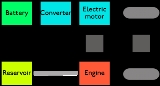
Hybrid vehicle drivetrain
Encyclopedia
Hybrid vehicle
s are vehicles with two or more power sources in the drivetrain
. There are many different types of hybrid vehicles, although only the gasoline-electric hybrid is currently commercially available.
Hybrids are classified by the division of power between sources; both sources may operate in parallel to simultaneously provide acceleration, or they may operate in series with one source exclusively providing the acceleration and the second being used to augment the first's power reserve. The sources can also be used in both series and parallel as needed, the vehicle being primarily driven by one source but the second capable of providing direct additional acceleration if required.
Current hybrids use both an internal combustion (IC) engine and a battery/electric drive system (using ultracapacitors) to improve fuel consumption, emission, and performance. Electrically assisted pedal bicycles are a form of hybrid drive. Other combinations of energy storage and conversion are possible, although not yet in commercial production.
Combustion-electric hybrids have larger battery sets than what a normal combustion engine only vehicle would have. Battery and supercapacitor
technology is advancing. A potential advantage is that when these battery sets require renewing in the future, the newer battery sets will be potentially superior having higher energy storage giving greater range enhancing a vehicle.
 Parallel hybrid systems, which are most commonly produced at present, have both an internal combustion engine
Parallel hybrid systems, which are most commonly produced at present, have both an internal combustion engine
(ICE) and an electric motor coupled. If they are joined at an axis in parallel, the speeds at this axis must be identical and the supplied torques add together. Most electric bicycles are of this type. When only one of the two sources is being used, the other must either also rotate in an idling manner, be connected by a one-way clutch, or freewheel. With cars, the two sources are usually connected through a differential gear. Thus the torques supplied must be the same and the speeds add up, the exact ratio depending on the differential characteristics. When only one of the two sources is being used, the other must still supply a large part of the torque or be fitted with a reverse one-way clutch or automatic clamp.
Parallel hybrids can be further categorized depending upon how balanced the different portions are at providing motive power. In some cases, the combustion engine is dominant (the electric motor turns on only when a boost is needed) and vice versa. Others can run with just the electric system operating. But because current parallel hybrids are unable to provide all-electric (ICE=OFF) propulsion, they are often categorized as mild hybrids (see below).
Because parallel hybrids can use a smaller battery pack as they rely more on regenerative braking and the internal combustion engine can also act as a generator for supplemental recharging, they are more efficient on highway driving compared to urban stop-and-go conditions or city driving. Honda
's Insight
, Civic
, and Accord hybrids are examples of production parallel hybrids. General Motors Parallel Hybrid Truck (PHT) and BAS Hybrids such as the Saturn VUE and Aura Greenline and Chevrolet Malibu hybrids are also considered as utilizing a parallel architecture.
 Series hybrids have also been referred to as range-extended electric vehicles (REEV) where they are designed to be run mostly by the battery, but have a petrol or diesel generator to recharge the battery when going on a long drive. However, range extension can be accomplished with either series or parallel hybrid layouts.
Series hybrids have also been referred to as range-extended electric vehicles (REEV) where they are designed to be run mostly by the battery, but have a petrol or diesel generator to recharge the battery when going on a long drive. However, range extension can be accomplished with either series or parallel hybrid layouts.
Series-hybrid vehicles are driven only by electric traction. Unlike piston internal combustion engines, electric motors are efficient with exceptionally high power-to-weight ratio
s providing adequate torque over a wide speed range. Unlike combustion engines electric motors matched to the vehicle do not require a transmission between the engine and wheels shifting torque ratios. Transmissions add weight, bulk and sap power from the engine. Mechanical automatic shifting transmissions can be very complex. In a series-hybrid system, the combustion engine drives an electric generator instead of directly driving the wheels. The generator provides power for the driving electric motors. In short, a series-hybrid is simple, the vehicle is driven by electric motors with a generator set providing the electric power.
This arrangement is common in diesel-electric
locomotive
s and ships. Ferdinand Porsche
used this setup in the early 20th century in racing cars, effectively inventing the series-hybrid arrangement. Porsche named the system, System Mixt. A wheel hub motor
arrangement, with a motor in each of the two front wheels was used, setting speed records. This arrangement was sometimes referred to as an electric transmission, as the electric generator and driving motor replaced a mechanical transmission. The vehicle could not move unless the internal combustion engine was running.
The setup was difficult for production cars being unable to synchronize the electric driving motors with the generator set power, resulting in higher fuel consumption. No longer an issue with modern computer engine management systems optimizing when the generator runs to match the power needed. Electric motors have become substantially smaller, lighter and efficient over the years. These advances have given the advantage to the electric transmission in normal operating conditions, over a conventional internal combustion engine and mechanical automatic transmission. One of the advantages is the smoother progressive ride with no stepped gear ratio changes.
The electric transmission is currently viable in replacing the mechanical transmission. However, the modern series-hybrid vehicles takes the electric transmission to a higher plane adding greater value. There is a difference to an electric transmission. Modern series-hybrids contain:
The electric driving motor may run entirely fed by electricity from a large battery bank or via the generator turned by the internal combustion engine, or both. The battery bank may be charged by mains electricity reducing running costs as the range running under the electric motors only is extended. The vehicle conceptually resembles a Diesel-electric
locomotive
with the addition of large battery bank that may power the vehicle without the internal combustion engine running. The generator may simultaneously charge the battery bank and power the driving electric motor that moves the vehicle. The battery bank acts as an energy buffer. An advantage is that when the vehicle is stopped the combustion engine is switched off. When the vehicle moves it does so using the energy in the batteries. This reduces kerbside emissions greatly in cities and towns. Vehicles at traffic lights, or in slow moving stop start traffic need not be polluting when stationary.
In some arrangements when high levels of power are required, such as in vehicle acceleration, the electric driving motor draws electricity from both the batteries and the generator. With the Chevrolet Volt
if the battery bank is depleted the vehicle may run entirely with electricity provided only from the generator. Some prototype vehicle designs such as the Volvo ReCharge
and Ford F-Series
pickup have electric motors in wheel hubs reducing the need for a differential saving weight, space and power being sapped by the differential. Series-hybrids can be also fitted with a supercapacitor
or a flywheel
to store regenerative braking energy, which can improve efficiency by clawing back energy that otherwise would be lost being dissipated via heat through the braking system.
Because a series-hybrid omits a mechanical link between the combustion engine and the wheels, the engine can be run at a constant and efficient rate even as the vehicle changes speed. The vehicle speed and engine speed are not necessarily in synchronization. The engine can thus maintain an efficiency closer to the theoretical limit of 37%, rather than the current average of 20%. At low or mixed speeds this could result in ~50% increase in overall efficiency (19% vs 29%). The Lotus company has introduced an engine/generator set design that runs at two speeds, giving 15 kW of electrical power at 1,500 rpm and 35 kW at 3,500 rpm via the integrated electrical generator.
As the requirements for the engine are not directly linked to vehicle speed, this gives greater scope for more efficient or alternative engine designs, such as a microturbine, rotary Atkinson cycle engine or a linear combustion engine.
General Motors in 1999 made the experimental EV1 series hybrid using a turbine generator set. The turbine weighed 220 lb (99.8 kg), measured 20 inches (50.8 cm) in diameter by 22 inches (55.9 cm) long and ran between 100,000 and 140,000 rpm. Fuel consumption was 60 miles per US gallon to 100 miles per US gallon in hybrid mode. Depending on the driving conditions, a highway range of more than 390 miles (627.6 km) was achieved. The results were highly successful, and would have promised to be more successful if a smaller microturbine was used, yet the EV1 project was dropped.
There are stages of operation: power from the combustion engine to the generator and then to the electric motor and, depending on the design, may also run through the generator and into the battery pack then to the electric motor further reducing efficiency (see illustration). Each transformation through each stage results in a loss of energy. However in normal vehicle operating conditions the energy buffer of the battery bank, which stores clawed back energy from braking and the optimum running of the combustion engine may raise overall operating efficiency, despite each stage being an energy loss. The engine to a mechanical automatic shifting transmission efficiency is approximately 70%-80%. A conventional mechanical clutch transmission, has an engine to transmission efficiency of 98%. In a series-hybrid vehicle, during long-distance high speed highway driving, the combustion engine will need to supply the majority of the energy, in which case a series-hybrid may be 20%-30% less efficient than a parallel hybrid.
The use of a motor driving a wheel directly
eliminates the conventional mechanical transmission elements: gearbox, transmission shafts and differential, and can sometimes eliminate flexible couplings
. This offers great simplicity. If the motors are integrated into the wheels a disadvantage is that the unsprung mass increases and suspension responsiveness decreases which impacts ride performance and potentially safety. However the impact should be minimal if at all as electric motors in wheel hubs such as Hi-Pa Drive
, may be very small and light having exceptionally high power-to-weight ratio
s. The braking mechanisms can be lighter as the wheel motors brake the vehicle. Light aluminum wheels may be used reducing the unsprung mass of the wheel assembly. Vehicle designs may be optimized to lower the center of gravity having the heavy mechanics and battery banks at floor level. If the motors are attached to the vehicle body, flexible couplings
are still required. Advantages of individual wheel motors include simplified traction control
and all wheel drive if required, allowing lower floors, which is useful for buses. Some 8x8 all-wheel drive military vehicles
use individual wheel motors. Diesel-electric
locomotive
s have used this concept (albeit with the individual motors driving axles connecting pairs of wheels) for 70 years.
