.gif)
Inverter (electrical)
Encyclopedia
An inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current
(DC) to alternating current
(AC); the converted AC can be at any required voltage and frequency with the use of appropriate transformer
s, switching, and control circuits.
Solid-state inverters have no moving parts and are used in a wide range of applications, from small switching power supplies
in computers, to large electric utility
high-voltage direct current
applications that transport bulk power. Inverters are commonly used to supply AC power from DC sources such as solar panels or batteries.
The inverter performs the opposite function of a rectifier
.
output except that the output goes to zero volts for a time before switching positive or negative. It is simple and low cost (~$0.10USD/Watt) and is compatible with most electronic devices, except for sensitive or specialized equipment, for example certain laser printer
s, fluorescent lighting, audio equipment.
Most AC motors will run off this power source albeit at a reduction in efficiency of approximately 20%
) that is essentially the same as utility-supplied grid power. Thus it is compatible with all AC electronic devices. This is the type used in grid-tie inverters. Its design is more complex, and costs more per unit power.
The electrical inverter is a high-power electronic oscillator
. It is so named because early mechanical AC to DC converters
were made to work in reverse, and thus were "inverted", to convert DC to AC.
 An inverter converts the DC electricity from sources such as batteries, solar panels
An inverter converts the DC electricity from sources such as batteries, solar panels
, or fuel cell
s to AC electricity. The electricity can be at any required voltage; in particular it can operate AC equipment designed for mains operation, or rectified to produce DC at any desired voltage.
Micro-inverters convert direct current from individual solar panels into alternating current for the electric grid. They are grid tie designs by default.
(UPS) uses batteries and an inverter to supply AC power when main power is not available. When main power is restored, a rectifier
supplies DC power to recharge the batteries.
. To do this, AC power is first rectified
to provide DC power. The inverter then changes the DC power to high frequency AC power.
power transmission, AC power is rectified and high voltage DC power is transmitted to another location. At the receiving location, an inverter in a static inverter plant
converts the power back to AC.
so that DC power for the inverter can be provided from main AC power. Since an inverter is the key component, variable-frequency drives are sometimes called inverter drives or just inverters.
and diesel-electric rail vehicles as well as some battery electric vehicles and hybrid electric
highway vehicles such as the Toyota Prius
and Fisker Karma
. Various improvements in inverter technology are being developed specifically for electric vehicle applications.
In vehicles with regenerative braking, the inverter also takes power from the motor (now acting as a generator) and stores it in the batteries.
allows AC voltage to be stepped up or down to a desired voltage at the same frequency. Inverters, plus rectifiers for DC, can be designed to convert from any voltage, AC or DC, to any other voltage, also AC or DC, at any desired frequency. The output power can never exceed the input power, but efficiencies can be high, with a small proportion of the power dissipated as waste heat.


through the centre tap of the primary winding. A switch is rapidly switched back and forth to allow current to flow back to the DC source following two alternate paths through one end of the primary winding and then the other. The alternation of the direction of current in the primary winding of the transformer produces alternating current
(AC) in the secondary circuit..
The electromechanical version of the switching device includes two stationary contacts and a spring supported moving contact. The spring holds the movable contact against one of the stationary contacts and an electromagnet pulls the movable contact to the opposite stationary contact. The current in the electromagnet is interrupted by the action of the switch so that the switch continually switches rapidly back and forth. This type of electromechanical inverter switch, called a vibrator
or buzzer, was once used in vacuum tube
automobile radios. A similar mechanism has been used in door bells, buzzers and tattoo gun
s.
As they became available with adequate power ratings, transistors and various other types of semiconductor
switches have been incorporated into inverter circuit designs.
due to its simple off and on nature as opposed to the sinusoidal
waveform that is the usual waveform of an AC power supply. Using Fourier analysis, periodic
waveforms are represented as the sum of an infinite series of sine waves. The sine wave that has the same frequency
as the original waveform is called the fundamental component. The other sine waves, called harmonics, that are included in the series have frequencies that are integral multiples of the fundamental frequency.
The quality of the inverter output waveform can be expressed by using the Fourier analysis data to calculate the total harmonic distortion
(THD). The total harmonic distortion (THD) is the square root of the sum of the squares of the harmonic voltages divided by the fundamental voltage:

The quality of output waveform that is needed from an inverter depends on the characteristics of the connected load. Some loads need a nearly perfect sine wave voltage supply in order to work properly. Other loads may work quite well with a square wave voltage.
 There are many different power circuit topologies
There are many different power circuit topologies
and control strategies
used in inverter designs. Different design approaches address various issues that may be more or less important depending on the way that the inverter is intended to be used.
