
Tetrahydrofolic acid
Encyclopedia
Tetrahydrofolic acid, or tetrahydrofolate, is a folic acid
derivative.
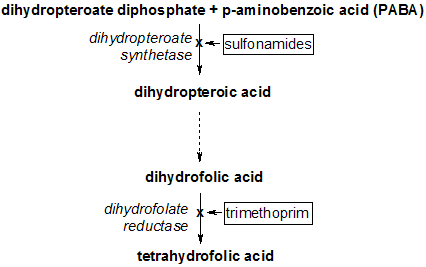
by dihydrofolate reductase
. This reaction is inhibited by methotrexate
.
It is converted into 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate
by serine hydroxymethyltransferase
.
to produce dihydropteroate
in bacteria
, an molecule without function in humans. This makes it a useful target for sulfonamide
antibiotics, which compete with the PABA
precursor.
s and nucleic acid
s. It acts as a donor of a group with one carbon atom. It gets this carbon atom by sequestering formaldehyde
produced in other processes. A shortage in THF can cause megaloblastic anemia
.
Methotrexate acts on dihydrofolate reductase, like pyrimethamine or trimethoprim, as an inhibitor and thus reduces the amount of tetrahydrofolate made. This may result in megaloblastic anemia.
Tetrahydrofolic acid is involved in the conversion of formiminoglutamic acid to glutamic acid; this may reduce the amount of histidine available for decarboxylation and protein synthesis, and hence the urinary histamine and formiminoglutamic acid may be decreased.
Folic acid
Folic acid and folate , as well as pteroyl-L-glutamic acid, pteroyl-L-glutamate, and pteroylmonoglutamic acid are forms of the water-soluble vitamin B9...
derivative.
Metabolism

Human synthesis
It is produced from dihydrofolic acidDihydrofolic acid
Dihydrofolic acid is a folic acid derivative acted upon by dihydrofolate reductase to produce tetrahydrofolic acid. Since tetrahydrofolate is needed to make both purines and pyrimidines, dihydrofolate reductase is targeted by various drugs to prevent nucleic acid synthesis. Dihydrofolic acid is...
by dihydrofolate reductase
Dihydrofolate reductase
- Function :Dihydrofolate reductase converts dihydrofolate into tetrahydrofolate, a methyl group shuttle required for the de novo synthesis of purines, thymidylic acid, and certain amino acids...
. This reaction is inhibited by methotrexate
Methotrexate
Methotrexate , abbreviated MTX and formerly known as amethopterin, is an antimetabolite and antifolate drug. It is used in treatment of cancer, autoimmune diseases, ectopic pregnancy, and for the induction of medical abortions. It acts by inhibiting the metabolism of folic acid. Methotrexate...
.
It is converted into 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate
5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate
5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate is the substrate used by the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase to generate 5-methyltetrahydrofolate ....
by serine hydroxymethyltransferase
Serine hydroxymethyltransferase
Serine hydroxymethyltransferase is an enzyme which plays an important role in cellular one-carbon pathways by catalyzing the reversible, simultaneous conversions of L-serine to glycine and tetrahydrofolate to 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate...
.
Bacterial synthesis
Many bacteria use dihydropteroate synthetaseDihydropteroate synthetase
Dihydropteroate synthetase is an enzyme classified under . It produces dihydropteroate in bacteria, but it is not expressed in most eukaryotes including humans...
to produce dihydropteroate
Dihydropteroate
Dihydropteroate is a pterin created from para-aminobenzoic acid by the enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase. It is an important intermediate in folate synthesis.Bacteriostatic agents, such as sulfonamides, target dihydropteroate synthetase...
in bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
, an molecule without function in humans. This makes it a useful target for sulfonamide
Sulfonamide (medicine)
Sulfonamide or sulphonamide is the basis of several groups of drugs. The original antibacterial sulfonamides are synthetic antimicrobial agents that contain the sulfonamide group. Some sulfonamides are also devoid of antibacterial activity, e.g., the anticonvulsant sultiame...
antibiotics, which compete with the PABA
4-Aminobenzoic acid
4-Aminobenzoic acid is an organic compound with the formula H2NC6H4CO2H. PABA is a white grey crystalline substance that is only slightly soluble in water...
precursor.
Functions
It is a coenzyme in many reactions, especially in the metabolism of amino acidAmino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
s and nucleic acid
Nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biological molecules essential for life, and include DNA and RNA . Together with proteins, nucleic acids make up the most important macromolecules; each is found in abundance in all living things, where they function in encoding, transmitting and expressing genetic information...
s. It acts as a donor of a group with one carbon atom. It gets this carbon atom by sequestering formaldehyde
Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula CH2O. It is the simplest aldehyde, hence its systematic name methanal.Formaldehyde is a colorless gas with a characteristic pungent odor. It is an important precursor to many other chemical compounds, especially for polymers...
produced in other processes. A shortage in THF can cause megaloblastic anemia
Megaloblastic anemia
Megaloblastic anemia is an anemia that results from inhibition of DNA synthesis in red blood cell production. When DNA synthesis is impaired, the cell cycle cannot progress from the G2 growth stage to the mitosis stage...
.
Methotrexate acts on dihydrofolate reductase, like pyrimethamine or trimethoprim, as an inhibitor and thus reduces the amount of tetrahydrofolate made. This may result in megaloblastic anemia.
Tetrahydrofolic acid is involved in the conversion of formiminoglutamic acid to glutamic acid; this may reduce the amount of histidine available for decarboxylation and protein synthesis, and hence the urinary histamine and formiminoglutamic acid may be decreased.

