
Hybrid Synergy Drive
Encyclopedia

Hybrid Synergy Drive is a set of hybrid car technologies developed by Toyota and used in the company's Auris
Toyota Auris
The Toyota Auris is a compact 3 door and 5 door hatchback which shares the same E150 platform with the Toyota Corolla.In Europe, Toyota positioned the Auris as the replacement of Corolla hatchback, while the notchback Sedan continued with the Corolla nameplate...
, Prius
Toyota Prius
The Toyota Prius is a full hybrid electric mid-size hatchback, formerly a compact sedan developed and manufactured by the Toyota Motor Corporation...
, Highlander Hybrid, Camry Hybrid, Estima
Toyota Previa
The Toyota Previa, also known as the Toyota Estima in Japan and the Toyota Tarago in Australia, is an MPV or multi-purpose vehicle produced by Toyota Motor Corporation since 1990...
, Alphard
Toyota Alphard
The Toyota Alphard is a luxury MPV produced by the Japanese automaker Toyota since 2002. It is available as a seven or eight-seater with 2.4 and 3.0 litre gasoline engines in 3 different model lines - Alphard G, Alphard V, and the Alphard Hybrid, which uses the 2.4 litre engine along with an...
, Lexus CT
Lexus CT
The Lexus CT 200h is a hybrid electric automobile introduced by Lexus and is an entry-level luxury hatchback. It made its debut at the March 2010 Geneva Auto Show, six months after the unveiling of the LF-Ch concept car; it is primarily targeted at the European market but will be sold worldwide and...
, Lexus RX 400h/RX 450h
Lexus RX
The Lexus RX is a crossover sport utility vehicle sold since 1998 by Lexus, the luxury division of the Japanese automobile manufacturer Toyota. Three generations of the Lexus RX have been produced to date, the first being compact in size, and the latter two classified as mid-size...
, Lexus GS 450h, Lexus LS 600h/LS 600hL, and Lexus HS 250h automobile
Automobile
An automobile, autocar, motor car or car is a wheeled motor vehicle used for transporting passengers, which also carries its own engine or motor...
s. Toyota also licenses its HSD technology to Nissan for use in that company's Nissan Altima
Nissan Altima
The Nissan Altima is a mid-size automobile manufactured by Nissan, and is arguably a continuation of the Nissan Bluebird line, which began in 1957. It has historically been larger, more powerful, and more luxurious than the Nissan Sentra but less so than the Nissan Maxima. The Altima is available...
Hybrid. Its parts supplier Aisin Seiki Co.
Aisin Seiki Co.
, also known as Aisin , is a Japanese corporation which develops and produces components and systems for the automotive industry. Aisin is a Fortune Global 500 company, ranked 347 on the 2007 rankings....
sells similar hybrid transmissions to other car companies.
HSD technology produces a full hybrid vehicle which allows the car to run on the electric motor only, as opposed to most other brand hybrids which cannot and are considered mild hybrid
Mild Hybrid
Mild hybrids are essentially conventional fossil-fuel vehicles equipped with a large electric machine allowing the engine to be turned off whenever the car is coasting, braking, or stopped, yet restart quickly...
s. The HSD also combines an electric drive
Electric vehicle
An electric vehicle , also referred to as an electric drive vehicle, uses one or more electric motors or traction motors for propulsion...
and a planetary gearset which performs similarly to a continuously variable transmission
Continuously variable transmission
A continuously variable transmission is a transmission that can change steplessly through an infinite number of effective gear ratios between maximum and minimum values. This contrasts with other mechanical transmissions that offer a fixed number of gear ratios...
. The Synergy Drive is a drive-by-wire system with no direct mechanical connection between the engine and the engine controls: both the gas pedal/accelerator and the gearshift lever
Gear stick
A gear stick is the lever used to change gear in a vehicle, such as an automobile, with manual transmission or several common forms of automatic transmission.The device is used to change gear; in a manual transmission vehicle this will normally be done whilst depressing...
in an HSD car merely send electrical signals to a control computer
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
.

HSD is a refinement of the original Toyota Hybrid System (THS) used in the 1997 to 2003 Toyota Prius. The second generation system THS II first appeared on the redesigned Prius in 2004. The name was changed in anticipation of its use in vehicles outside the Toyota brand (Lexus
Lexus
is the luxury vehicle division of Japanese automaker Toyota Motor Corporation. First introduced in 1989 in the United States, Lexus is now sold globally and has become Japan's largest-selling make of premium cars. The Lexus marque is marketed in over 70 countries and territories worldwide, and has...
