
Hindu–Arabic numeral system
Encyclopedia
The Hindu–Arabic numeral system or Hindu numeral system is a positional
decimal
numeral system
developed between the 1st and 5th centuries by Indian mathematicians
, adopted by Persian
(Al-Khwarizmi's circa 825 book On the Calculation with Hindu Numerals) and Arab mathematicians (Al-Kindi
's circa 830 volumes On the Use of the Indian Numerals), and spread to the western world by the High Middle Ages
.
The system is based on ten (originally nine) different glyphs. The symbols (glyphs) used to represent the system are in principle independent of the system itself. The glyphs in actual use are descended from Indian Brahmi numeral
s, and have split into various typographical variants since the Middle Ages
.
These symbol sets can be divided into three main families: the Indian numerals
used in India
, the Eastern Arabic numerals
used in Egypt
and the Middle East
and the West Arabic numerals used in the Maghreb
and in Europe
.
in a decimal
system. In a more developed form, positional notation also uses a decimal marker
(at first a mark over the ones digit but now more usually a decimal point or a decimal comma which separates the ones place from the tenths place), and also a symbol for "these digits recur ad infinitum
." In modern usage, this latter symbol is usually a vinculum (a horizontal line placed over the repeating digits). In this more developed form, the numeral system can symbolize any rational number
using only 13 symbols (the ten digits, decimal marker, vinculum, and an optional prepended dash
to indicate a negative number).
Despite the numeral system being described as the "Hindu–Arabic numeral system", the system was not jointly developed by Hindus (inhabitants of India
) and Arabs. It had been developed by Indian mathematicians and in use extensively throughout India, before being adopted by the Persian mathematicians in India and passed on to the Arabs further west. The numeral system was transmitted to Europe in the Middle Ages. The use of Arabic numerals spread around the world through European trade, books and colonialism. Today they are the most common symbolic representation of numbers in the world.
Although generally found in text written with the Arabic abjad
("alphabet"), numbers written with these numerals also place the most-significant digit to the left, so they read from left to right. The requisite changes in reading direction are found in text that mixes left-to-right writing systems with right-to-left systems.
Tobias Dantzig, the father of George Dantzig
, had this to say in Number:
s.
The symbols used to represent the system have split into various typographical variants since the Middle Ages
, arranged in three main groups:
 As in many numbering systems, the numbers 1, 2, and 3 represent simple tally marks. 1 being a single line, 2 being two lines (now connected by a diagonal) and 3 being three lines (now connected by two vertical lines). After three, numbers tend to become more complex symbols (examples are the Chinese/Japanese numbers and Roman numerals
As in many numbering systems, the numbers 1, 2, and 3 represent simple tally marks. 1 being a single line, 2 being two lines (now connected by a diagonal) and 3 being three lines (now connected by two vertical lines). After three, numbers tend to become more complex symbols (examples are the Chinese/Japanese numbers and Roman numerals
). Theorists believe that this is because it becomes difficult to instantaneously count objects past three
.
s at the basis of the system predate the Common Era. They replaced the earlier Kharosthi numerals used since the 4th century BC. Brandi and Prosthesis numerals were used alongside one another in the Maurya Empire
period, both appearing on the 3rd century BC edicts of Ashoka
.
Buddhist inscriptions from around 300 BC use the symbols that became 1, 4 and 6. One century later, their use of the symbols that became 2, 4, 6, 7 and 9 was recorded. These Brahmi numeral
s are the ancestors of the Hindu–Arabic glyphs 1 to 9, but they were not used as a positional system with a zero
, and there were rather separate numerals for each of the tens (10, 20, 30, etc.).
The actual numeral system, including positional notation and use of zero, is in principle independent of the glyphs used, and significantly younger than the Brahmi numerals.
. Although date of the composition of the manuscript is uncertain, the language used in the manuscript indicates that it could not have been composed any later than 400 AD. The development of the positional decimal system takes its origins in Indian mathematics
during the Gupta period.
Around 500 CE the astronomer Aryabhata
uses the word kha ("emptiness") to mark "zero" in tabular arrangements of digits.
The 7th century Brahmasphuta Siddhanta
contains a comparatively advanced understanding of the mathematical role of zero
.
The Sanskrit translation of the lost 5th century Prakrit Jaina cosmological
text Lokavibhaga
may preserve an early instance of positional use of zero.