In a typical road vehicle the whole series-hybrid power-transmission setup may be smaller and lighter than the equivalent conventional mechanical power-transmission setup which liberates space. As the combustion generator set only requires cables to the driving electric motors, there is greater flexibility in major component layout spread across the vehicle giving superior weight distribution and maximizing vehicle cabin space. This flexibility may lead to superior vehicle designs.
In 1997 Toyota released the first series-hybrid bus sold in Japan. Designline International of Ashburton, New Zealand produces city buses with a microturbine powered series-hybrid system. Supercapacitors combined with a lithium ion battery bank have been used by AFS Trinity
in a converted Saturn Vue SUV vehicle. Using supercapacitors they claim up to 150 mpg in a series-hybrid arrangement.
 Power-split hybrid or series-parallel hybrid are parallel hybrids. They incorporate power-split devices allowing for power paths from the engine to the wheels that can be either mechanical or electrical. The main principle behind this system is the decoupling of the power supplied by the engine (or other primary source) from the power demanded by the driver.
Power-split hybrid or series-parallel hybrid are parallel hybrids. They incorporate power-split devices allowing for power paths from the engine to the wheels that can be either mechanical or electrical. The main principle behind this system is the decoupling of the power supplied by the engine (or other primary source) from the power demanded by the driver.
A combustion engine's torque output is minimal at lower RPMs and, in a conventional vehicle, a larger engine is necessary for acceptable acceleration from standstill. The larger engine, however, has more power than needed for steady speed cruising. An electric motor, on the other hand, exhibits maximum torque at standstill and is well-suited to complement the engine's torque deficiency at low RPMs. In a power-split hybrid, a smaller, less flexible, and highly efficient engine can be used. The conventional Otto cycle
(higher power density, more low-rpm torque, lower fuel efficiency) is often also modified to a Miller cycle
or Atkinson cycle
(lower power density, less low-rpm torque, higher fuel efficiency). The smaller engine, using a more efficient cycle and often operating in the favorable region of the brake specific fuel consumption
map, contributes significantly to the higher overall efficiency of the vehicle.
Interesting variations of the simple design (pictured at right) found, for example, in the well-known Toyota Prius
are the:

The Toyota Hybrid System THS / Hybrid Synergy Drive
has a single power-split device (incorporated as a single 3 shaft planetary gearset) and can be classified as an Input-Split, since the power of the engine is split at the input to the transmission. This in turn makes this setup very simple in mechanical terms, but does have some drawbacks of its own. For example, the maximum speed is mainly limited by the speed of the smaller electric motor (usually functioning as a generator). Also, the efficiency of the transmission is heavily dependent on the amount of power being transmitted over the electrical path, as multiple conversions, each with their own, less than perfect efficiency, lead to a low efficiency of that path (~0.7) compared with the purely mechanical path (~0.98). Especially in higher speed regimes (>120 km/h or 70 mph) the efficiency (of the transmission alone) therefore drops below that of a generic automatic transmission with hydrodynamic coupler.
General Motors
, BMW
, and DaimlerChrysler
have developed in collaboration a system named "Two-Mode Hybrid" as part of the Global Hybrid Cooperation
. The technology was released in the fall of 2007 on the Chevrolet Tahoe Hybrid
. The system was also featured on the GMC Graphite SUV concept vehicle at the 2005 North American International Auto Show
in Detroit. BYD Auto
's F3DM
sedan is a series-parallel plug-in hybrid automobile, which went on sale in China on December 15, 2008.
The Two-Mode Hybrid name is intended to emphasize the drive-train's ability to operate in all-electric (Mode 1, or Input-Split) as well as hybrid (Mode 2, or Compound-Split) modes. The design, however, allows for operation in more than two modes; two power-split modes are available along with several fixed gear (essentially parallel hybrid) regimes. For this reason, the design can be referred to as a multi-regime design. The Two-Mode Hybrid powertrain design can be classified as a compound-split design, since the addition of four clutches within the transmission allows for multiple configurations of engine power-splitting. In addition to the clutches, this transmission also has a second planetary gearset. The objective of the design is to vary the percentage of mechanically vs. electrically transmitted power to cope both with low-speed and high-speed operating conditions. This enables smaller motors to do the job of larger motors when compared to single-mode systems, because the derived electrical peak power is proportional to the width of the continuous variation range. The four fixed gears enable the Two-Mode Hybrid to function like a conventional parallel hybrid under high continuous power regions such as sustained high speed cruising or trailer towing. Full electric boost is available in fixed gear modes.
 A full hybrid, sometimes also called a strong hybrid, is a vehicle that can run on just the engine, just the batteries, or a combination of both. The Toyota Prius
A full hybrid, sometimes also called a strong hybrid, is a vehicle that can run on just the engine, just the batteries, or a combination of both. The Toyota Prius
, Toyota Camry Hybrid, Ford Escape Hybrid/Mercury Mariner Hybrid, Ford Fusion Hybrid
/Mercury Milan Hybrid, Kia Optima Hybrid, as well as the General Motors 2-mode hybrid trucks and SUVs, are examples of this type of hybridization as they are able to be propelled on battery power alone. A large, high-capacity battery pack is needed for battery-only operation. These vehicles have a split power path that allows more flexibility in the drivetrain by inter-converting mechanical and electrical power, at some cost in complexity. To balance the forces from each portion, the vehicles use a differential-style linkage between the engine and motor connected to the head end of the transmission.
The Toyota brand name for this technology is Hybrid Synergy Drive, which is being used in the Prius, the Highlander Hybrid SUV
, and the Camry Hybrid. A computer oversees operation of the entire system, determining which half should be running, or if both should be in use. The operation of the Prius can be divided into six distinct regimes.
The hybrid drivetrain of the Prius, in combination with aerodynamics
and optimizations in the engine itself to reduce drag, results in 80%–100% gains in fuel economy
compared to four-door conventional cars of similar weight and size.
 Mild hybrids are essentially conventional vehicles with some degree of hybrid hardware, but with limited hybrid feature utilization. Typically they are a parallel system with start-stop only or possibly in combination with modest levels of engine assist or regenerative braking features. Unlike full hybrids, Mild hybrids generally cannot provide ICE-OFF all-electric (EV
Mild hybrids are essentially conventional vehicles with some degree of hybrid hardware, but with limited hybrid feature utilization. Typically they are a parallel system with start-stop only or possibly in combination with modest levels of engine assist or regenerative braking features. Unlike full hybrids, Mild hybrids generally cannot provide ICE-OFF all-electric (EV
) propulsion.
Mild hybrids like the General Motors 2004-07 Parallel Hybrid Truck (PHT) and the Honda
Eco-Assist hybrids are equipped with a 3-phase electric motor motor mounted within the bell-housing between the engine and transmission, allowing the engine to be turned off whenever the truck is coasting, braking, or stopped, yet restart quickly when required. Accessories can continue to run on electrical power while the engine is off, and as in other hybrid designs, the motor is used for regenerative braking to recapture energy. The large electric motor is used to spin up the engine to operating rpm speeds before injecting any fuel.
The 2004-07 Chevrolet Silverado
PHT, was a full-size pickup truck
. Chevrolet was able to get a 10% improvement on the Silverado's fuel efficiency by shutting down and restarting the engine on demand and using regenerative braking. However the electrical motor was not used to provide propulsion or assist, rather the electrical energy was used to drive accessories like the A/C and power steering.The GM PHT used a 42 volt systems
via a pack comprised three 12V vented lead acid batteries connected in series (36V total) to supply the power needed for the startup motor, as well as to compensate for the increasing number of electronic accessories on modern vehicles.
General Motors
followed the parallel hybrid truck with their BAS Hybrid system, another mild hybrid
implementation officially released on the 2007 Saturn Vue Green Line
. For its "start-stop" functionality, it operates similarly to the system in the Silverado, although via a belted connection to the motor/generator unit. However the GM BAS Hybridsystem has broader hybrid functionality as the electric motor can also provide modest assist under acceleration and during steady driving, and captures energy during regenerative (blended) braking. The BAS Hybrid can result in as much as a 27% improvement in combined fuel efficiency as noted by the EPA in testing of th 2009 Saturn VUE. The BAS Hybrid system can also be found on the 2008-09 Saturn Aura
and the 2008-2010 Chevrolet Malibu
hybrids.
Another way to provide for shutting off a car's engine when it is stopped, then immediately restarting it when it's time to go, is by employing a static start engine. Such an engine requires no starter motor, but employs sensors to determine the exact position of each piston, then precisely timing the injection and ignition of fuel to turn over the engine.
Mild hybrids are sometimes called Power assist hybrids as they use the engine for primary power, with a torque-boosting electric motor also connected to a largely conventional power train. The electric motor, mounted between the engine and transmission, is essentially a very large starter motor, which operates not only when the engine needs to be turned over, but also when the driver "steps on the gas" and requires extra power. The electric motor may also be used to re-start the combustion engine, deriving the same benefits from shutting down the main engine at idle, while the enhanced battery system is used to power accessories.GM is going to produce Buick LaCrosse
and [Buick Regal] mild hybrids dubbed Eassist.
Honda
's hybrids including the Insight
use this design, leveraging their reputation for design of small, efficient gasoline engines; their system is dubbed Integrated Motor Assist
(IMA). Assist hybrids differ fundamentally from full hybrids in that propulsion cannot be accomplished on electric power alone. However, since the amount of electrical power needed is much smaller, the size of the system is reduced.