The issue of waveform quality can be addressed in many ways. Capacitor
s and inductor
s can be used to filter
the waveform. If the design includes a transformer
, filtering can be applied to the primary or the secondary side of the transformer or to both sides. Low-pass filters are applied to allow the fundamental component of the waveform to pass to the output while limiting the passage of the harmonic components. If the inverter is designed to provide power at a fixed frequency, a resonant
filter can be used. For an adjustable frequency inverter, the filter must be tuned to a frequency that is above the maximum fundamental frequency.
Since most loads contain inductance, feedback rectifier
s or antiparallel
diodes
are often connected across each semiconductor
switch to provide a path for the peak inductive load current when the switch is turned off. The antiparallel diodes are somewhat similar to the freewheeling diodes
used in AC/DC converter circuits.
Fourier analysis reveals that a waveform, like a square wave, that is anti-symmetrical about the 180 degree point contains only odd harmonics, the 3rd, 5th, 7th, etc. Waveforms that have steps of certain widths and heights can attenuate certain lower harmonics at the expense of amplifying higher harmonics. For example, by inserting a zero-voltage step between the positive and negative sections of the square-wave, all of the harmonics that are divisible by three (3rd and 9th, etc.) can be eliminated. That leaves only the 5th, 7th, 11th, 13th etc. The required width of the steps is one third of the period for each of the positive and negative steps and one sixth of the period for each of the zero-voltage steps.
Changing the square wave as described above is an example of pulse-width modulation
(PWM). Modulating, or regulating the width of a square-wave pulse is often used as a method of regulating or adjusting an inverter's output voltage. When voltage control is not required, a fixed pulse width can be selected to reduce or eliminate selected harmonics. Harmonic elimination techniques are generally applied to the lowest harmonics because filtering is much more practical at high frequencies, where the filter components can be much smaller and less expensive. Multiple pulse-width or carrier based PWM control schemes produce waveforms that are composed of many narrow pulses. The frequency represented by the number of narrow pulses per second is called the switching frequency or carrier frequency. These control schemes are often used in variable-frequency motor control inverters because they allow a wide range of output voltage and frequency adjustment while also improving the quality of the waveform.
Multilevel inverters provide another approach to harmonic cancellation. Multilevel inverters provide an output waveform that exhibits multiple steps at several voltage levels. For example, it is possible to produce a more sinusoidal wave by having split-rail direct current
inputs at two voltages, or positive and negative inputs with a central ground
. By connecting the inverter output terminals in sequence between the positive rail and ground, the positive rail and the negative rail, the ground rail and the negative rail, then both to the ground rail, a stepped waveform is generated at the inverter output. This is an example of a three level inverter: the two voltages and ground.
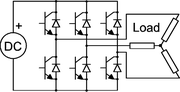 Three-phase
Three-phase
inverters are used for variable-frequency drive applications and for high power applications such as HVDC
power transmission. A basic three-phase inverter consists of three single-phase inverter switches each connected to one of the three load terminals. For the most basic control scheme, the operation of the three switches is coordinated so that one switch operates at each 60 degree point of the fundamental output waveform. This creates a line-to-line output waveform that has six steps. The six-step waveform has a zero-voltage step between the positive and negative sections of the square-wave such that the harmonics that are multiples of three are eliminated as described above. When carrier-based PWM techniques are applied to six-step waveforms, the basic overall shape, or envelope, of the waveform is retained so that the 3rd harmonic and its multiples are cancelled.
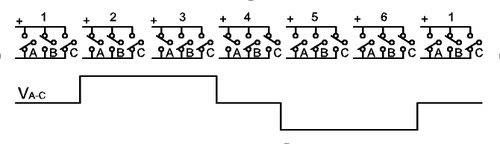 To construct inverters with higher power ratings, two six-step three-phase inverters can be connected in parallel for a higher current rating or in series for a higher voltage rating. In either case, the output waveforms are phase shifted to obtain a 12-step waveform. If additional inverters are combined, an 18-step inverter is obtained with three inverters etc. Although inverters are usually combined for the purpose of achieving increased voltage or current ratings, the quality of the waveform is improved as well.
To construct inverters with higher power ratings, two six-step three-phase inverters can be connected in parallel for a higher current rating or in series for a higher voltage rating. In either case, the output waveforms are phase shifted to obtain a 12-step waveform. If additional inverters are combined, an 18-step inverter is obtained with three inverters etc. Although inverters are usually combined for the purpose of achieving increased voltage or current ratings, the quality of the waveform is improved as well.
s or motor-generator
sets (M-G sets). In the early twentieth century, vacuum tubes and gas filled tube
s began to be used as switches in inverter circuits. The most widely used type of tube was the thyratron
.