These Indian developments were taken up in Islamic mathematics
in the 8th century, as recorded in al-Qifti
's Chronology of the scholars (early 13th century).
The numeral system came to be known to both the Muslim/Persian
mathematician Al-Khwarizmi, who wrote a book, On the Calculation with Hindu Numerals in about 825, and the Persian
mathematician Al-Kindi
, who wrote four volumes, On the Use of the Indian Numerals ( [kitāb fī isti'māl al-'adād al-hindī]) around 830. These earlier text did not used the Hindu numerals. Kushyar ibn Labban
who wrote Kitab fi usul hisab al-hind(Principles of Hindu Reckoning
) is one of the oldest surviving manuscript used the Hindu numerals. These books are principally responsible for the diffusion of the Indian system of numeration throughout the Islamic world and ultimately also to Europe http://www-gap.dcs.st-and.ac.uk/%7Ehistory/HistTopics/Indian_numerals.html.
The first dated and undisputed inscription showing the use of zero at is at Gwalior, dating to 876 AD.
In 10th century Islamic mathematics, the system was extended to include fraction
s, as recorded in a treatise by Syrian mathematician Abu'l-Hasan al-Uqlidisi
in 952–953.
 In Christian Europe, the first mention and representation of Hindu-Arabic numerals (from one to nine, without zero), is in the Codex Vigilanus
In Christian Europe, the first mention and representation of Hindu-Arabic numerals (from one to nine, without zero), is in the Codex Vigilanus
, an illuminated
compilation of various historical documents from the Visigothic period in Spain
, written in the year 976
by three monks of the Riojan
monastery of San Martín de Albelda
.
Between 967
and 969
, Gerbert of Aurillac discovered and studied Arab science in the Catalan abbeys. Later he obtained from these places the book De multiplicatione et divisione (On the multiplication and division). After having become pope Sylvester II in the year 999
, he introduced a new model of abacus
, the so called Abacus of Gerbert, by adopting tokens representing Hindu-Arab numerals, from one to nine.
Leonardo Fibonacci
brought this system to Europe. His book Liber Abaci
introduced Arabic numerals, the use of zero, and the decimal place system to the Latin world. The numeral system came to be called "Arabic" by the Europeans. It was used in European mathematics from the 12th century, and entered common use from the 15th century to replace Roman numerals
. Robert Chester
translated the Latin into English.
The familiar shape of the Western Arabic glyphs as now used with the Latin alphabet, (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9) are the product of the late 15th to early 16th century, when they enter early typesetting
.
Muslim scientists used the Babylonian numeral system
, and merchants used the Abjad numerals
, a system similar to the Greek numeral system
and the Hebrew numeral system
. Similarly, Fibonacci
's introduction of the system to Europe was restricted to learned circles.
The credit of first establishing widespread understanding and usage of the decimal positional notation among the general population goes to Adam Ries
, an author of the German Renaissance
, whose 1522 Rechenung auff der linihen und federn was targeted at the apprentices of businessmen and craftsmen.
, Gautama Siddha
introduced Indian numerals with zero in 718, but Chinese mathematicians
did not find them useful, as they had already had the decimal positional counting rods
.
In Chinese numerals, a circle (〇) is used to write zero in Suzhou numerals
. Many historians think it was imported from Indian numerals
by Gautama Siddha
in 718
, but some think it was created from the Chinese text space filler "□".
Chinese and Japan
ese finally adopted the Hindu–Arabic numerals in the 19th century, abandoning counting rods.
 The "Western Arabic" numerals as they were in common use in Europe since the Baroque
The "Western Arabic" numerals as they were in common use in Europe since the Baroque
period have secondarily found worldwide use together with the Latin alphabet
, and even significantly beyond the contemporary spread of the Latin alphabet, intruding into the writing systems in regions where other variants of the Hindu–Arabic numerals had been in use, but also in conjunction with Chinese and Japanese writing (see Chinese numerals
, Japanese numerals
).
Positional notation
Positional notation or place-value notation is a method of representing or encoding numbers. Positional notation is distinguished from other notations for its use of the same symbol for the different orders of magnitude...
decimal
Decimal
The decimal numeral system has ten as its base. It is the numerical base most widely used by modern civilizations....
numeral system
Numeral system
A numeral system is a writing system for expressing numbers, that is a mathematical notation for representing numbers of a given set, using graphemes or symbols in a consistent manner....
developed between the 1st and 5th centuries by Indian mathematicians
Indian mathematics
Indian mathematics emerged in the Indian subcontinent from 1200 BCE until the end of the 18th century. In the classical period of Indian mathematics , important contributions were made by scholars like Aryabhata, Brahmagupta, and Bhaskara II. The decimal number system in use today was first...