A variation on this type of hybrid is the Saturn Vue Green Line BAS Hybrid system that uses a smaller electric motor (mounted to the side of the engine), and battery pack than the Honda IMA, but functions similarly.
Another variation on this type is Mazda
's e-4WD system, offered on the Mazda Demio
sold in Japan. This front-wheel drive
vehicle has an electric motor which can drive the rear wheels when extra traction
is needed. The system is entirely disengaged in all other driving conditions, so it does not directly enhance performance or economy but allows the use of a smaller and more economical engine relative to total performance.
Ford has dubbed Honda's hybrids "mild" in their advertising for the Escape Hybrid, arguing that the Escape's full hybrid design is more efficient.
A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle
(PHEV) has two defining characteristics: 1) it can be plugged in to an electrical outlet to be charged and (2) has some range that can be traveled on the energy it stored while plugged in. They are full hybrid, able to run in electric-only mode, with larger batteries and the ability to recharge from the electric power grid
. And can be parallel or series hybrid designs. They are also called gas-optional, or griddable hybrids. Their main benefit is that they can be gasoline-independent for daily commuting, but also have the extended range of a hybrid for long trips. They can also be multi-fuel, with the electric power supplemented by diesel, biodiesel
, or hydrogen
. The Electric Power Research Institute's research indicates a lower total cost of ownership for PHEVs due to reduced service costs and gradually improving batteries. The "well-to-wheel" efficiency and emissions of PHEVs compared to gasoline hybrids depends on the energy sources of the grid (the US grid is 50% coal
; California's grid is primarily natural gas
, hydroelectric power, and wind power
). Particular interest in PHEVs is in California where a "million solar homes" initiative is under way, and global warming legislation has been enacted.
Prototype
s of PHEVs, with larger battery packs that can be recharged from the power grid, have been built in the U.S., notably at Prof. Andy Frank
's Hybrid Center at University of California, Davis
and one production PHEV, the Renault Kangoo
, went on sale in France in 2003. DaimlerChrysler
is currently building PHEVs based on the Mercedes-Benz Sprinter
van
. Light Trucks are also offered by Micro-Vett SPA
the so called Daily Bimodale.
The California Cars Initiative has converted the '04 and newer Toyota Prius to become a prototype of what it calls the PRIUS+. With the addition of 300 lb (136.1 kg) of lead-acid batteries, the PRIUS+ achieves roughly double the gasoline mileage
of a standard Prius and can make trips of up to 10 mi (16.1 km) miles using only electric power.
Chinese battery manufacturer and automaker BYD Auto
released the F3DM
PHEV-62 (PHEV-100 km) compact sedan to the Chinese fleet market on December 15, 2008. General Motors
expects to launch the 2011 Chevrolet Volt
series plug-in (PHEV-40) by November 2010.
Most hybrids, no matter the specific type, use regenerative braking to recover energy when slowing down the vehicle. This simply involves driving a motor so it acts as a generator.
Many designs also shut off the internal combustion engine when it is not needed in order to save energy. That concept is not unique to hybrids; Subaru
pioneered this feature in the early 1980s, and the Volkswagen Lupo 3L
is one example of a conventional vehicle that shuts off its engine when at a stop. Some provision must be made, however, for accessories such as air conditioning
which are normally driven by the engine. Furthermore, the lubrication systems of internal combustion engines are inherently least effective immediately after the engine starts; since it is upon startup that the majority of engine wear occurs, the frequent starting and stopping of such systems reduce the lifespan of the engine considerably. Also, start and stop cycles may reduce the engine's ability to operate at its optimum temperature, thus reducing the engine's efficiency.

vehicles are often fitted with a battery or supercapacitor to deliver peak acceleration power and to reduce the size and power constraints on the fuel cell (and thus its cost); this is effectively also a series hybrid configuration.
vehicle uses hydraulic and mechanical components instead of electrical ones. A variable displacement pump
replaces the motor/generator, and a hydraulic accumulator
(which stores energy as highly compressed nitrogen gas) replaces the batteries. The hydraulic accumulator, which is essentially a pressure tank, is potentially cheaper and more durable than batteries. Hydraulic hybrid technology was originally developed by Volvo Flygmotor and was used experimentally in buses from the early 1980s and is still an active area.
Initial concept involved a giant flywheel
(see Gyrobus
) for storage connected to a hydrostatic transmission, but it was later changed to a simpler system using a hydraulic accumulator connected to a hydraulic pump/motor. It is also being actively developed by Eaton
and several other companies, primarily in heavy vehicles like buses, trucks and military vehicles. An example is the Ford F-350 Mighty Tonka concept truck shown in 2002. It features an Eaton system that can accelerate the truck up to highway speeds.
The energy recovery rate is higher and therefore the system is more efficient than battery charged hybrids, demonstrating a 60% to 70% increase in economy in EPA testing. Under tests done by the EPA, a hydraulic hybrid Ford Expedition returned 32 miles per US gallon in urban driving, and 22 miles per US gallon on the highway. UPS currently has two trucks in service with this technology. While the system has faster and more efficient charge/discharge cycling, the accumulator size and pressure dictates total energy capacity, and requires more space than a battery.
s, or a human-electric hybrid vehicle
such as the Twike
. Also some series hybrids exist, see in hybrid vehicle
. Such vehicles can be tribrid vehicles, combining at the same time three power sources e.g. from on-board solar cells, from grid-charged batteries, and from pedals.

powertrain to a vehicle to hybridise it
.
The conmarket solution is used when the user buys the glider
(rolling chasis) and the hybrid (two engines) or all-electric (only an electric motor) powertrain kit to the automaker
and receives it installed in the car. Also an (electric or hybrid) powertrain can be added to a glider by a third party aftermarket installer.
A University of Central Florida
senior design team, On the Green, is currently developing a bolt-on hybrid conversion kit to transform an older model vehicle into a gas-electric hybrid.
Hybrid vehicle
A hybrid vehicle is a vehicle that uses two or more distinct power sources to move the vehicle. The term most commonly refers to hybrid electric vehicles , which combine an internal combustion engine and one or more electric motors.-Power:...
s are vehicles with two or more power sources in the drivetrain
Powertrain
In a motor vehicle, the term powertrain or powerplant refers to the group of components that generate power and deliver it to the road surface, water, or air. This includes the engine, transmission, drive shafts, differentials, and the final drive...
. There are many different types of hybrid vehicles, although only the gasoline-electric hybrid is currently commercially available.
Hybrids are classified by the division of power between sources; both sources may operate in parallel to simultaneously provide acceleration, or they may operate in series with one source exclusively providing the acceleration and the second being used to augment the first's power reserve. The sources can also be used in both series and parallel as needed, the vehicle being primarily driven by one source but the second capable of providing direct additional acceleration if required.
Current hybrids use both an internal combustion (IC) engine and a battery/electric drive system (using ultracapacitors) to improve fuel consumption, emission, and performance. Electrically assisted pedal bicycles are a form of hybrid drive. Other combinations of energy storage and conversion are possible, although not yet in commercial production.
Combustion-electric hybrids have larger battery sets than what a normal combustion engine only vehicle would have. Battery and supercapacitor
Supercapacitor
An electric double-layer capacitor , also known as supercapacitor, supercondenser, electrochemical double layer capacitor, or ultracapacitor, is an electrochemical capacitor with relatively high energy density. Their energy density is typically hundreds of times greater than conventional...
technology is advancing. A potential advantage is that when these battery sets require renewing in the future, the newer battery sets will be potentially superior having higher energy storage giving greater range enhancing a vehicle.
Parallel hybrid

Internal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
(ICE) and an electric motor coupled. If they are joined at an axis in parallel, the speeds at this axis must be identical and the supplied torques add together. Most electric bicycles are of this type. When only one of the two sources is being used, the other must either also rotate in an idling manner, be connected by a one-way clutch, or freewheel. With cars, the two sources are usually connected through a differential gear. Thus the torques supplied must be the same and the speeds add up, the exact ratio depending on the differential characteristics. When only one of the two sources is being used, the other must still supply a large part of the torque or be fitted with a reverse one-way clutch or automatic clamp.
Parallel hybrids can be further categorized depending upon how balanced the different portions are at providing motive power. In some cases, the combustion engine is dominant (the electric motor turns on only when a boost is needed) and vice versa. Others can run with just the electric system operating. But because current parallel hybrids are unable to provide all-electric (ICE=OFF) propulsion, they are often categorized as mild hybrids (see below).
Because parallel hybrids can use a smaller battery pack as they rely more on regenerative braking and the internal combustion engine can also act as a generator for supplemental recharging, they are more efficient on highway driving compared to urban stop-and-go conditions or city driving. Honda
Honda
is a Japanese public multinational corporation primarily known as a manufacturer of automobiles and motorcycles.Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, as well as the world's largest manufacturer of internal combustion engines measured by volume, producing more than...
's Insight
Honda Insight
The Honda Insight is a hybrid electric vehicle manufactured by Honda and the first production vehicle to feature Honda's Integrated Motor Assist system. The first-generation Insight was produced from 1999 to 2006 as a three-door hatchback...
, Civic
Honda Civic Hybrid
The Civic hybrid, based on the seventh generation Civic, was first introduced to the Japanese market in December 2001. Honda claimed it was the most fuel efficient 5-passenger gasoline-powered production vehicle in the world at the time. It was introduced to the U.S. in spring 2002 as a 2003 model...
, and Accord hybrids are examples of production parallel hybrids. General Motors Parallel Hybrid Truck (PHT) and BAS Hybrids such as the Saturn VUE and Aura Greenline and Chevrolet Malibu hybrids are also considered as utilizing a parallel architecture.
