
B
Encyclopedia
B is the second letter
in the basic modern Latin alphabet
. It is used to represent a variety of bilabial sounds
(depending on language), most commonly a voiced bilabial plosive
.
of the floorplan of a house in Egyptian hieroglyphs. By 1050 BC, the Phoenician alphabet
's letter had a linear form that served as the beth.
and most other languages that use the Latin alphabet, ⟨b⟩ denotes the voiced bilabial plosive
b, as in bib. In English it is sometimes silent; most instances are derived from old monosyllablic words with the b final and immediately preceded by an m, such as lamb and bomb; a few are examples of etymological
spelling to make the word more like its Latin original, such as debt or doubt. In Estonian
, Icelandic
, and in Chinese
, ⟨b⟩ does not denote a voiced consonant; instead, it represents a voiceless /p/ that contrasts with either a geminated /pp/ (in Estonian) or an aspirated /pʰ/ (in Chinese, Danish and Icelandic), represented by ⟨p⟩. In Fijian
⟨b⟩ represents a prenasalized
/mb/, whereas in Zulu
and Xhosa
it represents an implosive
/ɓ/, in contrast to the digraph
⟨bh⟩ which represents /b/.
Finnish
only uses ⟨b⟩ in loanwords.
In the International Phonetic Alphabet and X-SAMPA
, ⟨b⟩ denotes the voiced bilabial plosive
. Variants of ⟨b⟩ denote related bilabial consonant
s, like the voiced bilabial implosive and the bilabial trill
. In X-SAMPA
, capital ⟨B⟩ denotes the voiced bilabial fricative
.
⟨B⟩ is also a musical note. Its value varies depending on the region
; a ⟨b⟩ in Anglophone countries represents a note that is a semitone higher than the B note in Northern Continental Europe. (Anglophone B is represented in Northern Europe with ⟨H⟩.) Archaic forms of ⟨b⟩, the b quadratum (square b) and b rotundum (round b) remain in use for musical notation as the symbols for natural
and flat, respectively.
In Contracted (grade 2) English braille, ⟨b⟩ stands for "but" when in isolation.
1 and all encodings based on ASCII, including the DOS, Windows, ISO-8859 and Macintosh families of encodings.
Letter (alphabet)
A letter is a grapheme in an alphabetic system of writing, such as the Greek alphabet and its descendants. Letters compose phonemes and each phoneme represents a phone in the spoken form of the language....
in the basic modern Latin alphabet
Basic modern Latin alphabet
The International Organization for Standardization basic Latin alphabet consists of the following 26 letters:By the 1960s it became apparent to the computer and telecommunications industries in the First World that a non-proprietary method of encoding characters was needed...
. It is used to represent a variety of bilabial sounds
Bilabial consonant
In phonetics, a bilabial consonant is a consonant articulated with both lips. The bilabial consonants identified by the International Phonetic Alphabet are:...
(depending on language), most commonly a voiced bilabial plosive
Voiced bilabial plosive
The voiced bilabial plosive is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is b. The voiced bilabial plosive occurs in English, and it is the sound denoted by the...
.
History
⟨B⟩ may have started as a pictogramPictogram
A pictograph, also called pictogram or pictogramme is an ideogram that conveys its meaning through its pictorial resemblance to a physical object. Pictographs are often used in writing and graphic systems in which the characters are to considerable extent pictorial in appearance.Pictography is a...
of the floorplan of a house in Egyptian hieroglyphs. By 1050 BC, the Phoenician alphabet
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
's letter had a linear form that served as the beth.
| Egyptian hieroglyph cottage |
Phoenician Phoenician alphabet The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia... beth Bet (letter) Bet, Beth, Beh, or Vet is the second letter of many Semitic abjads, including Arabic alphabet , Aramaic, Hebrew , Phoenician and Syriac... |
Greek Greek alphabet The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega... Beta Beta (letter) Beta is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In Ancient Greek, beta represented the voiced bilabial plosive . In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced labiodental fricative .... |
Etruscan B |
Roman B |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
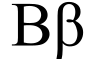 |
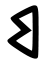 |
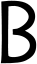 |
Typography
The modern lowercase ⟨b⟩ derives from later Roman times, when scribes began omitting the upper loop of the capital.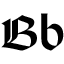 |
 |
|
| Blackletter Blackletter Blackletter, also known as Gothic script, Gothic minuscule, or Textura, was a script used throughout Western Europe from approximately 1150 to well into the 17th century. It continued to be used for the German language until the 20th century. Fraktur is a notable script of this type, and sometimes... B |
Uncial B | |
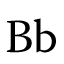 |
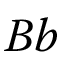 |
 |
| Modern Roman B | Modern Italic B | Modern Script B |
Usage
In EnglishEnglish language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
and most other languages that use the Latin alphabet, ⟨b⟩ denotes the voiced bilabial plosive
Voiced bilabial plosive
The voiced bilabial plosive is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is b. The voiced bilabial plosive occurs in English, and it is the sound denoted by the...
b, as in bib. In English it is sometimes silent; most instances are derived from old monosyllablic words with the b final and immediately preceded by an m, such as lamb and bomb; a few are examples of etymological
Etymology
Etymology is the study of the history of words, their origins, and how their form and meaning have changed over time.For languages with a long written history, etymologists make use of texts in these languages and texts about the languages to gather knowledge about how words were used during...
spelling to make the word more like its Latin original, such as debt or doubt. In Estonian
Estonian language
Estonian is the official language of Estonia, spoken by about 1.1 million people in Estonia and tens of thousands in various émigré communities...