, adopted by Persian
Persian people
The Persian people are part of the Iranian peoples who speak the modern Persian language and closely akin Iranian dialects and languages. The origin of the ethnic Iranian/Persian peoples are traced to the Ancient Iranian peoples, who were part of the ancient Indo-Iranians and themselves part of...
(Al-Khwarizmi's circa 825 book On the Calculation with Hindu Numerals) and Arab mathematicians (Al-Kindi
Al-Kindi
' , known as "the Philosopher of the Arabs", was a Muslim Arab philosopher, mathematician, physician, and musician. Al-Kindi was the first of the Muslim peripatetic philosophers, and is unanimously hailed as the "father of Islamic or Arabic philosophy" for his synthesis, adaptation and promotion...
's circa 830 volumes On the Use of the Indian Numerals), and spread to the western world by the High Middle Ages
High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages was the period of European history around the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries . The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which by convention end around 1500....
.
The system is based on ten (originally nine) different glyphs. The symbols (glyphs) used to represent the system are in principle independent of the system itself. The glyphs in actual use are descended from Indian Brahmi numeral
Brahmi numeral
The Brahmi numerals are an indigenous Indian numeral system attested from the 3rd century BCE . They are the direct graphic ancestors of the modern Indic and Hindu-Arabic numerals. However, they were conceptually distinct from these later systems, as they were not used as a positional system with a...
s, and have split into various typographical variants since the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
.
These symbol sets can be divided into three main families: the Indian numerals
Indian numerals
Most of the positional base 10 numeral systems in the world have originated from India, where the concept of positional numeration was first developed...
used in India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, the Eastern Arabic numerals
Eastern Arabic numerals
The Eastern Arabic numerals are the symbols used to represent the Hindu-Arabic numeral system in conjunction with the Arabic alphabet in the countries of the Arab world....
used in Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
and the Middle East
Middle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
and the West Arabic numerals used in the Maghreb
Maghreb
The Maghreb is the region of Northwest Africa, west of Egypt. It includes five countries: Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and Mauritania and the disputed territory of Western Sahara...
and in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
.
Positional notation
The Hindu numeral system is designed for positional notationPositional notation
Positional notation or place-value notation is a method of representing or encoding numbers. Positional notation is distinguished from other notations for its use of the same symbol for the different orders of magnitude...
in a decimal
Decimal
The decimal numeral system has ten as its base. It is the numerical base most widely used by modern civilizations....
system. In a more developed form, positional notation also uses a decimal marker
Decimal separator
Different symbols have been and are used for the decimal mark. The choice of symbol for the decimal mark affects the choice of symbol for the thousands separator used in digit grouping. Consequently the latter is treated in this article as well....
(at first a mark over the ones digit but now more usually a decimal point or a decimal comma which separates the ones place from the tenths place), and also a symbol for "these digits recur ad infinitum
Ad infinitum
Ad infinitum is a Latin phrase meaning "to infinity."In context, it usually means "continue forever, without limit" and thus can be used to describe a non-terminating process, a non-terminating repeating process, or a set of instructions to be repeated "forever," among other uses...
." In modern usage, this latter symbol is usually a vinculum (a horizontal line placed over the repeating digits). In this more developed form, the numeral system can symbolize any rational number
Rational number
In mathematics, a rational number is any number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction a/b of two integers, with the denominator b not equal to zero. Since b may be equal to 1, every integer is a rational number...
using only 13 symbols (the ten digits, decimal marker, vinculum, and an optional prepended dash
Dash
A dash is one of several kinds of punctuation mark. Dashes appear similar to hyphens, but differ from them primarily in length, and serve different functions. The most common versions of the dash are the en dash and the em dash .-Common dashes:...
to indicate a negative number).
Despite the numeral system being described as the "Hindu–Arabic numeral system", the system was not jointly developed by Hindus (inhabitants of India
Indian people
Indian people or Indisians constitute the Asian nation and pan-ethnic group native to India, which forms the south of Asia, containing 17.31% of the world's population. The Indian nationality is in essence made up of regional nationalities, reflecting the rich and complex history of India...
