Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase
Encyclopedia
Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) is an enzyme
that in humans is encoded by the MTHFR gene
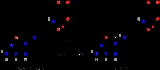
. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase catalyzes the conversion of 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate
to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate
, a cosubstrate for homocysteine
remethylation to methionine
. Genetic variation in this gene influences susceptibility to occlusive vascular disease, neural tube defects, colon cancer and acute leukemia, and mutations in this gene are associated with methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase deficiency.
(substrate) to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate
(product).
MTHFR contains a bound flavin cofactor
and uses NAD(P)H as the reducing agent
.
with the symbol MTHFR on chromosome 1 location p36.3 in humans.
There are DNA sequence variants (genetic polymorphisms) associated with this gene.
In 2000 a report brought the number of polymorphisms up to 24.
Two of the most investigated are C677T (rs1801133
) and A1298C (rs1801131) single nucleotide polymorphism
s (SNP).
at position 677 in the gene has two possibilities: C (cytosine
) or T (thymine
). C at position 677 (leading to an alanine at amino acid 222) is the normal allele
. The 677T allele (leading to a valine substitution at amino acid 222) encodes a thermolabile
enzyme with reduced activity.
Individual with two copies of 677C (677CC) have the "normal" or "wildtype" genotype. 677TT individuals (homozygous) are said to have mild MTHFR deficiency. 677CT individuals (heterozygotes) are almost the same as normal individuals because the normal MTHFR can make up for the thermolabile MTHFR. About ten percent of the North America
n population are T-homozygous for this polymorphism. There is ethnic variability in the frequency of the T allele – frequency in Mediterranean/Hispanics is greater than the frequency in Caucasians which, in turn, is greater than in Africans/African-Americans.
The degree of enzyme thermolability (assessed as residual activity after heat inactivation) is much greater in 677TT individuals (18-22%) compared with 677CT (56%) and 677CC (66-67%). Individuals of 677TT are predisposed to mild hyperhomocysteinemia
(high blood homocysteine levels), because they have less active MTHFR available to produce 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (which is used to decrease homocysteine). Low dietary intake of the vitamin
folic acid
can also cause mild hyperhomocysteinemia.
Low folate intake affects individuals with the 677TT genotype to a greater extent than those with the 677CC/CT genotypes. 677TT (but not 677CC/CT) individuals with lower plasma
folate levels are at risk for elevated plasma homocysteine levels. In studies of human recombinant MTHFR, the protein encoded by 677T loses its FAD cofactor three times faster than the wild-type protein. 5-Methyl-THF slows the rate of FAD release in both the wild-type and mutant enzymes, although it is to a much greater extent in the mutant enzyme.
Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) is an enzyme
that in humans is encoded by the MTHFR gene
. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase catalyzes the conversion of 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate
to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate
, a cosubstrate for homocysteine
remethylation to methionine
. Genetic variation in this gene influences susceptibility to occlusive vascular disease, neural tube defects, colon cancer and acute leukemia, and mutations in this gene are associated with methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase deficiency.
(substrate) to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate
(product).
MTHFR contains a bound flavin cofactor
and uses NAD(P)H as the reducing agent
.
with the symbol MTHFR on chromosome 1 location p36.3 in humans.
There are DNA sequence variants (genetic polymorphisms) associated with this gene.
In 2000 a report brought the number of polymorphisms up to 24.
Two of the most investigated are C677T (rs1801133
) and A1298C (rs1801131) single nucleotide polymorphism
s (SNP).
at position 677 in the gene has two possibilities: C (cytosine
) or T (thymine
). C at position 677 (leading to an alanine at amino acid 222) is the normal allele
. The 677T allele (leading to a valine substitution at amino acid 222) encodes a thermolabile
enzyme with reduced activity.
Individual with two copies of 677C (677CC) have the "normal" or "wildtype" genotype. 677TT individuals (homozygous) are said to have mild MTHFR deficiency. 677CT individuals (heterozygotes) are almost the same as normal individuals because the normal MTHFR can make up for the thermolabile MTHFR. About ten percent of the North America
n population are T-homozygous for this polymorphism. There is ethnic variability in the frequency of the T allele – frequency in Mediterranean/Hispanics is greater than the frequency in Caucasians which, in turn, is greater than in Africans/African-Americans.
The degree of enzyme thermolability (assessed as residual activity after heat inactivation) is much greater in 677TT individuals (18-22%) compared with 677CT (56%) and 677CC (66-67%). Individuals of 677TT are predisposed to mild hyperhomocysteinemia
(high blood homocysteine levels), because they have less active MTHFR available to produce 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (which is used to decrease homocysteine). Low dietary intake of the vitamin
folic acid
can also cause mild hyperhomocysteinemia.
