
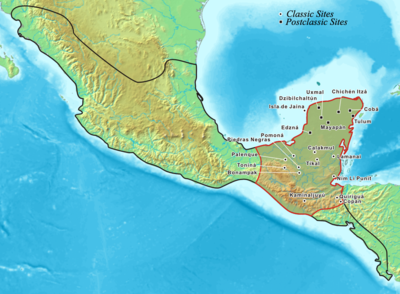
Maya city
Encyclopedia
A Maya city was a centre of population of the pre-Columbian
Maya civilization
of Mesoamerica
. It served the specialised roles of administration, commerce, manufacturing and religion
that characterised ancient cities worldwide. Maya cities tended to be more dispersed than cities in other societies, even within Mesoamerica, as a result of adaptation to a lowland tropical environment that allowed food production amidst areas dedicated to other activities. They lacked the grid plans of the highland cities of central Mexico, such as Teotihuacán
and Tenochtitlan. Maya kings
ruled their kingdoms from palaces that were situated within the centre of their cities. Cities tended to be located in places that controlled trade routes or that could supply essential products. This allowed the elites that controlled trade to increase their wealth and status. Such cities were able to construct temples for public ceremonies, thus attracting further inhabitants to the city. Those cities that had favourable conditions for food production, combined with access to trade routes were likely to develop into the capital cities of early Maya states.
The political relationship between Classic Maya city-state
s has been likened to the relationships between city-states in Classical Greece
and Renaissance Italy
. Some cities were linked to each other by straight limestone causeways, known as sacbeob
, although whether the exact function of these roads was commercial, political or religious has not been determined.
temples and other monumental architecture dedicated to elite activities, such as basal platforms that supported administrative or elite residential complexes. Sculpted monuments were raised to record the deeds of the ruling dynasty. City centres also featured plazas, sacred ballcourts
and buildings used for marketplaces and schools. Frequently causeways
linked the centre to outlying areas of the city. Some of these classes of architecture formed lesser groups in the outlying areas of the city, which served as sacred centres for non-royal lineages. The areas adjacent to these sacred compounds included residential complexes housing wealthy lineages. Art
excavated from these elite residential complexes varies in quality according to the rank and prestige of the lineage that it housed. The largest and richest of these elite compounds sometimes possessed sculpture and art of craftsmanship equal to that of royal art.
The ceremonial centre of the Maya city was where the ruling elite lived, and where the administrative functions of the city were performed, together with religious ceremonies. It was also where the inhabitants of the city gathered for public activities. Elite residential complexes occupied the best land around the city centre, while commoners had their residences dispersed further away from the ceremonial centre. Residential units were built on top of stone platforms to raise them above the level of the rain season floodwaters.
(1000-400 BC), small villages began to grow to form cities. By 500 BC these cities possessed large temple structures decorated with stucco
masks representing gods. Nakbe
in the Petén Department of Guatemala
is the earliest well-documented city in the Maya lowlands, where large structures have been dated to around 750 BC. Nakbe already featured the monumental masonry architecture
, sculpted monuments and causeways
that characterised later cities in the Maya lowlands.
(400 BC - 250 AD), the enormous city of El Mirador
grew to cover approximately 16 square kilometres (6.2 sq mi). It possessed paved avenues, massive triadic pyramid
complexes dated to around 150 BC, and stelae
and altars that were erected in its plazas. El Mirador is considered to be one of the first capital cities of the Maya civilization. The swamps of the Mirador Basin appear to have been the primary attraction for the first inhabitants of the area as evidenced by the unusual cluster of large cities around them.
The city of Tikal
, later to be one of the most important of the Classic Period
Maya cities, was already a significant city by around 350 BC, although it did not match El Mirador. The Late Preclassic cultural florescence collapsed in the 1st century AD and many of the great Maya cities of the epoch were abandoned; the cause of this collapse is as yet unknown.