Series hybrid

Series-hybrid vehicles are driven only by electric traction. Unlike piston internal combustion engines, electric motors are efficient with exceptionally high power-to-weight ratio
Power-to-weight ratio
Power-to-weight ratio is a calculation commonly applied to engines and mobile power sources to enable the comparison of one unit or design to another. Power-to-weight ratio is a measurement of actual performance of any engine or power sources...
s providing adequate torque over a wide speed range. Unlike combustion engines electric motors matched to the vehicle do not require a transmission between the engine and wheels shifting torque ratios. Transmissions add weight, bulk and sap power from the engine. Mechanical automatic shifting transmissions can be very complex. In a series-hybrid system, the combustion engine drives an electric generator instead of directly driving the wheels. The generator provides power for the driving electric motors. In short, a series-hybrid is simple, the vehicle is driven by electric motors with a generator set providing the electric power.
This arrangement is common in diesel-electric
Diesel-electric
Diesel-electric transmission or diesel-electric powertrain is used by a number of vehicle and ship types for providing locomotion.A diesel-electric transmission system includes a diesel engine connected to an electrical generator, creating electricity that powers electric traction motors...
locomotive
Locomotive
A locomotive is a railway vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. The word originates from the Latin loco – "from a place", ablative of locus, "place" + Medieval Latin motivus, "causing motion", and is a shortened form of the term locomotive engine, first used in the early 19th...
s and ships. Ferdinand Porsche
Ferdinand Porsche
Ferdinand Porsche was an Austrian automotive engineer and honorary Doctor of Engineering. He is best known for creating the first hybrid vehicle , the Volkswagen Beetle, and the Mercedes-Benz SS/SSK, as well as the first of many Porsche automobiles...
used this setup in the early 20th century in racing cars, effectively inventing the series-hybrid arrangement. Porsche named the system, System Mixt. A wheel hub motor
Wheel hub motor
The wheel hub motor is an electric motor that is incorporated into a hub of a wheel and drives it directly.-Uses in current and future vehicles:...
arrangement, with a motor in each of the two front wheels was used, setting speed records. This arrangement was sometimes referred to as an electric transmission, as the electric generator and driving motor replaced a mechanical transmission. The vehicle could not move unless the internal combustion engine was running.
The setup was difficult for production cars being unable to synchronize the electric driving motors with the generator set power, resulting in higher fuel consumption. No longer an issue with modern computer engine management systems optimizing when the generator runs to match the power needed. Electric motors have become substantially smaller, lighter and efficient over the years. These advances have given the advantage to the electric transmission in normal operating conditions, over a conventional internal combustion engine and mechanical automatic transmission. One of the advantages is the smoother progressive ride with no stepped gear ratio changes.
The electric transmission is currently viable in replacing the mechanical transmission. However, the modern series-hybrid vehicles takes the electric transmission to a higher plane adding greater value. There is a difference to an electric transmission. Modern series-hybrids contain:
- Electric traction only - using only one or more electric motors to turn the wheels.
- Combustion engine - that turns only a generator.
- A generator - turned by the combustion engine to make up a generator set that also acts as an engine starter.
- A battery bank - which acts as an energy buffer.
- Regenerative braking - Driving motor becomes a generator and recovers potential and kinetic (inertial) energies through its conversion to electrical energy, a process which in turn is able to slow the vehicle and thus preventing wasteful transfer of this energy as thermal losses within the friction brakes.
- May be plugged into the electric mains system to recharge the battery bank.
- May have supercapacitors to assist the battery bank and claw back most energy from braking - only fitted in proven prototypes currently.
The electric driving motor may run entirely fed by electricity from a large battery bank or via the generator turned by the internal combustion engine, or both. The battery bank may be charged by mains electricity reducing running costs as the range running under the electric motors only is extended. The vehicle conceptually resembles a Diesel-electric
Diesel-electric
Diesel-electric transmission or diesel-electric powertrain is used by a number of vehicle and ship types for providing locomotion.A diesel-electric transmission system includes a diesel engine connected to an electrical generator, creating electricity that powers electric traction motors...
locomotive
Locomotive
A locomotive is a railway vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. The word originates from the Latin loco – "from a place", ablative of locus, "place" + Medieval Latin motivus, "causing motion", and is a shortened form of the term locomotive engine, first used in the early 19th...
with the addition of large battery bank that may power the vehicle without the internal combustion engine running. The generator may simultaneously charge the battery bank and power the driving electric motor that moves the vehicle. The battery bank acts as an energy buffer. An advantage is that when the vehicle is stopped the combustion engine is switched off. When the vehicle moves it does so using the energy in the batteries. This reduces kerbside emissions greatly in cities and towns. Vehicles at traffic lights, or in slow moving stop start traffic need not be polluting when stationary.
In some arrangements when high levels of power are required, such as in vehicle acceleration, the electric driving motor draws electricity from both the batteries and the generator. With the Chevrolet Volt
Chevrolet Volt
The Chevrolet Volt is a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle manufactured by General Motors. The Volt has been on sale in the U.S. market since mid-December 2010, and is the most fuel-efficient compact car sold in the United States, as rated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency...
if the battery bank is depleted the vehicle may run entirely with electricity provided only from the generator. Some prototype vehicle designs such as the Volvo ReCharge
Volvo ReCharge
The Volvo ReCharge is a plug-in hybrid concept car created by Volvo. The vehicle is designed to run purely on electricity from on-board batteries for up to —which is a large enough distance to cover the daily commutes of most Americans, which is around...
and Ford F-Series
Ford F-Series
The F-Series is a series of full-size pickup trucks from Ford Motor Company which has been sold continuously for over six decades. The most popular variant of the F-Series is the F-150...
pickup have electric motors in wheel hubs reducing the need for a differential saving weight, space and power being sapped by the differential. Series-hybrids can be also fitted with a supercapacitor
Supercapacitor
An electric double-layer capacitor , also known as supercapacitor, supercondenser, electrochemical double layer capacitor, or ultracapacitor, is an electrochemical capacitor with relatively high energy density. Their energy density is typically hundreds of times greater than conventional...
or a flywheel
Flywheel
A flywheel is a rotating mechanical device that is used to store rotational energy. Flywheels have a significant moment of inertia, and thus resist changes in rotational speed. The amount of energy stored in a flywheel is proportional to the square of its rotational speed...
to store regenerative braking energy, which can improve efficiency by clawing back energy that otherwise would be lost being dissipated via heat through the braking system.
Because a series-hybrid omits a mechanical link between the combustion engine and the wheels, the engine can be run at a constant and efficient rate even as the vehicle changes speed. The vehicle speed and engine speed are not necessarily in synchronization. The engine can thus maintain an efficiency closer to the theoretical limit of 37%, rather than the current average of 20%. At low or mixed speeds this could result in ~50% increase in overall efficiency (19% vs 29%). The Lotus company has introduced an engine/generator set design that runs at two speeds, giving 15 kW of electrical power at 1,500 rpm and 35 kW at 3,500 rpm via the integrated electrical generator.
As the requirements for the engine are not directly linked to vehicle speed, this gives greater scope for more efficient or alternative engine designs, such as a microturbine, rotary Atkinson cycle engine or a linear combustion engine.
General Motors in 1999 made the experimental EV1 series hybrid using a turbine generator set. The turbine weighed 220 lb (99.8 kg), measured 20 inches (50.8 cm) in diameter by 22 inches (55.9 cm) long and ran between 100,000 and 140,000 rpm. Fuel consumption was 60 miles per US gallon to 100 miles per US gallon in hybrid mode. Depending on the driving conditions, a highway range of more than 390 miles (627.6 km) was achieved. The results were highly successful, and would have promised to be more successful if a smaller microturbine was used, yet the EV1 project was dropped.
There are stages of operation: power from the combustion engine to the generator and then to the electric motor and, depending on the design, may also run through the generator and into the battery pack then to the electric motor further reducing efficiency (see illustration). Each transformation through each stage results in a loss of energy. However in normal vehicle operating conditions the energy buffer of the battery bank, which stores clawed back energy from braking and the optimum running of the combustion engine may raise overall operating efficiency, despite each stage being an energy loss. The engine to a mechanical automatic shifting transmission efficiency is approximately 70%-80%. A conventional mechanical clutch transmission, has an engine to transmission efficiency of 98%. In a series-hybrid vehicle, during long-distance high speed highway driving, the combustion engine will need to supply the majority of the energy, in which case a series-hybrid may be 20%-30% less efficient than a parallel hybrid.
The use of a motor driving a wheel directly
Wheel hub motor
The wheel hub motor is an electric motor that is incorporated into a hub of a wheel and drives it directly.-Uses in current and future vehicles:...
eliminates the conventional mechanical transmission elements: gearbox, transmission shafts and differential, and can sometimes eliminate flexible couplings
Constant-velocity joint
Constant-velocity joints allow a drive shaft to transmit power through a variable angle, at constant rotational speed, without an appreciable increase in friction or play. They are mainly used in front wheel drive and all wheel drive cars...
. This offers great simplicity. If the motors are integrated into the wheels a disadvantage is that the unsprung mass increases and suspension responsiveness decreases which impacts ride performance and potentially safety. However the impact should be minimal if at all as electric motors in wheel hubs such as Hi-Pa Drive
Hi-Pa Drive
The Hi-Pa Drive system is an electric in-wheel motor power delivery system.-Demonstration vehicles:In 2006, PML Flightlink demonstrated the Hi-Pa Drive in a series-hybrid car at the British Motor Show in London, using a Mini dubbed the "Mini QED" with its in-wheel motor at all four wheels...