Low folate intake affects individuals with the 677TT genotype to a greater extent than those with the 677CC/CT genotypes. 677TT (but not 677CC/CT) individuals with lower plasma
folate levels are at risk for elevated plasma homocysteine levels. In studies of human recombinant MTHFR, the protein encoded by 677T loses its FAD cofactor three times faster than the wild-type protein. 5-Methyl-THF slows the rate of FAD release in both the wild-type and mutant enzymes, although it is to a much greater extent in the mutant enzyme.
Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) is an enzyme
that in humans is encoded by the MTHFR gene
. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase catalyzes the conversion of 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate
to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate
, a cosubstrate for homocysteine
remethylation to methionine
. Genetic variation in this gene influences susceptibility to occlusive vascular disease, neural tube defects, colon cancer and acute leukemia, and mutations in this gene are associated with methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase deficiency.
(substrate) to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate
(product).
MTHFR contains a bound flavin cofactor
and uses NAD(P)H as the reducing agent
.
with the symbol MTHFR on chromosome 1 location p36.3 in humans.
There are DNA sequence variants (genetic polymorphisms) associated with this gene.
In 2000 a report brought the number of polymorphisms up to 24.
Two of the most investigated are C677T (rs1801133
) and A1298C (rs1801131) single nucleotide polymorphism
s (SNP).
at position 677 in the gene has two possibilities: C (cytosine
) or T (thymine
). C at position 677 (leading to an alanine at amino acid 222) is the normal allele
. The 677T allele (leading to a valine substitution at amino acid 222) encodes a thermolabile
enzyme with reduced activity.
Individual with two copies of 677C (677CC) have the "normal" or "wildtype" genotype. 677TT individuals (homozygous) are said to have mild MTHFR deficiency. 677CT individuals (heterozygotes) are almost the same as normal individuals because the normal MTHFR can make up for the thermolabile MTHFR. About ten percent of the North America
n population are T-homozygous for this polymorphism. There is ethnic variability in the frequency of the T allele – frequency in Mediterranean/Hispanics is greater than the frequency in Caucasians which, in turn, is greater than in Africans/African-Americans.
The degree of enzyme thermolability (assessed as residual activity after heat inactivation) is much greater in 677TT individuals (18-22%) compared with 677CT (56%) and 677CC (66-67%). Individuals of 677TT are predisposed to mild hyperhomocysteinemia
(high blood homocysteine levels), because they have less active MTHFR available to produce 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (which is used to decrease homocysteine). Low dietary intake of the vitamin
folic acid
can also cause mild hyperhomocysteinemia.
Low folate intake affects individuals with the 677TT genotype to a greater extent than those with the 677CC/CT genotypes. 677TT (but not 677CC/CT) individuals with lower plasma
folate levels are at risk for elevated plasma homocysteine levels. In studies of human recombinant MTHFR, the protein encoded by 677T loses its FAD cofactor three times faster than the wild-type protein. 5-Methyl-THF slows the rate of FAD release in both the wild-type and mutant enzymes, although it is to a much greater extent in the mutant enzyme.
This polymorphism and mild hyperhomocysteinemia are associated with neural tube defects
in offspring, arterial and venous thrombosis
, and cardiovascular disease
. 677TT individuals are at a decreased risk for certain leukemia
s and colon cancer.
Mutations in the MTHFR gene could be one of the factors leading to increased risk of developing schizophrenia
.
Schizophrenic patients having the risk allele (T\T) show more deficiencies in executive function tasks.
in their plasma and urine
as well as low to normal plasma methionine
levels.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that in humans is encoded by the MTHFR gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase catalyzes the conversion of 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate
5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate
5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate is the substrate used by the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase to generate 5-methyltetrahydrofolate ....
to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate
Levomefolic acid
Levomefolic acid or metafolin is the natural, active form of folic acid used at the cellular level for DNA reproduction, the cysteine cycle and the regulation of homocysteine among other functions. The un-methylated form, folic acid , is a synthetic form of folate found in nutritional supplements...
, a cosubstrate for homocysteine
Homocysteine
Homocysteine is a non-protein amino acid with the formula HSCH2CH2CHCO2H. It is a homologue of the amino acid cysteine, differing by an additional methylene group. It is biosynthesized from methionine by the removal of its terminal Cε methyl group...
remethylation to methionine
Methionine
Methionine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2SCH3. This essential amino acid is classified as nonpolar. This amino-acid is coded by the codon AUG, also known as the initiation codon, since it indicates mRNA's coding region where translation into protein...