in the distant Valley of Mexico
. At its height during the Late Classic, Tikal had expanded to have a population of well over 100,000. Tikal's great rival was Calakmul, another powerful city in the Petén Basin. In the southeast, Copán
was the most important city. Palenque
and Yaxchilán
were the most powerful cities in the Usumacinta
region. In the north of the Maya area, Coba
was the most important Maya capital. Capital cities of Maya kingdoms could vary considerably in size, apparently related to how many vassal cities were tied to the capital. Overlords of city-states that held sway over a greater number of subordinate lords could command greater quantities of tribute in the form of goods and labour. The most notable forms of tribute pictured on Maya ceramics
are cacao, textiles and feathers. During the 9th century AD, the central Maya region suffered major political collapse
, marked by the abandonment of cities, the ending of dynasties and a northward shift of population. During this period, known as the Terminal Classic, the northern cities of Chichen Itza
and Uxmal
show increased activity. Major cities in Mexico
's Yucatán Peninsula
continued to be inhabited long after the cities of the southern lowlands ceased to raise monuments.
at this time was Q'umarkaj, also known as Utatlán, the capital of the aggressive K'iche' Maya kingdom
.
s in the first half of the 16th century. The K'iche' capital, Q'umarkaj, fell to Pedro de Alvarado
in 1524. Shortly afterwards, the Spanish were invited as allies into Iximche
, the capital city of the Kaqchikel Maya. Good relations did not last and the city was abandoned a few months later. This was followed by the fall of Zaculeu
, the Mam
Maya capital, in 1525.
By the 19th century, the existence of five former Maya cities was known in the Petén region of Guatemala
. Tayasal
had been visited by Spanish conquistador Hernán Cortés
in 1524, followed by a number of missionaries at the beginning of the 17th century. The city was finally razed when it was conquered in 1697. Juan Galindo, governor of Petén, described the ruins of the Postclassic city of Topoxte
in 1834. Modesto Méndez, a later governor of Petén, published a description of the ruins of the once great city of Tikal in 1848. Teoberto Maler
described the ruins of the city of Motul de San José
in 1895. San Clemente was described by Karl Sapper
in the same year. The number of known cities grew enormously during the course of the 20th century, 24 cities in Petén alone had been described by 1938.
Until the 1960s, scholarly opinion was that the ruins of Maya centres were not true cities but were rather empty ceremonial centres where the priesthood performed religious rituals for the peasant farmers, who lived dispersed in the jungle. Since the 1960s, formal archaeological mapping projects have revealed that the ceremonial centres in fact formed the centres of dispersed cities that possessed populations that at some sites could reach tens of thousands.
Pre-Columbian era
The pre-Columbian era incorporates all period subdivisions in the history and prehistory of the Americas before the appearance of significant European influences on the American continents, spanning the time of the original settlement in the Upper Paleolithic period to European colonization during...
Maya civilization
Maya civilization
The Maya is a Mesoamerican civilization, noted for the only known fully developed written language of the pre-Columbian Americas, as well as for its art, architecture, and mathematical and astronomical systems. Initially established during the Pre-Classic period The Maya is a Mesoamerican...
of Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a region and culture area in the Americas, extending approximately from central Mexico to Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica, within which a number of pre-Columbian societies flourished before the Spanish colonization of the Americas in the 15th and...
. It served the specialised roles of administration, commerce, manufacturing and religion
Maya religion
The traditional Maya religion of western Honduras, Guatemala, Belize, and Mexico is a southeastern variant of Mesoamerican religion. As is the case with many other contemporary Mesoamerican religions, it results from centuries of symbiosis with Roman Catholicism...
that characterised ancient cities worldwide. Maya cities tended to be more dispersed than cities in other societies, even within Mesoamerica, as a result of adaptation to a lowland tropical environment that allowed food production amidst areas dedicated to other activities. They lacked the grid plans of the highland cities of central Mexico, such as Teotihuacán
Teotihuacán
Teotihuacan – also written Teotihuacán, with a Spanish orthographic accent on the last syllable – is an enormous archaeological site in the Basin of Mexico, just 30 miles northeast of Mexico City, containing some of the largest pyramidal structures built in the pre-Columbian Americas...
and Tenochtitlan. Maya kings
Maya rulers
Mayan kings were the centers of power for Mayan civilization. Each Mayan city-state was controlled by a dynasty of kings, who collectively drove the empire forward.-Symbols of power:...
ruled their kingdoms from palaces that were situated within the centre of their cities. Cities tended to be located in places that controlled trade routes or that could supply essential products. This allowed the elites that controlled trade to increase their wealth and status. Such cities were able to construct temples for public ceremonies, thus attracting further inhabitants to the city. Those cities that had favourable conditions for food production, combined with access to trade routes were likely to develop into the capital cities of early Maya states.