The origins of electromechanical inverters explain the source of the term inverter. Early AC-to-DC converters used an induction or synchronous AC motor direct-connected to a generator (dynamo) so that the generator's commutator reversed its connections at exactly the right moments to produce DC. A later development is the synchronous converter, in which the motor and generator windings are combined into one armature, with slip rings at one end and a commutator at the other and only one field frame. The result with either is AC-in, DC-out. With an M-G set, the DC can be considered to be separately generated from the AC; with a synchronous converter, in a certain sense it can be considered to be "mechanically rectified AC". Given the right auxiliary and control equipment, an M-G set or rotary converter can be "run backwards", converting DC to AC. Hence an inverter is an inverted converter.
or silicon-controlled rectifier
(SCR) that initiated the transition to solid state inverter circuits.
The commutation requirements of SCRs are a key consideration in SCR circuit designs. SCRs do not turn off or commutate automatically when the gate control signal is shut off. They only turn off when the forward current is reduced to below the minimum holding current, which varies with each kind of SCR, through some external process. For SCRs connected to an AC power source, commutation occurs naturally every time the polarity of the source voltage reverses. SCRs connected to a DC power source usually require a means of forced commutation that forces the current to zero when commutation is required. The least complicated SCR circuits employ natural commutation rather than forced commutation. With the addition of forced commutation circuits, SCRs have been used in the types of inverter circuits described above.
In applications where inverters transfer power from a DC power source to an AC power source, it is possible to use AC-to-DC controlled rectifier circuits operating in the inversion mode. In the inversion mode, a controlled rectifier circuit operates as a line commutated inverter. This type of operation can be used in HVDC power transmission systems and in regenerative braking
operation of motor control systems.
Another type of SCR inverter circuit is the current source input (CSI) inverter. A CSI inverter is the dual
of a six-step voltage source inverter. With a current source inverter, the DC power supply is configured as a current source
rather than a voltage source
. The inverter SCRs are switched in a six-step sequence to direct the current to a three-phase AC load as a stepped current waveform. CSI inverter commutation methods include load commutation and parallel capacitor commutation. With both methods, the input current regulation assists the commutation. With load commutation, the load is a synchronous motor operated at a leading power factor.
As they have become available in higher voltage and current ratings, semiconductors such as transistors or IGBTs that can be turned off by means of control signals have become the preferred switching components for use in inverter circuits.
With three-phase rectifiers, two or more rectifiers are sometimes connected in series or parallel to obtain higher voltage or current ratings. The rectifier inputs are supplied from special transformers that provide phase shifted outputs. This has the effect of phase multiplication. Six phases are obtained from two transformers, twelve phases from three transformers and so on. The associated rectifier circuits are 12-pulse rectifiers, 18-pulse rectifiers and so on.
When controlled rectifier circuits are operated in the inversion mode, they would be classified by pulse number also. Rectifier circuits that have a higher pulse number have reduced harmonic content in the AC input current and reduced ripple in the DC output voltage. In the inversion mode, circuits that have a higher pulse number have lower harmonic content in the AC output voltage waveform.
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
(DC) to alternating current
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
(AC); the converted AC can be at any required voltage and frequency with the use of appropriate transformer
Transformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
s, switching, and control circuits.
Solid-state inverters have no moving parts and are used in a wide range of applications, from small switching power supplies
Switched-mode power supply
A switched-mode power supply is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator in order to be highly efficient in the conversion of electrical power...
in computers, to large electric utility
Electric utility
An electric utility is a company that engages in the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity for sale generally in a regulated market. The electrical utility industry is a major provider of energy in most countries. It is indispensable to factories, commercial establishments,...
high-voltage direct current
High-voltage direct current
A high-voltage, direct current electric power transmission system uses direct current for the bulk transmission of electrical power, in contrast with the more common alternating current systems. For long-distance transmission, HVDC systems may be less expensive and suffer lower electrical losses...
applications that transport bulk power. Inverters are commonly used to supply AC power from DC sources such as solar panels or batteries.
The inverter performs the opposite function of a rectifier
Rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
.
Modified sine wave
The output of a modified sine wave inverter is similar to a square waveSquare wave
A square wave is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform, most typically encountered in electronics and signal processing. An ideal square wave alternates regularly and instantaneously between two levels...
output except that the output goes to zero volts for a time before switching positive or negative. It is simple and low cost (~$0.10USD/Watt) and is compatible with most electronic devices, except for sensitive or specialized equipment, for example certain laser printer
Laser printer
A laser printer is a common type of computer printer that rapidly produces high quality text and graphics on plain paper. As with digital photocopiers and multifunction printers , laser printers employ a xerographic printing process, but differ from analog photocopiers in that the image is produced...
s, fluorescent lighting, audio equipment.