. Genetic variation in this gene influences susceptibility to occlusive vascular disease, neural tube defects, colon cancer and acute leukemia, and mutations in this gene are associated with methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase deficiency.
Biochemistry
MTHFR irreversibly reduces 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate
5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate is the substrate used by the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase to generate 5-methyltetrahydrofolate ....
(substrate) to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate
5-Methyltetrahydrofolate
Levomefolic acid or metafolin is the natural, active form of folic acid used at the cellular level for DNA reproduction, the cysteine cycle and the regulation of homocysteine among other functions. The un-methylated form, folic acid , is a synthetic form of folate found in nutritional supplements...
(product).
- 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate is used to convert dUMP to dTMP for de novo thymidineThymidineThymidine is a chemical compound, more precisely a pyrimidine deoxynucleoside. Deoxythymidine is the DNA nucleoside T, which pairs with deoxyadenosine in double-stranded DNA...
synthesis. - 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate is used to convert homocysteineHomocysteineHomocysteine is a non-protein amino acid with the formula HSCH2CH2CHCO2H. It is a homologue of the amino acid cysteine, differing by an additional methylene group. It is biosynthesized from methionine by the removal of its terminal Cε methyl group...
(a potentially toxic amino acidAmino acidAmino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
) to methionineMethionineMethionine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2SCH3. This essential amino acid is classified as nonpolar. This amino-acid is coded by the codon AUG, also known as the initiation codon, since it indicates mRNA's coding region where translation into protein...
by the enzyme methionine synthase. (Note that homocysteine can also be converted to methionine by the folate-independent enzyme betaine-homocysteine methyltransferase (BHMT))
MTHFR contains a bound flavin cofactor
Cofactor (biochemistry)
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound that is bound to a protein and is required for the protein's biological activity. These proteins are commonly enzymes, and cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations....
and uses NAD(P)H as the reducing agent
Reducing agent
A reducing agent is the element or compound in a reduction-oxidation reaction that donates an electron to another species; however, since the reducer loses an electron we say it is "oxidized"...
.
Structure
Mammalian MTHFR is composed of an N-terminal catalytic domain and a C-terminal regulatory domain. MTHFR has at least two promoters and two isoforms (70 kDa and 77 kDa).Regulation
MTHFR activity may be inhibited by binding of dihydrofolate (DHF) and S-adenosylmethionine (SAM, or AdoMet). MTHFR can also be phosphorylated - this decreases its activity by ~20% and allows it to be more easily inhibited by SAM.Interactive pathway map
Genetics
The enzyme is coded by the geneGene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
with the symbol MTHFR on chromosome 1 location p36.3 in humans.
There are DNA sequence variants (genetic polymorphisms) associated with this gene.
In 2000 a report brought the number of polymorphisms up to 24.
Two of the most investigated are C677T (rs1801133
Rs1801133
C677T or rs1801133 is a genetic variation—a single nucleotide polymorphism —in the MTHFR gene.Among Americans the frequency of T-homezygosity ranges from 1% or less among Blacks to 20% or more among Italians and Hispanics....
) and A1298C (rs1801131) single nucleotide polymorphism
Single nucleotide polymorphism
A single-nucleotide polymorphism is a DNA sequence variation occurring when a single nucleotide — A, T, C or G — in the genome differs between members of a biological species or paired chromosomes in an individual...
s (SNP).
C677T SNP (Ala222Val)
The MTHFR nucleotideNucleotide
Nucleotides are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides participate in cellular signaling , and are incorporated into important cofactors of enzymatic reactions...
at position 677 in the gene has two possibilities: C (cytosine
Cytosine
Cytosine is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine . It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached . The nucleoside of cytosine is cytidine...
) or T (thymine
Thymine
Thymine is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine nucleobase. As the name suggests, thymine may be derived by methylation of uracil at...
). C at position 677 (leading to an alanine at amino acid 222) is the normal allele
Allele
An allele is one of two or more forms of a gene or a genetic locus . "Allel" is an abbreviation of allelomorph. Sometimes, different alleles can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation...
. The 677T allele (leading to a valine substitution at amino acid 222) encodes a thermolabile
Thermolabile
Thermolabile refers to a substance which is subject to destruction/decomposition or change in response to heat. This term is often used to describe biochemical substances....
enzyme with reduced activity.
Individual with two copies of 677C (677CC) have the "normal" or "wildtype" genotype. 677TT individuals (homozygous) are said to have mild MTHFR deficiency. 677CT individuals (heterozygotes) are almost the same as normal individuals because the normal MTHFR can make up for the thermolabile MTHFR. About ten percent of the North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
n population are T-homozygous for this polymorphism. There is ethnic variability in the frequency of the T allele – frequency in Mediterranean/Hispanics is greater than the frequency in Caucasians which, in turn, is greater than in Africans/African-Americans.