; the HSD-derived systems used in Lexus vehicles have been termed Lexus Hybrid Drive since 2006). The Lexus Hybrid Drive system is tuned for increased power and performance along with efficiency concerns; it was introduced on all-wheel drive and rear-wheel drive Lexus models. By May 2007 Toyota had sold one million hybrids worldwide and by the end of August 2009 had sold a total of two million. Toyota-produced hybrids make up approximately 75% of United States hybrid sales.
Principle
The Toyota HSD replaces a normal geared transmissionTransmission (mechanics)
A machine consists of a power source and a power transmission system, which provides controlled application of the power. Merriam-Webster defines transmission as: an assembly of parts including the speed-changing gears and the propeller shaft by which the power is transmitted from an engine to a...
with an electromechanical system. Because an internal combustion engine
Internal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
(ICE) delivers power best only over a small range of torque
Torque
Torque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
s and speed
Speed
In kinematics, the speed of an object is the magnitude of its velocity ; it is thus a scalar quantity. The average speed of an object in an interval of time is the distance traveled by the object divided by the duration of the interval; the instantaneous speed is the limit of the average speed as...
s, the crankshaft
Crankshaft
The crankshaft, sometimes casually abbreviated to crank, is the part of an engine which translates reciprocating linear piston motion into rotation...
of the engine is usually attached to an automatic or manual transmission by a clutch or torque converter that allows the driver to adjust the speed and torque that can be delivered by the engine to the torque and speed needed to drive the wheels of the car. When required to classify the transmission type of an HSD vehicle (such as in standard specification lists or for regulatory purposes), Toyota describes HSD-equipped vehicles as having an e-CVT (electronic continuously variable transmission).
Power sources
In the "standard" car design the alternator (AC generator) and starter (DC motor) are considered accessories that are attached to the internal combustion engine (ICE) which normally drives a transmission to power the wheels propelling the vehicle. A battery is used only to start the car's internal combustion engine and run accessories when the engine is not running. The alternator is used to recharge the battery and run the accessories when the engine is running. HSD replaces the gear box (transmission), alternator and starter motor with a pair of powerful motor-generatorMotor-generator
A motor-generator is a device for converting electrical power to another form. Motor-generator sets are used to convert frequency, voltage, or phase of power. They may also be used to isolate electrical loads from the electrical power supply line...
s (designated MG1 and MG2, ~60 Hp total) with a computerized shunt system to control them, a mechanical power splitter that acts as a second differential
Differential (mechanics)
A differential is a device, usually, but not necessarily, employing gears, capable of transmitting torque and rotation through three shafts, almost always used in one of two ways: in one way, it receives one input and provides two outputs—this is found in most automobiles—and in the other way, it...
, and a battery pack
Battery pack
A battery pack is a set of any number of identical batteries or individual battery cells. They may be configured in a series, parallel or a mixture of both to deliver the desired voltage, capacity, or power density...
that serves as an energy reservoir. The motor-generator
Motor-generator
A motor-generator is a device for converting electrical power to another form. Motor-generator sets are used to convert frequency, voltage, or phase of power. They may also be used to isolate electrical loads from the electrical power supply line...
uses power from the battery pack to propel the vehicle at startup and at low speeds or under acceleration. The ICE may or may not be running at startup. When higher speeds, faster acceleration or more power for charging the batteries is needed the ICE is started by the motor-generator (acting as a starter). These features allow the ICE to normally be turned off for traffic stops—accessory power (including air conditioning if needed) is normally provided by the battery pack.

MG1 and MG2
- MG1 (motor generator 1): generates electrical power. MG1 recharges the EV battery and supplies electrical power to drive MG2. In addition, by regulating the amount of electrical power generated (thus varying MG1's internal resistance and rpm), MG1 effectively controls the transaxleTransaxleIn the automotive field, a transaxle is a major mechanical component that combines the functionality of the transmission, the differential, and associated components of the driven axle into one integrated assembly....
's continuously variable transmissionContinuously variable transmissionA continuously variable transmission is a transmission that can change steplessly through an infinite number of effective gear ratios between maximum and minimum values. This contrasts with other mechanical transmissions that offer a fixed number of gear ratios...
. MG1 also serves as the engine starter. - MG2 (motor generator 2): drives the vehicle. MG2 and the engine work together to drive the wheels. The addition of MG2's strong torque characteristics help achieve excellent dynamic performance, including smooth start-off and acceleration. During regenerative braking, MG2 converts kinetic energy into electrical energy, which is then stored in the EV battery.
