
Micellar electrokinetic chromatography
Encyclopedia
Micellar electrokinetic chromatography (MEKC), is a chromatography
technique, used in analytical chemistry
. It is a modification of capillary electrophoresis
(CE), where the samples are separated by differential partitioning between micelles (pseudo-stationary phase) and a surrounding aqueous buffer solution
(mobile phase).
The basic set-up and detection methods used for MEKC are the same as those used in CE. The difference is that the solution contains a surfactant
at a concentration
that is greater than the critical micelle concentration
(CMC). Above this concentration, surfactant monomers are in equilibrium
with micelles.
In most applications, MEKC is performed in open capillaries under alkaline conditions to generate a strong electroosmotic flow
. Sodium dodecyl sulfate
(SDS) is the most commonly used surfactant in MEKC applications. The anionic character of the sulfate groups of SDS cause the surfactant and micelles to have electrophoretic mobility
that is counter to the direction of the strong electroosmotic flow. As a result, the surfactant monomers and micelles migrate quite slowly, though their net movement is still toward the cathode
. During a MEKC separation, analyte
s distribute themselves between the hydrophobic
interior of the micelle and hydrophilic
buffer solution as shown in figure 1.
 Analytes that are insoluble in the interior of micelles should migrate at the electroosmotic flow velocity,
Analytes that are insoluble in the interior of micelles should migrate at the electroosmotic flow velocity,  , and be detected at the retention time of the buffer,
, and be detected at the retention time of the buffer,  . Analytes that solubilize completely within the micelles (analytes that are highly hydrophobic) should migrate at the micelle velocity,
. Analytes that solubilize completely within the micelles (analytes that are highly hydrophobic) should migrate at the micelle velocity,  , and elute
, and elute
at the final elution time, .
.

where is the electrophoretic velocity of a micelle.
is the electrophoretic velocity of a micelle.
The retention time of a given sample should depend on the capacity factor, :
:

where is the total number of moles
is the total number of moles
of solute in the micelle and is the total moles in the aqueous phase. The retention time of a solute should then be within the range:
is the total moles in the aqueous phase. The retention time of a solute should then be within the range:

Charged analytes have a more complex interaction in the capillary because they exhibit electrophoretic mobility, engage in electrostatic
interactions with the micelle, and participate in hydrophobic partitioning.
The fraction of the sample in the aqueous phase, , is given by:
, is given by:
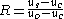
where is the migration velocity of the solute. The value
is the migration velocity of the solute. The value  can also be expressed in terms of the capacity factor:
can also be expressed in terms of the capacity factor:

Using the relationship between velocity, tube length from the injection end to the detector cell (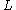 ), and retention time,
), and retention time,  ,
,  and
and 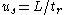 , a relationship between the capacity factor and retention times can be formulated:
, a relationship between the capacity factor and retention times can be formulated:

The extra term enclosed in parenthesis accounts for the partial mobility of the hydrophobic phase in MEKC. This equation resembles an expression derived for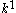 in conventional packed bed
in conventional packed bed
chromatography:
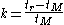
A rearrangement of the previous equation can be used to write an expression for the retention factor:

