
Middle Bronze Age alphabets
Encyclopedia

Proto-Sinaitic is a Middle Bronze Age script attested in a very small collection of inscriptions at Serabit el-Khadim
Serabit el-Khadim
Serabit el-Khadim is a locality in the south-west Sinai Peninsula where turquoise was mined extensively in antiquity, mainly by the ancient Egyptians...
in the Sinai Peninsula
Sinai Peninsula
The Sinai Peninsula or Sinai is a triangular peninsula in Egypt about in area. It is situated between the Mediterranean Sea to the north, and the Red Sea to the south, and is the only part of Egyptian territory located in Asia as opposed to Africa, effectively serving as a land bridge between two...
. Due to the extreme scarcity of Proto-Sinaitic signs, very little is known with certainty about the nature of the script. Because the script co-existed with Egyptian hieroglyphs
Egyptian hieroglyphs
Egyptian hieroglyphs were a formal writing system used by the ancient Egyptians that combined logographic and alphabetic elements. Egyptians used cursive hieroglyphs for religious literature on papyrus and wood...
, it is likely that it represented true writing
Writing
Writing is the representation of language in a textual medium through the use of a set of signs or symbols . It is distinguished from illustration, such as cave drawing and painting, and non-symbolic preservation of language via non-textual media, such as magnetic tape audio.Writing most likely...
, but this is by no means certain. It has also been argued that Proto-Sinaitic was an alphabet
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letters—basic written symbols or graphemes—each of which represents a phoneme in a spoken language, either as it exists now or as it was in the past. There are other systems, such as logographies, in which each character represents a word, morpheme, or semantic...
and the ancestor of the Phoenician alphabet
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
, from which nearly all modern alphabets descend.
There have been two major discoveries of inscriptions that may be related to the Proto-Sinaitic script, the first in the winter of 1904–1905 in Sinai by Hilda and Flinders Petrie, dated to the mid 19th century BCE, and more recently in 1999 in Middle Egypt
Middle Egypt
Middle Egypt is the section of land between Lower Egypt and Upper Egypt, stretching upstream from Asyut in the south to Memphis in the north. At the time, Ancient Egypt was divided into Lower and Upper Egypt, though Middle Egypt was technically a subdivision of Upper Egypt. It was not until the...
by John and Deborah Darnell, dated to the 18th century BCE.
Serabit inscriptions
The Sinai inscriptions are best known from carved graffitiGraffiti
Graffiti is the name for images or lettering scratched, scrawled, painted or marked in any manner on property....
and votive texts from a mountain in the Sinai called Serabit el-Khadim
Serabit el-Khadim
Serabit el-Khadim is a locality in the south-west Sinai Peninsula where turquoise was mined extensively in antiquity, mainly by the ancient Egyptians...
and its temple to the Egyptian goddess Hathor
Hathor
Hathor , is an Ancient Egyptian goddess who personified the principles of love, beauty, music, motherhood and joy. She was one of the most important and popular deities throughout the history of Ancient Egypt...
. The mountain contained turquoise
Turquoise
Turquoise is an opaque, blue-to-green mineral that is a hydrous phosphate of copper and aluminium, with the chemical formula CuAl648·4. It is rare and valuable in finer grades and has been prized as a gem and ornamental stone for thousands of years owing to its unique hue...
mines which were visited by repeated expeditions over 800 years. Many of the workers and officials were from the Nile Delta
Nile Delta
The Nile Delta is the delta formed in Northern Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east, it covers some 240 km of Mediterranean coastline—and is a rich...
, and included large numbers of "Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
tics", speakers of the Canaanite language that was ancestral to Phoenician and Hebrew
Hebrew language
Hebrew is a Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Culturally, is it considered by Jews and other religious groups as the language of the Jewish people, though other Jewish languages had originated among diaspora Jews, and the Hebrew language is also used by non-Jewish groups, such...
, who had been allowed to settle the eastern Delta.
Most of the thirty or so inscriptions have been found among much more numerous hieratic
Hieratic
Hieratic refers to a cursive writing system that was used in the provenance of the pharaohs in Egypt and Nubia that developed alongside the hieroglyphic system, to which it is intimately related...
and hieroglyphic inscriptions, scratched on rocks near and in the turquoise mines and along the roads leading to the temple. Four inscriptions have been found in the temple, on two small human statues and on either side of a small stone sphinx
Sphinx
A sphinx is a mythical creature with a lion's body and a human head or a cat head.The sphinx, in Greek tradition, has the haunches of a lion, the wings of a great bird, and the face of a woman. She is mythicised as treacherous and merciless...