The political relationship between Classic Maya city-state
City-state
A city-state is an independent or autonomous entity whose territory consists of a city which is not administered as a part of another local government.-Historical city-states:...
s has been likened to the relationships between city-states in Classical Greece
Classical Greece
Classical Greece was a 200 year period in Greek culture lasting from the 5th through 4th centuries BC. This classical period had a powerful influence on the Roman Empire and greatly influenced the foundation of Western civilizations. Much of modern Western politics, artistic thought, such as...
and Renaissance Italy
Italian Renaissance
The Italian Renaissance began the opening phase of the Renaissance, a period of great cultural change and achievement in Europe that spanned the period from the end of the 13th century to about 1600, marking the transition between Medieval and Early Modern Europe...
. Some cities were linked to each other by straight limestone causeways, known as sacbeob
Sacbe
right|thumb|Sacbe at Dzibilchaltun in the Yucatánthumb|right|Arch at the end of the sacbé, Kabah, YucatánSacbe, plural Sacbeob, or "white ways" are raised paved roads built by the Maya civilization of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica...
, although whether the exact function of these roads was commercial, political or religious has not been determined.
Architectural organisation
Maya cities were not formally planned like the cities of highland Mexico and were subject to irregular expansion, with the haphazard addition of palaces, temples and other buildings. Maya cities usually had a ceremonial and administrative centre surrounded by a vast irregular sprawl of residential complexes. The centres of all Maya cities featured sacred precincts, sometimes separated from nearby residential areas by walls. These precincts contained pyramidMesoamerican pyramids
Mesoamerican pyramids, pyramid-shaped structures, are an important part of ancient Mesoamerican architecture. These structures were usually step pyramids with temples on top – more akin to the ziggurats of Mesopotamia than to the pyramids of Ancient Egypt...
temples and other monumental architecture dedicated to elite activities, such as basal platforms that supported administrative or elite residential complexes. Sculpted monuments were raised to record the deeds of the ruling dynasty. City centres also featured plazas, sacred ballcourts
Mesoamerican ballcourt
A Mesoamerican ballcourt is a large masonry structure of a type used in Mesoamerica for over 2,700 years to play the Mesoamerican ballgame, particularly the hip-ball version of the ballgame. Over 1,300 ballcourts have been identified, 60% in the last 20 years alone...
and buildings used for marketplaces and schools. Frequently causeways
Sacbe
right|thumb|Sacbe at Dzibilchaltun in the Yucatánthumb|right|Arch at the end of the sacbé, Kabah, YucatánSacbe, plural Sacbeob, or "white ways" are raised paved roads built by the Maya civilization of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica...
linked the centre to outlying areas of the city. Some of these classes of architecture formed lesser groups in the outlying areas of the city, which served as sacred centres for non-royal lineages. The areas adjacent to these sacred compounds included residential complexes housing wealthy lineages. Art
Maya art
Maya art, here taken to mean the visual arts, is the artistic style typical of the Maya civilization, that took shape in the course the Preclassic period , and grew greater during the Classic period Maya art, here taken to mean the visual arts, is the artistic style typical of the Maya...
excavated from these elite residential complexes varies in quality according to the rank and prestige of the lineage that it housed. The largest and richest of these elite compounds sometimes possessed sculpture and art of craftsmanship equal to that of royal art.
The ceremonial centre of the Maya city was where the ruling elite lived, and where the administrative functions of the city were performed, together with religious ceremonies. It was also where the inhabitants of the city gathered for public activities. Elite residential complexes occupied the best land around the city centre, while commoners had their residences dispersed further away from the ceremonial centre. Residential units were built on top of stone platforms to raise them above the level of the rain season floodwaters.
Middle Preclassic Period
During the Middle Preclassic PeriodMesoamerican chronology
Mesoamerican chronology divides the history of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica into several periods: the Paleo-Indian , the Archaic , the Preclassic , the Classic , and the Postclassic...