) and Arabs. It had been developed by Indian mathematicians and in use extensively throughout India, before being adopted by the Persian mathematicians in India and passed on to the Arabs further west. The numeral system was transmitted to Europe in the Middle Ages. The use of Arabic numerals spread around the world through European trade, books and colonialism. Today they are the most common symbolic representation of numbers in the world.
Although generally found in text written with the Arabic abjad
Abjad
An abjad is a type of writing system in which each symbol always or usually stands for a consonant; the reader must supply the appropriate vowel....
("alphabet"), numbers written with these numerals also place the most-significant digit to the left, so they read from left to right. The requisite changes in reading direction are found in text that mixes left-to-right writing systems with right-to-left systems.
Tobias Dantzig, the father of George Dantzig
George Dantzig
George Bernard Dantzig was an American mathematical scientist who made important contributions to operations research, computer science, economics, and statistics....
, had this to say in Number:
- "This long period of nearly five thousand years saw the rise and fall of many a civilization, each leaving behind it a heritage of literature, art, philosophy, and religion. But what was the net achievement in the field of reckoning, the earliest art practiced by man? An inflexible numeration so crude as to make progress well nigh impossible, and a calculating device so limited in scope that even elementary calculations called for the services of an expert [...] Man used these devices for thousands of years without contributing a single important idea to the system [...] Even when compared with the slow growth of ideas during the dark ages, the history of reckoning presents a peculiar picture of desolate stagnation. When viewed in this light, the achievements of the unknown Hindu, who some time in the first centuries of our era discovered the principle of position, assumes the importance of a world event."
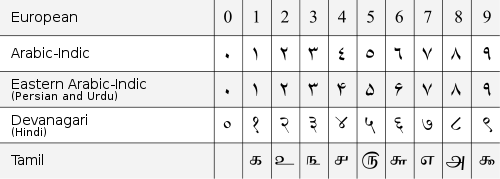
Symbols
Various symbol sets are used to represent numbers in the Hindu–Arabic numeral, all of which evolved from the Brahmi numeralBrahmi numeral
The Brahmi numerals are an indigenous Indian numeral system attested from the 3rd century BCE . They are the direct graphic ancestors of the modern Indic and Hindu-Arabic numerals. However, they were conceptually distinct from these later systems, as they were not used as a positional system with a...
s.
The symbols used to represent the system have split into various typographical variants since the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
, arranged in three main groups:
- the widespread Western "Arabic numeralsArabic numeralsArabic numerals or Hindu numerals or Hindu-Arabic numerals or Indo-Arabic numerals are the ten digits . They are descended from the Hindu-Arabic numeral system developed by Indian mathematicians, in which a sequence of digits such as "975" is read as a numeral...
" used with the LatinLatin alphabetThe Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
, CyrillicCyrillic alphabetThe Cyrillic script or azbuka is an alphabetic writing system developed in the First Bulgarian Empire during the 10th century AD at the Preslav Literary School...
, and Greek alphabetGreek alphabetThe Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
s in the table below labelled "European", descended from the "West Arabic numerals" which were developed in al-AndalusAl-AndalusAl-Andalus was the Arabic name given to a nation and territorial region also commonly referred to as Moorish Iberia. The name describes parts of the Iberian Peninsula and Septimania governed by Muslims , at various times in the period between 711 and 1492, although the territorial boundaries...
and the MaghrebMaghrebThe Maghreb is the region of Northwest Africa, west of Egypt. It includes five countries: Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and Mauritania and the disputed territory of Western Sahara...
(There are two typographicTypographyTypography is the art and technique of arranging type in order to make language visible. The arrangement of type involves the selection of typefaces, point size, line length, leading , adjusting the spaces between groups of letters and adjusting the space between pairs of letters...
styles for rendering European numerals, known as lining figures and text figuresText figuresText figures are numerals typeset with varying heights in a fashion that resembles a typical line of running text, hence the name...
). - the "Arabic–Indic" or "Eastern Arabic numeralsEastern Arabic numeralsThe Eastern Arabic numerals are the symbols used to represent the Hindu-Arabic numeral system in conjunction with the Arabic alphabet in the countries of the Arab world....
" used with the Arabic alphabetArabic alphabetThe Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has...
