or vesicular, or frothy scoria. Unweathered basalt is black or grey...
ic, andesitic
Andesite
Andesite is an extrusive igneous, volcanic rock, of intermediate composition, with aphanitic to porphyritic texture. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between basalt and dacite. The mineral assemblage is typically dominated by plagioclase plus pyroxene and/or hornblende. Magnetite,...
, and dioritic
Diorite
Diorite is a grey to dark grey intermediate intrusive igneous rock composed principally of plagioclase feldspar , biotite, hornblende, and/or pyroxene. It may contain small amounts of quartz, microcline and olivine. Zircon, apatite, sphene, magnetite, ilmenite and sulfides occur as accessory...
volcanoclastics, tuff
Tuff
Tuff is a type of rock consisting of consolidated volcanic ash ejected from vents during a volcanic eruption. Tuff is sometimes called tufa, particularly when used as construction material, although tufa also refers to a quite different rock. Rock that contains greater than 50% tuff is considered...
s, lava
Lava
Lava refers both to molten rock expelled by a volcano during an eruption and the resulting rock after solidification and cooling. This molten rock is formed in the interior of some planets, including Earth, and some of their satellites. When first erupted from a volcanic vent, lava is a liquid at...
s, dikes
Dike (geology)
A dike or dyke in geology is a type of sheet intrusion referring to any geologic body that cuts discordantly across* planar wall rock structures, such as bedding or foliation...
, and sills
Sill (geology)
In geology, a sill is a tabular sheet intrusion that has intruded between older layers of sedimentary rock, beds of volcanic lava or tuff, or even along the direction of foliation in metamorphic rock. The term sill is synonymous with concordant intrusive sheet...
. Cretaceous rocks are composed of basalts and interbedded argillite
Argillite
An argillite is a fine-grained sedimentary rock composed predominantly of indurated clay particles. Argillaceous rocks are basically lithified muds and oozes. They contain variable amounts of silt-sized particles. The argillites grade into shale when the fissile layering typical of shale is...
s, sandstone
Sandstone
Sandstone is a sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized minerals or rock grains.Most sandstone is composed of quartz and/or feldspar because these are the most common minerals in the Earth's crust. Like sand, sandstone may be any colour, but the most common colours are tan, brown, yellow,...
s and minor coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
s. The youngest rocks exposed within the De Long Islands are Neogene basaltic volcanic rocks.
History
Jeannette Island, Henrietta Island, and Bennett Island were discovered in 1881 by the ill-fated JeannetteUSS Jeannette (1878)
The first USS Jeannette was originally HMS Pandora, a Philomel-class gunvessel of the Royal Navy, and was purchased in 1875 by Sir Allen Young for his arctic voyages in 1875-1876. The ship was purchased in 1878 by James Gordon Bennett, Jr., owner of the New York Herald; and renamed Jeannette...
expedition, commanded by Lieutenant Commander George W. DeLong
George W. DeLong
George Washington DeLong was a United States Navy officer and explorer.- Biography :Born in New York City, he was educated at the United States Naval Academy in Newport, Rhode Island...
, USN
United States Navy
The United States Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the seven uniformed services of the United States. The U.S. Navy is the largest in the world; its battle fleet tonnage is greater than that of the next 13 largest navies combined. The U.S...
. De Long claimed these islands for the U.S. The United States Department of State
United States Department of State
The United States Department of State , is the United States federal executive department responsible for international relations of the United States, equivalent to the foreign ministries of other countries...
has asserted that claim has never been made by the United States to any of the islands, and the US recognizes it as Russian territory. though the United States Department of the Navy
United States Department of the Navy
The Department of the Navy of the United States of America was established by an Act of Congress on 30 April 1798, to provide a government organizational structure to the United States Navy and, from 1834 onwards, for the United States Marine Corps, and when directed by the President, of the...
has asserted that Henrietta Island had been possessed.
During 1916 the Russian ambassador in London issued an official notice to the effect that the Imperial government considered these islands were integral parts of the Russian Empire. This territorial claim was later maintained by the Soviet Union. A resolution of the Alaska State Senate in 1988 supported an American claim to the islands, but during 1994 the Alaska State Supreme Court ruled in D. Denardo v. State of Alaska that Bennett Island, along with several islands, is not part of Alaska.
In August 1901 Russian Arctic ship Zarya
Zarya (polar ship)
Zarya was a steam- and sail-powered brig used by the Russian Academy of Sciences for a polar exploration during 1900–1903.Toward the end of the 19th century, the Russian Academy of Sciences sought to build a general-purpose research vessel for long-term expeditions. The first such Russian...
headed across the Laptev Sea
Laptev Sea
The Laptev Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, the Taimyr Peninsula, Severnaya Zemlya and the New Siberian Islands. Its northern boundary passes from the Arctic Cape to a point with co-ordinates of 79°N and 139°E, and ends at the Anisiy...
, searching for the legendary Sannikov Land
Sannikov Land
Sannikov Land was a phantom island in the Arctic Ocean. Its supposed existence became something of a myth in 19th-century Russia.Yakov Sannikov and Matvei Gedenschtrom claimed to have seen it during their 1809-1810 cartographic expedition to the New Siberian Islands...
(Zemlya Sannikova) but was soon blocked by floating pack ice in the New Siberian Islands
New Siberian Islands
The New Siberian Islands are an archipelago, located to the North of the East Siberian coast between the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea north of the Sakha Republic....
. During 1902 the attempts to reach Sannikov Land, deemed to be beyond the De Long Islands, continued while Zarya was trapped in fast ice. Leaving the ship, Russian Arctic explorer Baron Eduard Toll
Eduard Toll
Eduard Gustav von Toll was a Baltic German geologist and Arctic explorer in Russian service. Often referred to as Baron von Toll or as Eduard v. Toll, in Russia he is known as Eduard Vasiliyevich Toll . Eduard Toll was born on and he died in 1902 in an unknown location in the Arctic Ocean)...
and three companions vanished forever in November 1902 in the while travelling away from Bennett Island
Bennett Island
Bennett Island is the largest of the islands of the De Long group in the northern part of the East Siberian Sea. The area of this island is approximately 150 km² ...
towards the south on loose ice floes.
Vilkitsky Island (East Siberian Sea) and Zhokhov Island were discovered by Boris Vilkitsky
Boris Vilkitsky
Boris Andreyevich Vilkitsky was a Russian hydrographer and surveyor. He was the son of Andrey Ippolitovich Vilkitsky....
during the Imperial Russian Arctic Ocean Hydrographic Expedition he led in 1913 and 1914 respectively. They lie slightly further south (around 76°N), are unglaciated, and lower lying.
Henrietta was the site of a research station from 1937 to 1963.