Most AC motors will run off this power source albeit at a reduction in efficiency of approximately 20%
Pure sine wave
A pure sine wave inverter produces a nearly perfect sine wave output (<3% total harmonic distortionTotal harmonic distortion
The total harmonic distortion, or THD, of a signal is a measurement of the harmonic distortion present and is defined as the ratio of the sum of the powers of all harmonic components to the power of the fundamental frequency...
) that is essentially the same as utility-supplied grid power. Thus it is compatible with all AC electronic devices. This is the type used in grid-tie inverters. Its design is more complex, and costs more per unit power.
The electrical inverter is a high-power electronic oscillator
Electronic oscillator
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a repetitive electronic signal, often a sine wave or a square wave. They are widely used in innumerable electronic devices...
. It is so named because early mechanical AC to DC converters
Mechanical rectifier
A mechanical rectifier is a device for converting alternating current to direct current by means of mechanically-operated switches. The best-known type is the commutator, which is an integral part of a DC dynamo but, before solid-state devices became available, independent mechanical rectifiers...
were made to work in reverse, and thus were "inverted", to convert DC to AC.
Grid tie inverter
A grid tie inverter is a sine wave inverter designed to inject electricity into the electric power distribution system. Such inverters must synchronise with the frequency of the grid. They usually contain one or more Maximum power point tracking features to extract the maximum amount of power, and also include safety features.DC power source utilization

Photovoltaics
Photovoltaics is a method of generating electrical power by converting solar radiation into direct current electricity using semiconductors that exhibit the photovoltaic effect. Photovoltaic power generation employs solar panels composed of a number of solar cells containing a photovoltaic material...
, or fuel cell
Fuel cell
A fuel cell is a device that converts the chemical energy from a fuel into electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen or another oxidizing agent. Hydrogen is the most common fuel, but hydrocarbons such as natural gas and alcohols like methanol are sometimes used...
s to AC electricity. The electricity can be at any required voltage; in particular it can operate AC equipment designed for mains operation, or rectified to produce DC at any desired voltage.
Micro-inverters convert direct current from individual solar panels into alternating current for the electric grid. They are grid tie designs by default.
Uninterruptible power supplies
An uninterruptible power supplyUninterruptible power supply
An uninterruptible power supply, also uninterruptible power source, UPS or battery/flywheel backup, is an electrical apparatus that provides emergency power to a load when the input power source, typically mains power, fails...
(UPS) uses batteries and an inverter to supply AC power when main power is not available. When main power is restored, a rectifier
Rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
supplies DC power to recharge the batteries.
Induction heating
Inverters convert low frequency main AC power to higher frequency for use in induction heatingInduction heating
Induction heating is the process of heating an electrically conducting object by electromagnetic induction, where eddy currents are generated within the metal and resistance leads to Joule heating of the metal...
. To do this, AC power is first rectified
Rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
to provide DC power. The inverter then changes the DC power to high frequency AC power.
HVDC power transmission
With HVDCHigh-voltage direct current
A high-voltage, direct current electric power transmission system uses direct current for the bulk transmission of electrical power, in contrast with the more common alternating current systems. For long-distance transmission, HVDC systems may be less expensive and suffer lower electrical losses...
power transmission, AC power is rectified and high voltage DC power is transmitted to another location. At the receiving location, an inverter in a static inverter plant
Static inverter plant
A static inverter station, also known as an HVDC Converter Station, is the terminal equipment for a high-voltage direct-current transmission line, in which direct current is converted to three-phase alternating current, and, usually, the reverse...
converts the power back to AC.
Variable-frequency drives
A variable-frequency drive controls the operating speed of an AC motor by controlling the frequency and voltage of the power supplied to the motor. An inverter provides the controlled power. In most cases, the variable-frequency drive includes a rectifierRectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
so that DC power for the inverter can be provided from main AC power. Since an inverter is the key component, variable-frequency drives are sometimes called inverter drives or just inverters.
Electric vehicle drives
Adjustable speed motor control inverters are currently used to power the traction motors in some electricRailway electrification system
A railway electrification system supplies electrical energy to railway locomotives and multiple units as well as trams so that they can operate without having an on-board prime mover. There are several different electrification systems in use throughout the world...
and diesel-electric rail vehicles as well as some battery electric vehicles and hybrid electric
Hybrid vehicle
A hybrid vehicle is a vehicle that uses two or more distinct power sources to move the vehicle. The term most commonly refers to hybrid electric vehicles , which combine an internal combustion engine and one or more electric motors.-Power:...
highway vehicles such as the Toyota Prius
Toyota Prius
The Toyota Prius is a full hybrid electric mid-size hatchback, formerly a compact sedan developed and manufactured by the Toyota Motor Corporation...
and Fisker Karma
Fisker Karma
The Fisker Karma is a plug-in hybrid luxury sports sedan produced by Fisker Automotive and manufactured at Valmet Automotive in Finland. The United States Environmental Protection Agency rated the Karma's combined city/highway fuel economy at equivalent in all-electric mode, and at in...