. They are crudely done, suggesting that the workers who made them were illiterate apart from this script. In 1916, Alan Gardiner
Alan Gardiner
Sir Alan Henderson Gardiner was one of the premier British Egyptologists of the early and mid-20th century...
, using sound values derived from the alphabet hypothesis, translated a collection of signs as לבעלת (to the Lady) One of the instances of this collection of signs was on the small stone sphinx, which contained a bilingual inscription: The Egyptian reads The beloved of Hathor, the mistress of turquoise, and according to Gardiner's translation, the Proto-Sinaitic reads (the beloved of the Lady; beloved), with the final t of (Lady) not surviving. Egyptologist Orly Goldwasser
Orly Goldwasser
Orly Goldwasser is an Israeli Egyptologist, professor of Egyptology at the Hebrew University.Orly Goldwasser received her B.A. at Tel Aviv University, continued studying at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem, where she was awarded her M.A. and PhD degrees...
believes the script was most likely invented during the reign of pharaoh Amenemhet III of the Twelfth Dynasty.
The script has graphic similarities with the Egyptian hieratic
Hieratic
Hieratic refers to a cursive writing system that was used in the provenance of the pharaohs in Egypt and Nubia that developed alongside the hieroglyphic system, to which it is intimately related...
script, the less elaborate form of the hieroglyph
Egyptian hieroglyphs
Egyptian hieroglyphs were a formal writing system used by the ancient Egyptians that combined logographic and alphabetic elements. Egyptians used cursive hieroglyphs for religious literature on papyrus and wood...
s. In the 1950s and 60s it was common to show the derivation of the Canaanite alphabet from hieratic, using William Albright
William F. Albright
William Foxwell Albright was an American archaeologist, biblical scholar, philologist and expert on ceramics. From the early twentieth century until his death, he was the dean of biblical archaeologists and the universally acknowledged founder of the Biblical archaeology movement...
's interpretations of Proto-Sinaitic as the key. It was generally accepted that the language of the inscriptions was Semitic and that the script had a hieratic prototype. If correctly translated, the word (Lady) lends credence to the identification of the language as Semitic. However, the lack of further progress in decipherment casts doubt over the other suppositions, and the identification of the hieratic prototypes remains speculative.
Alphabet hypothesis
Proto-Sinaitic is hypothesized to be an intermediate step between Egyptian hieroglyphsEgyptian hieroglyphs
Egyptian hieroglyphs were a formal writing system used by the ancient Egyptians that combined logographic and alphabetic elements. Egyptians used cursive hieroglyphs for religious literature on papyrus and wood...
and the Phoenician alphabet
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
. If this is the case, Proto-Sinaitic may be the first alphabet. According to the alphabet theory, the alphabet began with Proto-Sinaitic at the end of the Middle Bronze Age and split into the South Arabian script and the Proto-Canaanite script
Proto-Canaanite alphabet
Proto-Canaanite is the name given to the Proto-Sinaitic script when found in Canaan. the early Phoenician script before some cut-off date, typically 1050 BCE. The Phoenician, Hebrew, and other Canaanite dialects were largely indistinguishable before that time...
in the Late Bronze Age. The Proto-Canaanite script would then have evolved into Phoenician proper by 1100 BCE. The theory centers around the idea that only the graphic form of the Proto-Sinaitic characters derive from Egyptian hieroglyphs, and that they were given the sound value of the first consonant of the Semitic translation of the hieroglyph. (Using a character for the first sound of its name is the acrophonic principle
Acrophony
Acrophony is the naming of letters of an alphabetic writing system so that a letter's name begins with the letter itself. For example, Greek letter names are acrophonic: the names of the letters α, β, γ, δ, are spelled with the respective letters: ....
.) For example, the hieroglyph for pr "house" (a rectangle partially open along one side, "O1" in Gardiner's sign list
Gardiner's Sign List
Gardiner's Sign List is a list of common Egyptian hieroglyphs compiled by Sir Alan Gardiner. It is considered a standard reference in the study of Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs....
) was adopted to write Semitic /b/, after the first consonant of baytu, the Semitic word for "house". According to the alphabet hypothesis, the shapes of the letters would have evolved from Proto-Sinaitic forms into Phoenician forms, but the names of the letters would have remained the same. Below is a table showing selected Proto-Sinaitic signs and the proposed correspondences with Phoenician letters. Also shown are the sound values, names, and descendants of the Phoenician letters.