, Icelandic
Icelandic language
Icelandic is a North Germanic language, the main language of Iceland. Its closest relative is Faroese.Icelandic is an Indo-European language belonging to the North Germanic or Nordic branch of the Germanic languages. Historically, it was the westernmost of the Indo-European languages prior to the...
, and in Chinese
Chinese language
The Chinese language is a language or language family consisting of varieties which are mutually intelligible to varying degrees. Originally the indigenous languages spoken by the Han Chinese in China, it forms one of the branches of Sino-Tibetan family of languages...
, ⟨b⟩ does not denote a voiced consonant; instead, it represents a voiceless /p/ that contrasts with either a geminated /pp/ (in Estonian) or an aspirated /pʰ/ (in Chinese, Danish and Icelandic), represented by ⟨p⟩. In Fijian
Fijian language
Fijian is an Austronesian language of the Malayo-Polynesian family spoken in Fiji. It has 450,000 first-language speakers, which is less than half the population of Fiji, but another 200,000 speak it as a second language...
⟨b⟩ represents a prenasalized
Prenasalized consonant
Prenasalized consonants are phonetic sequences of a nasal and an obstruent that behave phonologically like single consonants. The reasons for considering these sequences to be single consonants is in their behavior, not in their actual composition...
/mb/, whereas in Zulu
Zulu language
Zulu is the language of the Zulu people with about 10 million speakers, the vast majority of whom live in South Africa. Zulu is the most widely spoken home language in South Africa as well as being understood by over 50% of the population...
and Xhosa
Xhosa language
Xhosa is one of the official languages of South Africa. Xhosa is spoken by approximately 7.9 million people, or about 18% of the South African population. Like most Bantu languages, Xhosa is a tonal language, that is, the same sequence of consonants and vowels can have different meanings when said...
it represents an implosive
Implosive consonant
Implosive consonants are stops with a mixed glottalic ingressive and pulmonic egressive airstream mechanism. That is, the airstream is controlled by moving the glottis downward in addition to expelling air from the lungs. Therefore, unlike the purely glottalic ejective consonants, implosives can...
/ɓ/, in contrast to the digraph
Digraph (orthography)
A digraph or digram is a pair of characters used to write one phoneme or a sequence of phonemes that does not correspond to the normal values of the two characters combined...
⟨bh⟩ which represents /b/.
Finnish
Finnish language
Finnish is the language spoken by the majority of the population in Finland Primarily for use by restaurant menus and by ethnic Finns outside Finland. It is one of the two official languages of Finland and an official minority language in Sweden. In Sweden, both standard Finnish and Meänkieli, a...
only uses ⟨b⟩ in loanwords.
In the International Phonetic Alphabet and X-SAMPA
X-SAMPA
The Extended Speech Assessment Methods Phonetic Alphabet is a variant of SAMPA developed in 1995 by John C. Wells, professor of phonetics at the University of London. It is designed to unify the individual language SAMPA alphabets, and extend SAMPA to cover the entire range of characters in the...
, ⟨b⟩ denotes the voiced bilabial plosive
Voiced bilabial plosive
The voiced bilabial plosive is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is b. The voiced bilabial plosive occurs in English, and it is the sound denoted by the...
. Variants of ⟨b⟩ denote related bilabial consonant
Bilabial consonant
In phonetics, a bilabial consonant is a consonant articulated with both lips. The bilabial consonants identified by the International Phonetic Alphabet are:...
s, like the voiced bilabial implosive and the bilabial trill
Bilabial trill
-External links:*...
. In X-SAMPA
X-SAMPA
The Extended Speech Assessment Methods Phonetic Alphabet is a variant of SAMPA developed in 1995 by John C. Wells, professor of phonetics at the University of London. It is designed to unify the individual language SAMPA alphabets, and extend SAMPA to cover the entire range of characters in the...
, capital ⟨B⟩ denotes the voiced bilabial fricative
Voiced bilabial fricative
-See also:* List of phonetics topics...
.
⟨B⟩ is also a musical note. Its value varies depending on the region
Region
Region is most commonly found as a term used in terrestrial and astrophysics sciences also an area, notably among the different sub-disciplines of geography, studied by regional geographers. Regions consist of subregions that contain clusters of like areas that are distinctive by their uniformity...