Transmission
The mechanical gearing design of the system allows the mechanical power from the ICE to be split three ways: extra torque at the wheels (under constant rotation speed), extra rotation speed at the wheels (under constant torque), and power for an electric generator. A computer program running appropriate actuators controls the systems and directs the power flow from the different engine + motor sources. This power split achieves the benefits of a continuously variable transmissionContinuously variable transmission
A continuously variable transmission is a transmission that can change steplessly through an infinite number of effective gear ratios between maximum and minimum values. This contrasts with other mechanical transmissions that offer a fixed number of gear ratios...
(CVT), except that the torque/speed conversion uses an electric motor rather than a direct mechanical gear train connection. An HSD car cannot operate without the computer, power electronics, battery pack and motor-generators, though in principle it could operate while missing the internal combustion engine. (See: Plug-in hybrid) In practice, HSD equipped cars can be driven a mile or two without gasoline, as an emergency measure to reach a gas station
Filling station
A filling station, also known as a fueling station, garage, gasbar , gas station , petrol bunk , petrol pump , petrol garage, petrol kiosk , petrol station "'servo"' in Australia or service station, is a facility which sells fuel and lubricants...
.
An HSD transaxle
Transaxle
In the automotive field, a transaxle is a major mechanical component that combines the functionality of the transmission, the differential, and associated components of the driven axle into one integrated assembly....
contains a planetary gear set that adjusts and blends the amount of torque from the engine and motor(s) as it’s needed by the front wheels. It is a sophisticated and complicated combination of gearing, electrical motor-generators and computer controlled electronic controls. One of the motor-generators (MG2 in Toyota manuals; sometimes called "MG-T" for "Torque") is mounted on the drive shaft, and thus couples torque into or out of the drive shafts: feeding electricity into MG2 adds torque at the wheels. The engine end of the drive shaft has a second differential
Differential (mechanics)
A differential is a device, usually, but not necessarily, employing gears, capable of transmitting torque and rotation through three shafts, almost always used in one of two ways: in one way, it receives one input and provides two outputs—this is found in most automobiles—and in the other way, it...
; one leg of this differential is attached to the internal combustion engine and the other leg is attached to a second motor-generator (MG1 in Toyota manuals; sometimes "MG-S" for "Speed"). The differential relates the rotation speed of the wheels to the rotation speeds of the engine and MG1, with MG1 used to absorb the difference between wheel and engine speed. The differential is an epicyclic gear set
Epicyclic gearing
Epicyclic gearing or planetary gearing is a gear system consisting of one or more outer gears, or planet gears, revolving about a central, or sun gear. Typically, the planet gears are mounted on a movable arm or carrier which itself may rotate relative to the sun gear...
(also called a "power split device"); that and the two motor-generators are all contained in a single transaxle housing that is bolted to the engine
Engine
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert energy into useful mechanical motion. Heat engines, including internal combustion engines and external combustion engines burn a fuel to create heat which is then used to create motion...
. Special couplings and sensors monitor rotation speed of each shaft and the total torque on the drive shafts, for feedback to the control computer.
Operations
The HSD drive works by shunting electrical power between the two motor generators, running off the battery pack, to even out the load on the internal combustion engine. Since a power boost from the electrical motors is available for periods of rapid acceleration, the ICE can be downsized to match only the average load on the car, rather than sized by peak power demands for rapid acceleration. The smaller internal combustion engine can be designed to run more efficiently. Furthermore, during normal operation the engine can be operated at or near its ideal speed and torque level for power, economy, or emissions, with the battery pack absorbing or supplying power as appropriate to balance the demand placed by the driverDriving
Driving is the controlled operation and movement of a land vehicle, such as a car, truck or bus.Although direct operation of a bicycle and a mounted animal are commonly referred to as riding, such operators are legally considered drivers and are required to obey the rules of the road...
. During traffic stops the internal combustion engine can even be turned off for even more economy.
The combination of efficient car design, regenerative braking, turning the engine off for traffic stops, significant electrical energy storage and efficient internal combustion engine design give the HSD powered car significant efficiency advantages—particularly in city driving.
Phases of operation

- Engine start: To start the engine, power is applied to MG1 to act as a starter. Because of the size of the motor generators, starting the engine requires relatively little power from MG1 and the conventional starter motor sound is not heard. Engine start can occur while stopped or moving.
- Low gear (equivalent): When accelerating at low speeds in normal operation, the engine turns more rapidly than the wheels but does not develop sufficient torque. The extra engine speed is fed to MG1 acting as a generator. The output of MG1 is fed to MG2, acting as a motor and adding torque at the driveshaft.