. Various improvements in inverter technology are being developed specifically for electric vehicle applications.
In vehicles with regenerative braking, the inverter also takes power from the motor (now acting as a generator) and stores it in the batteries.
Air conditioning
An air conditioner bearing the inverter tag uses a variable-frequency drive to control the speed of the motor and thus the compressor.The general case
A transformerTransformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
allows AC voltage to be stepped up or down to a desired voltage at the same frequency. Inverters, plus rectifiers for DC, can be designed to convert from any voltage, AC or DC, to any other voltage, also AC or DC, at any desired frequency. The output power can never exceed the input power, but efficiencies can be high, with a small proportion of the power dissipated as waste heat.
Circuit description


Basic designs
In one simple inverter circuit, DC power is connected to a transformerTransformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
through the centre tap of the primary winding. A switch is rapidly switched back and forth to allow current to flow back to the DC source following two alternate paths through one end of the primary winding and then the other. The alternation of the direction of current in the primary winding of the transformer produces alternating current
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
(AC) in the secondary circuit..
The electromechanical version of the switching device includes two stationary contacts and a spring supported moving contact. The spring holds the movable contact against one of the stationary contacts and an electromagnet pulls the movable contact to the opposite stationary contact. The current in the electromagnet is interrupted by the action of the switch so that the switch continually switches rapidly back and forth. This type of electromechanical inverter switch, called a vibrator
Vibrator (electronic)
In early electronics vibrators were used in inverter circuits to provide an alternating current electric power supply from a direct current source....
or buzzer, was once used in vacuum tube
Vacuum tube
In electronics, a vacuum tube, electron tube , or thermionic valve , reduced to simply "tube" or "valve" in everyday parlance, is a device that relies on the flow of electric current through a vacuum...
automobile radios. A similar mechanism has been used in door bells, buzzers and tattoo gun
Tattoo gun
A tattoo machine is a hand-held device generally used to create a tattoo, a permanent marking of the skin with indelible ink. Modern tattoo machines use electromagnetic coils to move an armature bar up and down, Connected to said armature bar is a barred needle grouping that pushes ink into the skin...
s.
As they became available with adequate power ratings, transistors and various other types of semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
switches have been incorporated into inverter circuit designs.
Output waveforms
The switch in the simple inverter described above, when not coupled to an output transformer, produces a square voltage waveformWaveform
Waveform means the shape and form of a signal such as a wave moving in a physical medium or an abstract representation.In many cases the medium in which the wave is being propagated does not permit a direct visual image of the form. In these cases, the term 'waveform' refers to the shape of a graph...
due to its simple off and on nature as opposed to the sinusoidal
Sine wave
The sine wave or sinusoid is a mathematical function that describes a smooth repetitive oscillation. It occurs often in pure mathematics, as well as physics, signal processing, electrical engineering and many other fields...
waveform that is the usual waveform of an AC power supply. Using Fourier analysis, periodic
Periodic function
In mathematics, a periodic function is a function that repeats its values in regular intervals or periods. The most important examples are the trigonometric functions, which repeat over intervals of length 2π radians. Periodic functions are used throughout science to describe oscillations,...
waveforms are represented as the sum of an infinite series of sine waves. The sine wave that has the same frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
as the original waveform is called the fundamental component. The other sine waves, called harmonics, that are included in the series have frequencies that are integral multiples of the fundamental frequency.
The quality of the inverter output waveform can be expressed by using the Fourier analysis data to calculate the total harmonic distortion
Total harmonic distortion
The total harmonic distortion, or THD, of a signal is a measurement of the harmonic distortion present and is defined as the ratio of the sum of the powers of all harmonic components to the power of the fundamental frequency...
(THD). The total harmonic distortion (THD) is the square root of the sum of the squares of the harmonic voltages divided by the fundamental voltage:

The quality of output waveform that is needed from an inverter depends on the characteristics of the connected load. Some loads need a nearly perfect sine wave voltage supply in order to work properly. Other loads may work quite well with a square wave voltage.