The degree of enzyme thermolability (assessed as residual activity after heat inactivation) is much greater in 677TT individuals (18-22%) compared with 677CT (56%) and 677CC (66-67%). Individuals of 677TT are predisposed to mild hyperhomocysteinemia
Hyperhomocysteinemia
Hyperhomocysteinemia or hyperhomocysteinaemia is a medical condition characterized by an abnormally large level of homocysteine in the blood....
(high blood homocysteine levels), because they have less active MTHFR available to produce 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (which is used to decrease homocysteine). Low dietary intake of the vitamin
Vitamin
A vitamin is an organic compound required as a nutrient in tiny amounts by an organism. In other words, an organic chemical compound is called a vitamin when it cannot be synthesized in sufficient quantities by an organism, and must be obtained from the diet. Thus, the term is conditional both on...
folic acid
Folic acid
Folic acid and folate , as well as pteroyl-L-glutamic acid, pteroyl-L-glutamate, and pteroylmonoglutamic acid are forms of the water-soluble vitamin B9...
can also cause mild hyperhomocysteinemia.
Low folate intake affects individuals with the 677TT genotype to a greater extent than those with the 677CC/CT genotypes. 677TT (but not 677CC/CT) individuals with lower plasma
Blood plasma
Blood plasma is the straw-colored liquid component of blood in which the blood cells in whole blood are normally suspended. It makes up about 55% of the total blood volume. It is the intravascular fluid part of extracellular fluid...
folate levels are at risk for elevated plasma homocysteine levels. In studies of human recombinant MTHFR, the protein encoded by 677T loses its FAD cofactor three times faster than the wild-type protein. 5-Methyl-THF slows the rate of FAD release in both the wild-type and mutant enzymes, although it is to a much greater extent in the mutant enzyme.
Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) is an enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that in humans is encoded by the MTHFR gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase catalyzes the conversion of 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate
5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate
5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate is the substrate used by the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase to generate 5-methyltetrahydrofolate ....
to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate
Levomefolic acid
Levomefolic acid or metafolin is the natural, active form of folic acid used at the cellular level for DNA reproduction, the cysteine cycle and the regulation of homocysteine among other functions. The un-methylated form, folic acid , is a synthetic form of folate found in nutritional supplements...
, a cosubstrate for homocysteine
Homocysteine
Homocysteine is a non-protein amino acid with the formula HSCH2CH2CHCO2H. It is a homologue of the amino acid cysteine, differing by an additional methylene group. It is biosynthesized from methionine by the removal of its terminal Cε methyl group...
remethylation to methionine
Methionine
Methionine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2SCH3. This essential amino acid is classified as nonpolar. This amino-acid is coded by the codon AUG, also known as the initiation codon, since it indicates mRNA's coding region where translation into protein...
. Genetic variation in this gene influences susceptibility to occlusive vascular disease, neural tube defects, colon cancer and acute leukemia, and mutations in this gene are associated with methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase deficiency.
Biochemistry
MTHFR irreversibly reduces 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate
5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate is the substrate used by the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase to generate 5-methyltetrahydrofolate ....
(substrate) to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate
5-Methyltetrahydrofolate
Levomefolic acid or metafolin is the natural, active form of folic acid used at the cellular level for DNA reproduction, the cysteine cycle and the regulation of homocysteine among other functions. The un-methylated form, folic acid , is a synthetic form of folate found in nutritional supplements...
(product).
- 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate is used to convert dUMP to dTMP for de novo thymidineThymidineThymidine is a chemical compound, more precisely a pyrimidine deoxynucleoside. Deoxythymidine is the DNA nucleoside T, which pairs with deoxyadenosine in double-stranded DNA...
synthesis. - 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate is used to convert homocysteineHomocysteineHomocysteine is a non-protein amino acid with the formula HSCH2CH2CHCO2H. It is a homologue of the amino acid cysteine, differing by an additional methylene group. It is biosynthesized from methionine by the removal of its terminal Cε methyl group...
(a potentially toxic amino acidAmino acidAmino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
) to methionineMethionineMethionine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2SCH3. This essential amino acid is classified as nonpolar. This amino-acid is coded by the codon AUG, also known as the initiation codon, since it indicates mRNA's coding region where translation into protein...
by the enzyme methionine synthase. (Note that homocysteine can also be converted to methionine by the folate-independent enzyme betaine-homocysteine methyltransferase (BHMT))
MTHFR contains a bound flavin cofactor
Cofactor (biochemistry)
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound that is bound to a protein and is required for the protein's biological activity. These proteins are commonly enzymes, and cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations....
and uses NAD(P)H as the reducing agent
Reducing agent
A reducing agent is the element or compound in a reduction-oxidation reaction that donates an electron to another species; however, since the reducer loses an electron we say it is "oxidized"...