, developed primarily in what is now IraqIraqIraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
. A variant of the Eastern Arabic numerals used in Persian and Urdu. There is substantial variation in usage of glyphs for the Eastern Arabic-Indic digits, especially for the digits four, five, six, and seven. - the Indian numeralsIndian numeralsMost of the positional base 10 numeral systems in the world have originated from India, where the concept of positional numeration was first developed...
in use with scripts of the Brahmic familyBrahmic familyThe Brahmic or Indic scripts are a family of abugida writing systems. They are used throughout South Asia , Southeast Asia, and parts of Central and East Asia, and are descended from the Brāhmī script of the ancient Indian subcontinent...
in India and Southeast Asia.

Roman numerals
The numeral system of ancient Rome, or Roman numerals, uses combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet to signify values. The numbers 1 to 10 can be expressed in Roman numerals as:...
). Theorists believe that this is because it becomes difficult to instantaneously count objects past three
Subitizing and counting
Subitizing, coined in 1949 by E.L. Kaufman et al. refers to the rapid, accurate, and confident judgments of number performed for small numbers of items. The term is derived from the Latin adjective subitus and captures a feeling of immediately knowing how many items lie within the visual scene,...
.
History
Predecessors
The Brahmi numeralBrahmi numeral
The Brahmi numerals are an indigenous Indian numeral system attested from the 3rd century BCE . They are the direct graphic ancestors of the modern Indic and Hindu-Arabic numerals. However, they were conceptually distinct from these later systems, as they were not used as a positional system with a...
s at the basis of the system predate the Common Era. They replaced the earlier Kharosthi numerals used since the 4th century BC. Brandi and Prosthesis numerals were used alongside one another in the Maurya Empire
Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in ancient India, ruled by the Mauryan dynasty from 321 to 185 BC...
period, both appearing on the 3rd century BC edicts of Ashoka
Edicts of Ashoka
The Edicts of Ashoka are a collection of 33 inscriptions on the Pillars of Ashoka, as well as boulders and cave walls, made by the Emperor Ashoka of the Mauryan dynasty during his reign from 269 BCE to 231 BCE. These inscriptions are dispersed throughout the areas of modern-day Bangladesh, India,...
.
Buddhist inscriptions from around 300 BC use the symbols that became 1, 4 and 6. One century later, their use of the symbols that became 2, 4, 6, 7 and 9 was recorded. These Brahmi numeral
Brahmi numeral
The Brahmi numerals are an indigenous Indian numeral system attested from the 3rd century BCE . They are the direct graphic ancestors of the modern Indic and Hindu-Arabic numerals. However, they were conceptually distinct from these later systems, as they were not used as a positional system with a...
s are the ancestors of the Hindu–Arabic glyphs 1 to 9, but they were not used as a positional system with a zero
0 (number)
0 is both a numberand the numerical digit used to represent that number in numerals.It fulfills a central role in mathematics as the additive identity of the integers, real numbers, and many other algebraic structures. As a digit, 0 is used as a placeholder in place value systems...
, and there were rather separate numerals for each of the tens (10, 20, 30, etc.).
The actual numeral system, including positional notation and use of zero, is in principle independent of the glyphs used, and significantly younger than the Brahmi numerals.
Development
The place-value system is used in the Bakhshali ManuscriptBakhshali Manuscript
The Bakhshali Manuscript is an Ancient Indian mathematical manuscript written on birch bark which was found near the village of Bakhshali in 1881 in what was then the North-West Frontier Province of British India...
. Although date of the composition of the manuscript is uncertain, the language used in the manuscript indicates that it could not have been composed any later than 400 AD. The development of the positional decimal system takes its origins in Indian mathematics
Indian mathematics
Indian mathematics emerged in the Indian subcontinent from 1200 BCE until the end of the 18th century. In the classical period of Indian mathematics , important contributions were made by scholars like Aryabhata, Brahmagupta, and Bhaskara II. The decimal number system in use today was first...
during the Gupta period.
Around 500 CE the astronomer Aryabhata
Aryabhata
Aryabhata was the first in the line of great mathematician-astronomers from the classical age of Indian mathematics and Indian astronomy...
uses the word kha ("emptiness") to mark "zero" in tabular arrangements of digits.
The 7th century Brahmasphuta Siddhanta
Brahmasphutasiddhanta
The main work of Brahmagupta, Brāhmasphuṭasiddhānta , written c.628, contains ideas including a good understanding of the mathematical role of zero, rules for manipulating both negative and positive numbers, a method for computing square roots, methods of solving linear and some quadratic...
contains a comparatively advanced understanding of the mathematical role of zero
0 (number)
0 is both a numberand the numerical digit used to represent that number in numerals.It fulfills a central role in mathematics as the additive identity of the integers, real numbers, and many other algebraic structures. As a digit, 0 is used as a placeholder in place value systems...