(1000-400 BC), small villages began to grow to form cities. By 500 BC these cities possessed large temple structures decorated with stucco
Stucco
Stucco or render is a material made of an aggregate, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as decorative coating for walls and ceilings and as a sculptural and artistic material in architecture...
masks representing gods. Nakbe
Nakbe
Nakbe is one of the largest early Maya archaeological sites, rivaled by El Mirador. Nakbe is located in the The Mirador Basin, in El Petén region of Guatemala, approximately 13 kilometers south of the Largest Maya city of El Mirador...
in the Petén Department of Guatemala
Guatemala
Guatemala is a country in Central America bordered by Mexico to the north and west, the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, Belize to the northeast, the Caribbean to the east, and Honduras and El Salvador to the southeast...
is the earliest well-documented city in the Maya lowlands, where large structures have been dated to around 750 BC. Nakbe already featured the monumental masonry architecture
Maya architecture
A unique and spectacular style, Maya architecture spans several thousands of years. Often the most dramatic and easily recognizable as Maya are the stepped pyramids from the Terminal Pre-classic period and beyond. Being based on the general Mesoamerican architectural traditions these pyramids...
, sculpted monuments and causeways
Sacbe
right|thumb|Sacbe at Dzibilchaltun in the Yucatánthumb|right|Arch at the end of the sacbé, Kabah, YucatánSacbe, plural Sacbeob, or "white ways" are raised paved roads built by the Maya civilization of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica...
that characterised later cities in the Maya lowlands.
Late Preclassic Period
In the Late Preclassic PeriodMesoamerican chronology
Mesoamerican chronology divides the history of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica into several periods: the Paleo-Indian , the Archaic , the Preclassic , the Classic , and the Postclassic...
(400 BC - 250 AD), the enormous city of El Mirador
El Mirador
El Mirador is a large pre-Columbian Mayan settlement, located in the north of the modern department of El Petén, Guatemala.-Discovery:El Mirador was first discovered in 1926, and was photographed from the air in 1930, but the remote site deep in the jungle had little more attention paid to it until...
grew to cover approximately 16 square kilometres (6.2 sq mi). It possessed paved avenues, massive triadic pyramid
Triadic pyramid
Triadic pyramids are a Preclassic Maya civilization innovation consisting of a dominant structure flanked by two smaller inward-facing buildings, all mounted upon a single basal platform...
complexes dated to around 150 BC, and stelae
Maya stelae
Maya stelae are monuments that were fashioned by the Maya civilization of ancient Mesoamerica. They consist of tall sculpted stone shafts and are often associated with low circular stones referred to as altars, although their actual function is uncertain. Many stelae were sculpted in low relief,...
and altars that were erected in its plazas. El Mirador is considered to be one of the first capital cities of the Maya civilization. The swamps of the Mirador Basin appear to have been the primary attraction for the first inhabitants of the area as evidenced by the unusual cluster of large cities around them.
The city of Tikal
Tikal
Tikal is one of the largest archaeological sites and urban centres of the pre-Columbian Maya civilization. It is located in the archaeological region of the Petén Basin in what is now northern Guatemala...
, later to be one of the most important of the Classic Period
Mesoamerican chronology
Mesoamerican chronology divides the history of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica into several periods: the Paleo-Indian , the Archaic , the Preclassic , the Classic , and the Postclassic...
Maya cities, was already a significant city by around 350 BC, although it did not match El Mirador. The Late Preclassic cultural florescence collapsed in the 1st century AD and many of the great Maya cities of the epoch were abandoned; the cause of this collapse is as yet unknown.
Classic Period
During the Classic Period (AD 250-900), the Maya civilization achieved its greatest florescence. During the Early Classic (AD 250-600), cities throughout the Maya region were influenced by the great metropolis of TeotihuacanTeotihuacan
Teotihuacan – also written Teotihuacán, with a Spanish orthographic accent on the last syllable – is an enormous archaeological site in the Basin of Mexico, just 30 miles northeast of Mexico City, containing some of the largest pyramidal structures built in the pre-Columbian Americas...
in the distant Valley of Mexico
Valley of Mexico
The Valley of Mexico is a highlands plateau in central Mexico roughly coterminous with the present-day Distrito Federal and the eastern half of the State of Mexico. Surrounded by mountains and volcanoes, the Valley of Mexico was a centre for several pre-Columbian civilizations, including...