| Proto-Sinaitic | Phoenician Phoenician alphabet The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia... |
Phoen. value | Phoen. name | Hebrew | Greek | Latin | Arabic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
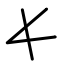 |
"ox" | א Aleph * Aleph or Alef is the first letter of the Semitic abjads descended from Proto-Canaanite, Arabic alphabet, Phoenician alphabet, Hebrew alphabet, Syriac alphabet-People:*Aleph , an Italo disco artist and alias of Dave Rodgers... |
Α Alpha (letter) Alpha is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 1. It was derived from the Phoenician letter Aleph... |
A A A is the first letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet. It is similar to the Ancient Greek letter Alpha, from which it derives.- Origins :... |
ا | |
 |
 |
bet "house" | ב Bet (letter) Bet, Beth, Beh, or Vet is the second letter of many Semitic abjads, including Arabic alphabet , Aramaic, Hebrew , Phoenician and Syriac... |
Β Beta (letter) Beta is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In Ancient Greek, beta represented the voiced bilabial plosive . In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced labiodental fricative .... |
B B B is the second letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet. It is used to represent a variety of bilabial sounds , most commonly a voiced bilabial plosive.-History:... |
ب | |
 |
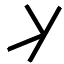 |
kap Kaph Kaph is the eleventh letter of many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Kaf , Arabic alphabet , Persian alphabet... "hand" |
כ Kaph Kaph is the eleventh letter of many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Kaf , Arabic alphabet , Persian alphabet... |
Κ Kappa Kappa is the 10th letter of the Greek alphabet, used to represent the voiceless velar stop, or "k", sound in Ancient and Modern Greek. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 20. It was derived from the Phoenician letter Kaph... |
K K K is the eleventh letter of the English and basic modern Latin alphabet.-History and usage:In English, the letter K usually represents the voiceless velar plosive; this sound is also transcribed by in the International Phonetic Alphabet and X-SAMPA.... |
ك | |
 |
 |
mem Mem Mem is the thirteenth letter of many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Arabic... "water" |
מ Mem Mem is the thirteenth letter of many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Arabic... |
Μ Mu (letter) Carlos Alberto Vives Restrepo is a Grammy Award and three-time Latin Grammy Award winning-Colombian singer, composer and actor.-Biography:... |
M M M is the thirteenth letter of the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The letter M is derived from the Phoenician Mem, via the Greek Mu . Semitic Mem probably originally pictured water... |
م | |
 |
"eye" | ע Ayin ' or ' is the sixteenth letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Arabic . It is the twenty-first letter in the new Persian alphabet... |
Ο Omicron Omicron is the 15th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 70. It is rarely used in mathematics because it is indistinguishable from the Latin letter O and easily confused with the digit 0... |
O O O is the fifteenth letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet.The letter was derived from the Semitic `Ayin , which represented a consonant, probably , the sound represented by the Arabic letter ع called `Ayn. This Semitic letter in its original form seems to have been inspired by a... |
ع | ||
 |
 |
"head" | ר Resh Resh is the twentieth letter of many Semitic alphabets, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Arabic alphabet . Its sound value is one of a number of rhotic consonants: usually or , but also or in Hebrew.... |
Ρ Rho (letter) Rho is the 17th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 100. It is derived from Semitic resh "head"... |
R R R is the eighteenth letter of the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The original Semitic letter may have been inspired by an Egyptian hieroglyph for tp, "head". It was used for by Semites because in their language, the word for "head" was rêš . It developed into Greek Ρ and Latin R... |
ر |
Proto-Canaanite inscriptions
Only a few inscriptions have been found in CanaanCanaan
Canaan is a historical region roughly corresponding to modern-day Israel, Palestine, Lebanon, and the western parts of Jordan...
itself, dated from ca. the 17th century BCE. They are all very short, most consisting of only a couple of letters, and may have been written by Canaanite caravaners or soldiers from Egypt. They sometimes go by the name Proto-Canaanite, although the term "Proto-Canaanite" is also applied to early Phoenician or Hebrew inscriptions.
Wadi el-Hol inscriptions
The Wadi el-Hol inscriptions (Arabic وادي الهول 'Ravine of Terror') were carved on the stone sides of an ancient high-desert military and trade road linking ThebesThebes, Egypt
Thebes is the Greek name for a city in Ancient Egypt located about 800 km south of the Mediterranean, on the east bank of the river Nile within the modern city of Luxor. The Theban Necropolis is situated nearby on the west bank of the Nile.-History:...
and Abydos
Abydos, Egypt
Abydos is one of the most ancient cities of Upper Egypt, and also of the eight Upper Nome, of which it was the capital city. It is located about 11 kilometres west of the Nile at latitude 26° 10' N, near the modern Egyptian towns of el-'Araba el Madfuna and al-Balyana...