From this equation it can be seen that all analytes that partition strongly into the micellar phase (where is essentially ∞) migrate at the same time,
is essentially ∞) migrate at the same time,  . In conventional chromatography, separation of similar compounds can be improved by gradient
. In conventional chromatography, separation of similar compounds can be improved by gradient
elution. In MEKC, however, techniques must be used to extend the elution range to separate strongly retained analytes.
Elution ranges can be extended by several techniques including the use of organic
modifiers, cyclodextrin
s, and mixed micelle systems. Short-chain alcohols or acetonitrile
can be used as organic modifiers that decrease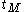 and
and 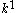 to improve the resolution of analytes that co-elute with the micellar phase. These agents, however, may alter the level of the EOF. Cyclodextrins are cyclic polysaccharide
to improve the resolution of analytes that co-elute with the micellar phase. These agents, however, may alter the level of the EOF. Cyclodextrins are cyclic polysaccharide
s that form inclusion complexes that can cause competitive hydrophobic partitioning of the analyte. Since analyte-cyclodextrin complexes are neutral, they will migrate toward the cathode at a higher velocity than that of the negatively charged micelles. Mixed micelle systems, such as the one formed by combining SDS with the neutral surfactant Brij-35, can also be used to alter the selectivity of MEKC.
(CE) instrumentation to be used in the separation of neutral (as well as ionic) species.
selectors or chiral surfactants to the system. Unfortunately, this technique is not suitable for protein analysis because proteins are generally too large to partition into a surfactant micelle and tend to bind to surfactant monomer
s to form SDS-protein complexes.
Recent applications of MEKC include the analysis of uncharged pesticide
s, essential and branched-chain amino acid
s in nutraceutical products, hydrocarbon
and alcohol contents of the marjoram
herb.
MEKC has also been targeted for its potential to be used in combinatorial chemical analysis. The advent of combinatorial chemistry
has enabled medicinal chemists
to synthesize and identify large numbers of potential drugs
in relatively short periods of time. Small sample and solvent
requirements and the high resolving power of MEKC have enabled this technique to be used to quickly analyze a large number of compounds with good resolution.
Traditional methods of analysis, like high-performance liquid chromatography
(HPLC), can be used to identify the purity of a combinatorial library, but assays need to be rapid with good resolution for all components to provide useful information for the chemist. The introduction of surfactant to traditional capillary electrophoresis instrumentation has dramatically expanded the scope of analytes that can be separated by capillary electrophoresis.
Chromatography
Chromatography is the collective term for a set of laboratory techniques for the separation of mixtures....
technique, used in analytical chemistry
Analytical chemistry
Analytical chemistry is the study of the separation, identification, and quantification of the chemical components of natural and artificial materials. Qualitative analysis gives an indication of the identity of the chemical species in the sample and quantitative analysis determines the amount of...
. It is a modification of capillary electrophoresis
Capillary electrophoresis
Capillary electrophoresis , also known as capillary zone electrophoresis , can be used to separate ionic species by their charge and frictional forces and hydrodynamic radius. In traditional electrophoresis, electrically charged analytes move in a conductive liquid medium under the influence of an...
(CE), where the samples are separated by differential partitioning between micelles (pseudo-stationary phase) and a surrounding aqueous buffer solution
Buffer solution
A buffer solution is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. It has the property that the pH of the solution changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. Buffer solutions are used as a...
(mobile phase).
The basic set-up and detection methods used for MEKC are the same as those used in CE. The difference is that the solution contains a surfactant
Surfactant
Surfactants are compounds that lower the surface tension of a liquid, the interfacial tension between two liquids, or that between a liquid and a solid...
at a concentration
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
that is greater than the critical micelle concentration
Critical micelle concentration
In colloidal and surface chemistry, the critical micelle concentration is defined as the concentration of surfactants above which micelles form and almost all additional surfactants added to the system go to micelles....
(CMC). Above this concentration, surfactant monomers are in equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which the concentrations of the reactants and products have not yet changed with time. It occurs only in reversible reactions, and not in irreversible reactions. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same...
with micelles.
In most applications, MEKC is performed in open capillaries under alkaline conditions to generate a strong electroosmotic flow
Electro-osmosis
Electroosmotic flow is the motion of liquid induced by an applied potential across a porous material, capillary tube, membrane, microchannel, or any other fluid conduit...
. Sodium dodecyl sulfate
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
Sodium dodecyl sulfate , sodium laurilsulfate or sodium lauryl sulfate is an organic compound with the formula CH311OSO3Na). It is an anionic surfactant used in many cleaning and hygiene products...
(SDS) is the most commonly used surfactant in MEKC applications. The anionic character of the sulfate groups of SDS cause the surfactant and micelles to have electrophoretic mobility
Electrophoresis
Electrophoresis, also called cataphoresis, is the motion of dispersed particles relative to a fluid under the influence of a spatially uniform electric field. This electrokinetic phenomenon was observed for the first time in 1807 by Reuss , who noticed that the application of a constant electric...
that is counter to the direction of the strong electroosmotic flow. As a result, the surfactant monomers and micelles migrate quite slowly, though their net movement is still toward the cathode
Cathode
A cathode is an electrode through which electric current flows out of a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: CCD .Cathode polarity is not always negative...
. During a MEKC separation, analyte
Analyte
An analyte, or component , is a substance or chemical constituent that is of interest in an analytical procedure. Grammatically, it is important to note that experiments always seek to measure properties of analytes—and that analytes themselves can never be measured. For instance, one cannot...
s distribute themselves between the hydrophobic
Hydrophobe
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is repelled from a mass of water....
interior of the micelle and hydrophilic
Hydrophile
A hydrophile, from the Greek "water" and φιλια "love," is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to, and tends to be dissolved by water. A hydrophilic molecule or portion of a molecule is one that has a tendency to interact with or be dissolved by, water and other polar substances...
buffer solution as shown in figure 1.