, may be very small and light having exceptionally high power-to-weight ratio
Power-to-weight ratio
Power-to-weight ratio is a calculation commonly applied to engines and mobile power sources to enable the comparison of one unit or design to another. Power-to-weight ratio is a measurement of actual performance of any engine or power sources...
s. The braking mechanisms can be lighter as the wheel motors brake the vehicle. Light aluminum wheels may be used reducing the unsprung mass of the wheel assembly. Vehicle designs may be optimized to lower the center of gravity having the heavy mechanics and battery banks at floor level. If the motors are attached to the vehicle body, flexible couplings
Constant-velocity joint
Constant-velocity joints allow a drive shaft to transmit power through a variable angle, at constant rotational speed, without an appreciable increase in friction or play. They are mainly used in front wheel drive and all wheel drive cars...
are still required. Advantages of individual wheel motors include simplified traction control
Traction control system
A traction control system , also known as anti-slip regulation , is typically a secondary function of the anti-lock braking system on production motor vehicles, designed to prevent loss of traction of driven road wheels...
and all wheel drive if required, allowing lower floors, which is useful for buses. Some 8x8 all-wheel drive military vehicles
Heavy Expanded Mobility Tactical Truck
The Heavy Expanded Mobility Tactical Truck series is a range of eight-wheel drive diesel-powered off-road capable trucks, used by the US military. Formally described as "Truck, Cargo: 10-Ton, 8x8", it has been nicknamed the "Dragon Wagon". HEMTT trucks first went into service with the U.S...
use individual wheel motors. Diesel-electric
Diesel-electric
Diesel-electric transmission or diesel-electric powertrain is used by a number of vehicle and ship types for providing locomotion.A diesel-electric transmission system includes a diesel engine connected to an electrical generator, creating electricity that powers electric traction motors...
locomotive
Locomotive
A locomotive is a railway vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. The word originates from the Latin loco – "from a place", ablative of locus, "place" + Medieval Latin motivus, "causing motion", and is a shortened form of the term locomotive engine, first used in the early 19th...
s have used this concept (albeit with the individual motors driving axles connecting pairs of wheels) for 70 years.
In a typical road vehicle the whole series-hybrid power-transmission setup may be smaller and lighter than the equivalent conventional mechanical power-transmission setup which liberates space. As the combustion generator set only requires cables to the driving electric motors, there is greater flexibility in major component layout spread across the vehicle giving superior weight distribution and maximizing vehicle cabin space. This flexibility may lead to superior vehicle designs.
In 1997 Toyota released the first series-hybrid bus sold in Japan. Designline International of Ashburton, New Zealand produces city buses with a microturbine powered series-hybrid system. Supercapacitors combined with a lithium ion battery bank have been used by AFS Trinity
AFS Trinity
AFS Trinity Power Corporation is an American corporation headquartered in Medina, WA with an engineering center in Livermore, CA that develops technology for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. The company has developed PHEV technology that actively combines batteries with ultracapacitors...
in a converted Saturn Vue SUV vehicle. Using supercapacitors they claim up to 150 mpg in a series-hybrid arrangement.
Power-split or series-parallel hybrid

A combustion engine's torque output is minimal at lower RPMs and, in a conventional vehicle, a larger engine is necessary for acceptable acceleration from standstill. The larger engine, however, has more power than needed for steady speed cruising. An electric motor, on the other hand, exhibits maximum torque at standstill and is well-suited to complement the engine's torque deficiency at low RPMs. In a power-split hybrid, a smaller, less flexible, and highly efficient engine can be used. The conventional Otto cycle
Otto cycle
An Otto cycle is an idealized thermodynamic cycle which describes the functioning of a typical reciprocating piston engine, the thermodynamic cycle most commonly found in automobile engines....
(higher power density, more low-rpm torque, lower fuel efficiency) is often also modified to a Miller cycle
Miller cycle
In engineering, the Miller cycle is a combustion process used in a type of four-stroke internal combustion engine. The Miller cycle was patented by Ralph Miller, an American engineer, in the 1940s.- Overview :...
or Atkinson cycle
Atkinson cycle
The Atkinson cycle engine is a type of internal combustion engine invented by James Atkinson in 1882. The Atkinson cycle is designed to provide efficiency at the expense of power density, and is used in some modern hybrid electric applications.-Design:...
(lower power density, less low-rpm torque, higher fuel efficiency). The smaller engine, using a more efficient cycle and often operating in the favorable region of the brake specific fuel consumption
Brake specific fuel consumption
Brake Specific Fuel Consumption is a measure of fuel efficiency within a shaft reciprocating engine.It is the rate of fuel consumption divided by the power produced. It may also be thought of as power-specific fuel consumption, for this reason...
map, contributes significantly to the higher overall efficiency of the vehicle.
Interesting variations of the simple design (pictured at right) found, for example, in the well-known Toyota Prius
Toyota Prius
The Toyota Prius is a full hybrid electric mid-size hatchback, formerly a compact sedan developed and manufactured by the Toyota Motor Corporation...
are the:
- addition of a fixed gear second planetary gearset as used in the Lexus RX400h and Toyota Highlander Hybrid. This allows for a motor with less torque but higher power (and higher maximum rotary speed), i.e. higher power density
- addition of a Ravigneaux-type planetary gear (planetary gear with 4 shafts instead of 3) and two clutches as used in the Lexus GS450h. By switching the clutches, the gear ratio from MG2 (the "drive" motor) to the wheel shaft is switched, either for higher torque or higher speed (up to 250 km/h / 155 mph) while sustaining better transmission efficiency.

- addition of 2 additional planetary gear sets in combination with 4 clutches to create a Two-Mode Hybrid configuration able to operate in all-electric, blended electric and ICE, or ICE alone with 4 fixed gears. Examples of Two-Mode Hybrids include the General MotorsGeneral MotorsGeneral Motors Company , commonly known as GM, formerly incorporated as General Motors Corporation, is an American multinational automotive corporation headquartered in Detroit, Michigan and the world's second-largest automaker in 2010...
Two-Mode Hybrid full-size trucks and SUVs, the BMW X6 ActiveHybridBMW X6The BMW X6 is a mid-size luxury crossover released for sale in the second quarter of 2008 by German automaker BMW. The X6 was marketed as a Sports Activity Coupé by BMW...
and the Mercedes ML 450 hybrid
The Toyota Hybrid System THS / Hybrid Synergy Drive
Hybrid Synergy Drive
Hybrid Synergy Drive is a set of hybrid car technologies developed by Toyota and used in the company's Auris, Prius, Highlander Hybrid, Camry Hybrid, Estima, Alphard, Lexus CT, Lexus RX 400h/RX 450h, Lexus GS 450h, Lexus LS 600h/LS 600hL, and Lexus HS 250h automobiles. Toyota also licenses its HSD...
has a single power-split device (incorporated as a single 3 shaft planetary gearset) and can be classified as an Input-Split, since the power of the engine is split at the input to the transmission. This in turn makes this setup very simple in mechanical terms, but does have some drawbacks of its own. For example, the maximum speed is mainly limited by the speed of the smaller electric motor (usually functioning as a generator). Also, the efficiency of the transmission is heavily dependent on the amount of power being transmitted over the electrical path, as multiple conversions, each with their own, less than perfect efficiency, lead to a low efficiency of that path (~0.7) compared with the purely mechanical path (~0.98). Especially in higher speed regimes (>120 km/h or 70 mph) the efficiency (of the transmission alone) therefore drops below that of a generic automatic transmission with hydrodynamic coupler.
General Motors
General Motors
General Motors Company , commonly known as GM, formerly incorporated as General Motors Corporation, is an American multinational automotive corporation headquartered in Detroit, Michigan and the world's second-largest automaker in 2010...
, BMW
BMW
Bayerische Motoren Werke AG is a German automobile, motorcycle and engine manufacturing company founded in 1916. It also owns and produces the Mini marque, and is the parent company of Rolls-Royce Motor Cars. BMW produces motorcycles under BMW Motorrad and Husqvarna brands...
, and DaimlerChrysler
DaimlerChrysler
Daimler AG is a German car corporation. By unit sales, it is the thirteenth-largest car manufacturer and second-largest truck manufacturer in the world. In addition to automobiles, Daimler manufactures buses and provides financial services through its Daimler Financial Services arm...
have developed in collaboration a system named "Two-Mode Hybrid" as part of the Global Hybrid Cooperation
Global Hybrid Cooperation
Global Hybrid Cooperation is a set of hybrid vehicle technologies jointly developed by General Motors, Daimler, and Chrysler LLC, with BMW joining in 2005...
. The technology was released in the fall of 2007 on the Chevrolet Tahoe Hybrid
Chevrolet Tahoe
The Chevrolet Tahoe are full-size SUVs from General Motors. Chevrolet and GMC sold two different-sized SUVs under their Blazer/Jimmy model names through the early 1990s. This situation changed when GMC rebadged the full-size Jimmy as the Yukon in 1992...
. The system was also featured on the GMC Graphite SUV concept vehicle at the 2005 North American International Auto Show
North American International Auto Show
The North American International Auto Show is an annual auto show held in Detroit, Michigan at Cobo Center, usually in January. It is among the largest auto shows in North America.-History:...
in Detroit. BYD Auto
BYD Auto
BYD Automobile Co Ltd is a Chinese automobile manufacturer based in Shenzhen, Guangdong Province...