. At its height during the Late Classic, Tikal had expanded to have a population of well over 100,000. Tikal's great rival was Calakmul, another powerful city in the Petén Basin. In the southeast, Copán
Copán
Copán is an archaeological site of the Maya civilization located in the Copán Department of western Honduras, not far from the border with Guatemala. It was the capital city of a major Classic period kingdom from the 5th to 9th centuries AD...
was the most important city. Palenque
Palenque
Palenque was a Maya city state in southern Mexico that flourished in the 7th century. The Palenque ruins date back to 100 BC to its fall around 800 AD...
and Yaxchilán
Yaxchilan
Yaxchilan is an ancient Maya city located on the bank of the Usumacinta River in what is now the state of Chiapas, Mexico. In the Late Classic Period Yaxchilan was one of the most powerful Maya states along the course of the Usumacinta, with Piedras Negras as its major rival...
were the most powerful cities in the Usumacinta
Usumacinta River
The Usumacinta River is a river in southeastern Mexico and northwestern Guatemala. It is formed by the junction of the Pasión River, which arises in the Sierra de Santa Cruz and the Salinas River, also known as the Chixoy, or the Negro, which descends from the Sierra Madre de Guatemala...
region. In the north of the Maya area, Coba
Coba
Coba is a large ruined city of the Pre-Columbian Maya civilization, located in the state of Quintana Roo, Mexico. It is located about 90 km east of the Maya site of Chichen Itza, about 40 km west of the Caribbean Sea, and 44 km northwest of the site of Tulum, with which it is...
was the most important Maya capital. Capital cities of Maya kingdoms could vary considerably in size, apparently related to how many vassal cities were tied to the capital. Overlords of city-states that held sway over a greater number of subordinate lords could command greater quantities of tribute in the form of goods and labour. The most notable forms of tribute pictured on Maya ceramics
Maya ceramics
Maya ceramics are important in the study of the Pre-Columbian Maya culture of Mesoamerica. Through the years, the vessels took on different shapes, colors, sizes, and purposes...
are cacao, textiles and feathers. During the 9th century AD, the central Maya region suffered major political collapse
Classic Maya collapse
The Classic Maya Collapse refers to the decline and abandonment of the Classic Period Maya cities of the southern Maya lowlands of Mesoamerica between the 8th and 9th centuries. This should not be confused with the collapse of the Preclassic Maya in the 2nd century AD...
, marked by the abandonment of cities, the ending of dynasties and a northward shift of population. During this period, known as the Terminal Classic, the northern cities of Chichen Itza
Chichen Itza
Chichen Itza is a large pre-Columbian archaeological site built by the Maya civilization located in the northern center of the Yucatán Peninsula, in the Municipality of Tinúm, Yucatán state, present-day Mexico....
and Uxmal
Uxmal
Uxmal was dominant from 875 to 900 CE. The site appears to have been the capital of a regional state in the Puuc region from 850-950 CE. The Maya dynasty expanded their dominion over their neighbors. This prominence didn't last long...
show increased activity. Major cities in Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
's Yucatán Peninsula
Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula, in southeastern Mexico, separates the Caribbean Sea from the Gulf of Mexico, with the northern coastline on the Yucatán Channel...
continued to be inhabited long after the cities of the southern lowlands ceased to raise monuments.
Postclassic Period
The Postclassic Period (AD 900-c.1524) was marked by a series of changes that distinguished its cities from those of the preceding Classic Period. Chichen Itza, in the north, became what was probably the largest, most powerful and most cosmopolitan of all Maya cities. One of the most important cities in the Guatemalan HighlandsGuatemalan Highlands
The Guatemalan Highlands is an upland region in southern Guatemala, lying between the Sierra Madre de Chiapas to the south and the Petén lowlands to the north....
at this time was Q'umarkaj, also known as Utatlán, the capital of the aggressive K'iche' Maya kingdom
K'iche' Kingdom of Q'umarkaj
The K'iche' Kingdom of Q'umarkaj was a state in the highlands of modern day Guatemala which was founded by the K'iche' Maya in the thirteenth century, and which expanded through the fifteenth century until it was conquered by Spanish and Nahua forces led by Pedro de Alvarado in 1524.The K'iche'...