.
The Sanskrit translation of the lost 5th century Prakrit Jaina cosmological
Jain cosmology
Jain cosmology is the description of the shape and functioning of the physical and metaphysical Universe and its constituents according to Jainism, which includes the canonical Jain texts, commentaries and the writings of the Jain philosopher-monks...
text Lokavibhaga
Lokavibhaga
The Lokavibhaga is a Jain cosmological text originally composed in Prakrit by a Digambara monk, Sarvanandi, surviving in a Sanskrit version compiled by one Simhasuri...
may preserve an early instance of positional use of zero.
These Indian developments were taken up in Islamic mathematics
Islamic mathematics
In the history of mathematics, mathematics in medieval Islam, often termed Islamic mathematics or Arabic mathematics, covers the body of mathematics preserved and developed under the Islamic civilization between circa 622 and 1600...
in the 8th century, as recorded in al-Qifti
Al-Qifti
Al-Qifti or Ibn al-Qifti was a medieval Muslim writer. He is remembered today mainly for his History of Learned Men.-Life and Works:...
's Chronology of the scholars (early 13th century).
The numeral system came to be known to both the Muslim/Persian
Persian people
The Persian people are part of the Iranian peoples who speak the modern Persian language and closely akin Iranian dialects and languages. The origin of the ethnic Iranian/Persian peoples are traced to the Ancient Iranian peoples, who were part of the ancient Indo-Iranians and themselves part of...
mathematician Al-Khwarizmi, who wrote a book, On the Calculation with Hindu Numerals in about 825, and the Persian
Persian people
The Persian people are part of the Iranian peoples who speak the modern Persian language and closely akin Iranian dialects and languages. The origin of the ethnic Iranian/Persian peoples are traced to the Ancient Iranian peoples, who were part of the ancient Indo-Iranians and themselves part of...
mathematician Al-Kindi
Al-Kindi
' , known as "the Philosopher of the Arabs", was a Muslim Arab philosopher, mathematician, physician, and musician. Al-Kindi was the first of the Muslim peripatetic philosophers, and is unanimously hailed as the "father of Islamic or Arabic philosophy" for his synthesis, adaptation and promotion...
, who wrote four volumes, On the Use of the Indian Numerals ( [kitāb fī isti'māl al-'adād al-hindī]) around 830. These earlier text did not used the Hindu numerals. Kushyar ibn Labban
Kushyar ibn Labban
Abul-Hasan Kūshyār ibn Labbān ibn Bashahri Gilani , also known as Kūshyār Gīlānī , was a Persian mathematician, geographer, and astronomer from Gilan, south of the Caspian Sea, Iran....
who wrote Kitab fi usul hisab al-hind(Principles of Hindu Reckoning
Principles of Hindu Reckoning
Principles of Hindu Reckoning is a mathematics book written by 10th–11th-century Persian mathematician Kushyar ibn Labban...
) is one of the oldest surviving manuscript used the Hindu numerals. These books are principally responsible for the diffusion of the Indian system of numeration throughout the Islamic world and ultimately also to Europe http://www-gap.dcs.st-and.ac.uk/%7Ehistory/HistTopics/Indian_numerals.html.
The first dated and undisputed inscription showing the use of zero at is at Gwalior, dating to 876 AD.
In 10th century Islamic mathematics, the system was extended to include fraction
Fraction
In common usage a fraction is any part of a unit.Fraction may also mean:*Fraction , one of more equal parts of something, eg...
s, as recorded in a treatise by Syrian mathematician Abu'l-Hasan al-Uqlidisi
Abu'l-Hasan al-Uqlidisi
Abu'l Hasan Ahmad ibn Ibrahim Al-Uqlidisi was an Arab mathematician who was active in Damascus and Baghdad. As his surname indicates, he was a copyist of Euclid's works. He wrote the earliest surviving book on the positional use of the Arabic numerals, Kitab al-Fusul fi al-Hisab al-Hindi around 952...
in 952–953.
Adoption in Europe

Codex Vigilanus
The Codex Vigilanus or Códice Albeldense , full name Codex Conciliorum Albeldensis seu Vigilanus, is an illuminated compilation of various historical documents from the Visigothic period in Spain...