's F3DM
BYD F3DM
The BYD F3DM is a plug-in hybrid compact sedan manufactured by BYD Auto with an all-electric range of and a hybrid electric powertrain that can extend the range an additional . The F3DM is the world's first mass produced plug-in hybrid automobile and went on sale to government agencies and...
sedan is a series-parallel plug-in hybrid automobile, which went on sale in China on December 15, 2008.
The Two-Mode Hybrid name is intended to emphasize the drive-train's ability to operate in all-electric (Mode 1, or Input-Split) as well as hybrid (Mode 2, or Compound-Split) modes. The design, however, allows for operation in more than two modes; two power-split modes are available along with several fixed gear (essentially parallel hybrid) regimes. For this reason, the design can be referred to as a multi-regime design. The Two-Mode Hybrid powertrain design can be classified as a compound-split design, since the addition of four clutches within the transmission allows for multiple configurations of engine power-splitting. In addition to the clutches, this transmission also has a second planetary gearset. The objective of the design is to vary the percentage of mechanically vs. electrically transmitted power to cope both with low-speed and high-speed operating conditions. This enables smaller motors to do the job of larger motors when compared to single-mode systems, because the derived electrical peak power is proportional to the width of the continuous variation range. The four fixed gears enable the Two-Mode Hybrid to function like a conventional parallel hybrid under high continuous power regions such as sustained high speed cruising or trailer towing. Full electric boost is available in fixed gear modes.
Full Hybrids

Toyota Prius
The Toyota Prius is a full hybrid electric mid-size hatchback, formerly a compact sedan developed and manufactured by the Toyota Motor Corporation...
, Toyota Camry Hybrid, Ford Escape Hybrid/Mercury Mariner Hybrid, Ford Fusion Hybrid
Ford Fusion Hybrid
The Ford Fusion Hybrid is a gasoline-electric hybrid powered version of the mid-size Ford Fusion sedan developed by the Ford Motor Company, and launched to the U.S. market in March 2009 as a 2010 model, together with its twin the Mercury Milan Hybrid. The Fusion Hybrid is manufactured at Ford's...
/Mercury Milan Hybrid, Kia Optima Hybrid, as well as the General Motors 2-mode hybrid trucks and SUVs, are examples of this type of hybridization as they are able to be propelled on battery power alone. A large, high-capacity battery pack is needed for battery-only operation. These vehicles have a split power path that allows more flexibility in the drivetrain by inter-converting mechanical and electrical power, at some cost in complexity. To balance the forces from each portion, the vehicles use a differential-style linkage between the engine and motor connected to the head end of the transmission.
The Toyota brand name for this technology is Hybrid Synergy Drive, which is being used in the Prius, the Highlander Hybrid SUV
Sport utility vehicle
A sport utility vehicle is a generic marketing term for a vehicle similar to a station wagon, but built on a light-truck chassis. It is usually equipped with four-wheel drive for on- or off-road ability, and with some pretension or ability to be used as an off-road vehicle. Not all four-wheel...
, and the Camry Hybrid. A computer oversees operation of the entire system, determining which half should be running, or if both should be in use. The operation of the Prius can be divided into six distinct regimes.
- Electric vehicle mode: The engine is off, and the battery provides electrical energy to power the motor (or the reverse when regenerative braking is engaged). Used for idling as well when the battery State Of ChargeState of chargeState of charge is the equivalent of a fuel gauge for the battery pack in a battery electric vehicle , hybrid vehicle , or plug-in hybrid electric vehicle...
(SOC) is high.
- Cruise mode: The vehicle is cruising (i.e. not accelerating), and the engine can meet the road load demand. The power from the engine is split between the mechanical path and the generator. The battery provides electrical energy to power the motor, whose power is summed mechanically with the engine. If the battery state-of-charge is low, part of the power from the generator is directed towards charging the battery.
- Overdrive mode: A portion of the rotational energy is siphoned off by the main electric motor, operating as a generator, to produce electricity. This electrical energy is used to drive the sun gear in the direction opposite its usual rotation. The end result has the ring gear rotating faster than the engine, albeit at lower torque.
- Battery charge mode: Also used for idling, except that in this case the battery state-of-charge is low and requires charging, which is provided by the engine and generator.
- Power boost mode: Employed in situations where the engine cannot meet the road load demand. The battery is then used to power the motor to provide a boost to the engine power.
- Negative split mode: The vehicle is cruising and the battery state-of-charge is high. The battery provides power to both the motor (to provide mechanical power) and to the generator. The generator converts this to mechanical energy that it directs towards the engine shaft, slowing it down (although not altering its torque output). The purpose of this engine "lugging" is to increase the fuel economy of the vehicle.
The hybrid drivetrain of the Prius, in combination with aerodynamics
Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics is a branch of dynamics concerned with studying the motion of air, particularly when it interacts with a moving object. Aerodynamics is a subfield of fluid dynamics and gas dynamics, with much theory shared between them. Aerodynamics is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, with...
and optimizations in the engine itself to reduce drag, results in 80%–100% gains in fuel economy
Fuel economy in automobiles
Fuel usage in automobiles refers to the fuel efficiency relationship between distance traveled by an automobile and the amount of fuel consumed....
compared to four-door conventional cars of similar weight and size.
Mild Hybrids

EV
EV, eV, e. V. may refer to:* Electronvolt, a unit of energy* Eingetragener Verein, a registered voluntary association in Germany* Estonia's official name, Republic of Estonia, in Estonian: Eesti Vabariik*Everett Railroad's reporting mark...
) propulsion.
Mild hybrids like the General Motors 2004-07 Parallel Hybrid Truck (PHT) and the Honda
Honda
is a Japanese public multinational corporation primarily known as a manufacturer of automobiles and motorcycles.Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, as well as the world's largest manufacturer of internal combustion engines measured by volume, producing more than...
Eco-Assist hybrids are equipped with a 3-phase electric motor motor mounted within the bell-housing between the engine and transmission, allowing the engine to be turned off whenever the truck is coasting, braking, or stopped, yet restart quickly when required. Accessories can continue to run on electrical power while the engine is off, and as in other hybrid designs, the motor is used for regenerative braking to recapture energy. The large electric motor is used to spin up the engine to operating rpm speeds before injecting any fuel.
The 2004-07 Chevrolet Silverado
Chevrolet Silverado
The Chevrolet Silverado , is the latest line of full-size pickup trucks from General Motors.-History:...
PHT, was a full-size pickup truck
Pickup truck
A pickup truck is a light motor vehicle with an open-top rear cargo area .-Definition:...
. Chevrolet was able to get a 10% improvement on the Silverado's fuel efficiency by shutting down and restarting the engine on demand and using regenerative braking. However the electrical motor was not used to provide propulsion or assist, rather the electrical energy was used to drive accessories like the A/C and power steering.The GM PHT used a 42 volt systems
42-volt electrical system
In automobiles, a 42-volt electrical system was a proposed electrical power standard in the late 1990s intended to allow more powerful electrically driven accessories, and lighter automobile wiring harnesses...
via a pack comprised three 12V vented lead acid batteries connected in series (36V total) to supply the power needed for the startup motor, as well as to compensate for the increasing number of electronic accessories on modern vehicles.
General Motors
General Motors
General Motors Company , commonly known as GM, formerly incorporated as General Motors Corporation, is an American multinational automotive corporation headquartered in Detroit, Michigan and the world's second-largest automaker in 2010...
followed the parallel hybrid truck with their BAS Hybrid system, another mild hybrid
Mild Hybrid
Mild hybrids are essentially conventional fossil-fuel vehicles equipped with a large electric machine allowing the engine to be turned off whenever the car is coasting, braking, or stopped, yet restart quickly...
implementation officially released on the 2007 Saturn Vue Green Line
Saturn VUE
The Saturn Vue is a compact crossover SUV that was sold by General Motors' Saturn marque, and at one time was Saturn's best-selling model. It was the first vehicle to use the GM Theta platform when it was introduced in 2002. A second generation model was launched in 2007 for the 2008 model as a...
. For its "start-stop" functionality, it operates similarly to the system in the Silverado, although via a belted connection to the motor/generator unit. However the GM BAS Hybridsystem has broader hybrid functionality as the electric motor can also provide modest assist under acceleration and during steady driving, and captures energy during regenerative (blended) braking. The BAS Hybrid can result in as much as a 27% improvement in combined fuel efficiency as noted by the EPA in testing of th 2009 Saturn VUE. The BAS Hybrid system can also be found on the 2008-09 Saturn Aura
Saturn Aura
The Saturn Aura is a mid-size car produced under the Saturn brand of American automaker General Motors. It debuted as a concept car at the North American International Auto Show in January 2005. The production model of the Aura was shown at the 2006 New York Auto Show in April, with production...
and the 2008-2010 Chevrolet Malibu
Chevrolet Malibu
Malibus and all other Chevelles were completely restyled for 1968 with semi-fastback rooflines on two-door hardtops and wheelbases split to on two-door models and 118 for four-door sedans and station wagons. Engine offerings included a new V8 rated at that replaced the V8 that had served as the...
hybrids.
Another way to provide for shutting off a car's engine when it is stopped, then immediately restarting it when it's time to go, is by employing a static start engine. Such an engine requires no starter motor, but employs sensors to determine the exact position of each piston, then precisely timing the injection and ignition of fuel to turn over the engine.