- High gear (equivalent): When cruising at high speed, the engine turns more slowly than the wheels but develops more torque than needed. MG2 then runs as a generator to remove the excess engine torque, producing power that is fed to MG1 acting as a motor to increase the wheel speed. In steady state, the engine provides all of the power to propel the car unless the engine is unable to supply it (as during heavy acceleration, or driving up a steep incline at high speed). In this case, the battery supplies the difference. Whenever the required propulsion power changes, the battery quickly balances the power budget, allowing the engine to change power relatively slowly.
- Reverse gear: There is no reverse gear as in a conventional gearbox: the computer feeds negative voltage to MG2, applying negative torque to the wheels. Early models did not supply enough torque for some situations: there have been reports of early Prius owners not being able to back the car up steep hills in San Francisco. The problem has been fixed in recent models. If the battery is low, the system can simultaneously run the engine and draw power from MG1, although this will reduce available reverse torque at the wheels.
- Silent operation: At slow speeds and moderate torques the HSD can drive without running the internal combustion engine at all: electricity is supplied only to MG2, allowing MG1 to rotate freely (and thus decoupling the engine from the wheels). This is popularly known as "Stealth Mode". Provided that there is enough battery power, the car can be driven in this silent mode for some miles even without gasoline.
- Neutral gear: Most jurisdictions require automotive transmissions to have a neutral gear that decouples the engine and transmission. The HSD "neutral gear" is achieved by turning the electric motors off. Under this condition, the planetary gear is stationary (if the vehicle wheels are not turning); if the vehicle wheels are turning, the ring gear will rotate, causing the sun gear to rotate as well (the engine inertia will keep the carrier gear stationary unless the speed is high), while MG1 freewheels so no power is dissipated.

- Regenerative brakingRegenerative brakeA regenerative brake is an energy recovery mechanism which slows a vehicle or object down by converting its kinetic energy into another form, which can be either used immediately or stored until needed...
: By drawing power from MG2 and depositing it into the battery pack, the HSD can simulate the deceleration of normal engine brakingEngine brakingEngine braking is where the retarding forces within an engine are used to slow a vehicle down, as opposed to using an external braking mechanism, for example friction brakes or magnetic brakes....
while saving the power for future boost. The regenerative brakes in an HSD system absorb a significant amount of the normal braking load, so the conventional brakes on HSD vehicles are undersized compared to brakes on a conventional car of similar mass. - Engine brakingEngine brakingEngine braking is where the retarding forces within an engine are used to slow a vehicle down, as opposed to using an external braking mechanism, for example friction brakes or magnetic brakes....
: The HSD system has a special transmission setting labelled 'B' (for Brake), that takes the place of a conventional automatic transmissionAutomatic transmissionAn automatic transmission is one type of motor vehicle transmission that can automatically change gear ratios as the vehicle moves, freeing the driver from having to shift gears manually...
's 'L' setting, providing engine braking on hills. This can be manually selected in place of regenerative braking. During braking when the battery is approaching potentially damaging high charge levels, the electronic control system automatically switches to conventional engine brakingEngine brakingEngine braking is where the retarding forces within an engine are used to slow a vehicle down, as opposed to using an external braking mechanism, for example friction brakes or magnetic brakes....
, drawing power from MG2 and shunting it to MG1, speeding the engine with throttle closed to absorb energy and decelerate the vehicle. - Electric boost: The battery pack provides a reservoir of energy that allows the computer to match the demand on the engine to a predetermined optimal load curve, rather than operating at the torque and speed demanded by the driver and road. The computer manages the energy level stored in the battery, so as to have capacity to absorb extra energy where needed or supply extra energy to boost engine power.
- Battery charging: The HSD can charge its battery without moving the car, by running the engine and extracting electrical power from MG1. The power gets shunted into the battery, and no torque is supplied to the wheels.
Performance
The Toyota PriusToyota Prius
The Toyota Prius is a full hybrid electric mid-size hatchback, formerly a compact sedan developed and manufactured by the Toyota Motor Corporation...
has modest acceleration but has extremely high efficiency for a mid sized four-door sedan: Usually significantly better than 40 mpg (US) (5.9 l/100km) is typical of brief city jaunts; 55 mpg (4.3 l/100km) is not uncommon, especially for extended drives at modest speeds (a longer drive allows the engine to warm up fully). This is approximately twice the fuel efficiency of a similarly equipped four-door sedan with a conventional power train. Not all of the extra efficiency of the Prius is due to the HSD system: the Atkinson cycle
Atkinson cycle
The Atkinson cycle engine is a type of internal combustion engine invented by James Atkinson in 1882. The Atkinson cycle is designed to provide efficiency at the expense of power density, and is used in some modern hybrid electric applications.-Design:...