.
Population estimates

| Site name | Location | Maximum Population | Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coba Coba Coba is a large ruined city of the Pre-Columbian Maya civilization, located in the state of Quintana Roo, Mexico. It is located about 90 km east of the Maya site of Chichen Itza, about 40 km west of the Caribbean Sea, and 44 km northwest of the site of Tulum, with which it is... |
Quintana Roo Quintana Roo Quintana Roo officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Quintana Roo is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 10 municipalities and its capital city is Chetumal.... , Mexico |
50,000 | Late Classic |
| Copán Copán Copán is an archaeological site of the Maya civilization located in the Copán Department of western Honduras, not far from the border with Guatemala. It was the capital city of a major Classic period kingdom from the 5th to 9th centuries AD... |
Copán Department, Honduras Honduras Honduras is a republic in Central America. It was previously known as Spanish Honduras to differentiate it from British Honduras, which became the modern-day state of Belize... |
15,000-21,000 | Late Classic |
| Calakmul Calakmul Calakmul is a Maya archaeological site in the Mexican state of Campeche, deep in the jungles of the greater Petén Basin region. It is from the Guatemalan border. Calakmul was one of the largest and most powerful ancient cities ever uncovered in the Maya lowlands... |
Campeche Campeche Campeche is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. Located in Southeast Mexico, it is bordered by the states of Yucatán to the north east, Quintana Roo to the east, and Tabasco to the south west... , Mexico |
50,000 | Late Classic |
| Cival Cival Cival is an archaeological site in the Petén Basin region of the southern Maya lowlands, which was formerly a major city of the Pre-Columbian Maya civilization. It is located in the present-day Department of Petén, Guatemala.... |
Petén Department, Guatemala | 2,000-5,000 | Late Preclassic |
| Quiriguá Quiriguá Quiriguá is an ancient Maya archaeological site in the department of Izabal in south-eastern Guatemala. It is a medium-sized site covering approximately along the lower Motagua River, with the ceremonial center about from the north bank. During the Maya Classic Period , Quiriguá was situated at... |
Izabal Department, Guatemala | 1,200–1,600 | Late Classic |
| Q'umarkaj | Quiché Department, Guatemala | 15,000 | Late Postclassic |
| Santa Rita Corozal Santa Rita Corozal Santa Rita Corozal is a Maya ruin and an archaeological reserve on the outskirts of Corozal, Belize. Historical evidence suggests that it was probably the ancient and important Maya city known as Chetumal.-Early history:... |
Corozal District Corozal District Corozal District is the northernmost district of the nation of Belize. The population was 33,335 as of 2000. The district capital is Corozal Town.-The Villages of Corozal District:... , Belize Belize Belize is a constitutional monarchy and the northernmost country in Central America. Belize has a diverse society, comprising many cultures and languages. Even though Kriol and Spanish are spoken among the population, Belize is the only country in Central America where English is the official... |
7,000 | Late Postclassic |
| Sayil Sayil Sayil is a Maya archaeological site in the Mexican state of Yucatán, in the southwest of the state, south of Uxmal. It was incorporated together with Uxmal as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1996.... |
Yucatán Yucatán Yucatán officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Yucatán is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 106 municipalities and its capital city is Mérida.... , Mexico |
10,000 | Terminal Classic |
| Seibal Seibal Seibal, known as El Ceibal in Spanish, is a Classic Period archaeological site of the Maya civilization located in the northern Petén Department of Guatemala. It was the largest city in the Pasión River region.... |
Petén Department, Guatemala | 10,000 | Late Preclassic |
| Tikal Tikal Tikal is one of the largest archaeological sites and urban centres of the pre-Columbian Maya civilization. It is located in the archaeological region of the Petén Basin in what is now northern Guatemala... |
Petén Department, Guatemala | 100,000 | Late Classic |
Conquest and rediscovery
The cities of the Postclassic highland Maya kingdoms fell to the invading Spanish conquistadorConquistador
Conquistadors were Spanish soldiers, explorers, and adventurers who brought much of the Americas under the control of Spain in the 15th to 16th centuries, following Europe's discovery of the New World by Christopher Columbus in 1492...