, an illuminated
Illuminated manuscript
An illuminated manuscript is a manuscript in which the text is supplemented by the addition of decoration, such as decorated initials, borders and miniature illustrations...
compilation of various historical documents from the Visigothic period in Spain
Hispania
Another theory holds that the name derives from Ezpanna, the Basque word for "border" or "edge", thus meaning the farthest area or place. Isidore of Sevilla considered Hispania derived from Hispalis....
, written in the year 976
976
Year 976 was a leap year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar.- Byzantine Empire :* January 10 – Basil II becomes Eastern Roman Emperor .- Europe :...
by three monks of the Riojan
La Rioja (Spain)
La Rioja is an autonomous community and a province of northern Spain. Its capital is Logroño. Other cities and towns in the province include Calahorra, Arnedo, Alfaro, Haro, Santo Domingo de la Calzada, and Nájera.-History:...
monastery of San Martín de Albelda
San Martín de Albelda
San Martín de Albelda was a Riojan monastery, whose ruins now lie within the municipal boundaries of Albelda de Iregua. It was an important and advanced cultural centre in Spain and western Europe during the tenth century....
.
Between 967
967
Year 967 was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar.-Africa:* The Fatimid general Gawhar al-Siqilli launches a new victorious campaign in the West of the Magrib.- Europe :...
and 969
969
Year 969 was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar.- Byzantine Empire :* December 11 – John I Tzimiskes becomes Byzantine Emperor after assassinating Nikephoros II Phokas....
, Gerbert of Aurillac discovered and studied Arab science in the Catalan abbeys. Later he obtained from these places the book De multiplicatione et divisione (On the multiplication and division). After having become pope Sylvester II in the year 999
999
Year 999 was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar.- Europe :* Silesia is incorporated into territory ruled by Boleslaus I of Poland.* The Orsay commune is founded.- Asia :...
, he introduced a new model of abacus
Abacus
The abacus, also called a counting frame, is a calculating tool used primarily in parts of Asia for performing arithmetic processes. Today, abaci are often constructed as a bamboo frame with beads sliding on wires, but originally they were beans or stones moved in grooves in sand or on tablets of...
, the so called Abacus of Gerbert, by adopting tokens representing Hindu-Arab numerals, from one to nine.
Leonardo Fibonacci
Fibonacci
Leonardo Pisano Bigollo also known as Leonardo of Pisa, Leonardo Pisano, Leonardo Bonacci, Leonardo Fibonacci, or, most commonly, simply Fibonacci, was an Italian mathematician, considered by some "the most talented western mathematician of the Middle Ages."Fibonacci is best known to the modern...
brought this system to Europe. His book Liber Abaci
Liber Abaci
Liber Abaci is a historic book on arithmetic by Leonardo of Pisa, known later by his nickname Fibonacci...
introduced Arabic numerals, the use of zero, and the decimal place system to the Latin world. The numeral system came to be called "Arabic" by the Europeans. It was used in European mathematics from the 12th century, and entered common use from the 15th century to replace Roman numerals
Roman numerals
The numeral system of ancient Rome, or Roman numerals, uses combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet to signify values. The numbers 1 to 10 can be expressed in Roman numerals as:...
. Robert Chester
Robert Chester (poet)
Robert Chester is the mysterious author of the poem Love's Martyr which was published in 1601 as the main poem in a collection which also included much shorter poems by William Shakespeare, Ben Jonson, George Chapman and John Marston, along with the anonymous "Vatum Chorus" and "Ignoto"...
translated the Latin into English.
The familiar shape of the Western Arabic glyphs as now used with the Latin alphabet, (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9) are the product of the late 15th to early 16th century, when they enter early typesetting
Typesetting
Typesetting is the composition of text by means of types.Typesetting requires the prior process of designing a font and storing it in some manner...
.
Muslim scientists used the Babylonian numeral system
Babylonian numerals
Babylonian numerals were written in cuneiform, using a wedge-tipped reed stylus to make a mark on a soft clay tablet which would be exposed in the sun to harden to create a permanent record....
, and merchants used the Abjad numerals
Abjad numerals
The Abjad numerals are a decimal numeral system in which the 28 letters of the Arabic alphabet are assigned numerical values. They have been used in the Arabic-speaking world since before the 8th century Arabic numerals...