engine itself was also designed specifically to minimize engine drag via an offset crankshaft
Crankshaft
The crankshaft, sometimes casually abbreviated to crank, is the part of an engine which translates reciprocating linear piston motion into rotation...
to minimize piston drag during the power stroke, and a unique intake system to prevent drag caused by manifold vacuum
Manifold vacuum
Manifold vacuum, or engine vacuum in an internal combustion engine is the difference in air pressure between the engine's intake manifold and Earth's atmosphere....
versus the normal Otto cycle
Otto cycle
An Otto cycle is an idealized thermodynamic cycle which describes the functioning of a typical reciprocating piston engine, the thermodynamic cycle most commonly found in automobile engines....
in most engines. Furthermore, the Atkinson cycle recovers more energy per cycle than the Otto because of its longer power stroke. The downside of the Atkinson cycle is much reduced torque, particularly at low speed; but the HSD has enormous low-speed torque available from MG2.
The Highlander Hybrid (also sold as the Kluger in some countries) offers better acceleration performance compared to its non-hybrid version. The hybrid version goes from 0–60 mph in 7.2 seconds, trimming almost a second off the conventional version's time. Net hp is 268 hp compared to the conventional 215 hp. Top speed for all Highlanders is limited to 112 mi/h. Typical fuel economy for the Highlander Hybrid rates between 27 and 31 mpg (8.7-7.6 l/100km). A conventional Highlander is rated by the EPA with 19 city, 25 highway mpg (12.4 and 9.4 l/100km respectively).

- extended drives, especially in winter: Heating the internal cabin for the passengers runs counter to the design of the HSD. The HSD is designed to generate as little waste heat as possible. In a conventional car, this waste heat in winter is usually used to heat the internal cabin. In the Prius, running the heater will then require the engine to continue running to generate cabin-usable heat. This effect is most pronounced by turning the climate control (heater) off when at a stop when the engine is running. Normally the HSD control system will shut the engine off as it is not needed, and will not start it again until the generator reaches a maximum speed.
- moderate acceleration: Because hybrid cars can throttle back or completely shut off the engine during moderate, but not rapid, acceleration, they are more sensitive than conventional cars to driving style. Hard acceleration forces the engine into a high-power state while moderate acceleration keeps the engine in a lower power, high efficiency state (augmented by battery boost).
- gradual braking: Regenerative brakes re-use the energy of braking, but cannot absorb energy as fast as conventional brakes. Gradual braking recovers energy for re-use, boosting mileage; hard braking wastes the energy as heat, just as for a conventional car. Use of the "B" (braking) selector on the transmission control is useful on long downhill runs to reduce heat and wear on the conventional brakes, but it does not recover additional energy. Use of "B" constantly is discouraged by Toyota as it may promote excessive wear on certain gears.
Most HSD systems have batteries that are sized for maximal boost during a single acceleration from zero to the top speed of the vehicle; if there is more demand, the battery can be completely exhausted, so that this extra torque boost is not available. Then the system reverts to just the power available from the engine. This results in a large decline in performance under certain conditions: an early-model Prius can achieve over 90 mi/h on a 6 degree upward slope, but after about 2000 feet (609.6 m) of altitude climb the battery is exhausted and the car can only achieve 55–60 mph on the same slope (until the battery is recharged by driving under less demanding circumstances).
Subsequent developments
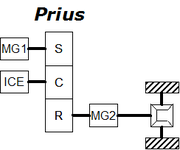
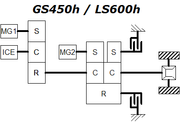
The schematic diagrams illustrate the paths of power flow between electric motor-generator 1 (MG1), gasoline internal combustion engine (ICE), planetary gearset "power split device" elements (S:central "sun", C:planetary carrier, R:outer ring) and motor-generator 2 (MG2).
There has been a continuous, gradual improvement in the specific capacity of the traction battery. The original Prius used shrink-wrapped 1.2 volt D cells, and all subsequent THS/HSD vehicles have used custom 7.2 V battery modules mounted in a carrier.
Called Toyota Hybrid System for initial Prius generations, THS was followed by THS II in the 2004 Prius, with subsequent versions termed Hybrid Synergy Drive. The THS relied on the voltage of the battery pack: between 276 and 288 V. The Hybrid Synergy Drive adds a DC to DC converter
DC to DC converter
A DC-to-DC converter is an electronic circuit which converts a source of direct current from one voltage level to another. It is a class of power converter.- Usage :...
boosting the potential of the battery to 500 V or more. This allows smaller battery packs to be used, and more powerful motors.