Mild hybrids are sometimes called Power assist hybrids as they use the engine for primary power, with a torque-boosting electric motor also connected to a largely conventional power train. The electric motor, mounted between the engine and transmission, is essentially a very large starter motor, which operates not only when the engine needs to be turned over, but also when the driver "steps on the gas" and requires extra power. The electric motor may also be used to re-start the combustion engine, deriving the same benefits from shutting down the main engine at idle, while the enhanced battery system is used to power accessories.GM is going to produce Buick LaCrosse
Buick LaCrosse
The Buick LaCrosse is a mid-size entry-level luxury sedan produced by General Motors. It replaced the Buick Century and Regal in North America beginning in the 2005 model year.-North America:...
and [Buick Regal] mild hybrids dubbed Eassist.
Honda
Honda
is a Japanese public multinational corporation primarily known as a manufacturer of automobiles and motorcycles.Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, as well as the world's largest manufacturer of internal combustion engines measured by volume, producing more than...
's hybrids including the Insight
Honda Insight
The Honda Insight is a hybrid electric vehicle manufactured by Honda and the first production vehicle to feature Honda's Integrated Motor Assist system. The first-generation Insight was produced from 1999 to 2006 as a three-door hatchback...
use this design, leveraging their reputation for design of small, efficient gasoline engines; their system is dubbed Integrated Motor Assist
Integrated Motor Assist
Integrated Motor Assist is Honda's hybrid car technology, introduced in 1999 on the Insight.It is a specific implementation of a parallel hybrid. It uses an electric motor mounted between the internal combustion engine and transmission to act as a starter motor, engine balancer, and assist...
(IMA). Assist hybrids differ fundamentally from full hybrids in that propulsion cannot be accomplished on electric power alone. However, since the amount of electrical power needed is much smaller, the size of the system is reduced.
A variation on this type of hybrid is the Saturn Vue Green Line BAS Hybrid system that uses a smaller electric motor (mounted to the side of the engine), and battery pack than the Honda IMA, but functions similarly.
Another variation on this type is Mazda
Mazda
is a Japanese automotive manufacturer based in Fuchū, Aki District, Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan.In 2007, Mazda produced almost 1.3 million vehicles for global sales...
's e-4WD system, offered on the Mazda Demio
Mazda Demio
The Mazda Demio is a subcompact car manufactured by Mazda introduced in 1996, now in its third generation, marketed globally also as the Mazda2 — and previously marketed under nameplates including Mazda 121, Mazda Metro and Ford Festiva Mini Wagon.The third generation Demio earned the 2008...
sold in Japan. This front-wheel drive
Front-wheel drive
Front-wheel drive is a form of engine/transmission layout used in motor vehicles, where the engine drives the front wheels only. Most modern front-wheel drive vehicles feature a transverse engine, rather than the conventional longitudinal engine arrangement generally found in rear-wheel drive and...
vehicle has an electric motor which can drive the rear wheels when extra traction
Traction (engineering)
Traction refers to the maximum frictional force that can be produced between surfaces without slipping.The units of traction are those of force, or if expressed as a coefficient of traction a ratio.-Traction:...
is needed. The system is entirely disengaged in all other driving conditions, so it does not directly enhance performance or economy but allows the use of a smaller and more economical engine relative to total performance.
Ford has dubbed Honda's hybrids "mild" in their advertising for the Escape Hybrid, arguing that the Escape's full hybrid design is more efficient.
Plug-in hybrid

A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicle
A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle , plug-in hybrid vehicle , or plug-in hybrid is a hybrid vehicle which utilizes rechargeable batteries, or another energy storage device, that can be restored to full charge by connecting a plug to an external electric power source...
(PHEV) has two defining characteristics: 1) it can be plugged in to an electrical outlet to be charged and (2) has some range that can be traveled on the energy it stored while plugged in. They are full hybrid, able to run in electric-only mode, with larger batteries and the ability to recharge from the electric power grid
Electric power transmission
Electric-power transmission is the bulk transfer of electrical energy, from generating power plants to Electrical substations located near demand centers...
. And can be parallel or series hybrid designs. They are also called gas-optional, or griddable hybrids. Their main benefit is that they can be gasoline-independent for daily commuting, but also have the extended range of a hybrid for long trips. They can also be multi-fuel, with the electric power supplemented by diesel, biodiesel
Biodiesel
Biodiesel refers to a vegetable oil- or animal fat-based diesel fuel consisting of long-chain alkyl esters. Biodiesel is typically made by chemically reacting lipids with an alcohol....
, or hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
. The Electric Power Research Institute's research indicates a lower total cost of ownership for PHEVs due to reduced service costs and gradually improving batteries. The "well-to-wheel" efficiency and emissions of PHEVs compared to gasoline hybrids depends on the energy sources of the grid (the US grid is 50% coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
; California's grid is primarily natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
, hydroelectric power, and wind power
Wind power
Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into a useful form of energy, such as using wind turbines to make electricity, windmills for mechanical power, windpumps for water pumping or drainage, or sails to propel ships....
). Particular interest in PHEVs is in California where a "million solar homes" initiative is under way, and global warming legislation has been enacted.
Prototype
Prototype
A prototype is an early sample or model built to test a concept or process or to act as a thing to be replicated or learned from.The word prototype derives from the Greek πρωτότυπον , "primitive form", neutral of πρωτότυπος , "original, primitive", from πρῶτος , "first" and τύπος ,...
s of PHEVs, with larger battery packs that can be recharged from the power grid, have been built in the U.S., notably at Prof. Andy Frank
Andrew A. Frank
Dr. Andrew Alfonso Frank is an American professor of mechanical and aeronautical engineering at UC Davis. He is recognized as the father of modern plug-in hybrids,, and coined the now-common term. He has a B.S. degree from the University of California, Berkeley, a M.S. , from the University of...
's Hybrid Center at University of California, Davis
University of California, Davis
The University of California, Davis is a public teaching and research university established in 1905 and located in Davis, California, USA. Spanning over , the campus is the largest within the University of California system and third largest by enrollment...
and one production PHEV, the Renault Kangoo
Renault Kangoo
The Renault Kangoo and Kangoo Express are panel van and leisure activity vehicle produced by French automaker Renault since 1997. The Kangoo is manufactured in the MCA plant in Maubeuge, France, and in Santa Isabel, Argentina. The version for the ASEAN markets was assembled by the Tan Chong Euro...
, went on sale in France in 2003. DaimlerChrysler
DaimlerChrysler
Daimler AG is a German car corporation. By unit sales, it is the thirteenth-largest car manufacturer and second-largest truck manufacturer in the world. In addition to automobiles, Daimler manufactures buses and provides financial services through its Daimler Financial Services arm...
is currently building PHEVs based on the Mercedes-Benz Sprinter
Mercedes-Benz Sprinter
The Mercedes-Benz Sprinter is a light and heavy commercial vehicle, built by Daimler AG of Stuttgart, Germany as a van, chassis cab and minibus, and sold as a Mercedes model, except in the U.S. where it is built from complete knock down kits and was sold by Freightliner until 2010 when Mercedes...
van
Van
A van is a kind of vehicle used for transporting goods or groups of people.In British English usage, it can be either specially designed or based on a saloon or sedan car, the latter type often including derivatives with open backs...
. Light Trucks are also offered by Micro-Vett SPA
Micro-Vett
Micro-Vett S.p.A. is Italian company producing electric, hybrid and bimodal vehicles, its located in Imola. It works closely with other Italian automotive companieslike Fiat, Piaggio and Iveco...
the so called Daily Bimodale.
The California Cars Initiative has converted the '04 and newer Toyota Prius to become a prototype of what it calls the PRIUS+. With the addition of 300 lb (136.1 kg) of lead-acid batteries, the PRIUS+ achieves roughly double the gasoline mileage
Mileage
-Motor Vehicles:* Fuel economy in automobiles * Distance travelled as measured by an odometer...
of a standard Prius and can make trips of up to 10 mi (16.1 km) miles using only electric power.
Chinese battery manufacturer and automaker BYD Auto
BYD Auto
BYD Automobile Co Ltd is a Chinese automobile manufacturer based in Shenzhen, Guangdong Province...
released the F3DM
BYD F3DM
The BYD F3DM is a plug-in hybrid compact sedan manufactured by BYD Auto with an all-electric range of and a hybrid electric powertrain that can extend the range an additional . The F3DM is the world's first mass produced plug-in hybrid automobile and went on sale to government agencies and...
PHEV-62 (PHEV-100 km) compact sedan to the Chinese fleet market on December 15, 2008. General Motors
General Motors
General Motors Company , commonly known as GM, formerly incorporated as General Motors Corporation, is an American multinational automotive corporation headquartered in Detroit, Michigan and the world's second-largest automaker in 2010...
expects to launch the 2011 Chevrolet Volt
Chevrolet Volt
The Chevrolet Volt is a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle manufactured by General Motors. The Volt has been on sale in the U.S. market since mid-December 2010, and is the most fuel-efficient compact car sold in the United States, as rated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency...
series plug-in (PHEV-40) by November 2010.
Electric-internal combustion engine hybrid
There are many ways to create an electric-Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) hybrid. The variety of electric-ICE designs can be differentiated by how the electric and combustion portions of the powertrain connect, at what times each portion is in operation, and what percent of the power is provided by each hybrid component. Two major categories are series hybrids and parallel hybrids, though parallel designs are most common today.Most hybrids, no matter the specific type, use regenerative braking to recover energy when slowing down the vehicle. This simply involves driving a motor so it acts as a generator.