 , and be detected at the retention time of the buffer,
, and be detected at the retention time of the buffer,  . Analytes that solubilize completely within the micelles (analytes that are highly hydrophobic) should migrate at the micelle velocity,
. Analytes that solubilize completely within the micelles (analytes that are highly hydrophobic) should migrate at the micelle velocity,  , and elute
, and eluteElution
Elution is a term used in analytical and organic chemistry to describe the process of extracting one material from another by washing with a solvent ....
at the final elution time,
 .
.Theory
The micelle velocity is defined by:
where
 is the electrophoretic velocity of a micelle.
is the electrophoretic velocity of a micelle.The retention time of a given sample should depend on the capacity factor,
 :
:
where
 is the total number of moles
is the total number of molesMole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
of solute in the micelle and
 is the total moles in the aqueous phase. The retention time of a solute should then be within the range:
is the total moles in the aqueous phase. The retention time of a solute should then be within the range:
Charged analytes have a more complex interaction in the capillary because they exhibit electrophoretic mobility, engage in electrostatic
Electrostatics
Electrostatics is the branch of physics that deals with the phenomena and properties of stationary or slow-moving electric charges....
interactions with the micelle, and participate in hydrophobic partitioning.
The fraction of the sample in the aqueous phase,
 , is given by:
, is given by: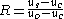
where
 is the migration velocity of the solute. The value
is the migration velocity of the solute. The value  can also be expressed in terms of the capacity factor:
can also be expressed in terms of the capacity factor:
Using the relationship between velocity, tube length from the injection end to the detector cell (
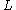 ), and retention time,
), and retention time,  ,
,  and
and 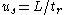 , a relationship between the capacity factor and retention times can be formulated:
, a relationship between the capacity factor and retention times can be formulated:
The extra term enclosed in parenthesis accounts for the partial mobility of the hydrophobic phase in MEKC. This equation resembles an expression derived for
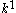 in conventional packed bed
in conventional packed bedPacked bed
In chemical processing, a packed bed is a hollow tube, pipe, or other vessel that is filled with a packing material. The packing can be randomly filled with small objects like Raschig rings or else it can be a specifically designed structured packing...
chromatography:
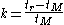
A rearrangement of the previous equation can be used to write an expression for the retention factor:

From this equation it can be seen that all analytes that partition strongly into the micellar phase (where
 is essentially ∞) migrate at the same time,
is essentially ∞) migrate at the same time,  . In conventional chromatography, separation of similar compounds can be improved by gradient
. In conventional chromatography, separation of similar compounds can be improved by gradientGradient
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar field is a vector field that points in the direction of the greatest rate of increase of the scalar field, and whose magnitude is the greatest rate of change....
elution. In MEKC, however, techniques must be used to extend the elution range to separate strongly retained analytes.
Elution ranges can be extended by several techniques including the use of organic
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
modifiers, cyclodextrin
Cyclodextrin
Cyclodextrins are a family of compounds made up of sugar molecules bound together in a ring ....
s, and mixed micelle systems. Short-chain alcohols or acetonitrile
Acetonitrile
Acetonitrile is the chemical compound with formula . This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile. It is produced mainly as a byproduct of acrylonitrile manufacture...
can be used as organic modifiers that decrease
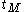 and
and 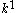 to improve the resolution of analytes that co-elute with the micellar phase. These agents, however, may alter the level of the EOF. Cyclodextrins are cyclic polysaccharide
to improve the resolution of analytes that co-elute with the micellar phase. These agents, however, may alter the level of the EOF. Cyclodextrins are cyclic polysaccharidePolysaccharide
Polysaccharides are long carbohydrate molecules, of repeated monomer units joined together by glycosidic bonds. They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Polysaccharides are often quite heterogeneous, containing slight modifications of the repeating unit. Depending on the structure,...
s that form inclusion complexes that can cause competitive hydrophobic partitioning of the analyte. Since analyte-cyclodextrin complexes are neutral, they will migrate toward the cathode at a higher velocity than that of the negatively charged micelles. Mixed micelle systems, such as the one formed by combining SDS with the neutral surfactant Brij-35, can also be used to alter the selectivity of MEKC.
History
In 1984, the Terabe group reported a technique that enabled capillary electrophoresisCapillary electrophoresis
Capillary electrophoresis , also known as capillary zone electrophoresis , can be used to separate ionic species by their charge and frictional forces and hydrodynamic radius. In traditional electrophoresis, electrically charged analytes move in a conductive liquid medium under the influence of an...
(CE) instrumentation to be used in the separation of neutral (as well as ionic) species.
Applications of MEKC
The simplicity and efficiency of MEKC have made it an attractive technique for a variety of applications. Further improvements can be made to the selectivity of MEKC by adding chiralChirality (chemistry)
A chiral molecule is a type of molecule that lacks an internal plane of symmetry and thus has a non-superimposable mirror image. The feature that is most often the cause of chirality in molecules is the presence of an asymmetric carbon atom....
selectors or chiral surfactants to the system. Unfortunately, this technique is not suitable for protein analysis because proteins are generally too large to partition into a surfactant micelle and tend to bind to surfactant monomer
Monomer
A monomer is an atom or a small molecule that may bind chemically to other monomers to form a polymer; the term "monomeric protein" may also be used to describe one of the proteins making up a multiprotein complex...
s to form SDS-protein complexes.
Recent applications of MEKC include the analysis of uncharged pesticide
Pesticide
Pesticides are substances or mixture of substances intended for preventing, destroying, repelling or mitigating any pest.A pesticide may be a chemical unicycle, biological agent , antimicrobial, disinfectant or device used against any pest...
s, essential and branched-chain amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
s in nutraceutical products, hydrocarbon
Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons from which one hydrogen atom has been removed are functional groups, called hydrocarbyls....
and alcohol contents of the marjoram
Marjoram
Marjoram is a somewhat cold-sensitive perennial herb or undershrub with sweet pine and citrus flavours...
herb.
MEKC has also been targeted for its potential to be used in combinatorial chemical analysis. The advent of combinatorial chemistry
Combinatorial chemistry
Combinatorial chemistry involves the rapid synthesis or the computer simulation of a large number of different but structurally related molecules or materials...
has enabled medicinal chemists
Medicinal chemistry
Medicinal chemistry and pharmaceutical chemistry are disciplines at the intersection of chemistry, especially synthetic organic chemistry, and pharmacology and various other biological specialties, where it is involved with design, chemical synthesis and development for market of pharmaceutical...
to synthesize and identify large numbers of potential drugs
Medication
A pharmaceutical drug, also referred to as medicine, medication or medicament, can be loosely defined as any chemical substance intended for use in the medical diagnosis, cure, treatment, or prevention of disease.- Classification :...
in relatively short periods of time. Small sample and solvent
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
requirements and the high resolving power of MEKC have enabled this technique to be used to quickly analyze a large number of compounds with good resolution.
Traditional methods of analysis, like high-performance liquid chromatography
High-performance liquid chromatography
High-performance liquid chromatography , HPLC, is a chromatographic technique that can separate a mixture of compounds and is used in biochemistry and analytical chemistry to identify, quantify and purify the individual components of the mixture.HPLC typically utilizes different types of stationary...
(HPLC), can be used to identify the purity of a combinatorial library, but assays need to be rapid with good resolution for all components to provide useful information for the chemist. The introduction of surfactant to traditional capillary electrophoresis instrumentation has dramatically expanded the scope of analytes that can be separated by capillary electrophoresis.
Sources
- Kealey, D.;Haines P.J.; instant notes, Analytical Chemistry page 182-188