Advanced designs

Topology (electronics)
The topology of an electronic circuit is the form taken by the network of interconnections of the circuit components. Different specific values or ratings of the components are regarded as being the same topology....
and control strategies
Control system
A control system is a device, or set of devices to manage, command, direct or regulate the behavior of other devices or system.There are two common classes of control systems, with many variations and combinations: logic or sequential controls, and feedback or linear controls...
used in inverter designs. Different design approaches address various issues that may be more or less important depending on the way that the inverter is intended to be used.
The issue of waveform quality can be addressed in many ways. Capacitor
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
s and inductor
Inductor
An inductor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in a magnetic field. An inductor's ability to store magnetic energy is measured by its inductance, in units of henries...
s can be used to filter
Electronic filter
Electronic filters are electronic circuits which perform signal processing functions, specifically to remove unwanted frequency components from the signal, to enhance wanted ones, or both...
the waveform. If the design includes a transformer
Transformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
, filtering can be applied to the primary or the secondary side of the transformer or to both sides. Low-pass filters are applied to allow the fundamental component of the waveform to pass to the output while limiting the passage of the harmonic components. If the inverter is designed to provide power at a fixed frequency, a resonant
Resonance
In physics, resonance is the tendency of a system to oscillate at a greater amplitude at some frequencies than at others. These are known as the system's resonant frequencies...
filter can be used. For an adjustable frequency inverter, the filter must be tuned to a frequency that is above the maximum fundamental frequency.
Since most loads contain inductance, feedback rectifier
Rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
s or antiparallel
Antiparallel (electronics)
In electronics, two anti-parallel or inverse-parallel devices are connected in parallel but with their polarities reversed.One example is the TRIAC, which is comparable to two thyristors connected back-to-back , but on a single piece of silicon.Two LEDs can be paired this way, so that each protects...
diodes
Diode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
are often connected across each semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
switch to provide a path for the peak inductive load current when the switch is turned off. The antiparallel diodes are somewhat similar to the freewheeling diodes
Flyback diode
A flyback diode is a diode used to eliminate flyback, the sudden voltage spike seen across an inductive load when its supply voltage is suddenly reduced or removed.- Working principle :In its most simplified form with a voltage source connected to an inductor with a switch, we...
used in AC/DC converter circuits.
| waveform | signal transitions per period | harmonics eliminated | harmonics amplified | System Description | THD Total harmonic distortion The total harmonic distortion, or THD, of a signal is a measurement of the harmonic distortion present and is defined as the ratio of the sum of the powers of all harmonic components to the power of the fundamental frequency... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | - | - | 2-level square wave |
~45% | |
| 4 | 3, 9, 27,... | - | 3-level "modified square wave" |
> 23.8% | |
| 8 | 5-level "modified square wave" |
> 6.5% | |||
| 10 | 3, 5, 9, 27 | 7, 11,... | 2-level very slow PWM |
||
| 12 | 3, 5, 9, 27 | 7, 11,... | 3-level very slow PWM |
Fourier analysis reveals that a waveform, like a square wave, that is anti-symmetrical about the 180 degree point contains only odd harmonics, the 3rd, 5th, 7th, etc. Waveforms that have steps of certain widths and heights can attenuate certain lower harmonics at the expense of amplifying higher harmonics. For example, by inserting a zero-voltage step between the positive and negative sections of the square-wave, all of the harmonics that are divisible by three (3rd and 9th, etc.) can be eliminated. That leaves only the 5th, 7th, 11th, 13th etc. The required width of the steps is one third of the period for each of the positive and negative steps and one sixth of the period for each of the zero-voltage steps.
Changing the square wave as described above is an example of pulse-width modulation
Pulse-width modulation
Pulse-width modulation , or pulse-duration modulation , is a commonly used technique for controlling power to inertial electrical devices, made practical by modern electronic power switches....
(PWM). Modulating, or regulating the width of a square-wave pulse is often used as a method of regulating or adjusting an inverter's output voltage. When voltage control is not required, a fixed pulse width can be selected to reduce or eliminate selected harmonics. Harmonic elimination techniques are generally applied to the lowest harmonics because filtering is much more practical at high frequencies, where the filter components can be much smaller and less expensive. Multiple pulse-width or carrier based PWM control schemes produce waveforms that are composed of many narrow pulses. The frequency represented by the number of narrow pulses per second is called the switching frequency or carrier frequency. These control schemes are often used in variable-frequency motor control inverters because they allow a wide range of output voltage and frequency adjustment while also improving the quality of the waveform.
Multilevel inverters provide another approach to harmonic cancellation. Multilevel inverters provide an output waveform that exhibits multiple steps at several voltage levels. For example, it is possible to produce a more sinusoidal wave by having split-rail direct current
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
inputs at two voltages, or positive and negative inputs with a central ground
Ground (electricity)
In electrical engineering, ground or earth may be the reference point in an electrical circuit from which other voltages are measured, or a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth....