Many designs also shut off the internal combustion engine when it is not needed in order to save energy. That concept is not unique to hybrids; Subaru
Subaru
; is the automobile manufacturing division of Japanese transportation conglomerate Fuji Heavy Industries .Subaru is internationally known for their use of the boxer engine layout popularized in cars by the Volkswagen Beetle and Porsche 911, in most of their vehicles above 1500 cc as well as...
pioneered this feature in the early 1980s, and the Volkswagen Lupo 3L
Volkswagen Lupo
The Lupo is a city car manufactured by German automaker Volkswagen from 1998 to 2005.-Model history:The Lupo was introduced in 1998 to fill a gap at the bottom of the VW model range caused by the increasing size and weight of the VW Polo. Rivals included the Ford Ka, the Opel/Vauxhall Agila and...
is one example of a conventional vehicle that shuts off its engine when at a stop. Some provision must be made, however, for accessories such as air conditioning
Air conditioning
An air conditioner is a home appliance, system, or mechanism designed to dehumidify and extract heat from an area. The cooling is done using a simple refrigeration cycle...
which are normally driven by the engine. Furthermore, the lubrication systems of internal combustion engines are inherently least effective immediately after the engine starts; since it is upon startup that the majority of engine wear occurs, the frequent starting and stopping of such systems reduce the lifespan of the engine considerably. Also, start and stop cycles may reduce the engine's ability to operate at its optimum temperature, thus reducing the engine's efficiency.

Electric-fuel cell hybrid
Fuel cellFuel cell
A fuel cell is a device that converts the chemical energy from a fuel into electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen or another oxidizing agent. Hydrogen is the most common fuel, but hydrocarbons such as natural gas and alcohols like methanol are sometimes used...
vehicles are often fitted with a battery or supercapacitor to deliver peak acceleration power and to reduce the size and power constraints on the fuel cell (and thus its cost); this is effectively also a series hybrid configuration.
Internal combustion engine-hydraulic hybrid
A hydraulic hybridHydraulic hybrid
Hydraulic Hybrid Vehicles or HHVs are vehicles that use pressurized fluid, instead of electric power, as an additional or alternative power source along with an engine.- Principle of Operation :...
vehicle uses hydraulic and mechanical components instead of electrical ones. A variable displacement pump
Variable displacement pump
A variable displacement pump is a device that converts mechanical energy to hydraulic energy. The displacement, or amount of fluid pumped per revolution of the pump's input shaft can be varied while the pump is running....
replaces the motor/generator, and a hydraulic accumulator
Hydraulic accumulator
A 'hydraulic accumulator' is an energy storage device. It is a pressure storage reservoir in which a non-compressible hydraulic fluid is held under pressure by an external source. That external source can be a spring, a raised weight, or a compressed gas...
(which stores energy as highly compressed nitrogen gas) replaces the batteries. The hydraulic accumulator, which is essentially a pressure tank, is potentially cheaper and more durable than batteries. Hydraulic hybrid technology was originally developed by Volvo Flygmotor and was used experimentally in buses from the early 1980s and is still an active area.
Initial concept involved a giant flywheel
Flywheel
A flywheel is a rotating mechanical device that is used to store rotational energy. Flywheels have a significant moment of inertia, and thus resist changes in rotational speed. The amount of energy stored in a flywheel is proportional to the square of its rotational speed...
(see Gyrobus
Gyrobus
A Gyrobus is an electric bus that uses flywheel energy storage, not overhead wires like a trolleybus. The name comes from the Greek language term for flywheel, gyros....
) for storage connected to a hydrostatic transmission, but it was later changed to a simpler system using a hydraulic accumulator connected to a hydraulic pump/motor. It is also being actively developed by Eaton
Eaton Corporation
Eaton Corporation is a global diversified power management company with 2010 sales of $13.7 billion. The company is a leading provider of electrical components and systems for power quality, distribution and control; hydraulics components, systems and services for industrial and mobile equipment;...
and several other companies, primarily in heavy vehicles like buses, trucks and military vehicles. An example is the Ford F-350 Mighty Tonka concept truck shown in 2002. It features an Eaton system that can accelerate the truck up to highway speeds.
The energy recovery rate is higher and therefore the system is more efficient than battery charged hybrids, demonstrating a 60% to 70% increase in economy in EPA testing. Under tests done by the EPA, a hydraulic hybrid Ford Expedition returned 32 miles per US gallon in urban driving, and 22 miles per US gallon on the highway. UPS currently has two trucks in service with this technology. While the system has faster and more efficient charge/discharge cycling, the accumulator size and pressure dictates total energy capacity, and requires more space than a battery.
Internal combustion engine-pneumatic hybrid
Compressed air can also power a hybrid car with a gasoline compressor to provide the power. Motor Development International in France is developing such air-powered cars. A team led by Tsu-Chin Tsao, a UCLA mechanical and aerospace engineering professor, is collaborating with engineers from Ford to get Pneumatic hybrid technology up and running. The system is similar to that of a hybrid-electric vehicle in that braking energy is harnessed and stored to assist the engine as needed during acceleration.Human power and environmental power hybrids
Many land and water vehicles use human power combined with a further power source. Common are parallel hybrids, e.g. a boat being rowed and also having a sail set, or motorized bicycleMotorized bicycle
A motorized bicycle, motorbike, cyclemotor, or vélomoteur is a bicycle with an attached motor and transmission used either to power the vehicle unassisted, or to assist with pedaling. Since it always retains both pedals and a discrete connected drive for rider-powered propulsion, the motorized...
s, or a human-electric hybrid vehicle
Human-electric hybrid vehicle
A human-electric hybrid vehicle is a hybrid vehicle, or more specifically a hybrid human powered vehicle, whose drivetrain consists of a human being and an electric motor/generator...
such as the Twike
TWIKE
The TWIKE is a human-electric hybrid vehicle /light electric vehicle designed to carry two passengers and cargo. It can be driven in electric-only mode or electric + pedal power mode .Constructed of lightweight materials such as aluminium and plastic, this...
. Also some series hybrids exist, see in hybrid vehicle
Hybrid vehicle
A hybrid vehicle is a vehicle that uses two or more distinct power sources to move the vehicle. The term most commonly refers to hybrid electric vehicles , which combine an internal combustion engine and one or more electric motors.-Power:...
. Such vehicles can be tribrid vehicles, combining at the same time three power sources e.g. from on-board solar cells, from grid-charged batteries, and from pedals.
Solar Photovoltaics (PV)
To date it has not been mentioned or done, the integration of photovoltaics with a Hybrid car as a way to extend the distance a car can travel on electric power alone or as a way to help keep batteries charged or to recharge them when a car is parked, or for that matter, standing at a traffic light. With the advent of thin-film photovoltaics the cost of integrating them could become negligible in mass production. (There are no citations for this as it is not being done or even considered at this time. This has been included to hopefully get people to think about adding Solar PV in car designs in the very near future. Richard Boettner)Hybrid vehicle operation modes
Hybrid vehicles can be used in different modes. The figure shows some typical modes for a parallel hybrid configuration.
Adding powertrains and aftermarket kits
One can install conmarket or aftermarketAftermarket (automotive)
The automotive aftermarket is the secondary market of the automotive industry, concerned with the manufacturing, remanufacturing, distribution, retailing, and installation of all vehicle parts, chemicals, tools, equipment and accessories for light and heavy vehicles, after the sale of the...
powertrain to a vehicle to hybridise it
Hybrid vehicle
A hybrid vehicle is a vehicle that uses two or more distinct power sources to move the vehicle. The term most commonly refers to hybrid electric vehicles , which combine an internal combustion engine and one or more electric motors.-Power:...
.
The conmarket solution is used when the user buys the glider
Electric vehicle conversion
An electric vehicle conversion is the modification of a conventional internal combustion engine vehicle to electric propulsion, creating an all-electric or plug-in hybrid electric vehicle.-Elements of a conversion:...
(rolling chasis) and the hybrid (two engines) or all-electric (only an electric motor) powertrain kit to the automaker
Automaker
The automotive industry designs, develops, manufactures, markets, and sells motor vehicles, and is one of the world's most important economic sectors by revenue....
and receives it installed in the car. Also an (electric or hybrid) powertrain can be added to a glider by a third party aftermarket installer.
A University of Central Florida
University of Central Florida
The University of Central Florida, commonly referred to as UCF, is a metropolitan public research university located in Orlando, Florida, United States...
senior design team, On the Green, is currently developing a bolt-on hybrid conversion kit to transform an older model vehicle into a gas-electric hybrid.
See also
- Battery electric vehicleBattery electric vehicleA battery electric vehicle, or BEV, is a type of electric vehicle that uses chemical energy stored in rechargeable battery packs. BEVs use electric motors and motor controllers instead of, or in addition to, internal combustion engines for propulsion.A battery-only electric vehicle or...
- Electric vehicleElectric vehicleAn electric vehicle , also referred to as an electric drive vehicle, uses one or more electric motors or traction motors for propulsion...
- Engine control unitEngine control unitAn engine control unit is a type of electronic control unit that determines the amount of fuel, ignition timing and other parameters an internal combustion engine needs to keep running...
- Hybrid electric vehicleHybrid electric vehicleA hybrid electric vehicle is a type of hybrid vehicle and electric vehicle which combines a conventional internal combustion engine propulsion system with an electric propulsion system. The presence of the electric powertrain is intended to achieve either better fuel economy than a conventional...