Hybrid Synergy Drive (HSD)
Although not part of the HSD as such, all HSD vehicles from the 2004 Prius onwards have been fitted with an electric air-conditioning compressor, instead of the conventional engine-driven type. This removes the need to continuously run the engine when cabin cooling is required. Two positive temperature coefficient heaters are fitted in the heater core to supplement the heat provided by the engine.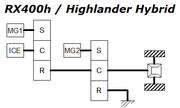
Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company is an American multinational automaker based in Dearborn, Michigan, a suburb of Detroit. The automaker was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. In addition to the Ford and Lincoln brands, Ford also owns a small stake in Mazda in Japan and Aston Martin in the UK...
has also developed a similar hybrid system, introduced in the Ford Escape Hybrid.
In 2006 and 2007, a further development of the HSD drivetrain, under the Lexus Hybrid Drive name, was applied on the Lexus GS 450h / LS 600h sedans. This system uses two clutches (or brakes) to switch the second motor's gear ratio to the wheels between a ratio of 3.9 and 1.9, for low and high speed driving regimes respectively. This decreases the power flowing from MG1 to MG2 (or vice versa) during higher speeds. The electrical path is only about 70% efficient, thus decreasing its power flow while increasing the overall performance of the transmission. The second planetary gearset is extended with a second carrier and sun gear to a ravigneaux-type gear
Ravigneaux planetary gearset
The Ravigneaux gearset is a double planetary gear set commonly used in automatic transmissions. This planetary gear set is constructed from two gear pairs, ring-planet and planet-planet. The Ravigneaux set has two sun gear wheels, a large sun and a small sun, and a single carrier gear with two...
with four shafts, two of which can be held still alternatively by a brake/clutch. The GS 450h and LS 600h systems utilized rear-wheel drive and all-wheel drive drivetrains, respectively, and were designed to be more powerful than non-hybrid versions of the same model lines, while providing comparable engine class efficiency.
Next generation
Katsuaki Watanabe
is vice chairman of Toyota Motor Corporation. He was president and CEO of the company before Akio Toyoda assumed those positions on June 23, 2009.Watanabe, who earned a degree in economics from Tokyo's Keio University, joined Toyota upon graduating from that university in 1964.He has gained...
said in a February 16, 2007 interview that Toyota was "aiming at reducing, by half, both the size and cost of the third-generation HSD system".
The new system will feature lithium-ion batteries in later years. Lithium-ion batteries have a higher energy capacity-to-weight ratio, but cost more, don't last as long as NiMH
NIMH
NIMH or NiMH may refer to:*Nickel-metal hydride battery, a type of rechargeable battery*National Institute of Mental Health, a part of the United States National Institutes of Health...
, and operate at higher temperatures, and are subject to thermal instability if not properly manufactured and controlled, raising safety concerns.
List of vehicles with HSD technology
The following is a list of vehicles with Hybrid Synergy Drive and related technologies (Toyota Hybrid System I/II; Lexus Hybrid Drive)- Toyota PriusToyota PriusThe Toyota Prius is a full hybrid electric mid-size hatchback, formerly a compact sedan developed and manufactured by the Toyota Motor Corporation...
- with THS: December 1997–October 2003
- with THSII: October 2003–present
- Lexus RX 400h / Toyota Harrier Hybrid (March 2005–)
- Toyota Highlander/Kluger Hybrid
- with THSI: July 2005–September 2008
- with THSII: October 2008–present
- Lexus GS 450h (March 2006–present)
- Toyota Camry Hybrid (May 2006–present)
- Lexus LS 600h/LS 600hL (April 2007–present)
- Toyota A-BAT (concept truck)
- Nissan Altima Hybrid (2007–present)
- Lexus RX 450hLexus RX (AL10)The Lexus RX is the third generation of the Lexus RX series of crossover SUVs, sold by Lexus since 2009. The vehicle series is a complete redesign of Lexus' crossover model line, with models debuting in 2009 including the RX 350 and RX 450h...
(2009–present) - Lexus HS 250hLexus HSThe Lexus HS is a dedicated hybrid vehicle introduced by Lexus as a new entry-level luxury compact sedan in 2009. It is classified as a compact under Japanese regulations concerning vehicle exterior dimensions and engine displacement...