.
Structure
Mammalian MTHFR is composed of an N-terminal catalytic domain and a C-terminal regulatory domain. MTHFR has at least two promoters and two isoforms (70 kDa and 77 kDa).Regulation
MTHFR activity may be inhibited by binding of dihydrofolate (DHF) and S-adenosylmethionine (SAM, or AdoMet). MTHFR can also be phosphorylated - this decreases its activity by ~20% and allows it to be more easily inhibited by SAM.Interactive pathway map
Genetics
The enzyme is coded by the geneGene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
with the symbol MTHFR on chromosome 1 location p36.3 in humans.
There are DNA sequence variants (genetic polymorphisms) associated with this gene.
In 2000 a report brought the number of polymorphisms up to 24.
Two of the most investigated are C677T (rs1801133
Rs1801133
C677T or rs1801133 is a genetic variation—a single nucleotide polymorphism —in the MTHFR gene.Among Americans the frequency of T-homezygosity ranges from 1% or less among Blacks to 20% or more among Italians and Hispanics....
) and A1298C (rs1801131) single nucleotide polymorphism
Single nucleotide polymorphism
A single-nucleotide polymorphism is a DNA sequence variation occurring when a single nucleotide — A, T, C or G — in the genome differs between members of a biological species or paired chromosomes in an individual...
s (SNP).
C677T SNP (Ala222Val)
The MTHFR nucleotideNucleotide
Nucleotides are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides participate in cellular signaling , and are incorporated into important cofactors of enzymatic reactions...
at position 677 in the gene has two possibilities: C (cytosine
Cytosine
Cytosine is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine . It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached . The nucleoside of cytosine is cytidine...
) or T (thymine
Thymine
Thymine is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine nucleobase. As the name suggests, thymine may be derived by methylation of uracil at...
). C at position 677 (leading to an alanine at amino acid 222) is the normal allele
Allele
An allele is one of two or more forms of a gene or a genetic locus . "Allel" is an abbreviation of allelomorph. Sometimes, different alleles can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation...
. The 677T allele (leading to a valine substitution at amino acid 222) encodes a thermolabile
Thermolabile
Thermolabile refers to a substance which is subject to destruction/decomposition or change in response to heat. This term is often used to describe biochemical substances....
enzyme with reduced activity.
Individual with two copies of 677C (677CC) have the "normal" or "wildtype" genotype. 677TT individuals (homozygous) are said to have mild MTHFR deficiency. 677CT individuals (heterozygotes) are almost the same as normal individuals because the normal MTHFR can make up for the thermolabile MTHFR. About ten percent of the North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
n population are T-homozygous for this polymorphism. There is ethnic variability in the frequency of the T allele – frequency in Mediterranean/Hispanics is greater than the frequency in Caucasians which, in turn, is greater than in Africans/African-Americans.
The degree of enzyme thermolability (assessed as residual activity after heat inactivation) is much greater in 677TT individuals (18-22%) compared with 677CT (56%) and 677CC (66-67%). Individuals of 677TT are predisposed to mild hyperhomocysteinemia
Hyperhomocysteinemia
Hyperhomocysteinemia or hyperhomocysteinaemia is a medical condition characterized by an abnormally large level of homocysteine in the blood....
(high blood homocysteine levels), because they have less active MTHFR available to produce 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (which is used to decrease homocysteine). Low dietary intake of the vitamin
Vitamin
A vitamin is an organic compound required as a nutrient in tiny amounts by an organism. In other words, an organic chemical compound is called a vitamin when it cannot be synthesized in sufficient quantities by an organism, and must be obtained from the diet. Thus, the term is conditional both on...
folic acid
Folic acid
Folic acid and folate , as well as pteroyl-L-glutamic acid, pteroyl-L-glutamate, and pteroylmonoglutamic acid are forms of the water-soluble vitamin B9...
can also cause mild hyperhomocysteinemia.
Low folate intake affects individuals with the 677TT genotype to a greater extent than those with the 677CC/CT genotypes. 677TT (but not 677CC/CT) individuals with lower plasma
Blood plasma
Blood plasma is the straw-colored liquid component of blood in which the blood cells in whole blood are normally suspended. It makes up about 55% of the total blood volume. It is the intravascular fluid part of extracellular fluid...
folate levels are at risk for elevated plasma homocysteine levels. In studies of human recombinant MTHFR, the protein encoded by 677T loses its FAD cofactor three times faster than the wild-type protein. 5-Methyl-THF slows the rate of FAD release in both the wild-type and mutant enzymes, although it is to a much greater extent in the mutant enzyme.
Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) is an enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that in humans is encoded by the MTHFR gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase catalyzes the conversion of 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate
5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate
5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate is the substrate used by the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase to generate 5-methyltetrahydrofolate ....
to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate
Levomefolic acid
Levomefolic acid or metafolin is the natural, active form of folic acid used at the cellular level for DNA reproduction, the cysteine cycle and the regulation of homocysteine among other functions. The un-methylated form, folic acid , is a synthetic form of folate found in nutritional supplements...
, a cosubstrate for homocysteine
Homocysteine
Homocysteine is a non-protein amino acid with the formula HSCH2CH2CHCO2H. It is a homologue of the amino acid cysteine, differing by an additional methylene group. It is biosynthesized from methionine by the removal of its terminal Cε methyl group...
remethylation to methionine
Methionine
Methionine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2SCH3. This essential amino acid is classified as nonpolar. This amino-acid is coded by the codon AUG, also known as the initiation codon, since it indicates mRNA's coding region where translation into protein...
. Genetic variation in this gene influences susceptibility to occlusive vascular disease, neural tube defects, colon cancer and acute leukemia, and mutations in this gene are associated with methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase deficiency.
Biochemistry
MTHFR irreversibly reduces 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate
5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate is the substrate used by the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase to generate 5-methyltetrahydrofolate ....
(substrate) to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate
5-Methyltetrahydrofolate
Levomefolic acid or metafolin is the natural, active form of folic acid used at the cellular level for DNA reproduction, the cysteine cycle and the regulation of homocysteine among other functions. The un-methylated form, folic acid , is a synthetic form of folate found in nutritional supplements...
(product).
- 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate is used to convert dUMP to dTMP for de novo thymidineThymidineThymidine is a chemical compound, more precisely a pyrimidine deoxynucleoside. Deoxythymidine is the DNA nucleoside T, which pairs with deoxyadenosine in double-stranded DNA...
synthesis. - 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate is used to convert homocysteineHomocysteineHomocysteine is a non-protein amino acid with the formula HSCH2CH2CHCO2H. It is a homologue of the amino acid cysteine, differing by an additional methylene group. It is biosynthesized from methionine by the removal of its terminal Cε methyl group...
(a potentially toxic amino acidAmino acidAmino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
) to methionineMethionineMethionine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2SCH3. This essential amino acid is classified as nonpolar. This amino-acid is coded by the codon AUG, also known as the initiation codon, since it indicates mRNA's coding region where translation into protein...
by the enzyme methionine synthase. (Note that homocysteine can also be converted to methionine by the folate-independent enzyme betaine-homocysteine methyltransferase (BHMT))
MTHFR contains a bound flavin cofactor
Cofactor (biochemistry)
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound that is bound to a protein and is required for the protein's biological activity. These proteins are commonly enzymes, and cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations....
and uses NAD(P)H as the reducing agent
Reducing agent
A reducing agent is the element or compound in a reduction-oxidation reaction that donates an electron to another species; however, since the reducer loses an electron we say it is "oxidized"...
.
Structure
Mammalian MTHFR is composed of an N-terminal catalytic domain and a C-terminal regulatory domain. MTHFR has at least two promoters and two isoforms (70 kDa and 77 kDa).Regulation
MTHFR activity may be inhibited by binding of dihydrofolate (DHF) and S-adenosylmethionine (SAM, or AdoMet). MTHFR can also be phosphorylated - this decreases its activity by ~20% and allows it to be more easily inhibited by SAM.Interactive pathway map
Genetics
The enzyme is coded by the geneGene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
with the symbol MTHFR on chromosome 1 location p36.3 in humans.
There are DNA sequence variants (genetic polymorphisms) associated with this gene.
In 2000 a report brought the number of polymorphisms up to 24.
Two of the most investigated are C677T (rs1801133
Rs1801133
C677T or rs1801133 is a genetic variation—a single nucleotide polymorphism —in the MTHFR gene.Among Americans the frequency of T-homezygosity ranges from 1% or less among Blacks to 20% or more among Italians and Hispanics....
) and A1298C (rs1801131) single nucleotide polymorphism
Single nucleotide polymorphism
A single-nucleotide polymorphism is a DNA sequence variation occurring when a single nucleotide — A, T, C or G — in the genome differs between members of a biological species or paired chromosomes in an individual...
s (SNP).