; a ⟨b⟩ in Anglophone countries represents a note that is a semitone higher than the B note in Northern Continental Europe. (Anglophone B is represented in Northern Europe with ⟨H⟩.) Archaic forms of ⟨b⟩, the b quadratum (square b) and b rotundum (round b) remain in use for musical notation as the symbols for natural
Natural (music)
In music theory, a natural is an accidental which cancels previous accidentals and represents the unaltered pitch of a note.A note is natural when it is neither flat nor sharp . Natural notes are the notes A, B, C, D, E, F, and G, and are represented by the white notes on the keyboard of a piano...
and flat, respectively.
In Contracted (grade 2) English braille, ⟨b⟩ stands for "but" when in isolation.
Related letters and other similar characters
- Β β : Greek letter BetaBeta (letter)Beta is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In Ancient Greek, beta represented the voiced bilabial plosive . In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced labiodental fricative ....
- В в : Cyrillic letter VeVe (Cyrillic)Ve is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It commonly represents the voiced labiodental fricative , like the pronunciation of ⟨v⟩ in "very"....
- Б б : Cyrillic letter BeBe (Cyrillic)Be is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet. It commonly represents the voiced bilabial plosive , like the English pronunciation of ⟨b⟩ in "bee"...
: Latin letter B with hook - Ъ ъ : Cyrillic letter YerYerThe letter yer of the Cyrillic alphabet, also spelled jer or er, is known as the hard sign in the modern Russian and Rusyn alphabets and as er golyam in the Bulgarian alphabet...
(also known as the hard sign, back yer, or tvyordiy znak) is shaped like the letter b, but has no phonetic value on its own in modern East SlavicEast Slavic languagesThe East Slavic languages constitute one of three regional subgroups of Slavic languages, currently spoken in Eastern Europe. It is the group with the largest numbers of speakers, far out-numbering the Western and Southern Slavic groups. Current East Slavic languages are Belarusian, Russian,...
languages. The ъ serves as an orthographic device that indicates that the consonant preceding the ъ is not palatalized. - Ь ь : Cyrillic letter Soft signSoft signThe soft sign , also known as yer, is a letter of the Cyrillic script. In Old Church Slavonic, it represented a short front vowel. As with its companion, the back yer, the vowel phoneme it designated was later partly dropped and partly merged with other vowels...
(also known as the front yer, or myagkiy znak) is also shaped like the letter b, but has no phonetic value on its own in modern East SlavicEast Slavic languagesThe East Slavic languages constitute one of three regional subgroups of Slavic languages, currently spoken in Eastern Europe. It is the group with the largest numbers of speakers, far out-numbering the Western and Southern Slavic groups. Current East Slavic languages are Belarusian, Russian,...
languages. The ь serves as orthographic device that indicates that the consonant preceding the ь is softened or palatalized. : German letter EszettßIn the German alphabet, ß is a letter that originated as a ligature of ss or sz. Like double "s", it is pronounced as an , but in standard spelling, it is only used after long vowels and diphthongs, while ss is used after short vowels...
, originally a ligature of long sLong sThe long, medial or descending s is a form of the minuscule letter s formerly used where s occurred in the middle or at the beginning of a word, for example "ſinfulneſs" . The modern letterform was called the terminal, round, or short s.-History:The long s is derived from the old Roman cursive...
⟨ſ⟩ with ⟨z⟩, now considered to stand for ⟨ss⟩. : Hebrew letter Bet
Computing codes
| character | B | b | ||
| Unicode name | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER B | LATIN SMALL LETTER B | ||
| character encoding | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode Unicode Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems... |
66 | 0042 | 98 | 0062 |
| UTF-8 UTF-8 UTF-8 is a multibyte character encoding for Unicode. Like UTF-16 and UTF-32, UTF-8 can represent every character in the Unicode character set. Unlike them, it is backward-compatible with ASCII and avoids the complications of endianness and byte order marks... |
66 | 42 | 98 | 62 |
| Numeric character reference Numeric character reference A numeric character reference is a common markup construct used in SGML and other SGML-related markup languages such as HTML and XML. It consists of a short sequence of characters that, in turn, represent a single character from the Universal Character Set of Unicode... |
B | B | b | b |
| EBCDIC EBCDIC Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code is an 8-bit character encoding used mainly on IBM mainframe and IBM midrange computer operating systems.... family |
194 | C2 | 130 | 82 |
| ASCII ASCII The American Standard Code for Information Interchange is a character-encoding scheme based on the ordering of the English alphabet. ASCII codes represent text in computers, communications equipment, and other devices that use text... 1 |
66 | 42 | 98 | 62 |
1 and all encodings based on ASCII, including the DOS, Windows, ISO-8859 and Macintosh families of encodings.