(2009–present) - Lexus CT 200hLexus CTThe Lexus CT 200h is a hybrid electric automobile introduced by Lexus and is an entry-level luxury hatchback. It made its debut at the March 2010 Geneva Auto Show, six months after the unveiling of the LF-Ch concept car; it is primarily targeted at the European market but will be sold worldwide and...
(late 2010–) - Toyota Auris (July 2010–)
Antonov
As of autumn 2005, the Antonov Automotive Technology BV Plc company has sued Toyota, the Lexus brand mother company, over alleged patent infringement relating to key components in the RX 400h's drivetrain and the Toyota Prius hybrid compact car. The case has been pending in secret since April 2005, but settlement negotiations did not bring a mutually acceptable result. Antonov eventually took legal recourse in the German court system, where decisions are usually made relatively swiftly. The patent holder seeks to impose a levy on each vehicle sold, which could make the hybrid SUV less competitive. Toyota fought back by seeking to officially invalidate Antonov's relevant patents. The court motion in Microsoft Word document format can be read here.On 1 September 2006 Antonov announced: The Board of Antonov plc announces that the Federal Patent Court in Munich has not upheld the validity of the German part of Antonov's patent (EP0414782) against Toyota. A few days earlier, a court in Düsseldorf had ruled that the Toyota Prius driveline breached the Antonov hybrid CVT patent. Equivalent patents are still in force in various countries worldwide. The position is therefore at an impasse, with the Toyota Prius probably breaching the Antonov hybrid CVT patents outside Europe, Antonov PLC lacking the financial muscle to enforce their patents, and Toyota prepared to try to get the Antonov patents cancelled elsewhere if Antonov tries to enforce them.
Ford
Ford Motor CompanyFord Motor Company
Ford Motor Company is an American multinational automaker based in Dearborn, Michigan, a suburb of Detroit. The automaker was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. In addition to the Ford and Lincoln brands, Ford also owns a small stake in Mazda in Japan and Aston Martin in the UK...
independently developed a system with key technologies similar to Toyota's HSD technology in 2004. As a result, Ford licensed 21 patents from Toyota in exchange for patents relating to emissions technology.
Paice
Paice LLC received a patent for an improved hybrid vehicle with a controllable torque transfer unit and has additional patents related to hybrid vehicles. In 2010 Toyota agreed to license Paice's patents; terms of the settlement were not disclosed.In the settlement "The parties agree that, although certain Toyota vehicles have been found to be equivalent to a Paice patent, Toyota invented, designed and developed the Prius and Toyota’s hybrid technology independent of any inventions of Dr. Severinsky and Paice as part of Toyota’s long history of innovation".
Paice earlier entered into an agreement with Ford for the license of Paice's patent.
Comparison with other hybrids
Aisin Seiki Co.Aisin Seiki Co.
, also known as Aisin , is a Japanese corporation which develops and produces components and systems for the automotive industry. Aisin is a Fortune Global 500 company, ranked 347 on the 2007 rankings....
, minority-owned by Toyota, supplies its versions of the HSD transmission system to Ford for use as the "Powersplit" e-CVT in the Ford Escape
Ford Escape
The Ford Escape is a compact SUV sold by the automaker Ford Motor Company introduced in 2000 as a 2001 model year and priced below the Ford Explorer. Although technically it's a crossover vehicle, it is marketed by Ford as part of its traditional SUV lineup rather than its separate crossover lineup...
hybrid and Ford Fusion hybrid.
Nissan licensed Toyota's HSD for use in the Nissan Altima
Nissan Altima
The Nissan Altima is a mid-size automobile manufactured by Nissan, and is arguably a continuation of the Nissan Bluebird line, which began in 1957. It has historically been larger, more powerful, and more luxurious than the Nissan Sentra but less so than the Nissan Maxima. The Altima is available...
hybrid, using the same Aisin Seiki T110 transaxle as in the Toyota Camry
Toyota Camry
The Toyota Camry is a series of mid-size automobiles manufactured by Toyota since 1982, and sold in the majority of automotive markets throughout the world...
Hybrid.
The 2011 Infiniti M35h uses a different system of one electric motor and two clutches.
In 2010 Toyota and Mazda announced a supply agreement for the hybrid technology used in Toyota's Prius
Toyota Prius
The Toyota Prius is a full hybrid electric mid-size hatchback, formerly a compact sedan developed and manufactured by the Toyota Motor Corporation...
model.
General Motors, DaimlerChrysler
DaimlerChrysler
Daimler AG is a German car corporation. By unit sales, it is the thirteenth-largest car manufacturer and second-largest truck manufacturer in the world. In addition to automobiles, Daimler manufactures buses and provides financial services through its Daimler Financial Services arm...