, a system similar to the Greek numeral system
Greek numerals
Greek numerals are a system of representing numbers using letters of the Greek alphabet. They are also known by the names Ionian numerals, Milesian numerals , Alexandrian numerals, or alphabetic numerals...
and the Hebrew numeral system
Hebrew numerals
The system of Hebrew numerals is a quasi-decimal alphabetic numeral system using the letters of the Hebrew alphabet.In this system, there is no notation for zero, and the numeric values for individual letters are added together...
. Similarly, Fibonacci
Fibonacci
Leonardo Pisano Bigollo also known as Leonardo of Pisa, Leonardo Pisano, Leonardo Bonacci, Leonardo Fibonacci, or, most commonly, simply Fibonacci, was an Italian mathematician, considered by some "the most talented western mathematician of the Middle Ages."Fibonacci is best known to the modern...
's introduction of the system to Europe was restricted to learned circles.
The credit of first establishing widespread understanding and usage of the decimal positional notation among the general population goes to Adam Ries
Adam Ries
Adam Ries was a German mathematician. He is also known by the name Adam Riese.- Life :Almost nothing is known about Ries' childhood, youth and education. It is not even possible to determine the year of his birth with certainty. The caption on the only known contemporary portrait of the...
, an author of the German Renaissance
German Renaissance
The German Renaissance, part of the Northern Renaissance, was a cultural and artistic movement that spread among German thinkers in the 15th and 16th centuries, which originated from the Italian Renaissance in Italy...
, whose 1522 Rechenung auff der linihen und federn was targeted at the apprentices of businessmen and craftsmen.
Adoption in East Asia
In ChinaChina
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
, Gautama Siddha
Gautama Siddha
Gautama Siddha, astronomer, astrologer and compiler of Indian descent, known for leading the compilation of the Treatise on Astrology of the Kaiyuan Era during the Tang Dynasty. He was born in Chang'an, and his family was originally from India, according to a tomb stele uncovered in 1977 in Xi'an...
introduced Indian numerals with zero in 718, but Chinese mathematicians
Chinese mathematics
Mathematics in China emerged independently by the 11th century BC. The Chinese independently developed very large and negative numbers, decimals, a place value decimal system, a binary system, algebra, geometry, and trigonometry....
did not find them useful, as they had already had the decimal positional counting rods
Counting rods
Counting rods are small bars, typically 3–14 cm long, used by mathematicians for calculation in China, Japan, Korea, and Vietnam. They are placed either horizontally or vertically to represent any number and any fraction....
.
In Chinese numerals, a circle (〇) is used to write zero in Suzhou numerals
Suzhou numerals
The Suzhou numerals or huama is a numeral system used in China before the introduction of Arabic numerals.-History:The Suzhou numeral system is the only surviving variation of the rod numeral system. The rod numeral system is a positional numeral system used by the Chinese in mathematics...
. Many historians think it was imported from Indian numerals
Indian numerals
Most of the positional base 10 numeral systems in the world have originated from India, where the concept of positional numeration was first developed...
by Gautama Siddha
Gautama Siddha
Gautama Siddha, astronomer, astrologer and compiler of Indian descent, known for leading the compilation of the Treatise on Astrology of the Kaiyuan Era during the Tang Dynasty. He was born in Chang'an, and his family was originally from India, according to a tomb stele uncovered in 1977 in Xi'an...
in 718
718
Year 718 was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 718 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.- Europe :* Tervel's reign as monarch of Bulgaria...
, but some think it was created from the Chinese text space filler "□".
Chinese and Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
ese finally adopted the Hindu–Arabic numerals in the 19th century, abandoning counting rods.
Spread of the Western Arabic variant

Baroque
The Baroque is a period and the style that used exaggerated motion and clear, easily interpreted detail to produce drama, tension, exuberance, and grandeur in sculpture, painting, literature, dance, and music...
period have secondarily found worldwide use together with the Latin alphabet
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
, and even significantly beyond the contemporary spread of the Latin alphabet, intruding into the writing systems in regions where other variants of the Hindu–Arabic numerals had been in use, but also in conjunction with Chinese and Japanese writing (see Chinese numerals
Chinese numerals
Chinese numerals are characters for writing numbers in Chinese. Today speakers of Chinese use three numeral systems:the ubiquitous Arabic numerals and two indigenous systems....
, Japanese numerals
Japanese numerals
The system of Japanese numerals is the system of number names used in the Japanese language. The Japanese numerals in writing are entirely based on the Chinese numerals and the grouping of large numbers follow the Chinese tradition of grouping by 10,000...
).