. By connecting the inverter output terminals in sequence between the positive rail and ground, the positive rail and the negative rail, the ground rail and the negative rail, then both to the ground rail, a stepped waveform is generated at the inverter output. This is an example of a three level inverter: the two voltages and ground.
Three phase inverters

Three-phase electric power
Three-phase electric power is a common method of alternating-current electric power generation, transmission, and distribution. It is a type of polyphase system and is the most common method used by grids worldwide to transfer power. It is also used to power large motors and other heavy loads...
inverters are used for variable-frequency drive applications and for high power applications such as HVDC
High-voltage direct current
A high-voltage, direct current electric power transmission system uses direct current for the bulk transmission of electrical power, in contrast with the more common alternating current systems. For long-distance transmission, HVDC systems may be less expensive and suffer lower electrical losses...
power transmission. A basic three-phase inverter consists of three single-phase inverter switches each connected to one of the three load terminals. For the most basic control scheme, the operation of the three switches is coordinated so that one switch operates at each 60 degree point of the fundamental output waveform. This creates a line-to-line output waveform that has six steps. The six-step waveform has a zero-voltage step between the positive and negative sections of the square-wave such that the harmonics that are multiples of three are eliminated as described above. When carrier-based PWM techniques are applied to six-step waveforms, the basic overall shape, or envelope, of the waveform is retained so that the 3rd harmonic and its multiples are cancelled.

Early inverters
From the late nineteenth century through the middle of the twentieth century, DC-to-AC power conversion was accomplished using rotary converterRotary converter
A rotary converter is a type of electrical machine which acts as a mechanical rectifier or inverter. It was used to convert AC to DC or DC to AC power before the advent of chemical or solid state power rectification...
s or motor-generator
Motor-generator
A motor-generator is a device for converting electrical power to another form. Motor-generator sets are used to convert frequency, voltage, or phase of power. They may also be used to isolate electrical loads from the electrical power supply line...
sets (M-G sets). In the early twentieth century, vacuum tubes and gas filled tube
Gas filled tube
A gas-filled tube, also known as a discharge tube, is an arrangement of electrodes in a gas within an insulating, temperature-resistant envelope. Although the envelope is typically glass, power tubes often use ceramics, and military tubes often use glass-lined metal...
s began to be used as switches in inverter circuits. The most widely used type of tube was the thyratron
Thyratron
A thyratron is a type of gas filled tube used as a high energy electrical switch and controlled rectifier. Triode, tetrode and pentode variations of the thyratron have been manufactured in the past, though most are of the triode design...
.
The origins of electromechanical inverters explain the source of the term inverter. Early AC-to-DC converters used an induction or synchronous AC motor direct-connected to a generator (dynamo) so that the generator's commutator reversed its connections at exactly the right moments to produce DC. A later development is the synchronous converter, in which the motor and generator windings are combined into one armature, with slip rings at one end and a commutator at the other and only one field frame. The result with either is AC-in, DC-out. With an M-G set, the DC can be considered to be separately generated from the AC; with a synchronous converter, in a certain sense it can be considered to be "mechanically rectified AC". Given the right auxiliary and control equipment, an M-G set or rotary converter can be "run backwards", converting DC to AC. Hence an inverter is an inverted converter.
Controlled rectifier inverters
Since early transistors were not available with sufficient voltage and current ratings for most inverter applications, it was the 1957 introduction of the thyristorThyristor
A thyristor is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating N and P-type material. They act as bistable switches, conducting when their gate receives a current trigger, and continue to conduct while they are forward biased .Some sources define silicon controlled rectifiers and...
or silicon-controlled rectifier
Silicon-controlled rectifier
A silicon-controlled rectifier is a four-layer solid state device that controls current. The name "silicon controlled rectifier" or SCR is General Electric's trade name for a type of thyristor. The SCR was developed by a team of power engineers led by Gordon Hall and commercialized by Frank W...
(SCR) that initiated the transition to solid state inverter circuits.
The commutation requirements of SCRs are a key consideration in SCR circuit designs. SCRs do not turn off or commutate automatically when the gate control signal is shut off. They only turn off when the forward current is reduced to below the minimum holding current, which varies with each kind of SCR, through some external process. For SCRs connected to an AC power source, commutation occurs naturally every time the polarity of the source voltage reverses. SCRs connected to a DC power source usually require a means of forced commutation that forces the current to zero when commutation is required. The least complicated SCR circuits employ natural commutation rather than forced commutation. With the addition of forced commutation circuits, SCRs have been used in the types of inverter circuits described above.