's and BMW
BMW
Bayerische Motoren Werke AG is a German automobile, motorcycle and engine manufacturing company founded in 1916. It also owns and produces the Mini marque, and is the parent company of Rolls-Royce Motor Cars. BMW produces motorcycles under BMW Motorrad and Husqvarna brands...
's Global Hybrid Cooperation
Global Hybrid Cooperation
Global Hybrid Cooperation is a set of hybrid vehicle technologies jointly developed by General Motors, Daimler, and Chrysler LLC, with BMW joining in 2005...
is similar in that it combines the power from a single engine and two motors. In 2009, the Presidential Task Force on the Auto Industry
Presidential Task Force on the Auto Industry
The Presidential Task Force on the Auto Industry is an ad hoc group of United States cabinet-level and other officials that was formed to deal with the financial bail out of automakers Chrysler Corporation and General Motors....
said that "GM is at least one generation behind Toyota on advanced, 'green' powertrain development".
In contrast, Honda
Honda
is a Japanese public multinational corporation primarily known as a manufacturer of automobiles and motorcycles.Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, as well as the world's largest manufacturer of internal combustion engines measured by volume, producing more than...
's Integrated Motor Assist
Integrated Motor Assist
Integrated Motor Assist is Honda's hybrid car technology, introduced in 1999 on the Insight.It is a specific implementation of a parallel hybrid. It uses an electric motor mounted between the internal combustion engine and transmission to act as a starter motor, engine balancer, and assist...
uses a more traditional ICE
Internal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
and transmission where the flywheel is replaced with an electric motor, thereby reducing complexity and increasing serviceability due to the familiar layout.
Aftermarket
Some early non-production plug-in hybrid electric vehiclePlug-in hybrid electric vehicle
A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle , plug-in hybrid vehicle , or plug-in hybrid is a hybrid vehicle which utilizes rechargeable batteries, or another energy storage device, that can be restored to full charge by connecting a plug to an external electric power source...
conversions
Electric vehicle conversion
An electric vehicle conversion is the modification of a conventional internal combustion engine vehicle to electric propulsion, creating an all-electric or plug-in hybrid electric vehicle.-Elements of a conversion:...
have been based on the version of HSD found in the 2004 and 2005 model year Prius. Early lead-acid battery
Lead-acid battery
Lead–acid batteries, invented in 1859 by French physicist Gaston Planté, are the oldest type of rechargeable battery. Despite having a very low energy-to-weight ratio and a low energy-to-volume ratio, their ability to supply high surge currents means that the cells maintain a relatively large...
conversions by CalCars have demonstrated 10 miles (16.1 km) of ev-only and 20 miles (32.2 km) of double mileage mixed-mode
Mixed-mode
Blended mode is a type of Charge-depleting mode of operation of a Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles in which a portion of the motive energy is supplied by the electric portion of the system whose batteries are recharged from an external source...
range. A company planning to offer conversions to consumers named EDrive systems will be using Valence Li-ion batteries and have 35 miles (56.3 km) of electric range. Both of these systems leave the existing HSD system mostly unchanged and could be similarly applied to other hybrid powertrain flavors by simply replacing the stock NiMH batteries with a higher capacity battery pack
Battery pack
A battery pack is a set of any number of identical batteries or individual battery cells. They may be configured in a series, parallel or a mixture of both to deliver the desired voltage, capacity, or power density...
and a charger to refill them for about $0.03 per mile from standard household outlets. Another provider of a plug-in module for the Toyota Prius is Hymotion.
See also
- Comparison of Toyota hybridsComparison of Toyota hybridsBy the end of 2006 there were about 15 hybrid vehicles from various car makers available in the U.S. By May 2007 Toyota sold its first million hybrids and had sold a total of two million hybrids at the end of August 2009....
- Hybrid car
- Inverter (electrical)Inverter (electrical)An inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current to alternating current ; the converted AC can be at any required voltage and frequency with the use of appropriate transformers, switching, and control circuits....
- IGBT transistor
- Variable-frequency drive
- Global Hybrid CooperationGlobal Hybrid CooperationGlobal Hybrid Cooperation is a set of hybrid vehicle technologies jointly developed by General Motors, Daimler, and Chrysler LLC, with BMW joining in 2005...
- Integrated Motor AssistIntegrated Motor AssistIntegrated Motor Assist is Honda's hybrid car technology, introduced in 1999 on the Insight.It is a specific implementation of a parallel hybrid. It uses an electric motor mounted between the internal combustion engine and transmission to act as a starter motor, engine balancer, and assist...
- List of hybrid vehicles