s in the first half of the 16th century. The K'iche' capital, Q'umarkaj, fell to Pedro de Alvarado
Pedro de Alvarado
Pedro de Alvarado y Contreras was a Spanish conquistador and governor of Guatemala. He participated in the conquest of Cuba, in Juan de Grijalva's exploration of the coasts of Yucatan and the Gulf of Mexico, and in the conquest of Mexico led by Hernan Cortes...
in 1524. Shortly afterwards, the Spanish were invited as allies into Iximche
Iximche
Iximche is a Pre-Columbian Mesoamerican archaeological site in the western highlands of Guatemala. Iximche was the capital of the Late Postclassic Kaqchikel Maya kingdom from 1470 until its abandonment in 1524. The architecture of the site included a number of pyramid-temples, palaces and two...
, the capital city of the Kaqchikel Maya. Good relations did not last and the city was abandoned a few months later. This was followed by the fall of Zaculeu
Zaculeu
Zaculeu or Saqulew is a pre-Columbian Maya archaeological site in the highlands of western Guatemala, about outside of the modern city of Huehuetenango. Occupation at the site dates back as far as the Early Classic period of Mesoamerican history...
, the Mam
Mam people
The Mam are a Native American people in the western highlands of Guatemala and in south-western Mexico.Most Mam live in Guatemala, in the departments of Huehuetenango, San Marcos, and Quetzaltenango...
Maya capital, in 1525.
By the 19th century, the existence of five former Maya cities was known in the Petén region of Guatemala
Guatemala
Guatemala is a country in Central America bordered by Mexico to the north and west, the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, Belize to the northeast, the Caribbean to the east, and Honduras and El Salvador to the southeast...
. Tayasal
Tayasal
Tayasal is a pre-Columbian Maya archaeological site that dates to the Postclassic period. The site is located in the southern Maya lowlands on a small island in Lake Petén Itzá, now part of the Department of Petén in northern Guatemala...
had been visited by Spanish conquistador Hernán Cortés
Hernán Cortés
Hernán Cortés de Monroy y Pizarro, 1st Marquis of the Valley of Oaxaca was a Spanish Conquistador who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire and brought large portions of mainland Mexico under the rule of the King of Castile in the early 16th century...
in 1524, followed by a number of missionaries at the beginning of the 17th century. The city was finally razed when it was conquered in 1697. Juan Galindo, governor of Petén, described the ruins of the Postclassic city of Topoxte
Topoxte
Topoxte is a pre-Columbian Maya archaeological site in the Petén Basin in northern Guatemala with a long occupational history dating as far back as the Middle Preclassic. As the capital of the Ko’woj Maya, it was the largest of the few Postclassic Mesoamerican sites in the area...
in 1834. Modesto Méndez, a later governor of Petén, published a description of the ruins of the once great city of Tikal in 1848. Teoberto Maler
Teoberto Maler
Teoberto Maler or Teobert Maler was an explorer who devoted his energies to documenting the ruins of the Maya civilization....
described the ruins of the city of Motul de San José
Motul de San José
Motul de San José is an ancient Maya site located just north of Lake Petén Itzá in the Petén Basin region of the southern Maya lowlands. It is located a few kilometres from the modern village of San José, in Guatemala's northern department of Petén...
in 1895. San Clemente was described by Karl Sapper
Karl Sapper
Karl Theodor Sapper was a German traveller, explorer, antiquarian and linguist, who is known for his research into the natural history, cultures and languages of Central America around the turn of the 20th century....
in the same year. The number of known cities grew enormously during the course of the 20th century, 24 cities in Petén alone had been described by 1938.
Until the 1960s, scholarly opinion was that the ruins of Maya centres were not true cities but were rather empty ceremonial centres where the priesthood performed religious rituals for the peasant farmers, who lived dispersed in the jungle. Since the 1960s, formal archaeological mapping projects have revealed that the ceremonial centres in fact formed the centres of dispersed cities that possessed populations that at some sites could reach tens of thousands.