In applications where inverters transfer power from a DC power source to an AC power source, it is possible to use AC-to-DC controlled rectifier circuits operating in the inversion mode. In the inversion mode, a controlled rectifier circuit operates as a line commutated inverter. This type of operation can be used in HVDC power transmission systems and in regenerative braking
Regenerative brake
A regenerative brake is an energy recovery mechanism which slows a vehicle or object down by converting its kinetic energy into another form, which can be either used immediately or stored until needed...
operation of motor control systems.
Another type of SCR inverter circuit is the current source input (CSI) inverter. A CSI inverter is the dual
Dual (electronics)
In physics, the electromagnetic dual concept is based on the idea that, in the static case, electromagnetism has two separate facets: electric fields and magnetic fields. Expressions in one of these will have a directly analogous, or dual, expression in the other...
of a six-step voltage source inverter. With a current source inverter, the DC power supply is configured as a current source
Current source
A current source is an electrical or electronic device that delivers or absorbs electric current. A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current sink is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply...
rather than a voltage source
Voltage source
In electric circuit theory, an ideal voltage source is a circuit element where the voltage across it is independent of the current through it. A voltage source is the dual of a current source. In analysis, a voltage source supplies a constant DC or AC potential between its terminals for any current...
. The inverter SCRs are switched in a six-step sequence to direct the current to a three-phase AC load as a stepped current waveform. CSI inverter commutation methods include load commutation and parallel capacitor commutation. With both methods, the input current regulation assists the commutation. With load commutation, the load is a synchronous motor operated at a leading power factor.
As they have become available in higher voltage and current ratings, semiconductors such as transistors or IGBTs that can be turned off by means of control signals have become the preferred switching components for use in inverter circuits.
Rectifier and inverter pulse numbers
Rectifier circuits are often classified by the number of current pulses that flow to the DC side of the rectifier per cycle of AC input voltage. A single-phase half-wave rectifier is a one-pulse circuit and a single-phase full-wave rectifier is a two-pulse circuit. A three-phase half-wave rectifier is a three-pulse circuit and a three-phase full-wave rectifier is a six-pulse circuit.With three-phase rectifiers, two or more rectifiers are sometimes connected in series or parallel to obtain higher voltage or current ratings. The rectifier inputs are supplied from special transformers that provide phase shifted outputs. This has the effect of phase multiplication. Six phases are obtained from two transformers, twelve phases from three transformers and so on. The associated rectifier circuits are 12-pulse rectifiers, 18-pulse rectifiers and so on.
When controlled rectifier circuits are operated in the inversion mode, they would be classified by pulse number also. Rectifier circuits that have a higher pulse number have reduced harmonic content in the AC input current and reduced ripple in the DC output voltage. In the inversion mode, circuits that have a higher pulse number have lower harmonic content in the AC output voltage waveform.
See also
- RectifierRectifierA rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
- Solar inverter
- Distributed inverter architecture
- Grid tie inverterGrid tie inverterA grid-tie inverter is a special type of inverter that converts direct current electricity into alternating current electricity and feeds it into an existing electrical grid...
- Push-pull converterPush-pull converterA push–pull converter is a type of DC to DC converter that uses a transformer to change the voltage of a DC power supply. The transformer's ratio is arbitrary but fixed; however, in many circuit implementations the duty cycle of the switching action can be varied to effect a range of voltage ratios...
- Static inverter plantStatic inverter plantA static inverter station, also known as an HVDC Converter Station, is the terminal equipment for a high-voltage direct-current transmission line, in which direct current is converted to three-phase alternating current, and, usually, the reverse...
- Switched-mode power supply (SMPS)Switched-mode power supplyA switched-mode power supply is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator in order to be highly efficient in the conversion of electrical power...
- Space vector modulationSpace vector modulationSpace vector modulation is an algorithm for the control of pulse width modulation . It is used for the creation of alternating current waveforms; most commonly to drive 3 phase AC powered motors at varying speeds from DC using multiple class-D amplifiers. There are various variations of SVM that...
- Variable-frequency drive
- Inverter (air conditioning)Inverter (air conditioning)The inverter tag found on some air conditioners signifies the ability of the unit to continuously regulate its thermal transfer flow by altering the speed of the compressor in response to cooling demand....
General references
- Dr. Ulrich Nicolai, Dr. Tobias Reimann, Prof. Jürgen Petzoldt, Josef Lutz: Application Manual IGBT and MOSFET Power Modules, 1. Edition, ISLE Verlag, 1998, ISBN 3-932633-24-5 PDF-Version