C677T SNP (Ala222Val)
The MTHFR nucleotideNucleotide
Nucleotides are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides participate in cellular signaling , and are incorporated into important cofactors of enzymatic reactions...
at position 677 in the gene has two possibilities: C (cytosine
Cytosine
Cytosine is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine . It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached . The nucleoside of cytosine is cytidine...
) or T (thymine
Thymine
Thymine is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine nucleobase. As the name suggests, thymine may be derived by methylation of uracil at...
). C at position 677 (leading to an alanine at amino acid 222) is the normal allele
Allele
An allele is one of two or more forms of a gene or a genetic locus . "Allel" is an abbreviation of allelomorph. Sometimes, different alleles can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation...
. The 677T allele (leading to a valine substitution at amino acid 222) encodes a thermolabile
Thermolabile
Thermolabile refers to a substance which is subject to destruction/decomposition or change in response to heat. This term is often used to describe biochemical substances....
enzyme with reduced activity.
Individual with two copies of 677C (677CC) have the "normal" or "wildtype" genotype. 677TT individuals (homozygous) are said to have mild MTHFR deficiency. 677CT individuals (heterozygotes) are almost the same as normal individuals because the normal MTHFR can make up for the thermolabile MTHFR. About ten percent of the North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
n population are T-homozygous for this polymorphism. There is ethnic variability in the frequency of the T allele – frequency in Mediterranean/Hispanics is greater than the frequency in Caucasians which, in turn, is greater than in Africans/African-Americans.
The degree of enzyme thermolability (assessed as residual activity after heat inactivation) is much greater in 677TT individuals (18-22%) compared with 677CT (56%) and 677CC (66-67%). Individuals of 677TT are predisposed to mild hyperhomocysteinemia
Hyperhomocysteinemia
Hyperhomocysteinemia or hyperhomocysteinaemia is a medical condition characterized by an abnormally large level of homocysteine in the blood....
(high blood homocysteine levels), because they have less active MTHFR available to produce 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (which is used to decrease homocysteine). Low dietary intake of the vitamin
Vitamin
A vitamin is an organic compound required as a nutrient in tiny amounts by an organism. In other words, an organic chemical compound is called a vitamin when it cannot be synthesized in sufficient quantities by an organism, and must be obtained from the diet. Thus, the term is conditional both on...
folic acid
Folic acid
Folic acid and folate , as well as pteroyl-L-glutamic acid, pteroyl-L-glutamate, and pteroylmonoglutamic acid are forms of the water-soluble vitamin B9...
can also cause mild hyperhomocysteinemia.
Low folate intake affects individuals with the 677TT genotype to a greater extent than those with the 677CC/CT genotypes. 677TT (but not 677CC/CT) individuals with lower plasma
Blood plasma
Blood plasma is the straw-colored liquid component of blood in which the blood cells in whole blood are normally suspended. It makes up about 55% of the total blood volume. It is the intravascular fluid part of extracellular fluid...
folate levels are at risk for elevated plasma homocysteine levels. In studies of human recombinant MTHFR, the protein encoded by 677T loses its FAD cofactor three times faster than the wild-type protein. 5-Methyl-THF slows the rate of FAD release in both the wild-type and mutant enzymes, although it is to a much greater extent in the mutant enzyme.
This polymorphism and mild hyperhomocysteinemia are associated with neural tube defects
Neural tube defects
Neural tube defects are one of the most common birth defects, occurring in approximately one in 1,000 live births in the United States. An NTD is an opening in the spinal cord or brain that occurs very early in human development. In the 2nd week of pregnancy called gastrulation, specialized cells...
in offspring, arterial and venous thrombosis
Thrombosis
Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel is injured, the body uses platelets and fibrin to form a blood clot to prevent blood loss...
, and cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease
Heart disease or cardiovascular disease are the class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels . While the term technically refers to any disease that affects the cardiovascular system , it is usually used to refer to those related to atherosclerosis...
. 677TT individuals are at a decreased risk for certain leukemia
Leukemia
Leukemia or leukaemia is a type of cancer of the blood or bone marrow characterized by an abnormal increase of immature white blood cells called "blasts". Leukemia is a broad term covering a spectrum of diseases...
s and colon cancer.
Mutations in the MTHFR gene could be one of the factors leading to increased risk of developing schizophrenia
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by a disintegration of thought processes and of emotional responsiveness. It most commonly manifests itself as auditory hallucinations, paranoid or bizarre delusions, or disorganized speech and thinking, and it is accompanied by significant social...
.
Schizophrenic patients having the risk allele (T\T) show more deficiencies in executive function tasks.