, in the heart of literate Egypt. They are in a wadi
Wadi
Wadi is the Arabic term traditionally referring to a valley. In some cases, it may refer to a dry riverbed that contains water only during times of heavy rain or simply an intermittent stream.-Variant names:...
in the Qena
Qena
Qena is a city in Upper Egypt, and the capital of the Qena Governorate. Situated on the east bank of the Nile, it was known as Kaine during the Greco-Roman period and as Cainepolis in antiquity.- Overview :...
bend of the Nile, at approx. 25°57′N 32°25′E, among dozens of hieratic and hieroglyphic inscriptions. The inscriptions are graphically very similar to the Serabit inscriptions, but show a greater hieroglyphic influence, such as a glyph for a man that was apparently not read alphabetically.

Some scholars (Darnell et al) think that the רב rb at the beginning of Inscription 1 is likely rebbe (chief; cognate with rabbi
Rabbi
In Judaism, a rabbi is a teacher of Torah. This title derives from the Hebrew word רבי , meaning "My Master" , which is the way a student would address a master of Torah...
); and that the אל ’l at the end of Inscription 2 is likely ’el
El (god)
is a Northwest Semitic word meaning "deity", cognate to Akkadian and then to Hebrew : Eli and Arabic )....
"(a) god".
Brian Colless has published a translation of the text, in which some of the signs are treated as logograms (representing a whole word, not just a single consonant) or rebuses [Antiguo Oriente 8 (2010) 91]
[V] “Excellent (R[’š]) banquet (mšt) of the celebration (H[illul]) of `Anat
(`nt). ’El (’l) will provide (ygš) [H] plenty (rb) of wine (wn) and victuals (mn)
for the celebration (H[illul]). We will sacrifice (ngt_) to her (h) an ox (’) and
(p) a prime (R[’sh]) fatling (mX).”
This interpretation fits into the pattern in some of the surrounding Egyptian inscriptions, with celebrations for the goddess Hathor involving inebriation.
See also
- AbjadAbjadAn abjad is a type of writing system in which each symbol always or usually stands for a consonant; the reader must supply the appropriate vowel....
- Byblos syllabaryByblos syllabaryThe Byblos syllabary, also known as the Pseudo-hieroglyphic script, Proto-Byblian, Proto-Byblic, or Byblic, is officially an undeciphered writing system, known from ten inscriptions found in Byblos. The inscriptions are engraved on bronze plates and spatulas, and carved in stone...
- Ugaritic script
Literature
- Albright, Wm. F. (1966) The Proto-Sinaitic Inscriptions and their Decipherment
- Colless, Brian E., "The proto-alphabetic inscriptions of Sinai", Abr-Nahrain 28 (1990) 1-52.
- Colless, Brian E., "The proto-alphabetic inscriptions of Canaan", Abr-Nahrain 29 (1991) 18-66.
- Colless, Brian E., “The Byblos Syllabary and the Proto-alphabet”, Abr-Nahrain 30 (1992) 15-62.
- Colless, Brian E., “Proto-alphabetic Inscriptions from the Wadi Arabah”, Antiguo Oriente 8 (2010) 75-96.
- Stefan Jakob Wimmer / Samaher Wimmer-Dweikat: The Alphabet from Wadi el-Hôl – A First Try, in: Göttinger MiszellenGöttinger MiszellenGöttinger Miszellen is a scientific journal published by the Seminar für Ägyptologie und Koptologie which contains short scholarly articles on Egyptological, Coptological, and other related subjects....
. Beiträge zur ägyptologischen Diskussion, Heft 180, Göttingen 2001, p. 107-111 - J. Darnell and C. Dobbs-Allsopp, et al., Two Early Alphabetic Inscriptions from the Wadi el-Hol: New Evidence for the Origin of the Alphabet from the Western Desert of Egypt, Annual of the American Schools of Oriental Research 2005.
- Hamilton, Gordon J, The origins of the West Semitic alphabet in Egyptian scripts (2006)
- Fellman, Bruce (2000) "The Birthplace of the ABCs." Yale Alumni Magazine, December 2000.http://www.yalealumnimagazine.com/issues/00_12/egypt.html
- Millard, A. R. (1986) "The Infancy of the Alphabet" World Archaeology. pp. 390–398.
- Ray, John D. (1986) "The Emergence of Writing in Egypt" Early Writing Systems; 17/3 pp. 307–316.
External links
- USC West Semitic Research Project site on Wadi el-Hol, with photos
- Photos of Proto-Sinaitic and later Semitic inscriptions
- Proto-Sinaitic TrueType font for your computer
- Ancient Hebrew Alphabet – chart for comparison
- Comprehensive study of Proto-Sinaitic corpus (in Spanish)
- The Tower of Babel – an academically-affiliated etymology database
- How the Alphabet Was Born from Hieroglyphs Biblical Archaeology Review, Mar/Apr 2010