A1298C SNP (Glu429Ala)
At nucleotide 1298 of the MTHFR, there are two possibilities: A or C. 1298A (leading to a Glu at amino acid 429) is the most common while 1298C (leading to an Ala substitution at amino acid 429) is less common. 1298AA is the "normal" homozygous, 1298AC the heterozygous, and 1298CC the homozygous for the "variant". In studies of human recombinant MTHFR, the protein encoded by 1298C cannot be distinguished from 1298A in terms of activity, thermolability, FAD release, or the protective effect of 5-methyl-THF. The C mutation does not appear to affect the MTHFR protein. It does not result in thermolabile MTHFR and does not appear to affect homocysteine levels.Compound Heterozygotes
Mutations at 677 and 1298 are different locations; however, they are both in the 'same' gene: MTHFR. Some studies have shown that the MTHFR protein in people with the genotype 677CT 1298AC does its job a bit less well than the normal MTHFR.Severe MTHFR deficiency
Severe MTHFR deficiency is rare (about 50 cases worldwide) and caused by mutations resulting in 0-20% residual enzyme activity. Patients exhibit developmental delay, motor and gait dysfunction, seizures, and neurological impairment and have extremely high levels of homocysteineHomocysteine
Homocysteine is a non-protein amino acid with the formula HSCH2CH2CHCO2H. It is a homologue of the amino acid cysteine, differing by an additional methylene group. It is biosynthesized from methionine by the removal of its terminal Cε methyl group...
in their plasma and urine
Urine
Urine is a typically sterile liquid by-product of the body that is secreted by the kidneys through a process called urination and excreted through the urethra. Cellular metabolism generates numerous by-products, many rich in nitrogen, that require elimination from the bloodstream...
as well as low to normal plasma methionine
Methionine
Methionine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2SCH3. This essential amino acid is classified as nonpolar. This amino-acid is coded by the codon AUG, also known as the initiation codon, since it indicates mRNA's coding region where translation into protein...
levels.
Reaction schematic and folate pathway
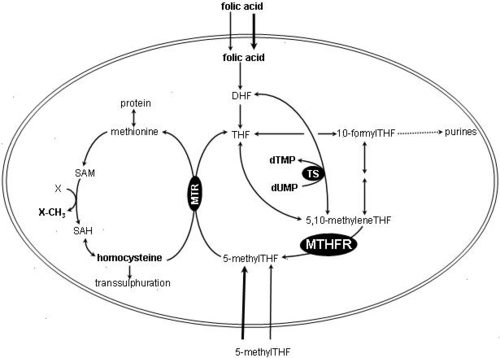 |
|||
| MTHFR = methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase | DHF = dihydrofolate | THF = tetrahydrofolate Tetrahydrofolic acid Tetrahydrofolic acid, or tetrahydrofolate, is a folic acid derivative.-Metabolism:-Human synthesis:It is produced from dihydrofolic acid by dihydrofolate reductase... |
|
| 5,10-methylene-THF = 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate 5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate 5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate is the substrate used by the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase to generate 5-methyltetrahydrofolate .... |
5-methyl-THF = 5-methyltetrahydrofolate 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate Levomefolic acid or metafolin is the natural, active form of folic acid used at the cellular level for DNA reproduction, the cysteine cycle and the regulation of homocysteine among other functions. The un-methylated form, folic acid , is a synthetic form of folate found in nutritional supplements... |
MTR = methionine synthase 5-methyltetrahydrofolate-homocysteine methyltransferase Methionine synthase also known as MS, MeSe, MetH is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MTR gene . This enzyme is responsible for the regeneration of methionine from homocysteine... |
SAH = S-adenosylhomocysteine S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine S-Adenosyl-L-homocysteine is an amino acid derivative used in several metabolic pathways in most organisms. It is an intermediate in the synthesis of cysteine and adenosine.... |
| NADPH = reduced Redox Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed.... form of Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or TPN in older notation , is a coenzyme used in anabolic reactions, such as lipid and nucleic acid synthesis, which require NADPH as a reducing agent.... |
NADP+ = oxidized Redox Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed.... form of Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or TPN in older notation , is a coenzyme used in anabolic reactions, such as lipid and nucleic acid synthesis, which require NADPH as a reducing agent.... |
SAM = S-Adenosyl methionine S-Adenosyl methionine S-Adenosyl methionine is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers. SAM was first discovered in Italy by G. L. Cantoni in 1952. It is made from adenosine triphosphate and methionine by methionine adenosyltransferase . Transmethylation, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation are the... |
TS = thymidylate synthase Thymidylate synthase Thymidylate synthetase is the enzyme used to generate thymidine monophosphate , which is subsequently phosphorylated to thymidine triphosphate for use in DNA synthesis and repair.... |

