HSP60
Encyclopedia
Heat shock proteins are generally responsible for preventing damage to proteins in response to high levels of heat. Heat shock proteins are classified into six major families based on their molecular mass: small HSPs, HSP40, HSP60, HSP70, HSP90, and HSP110
Heat shock protein 60 (HSP60) is a mitochondrial chaperonin
that is typically held responsible for the transportation and refolding of proteins from the cytoplasm
into the mitochondrial matrix
. In addition to its role as a heat shock protein, HSP60 functions as a chaperonin to assist in folding linear amino acid
chains into their respective three-dimensional structure. Through the extensive study of groEL
, HSP60’s bacterial homolog, HSP60 has been deemed essential in the synthesis and transportation of essential mitochondrial proteins from the cell's cytoplasm into the mitochondrial matrix. Further studies have linked HSP60 to diabetes, stress
response, cancer
and certain types of immunological disorders.
ian HSP60 was first reported as a mitochondrial P1 protein. It was subsequently cloned and sequenced by Radhey Gupta and coworkers. The amino acid sequence showed a strong homology to GroEL
. It was initially believed that HSP60 functioned only in the mitochondria and that there was no equivalent protein located in the cytoplasm
. Recent discoveries have discredited this claim and have suggested that there is a recognizable difference between HSP60 in the mitochondria and in the cytoplasm. A similar protein structure exists in the chloroplast
of certain plants. This protein presence provides evidence for the evolutionary relationship of the development of the mitochondria and the chloroplast by means of endosymbiosis.
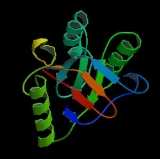
Each subunit of HSP60 has three domains
: the apical domain, the equatorial domain, and the intermediate domain. The equatorial domain contains the binding site for ATP
and for the other heptameric ring. The intermediate domain binds the equatorial domain and the apical domain together. The intermediate domain induces a conformational change when ATP is bound allowing for an alternation between the hydrophilic and hydrophobic substrate binding sites. In its inactive state, the protein is in a hydrophobic state. When activated by ATP, the intermediate domain undergoes a conformational change that exposes the hydrophilic region. This insures fidelity in protein binding. Chaperonin 10 aids HSP60 in folding by acting as a dome-like cover on the ATP active form of HSP60. This causes the central cavity to enlarge and aids in protein folding. See the above figure for further detail on the structure.
 The mitochondrial HSP60 sequence
The mitochondrial HSP60 sequence
contains a series of G repeats at the C-terminal. The structure and function of this sequence is not quite known. The N-terminal contains a leader sequence of hydroxylated amino acids, namely arginine
, lysine
, serine
, and threonine
, which serve as directors for the importation of the protein into the mitochondria.
The predicted structure of HSP60 includes several vertical sine waves, alpha helices, beta sheets, and 90 degree turns. There are regions of hydrophobicity where the protein presumably spans the membrane
. There are also three N-linked glycosylation sites at positions 104, 230, 436. The sequence and secondary structure for the mitochondrial protein are illustrated in the above image obtained from the Protein Data Bank.
Newer information has begun to suggest that the HSP60 found in the mitochondria differs from that of the cytoplasm. With respect to the amino acid sequence, the cytoplasmic HSP60 has an N-terminal sequence not found in the mitochondrial protein. In gel electrophoresis
analysis, significant differences were found in the migration of cytoplasmic and mitochondrial HSP60. The cytoplasmic HSP60 contains a signal sequence
of 26 amino acids on the N terminus. This sequence is highly degenerate and is capable of folding into amphiphilic helix. Antibodies against HSP60 targeted both the mitochondrial and cytoplasmic form. Nonetheless, antibodies against the signal sequence targeted only the cytoplasmic form. Under normal physiological condition, both are found in relatively equal concentrations. In times of stress or high need of HSP60 in either the cytoplasm or the mitochondria, the cell is capable for compensating by increasing the presence of HSP60 in one compartment and decreasing its concentration in the opposite compartment.
. The significant function, structural, and sequential homology between HSP60 and its prokaryotic homolog, groEL, demonstrates this level of conservation. Moreover, HSP60’s amino acid sequence bears a similarity to its homolog in plants, bacteria
, and humans. Heat shock proteins are primarily responsible for maintaining the integrity of cellular proteins particularly in response to environmental changes. Stresses such as temperature, concentration imbalance, pH change, and toxins can all induce heat shock proteins to maintain the conformation of the cell’s proteins. HSP60 constitutes approximately 15-30% of all cellular proteins. In additional to HSP60’s typical role as a heat shock protein, studies have shown that HSP60 plays an important role in the transport
and maintenance of mitochondrial proteins as well as the transmission
and replication
of mitochondrial DNA
.
. In extensive studies of HSP60 activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, scientists have proposed that HSP60 binds preferentially to the single stranded template DNA strand in a tetradecamer like complex
This tetradecamer complex interacts with other transcriptional elements to serve as a regulatory mechanism for the replication and transmission of mitochondrial DNA. Mutagenic studies have further supported HSP60 regulatory involvement in the replication and transmission of mitochondrial DNA. Mutations in HSP60 increase the levels of mitochondrial DNA and result in subsequent transmission defects.
in the cytoplasm. The cytoplasmic HSP60 forms a complex with proteins responsible for apoptosis and regulates the activity of these proteins. The cytoplasmic version is also involved in immune response and cancer
. These two aspects will be elaborated on later. Extremely recent investigations have begun to suggest a regulatory correlation between HSP60 and the glycolytic
enzyme, 6-phosphofructokinase-1. Although not much information is available, cytoplasmic HSP60 concentrations have influenced the expression of 6-phosphofructokinase in glycolysis
. Despite these marked differences between the cytoplasmic and mitochondrial form, experimental analysis has shown that the cell is quickly capable of moving cytoplasmic HSP60 into the mitochondria if environmental conditions demand a higher presence of mitochondrial HSP60.
and translated into the cytosol. These subunits then move into the mitochondria where they are processed by other HSP60 molecules. Several studies have shown how HSP60 proteins must be present in the mitochondria for the synthesis and assembly of additional HSP60 components. There is a direct positive correlation between the presence of HSP60 proteins in the mitochondria and the production of additional HSP60 protein complexes.
The kinetics
of assembly of HSP60 subunits into the 2-hepatmeric rings takes two minutes. The subsequent protease
-resistant HSP60 is formed in a half-time of 5–10 minutes. This rapid synthesis indicates that there is an ATP-dependent interaction where the formed HSP60 complex stabilizes the intermediate of the HSP60 assembly complex, effectively serving as a catalyst. The necessity of preexisting HSP60 in order to synthesize additional HSP60 molecules supports the endosymbiotic theory
of the origin of mitochondria. There must have been a rudimentary prokaryotic homologous protein that was capable of similar self-assembly.
Infection
and disease
are extremely stressful on the cell. When a cell is under stress, it naturally increases the production of stress proteins, including heat shock proteins such as HSP60. In order for HSP60 to act as a signal it must be present in the extracellular
environment. In recent research “it has emerged that…chaperonin 60 can be found on the surface of various prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, and can even be released from cells”. According to recent research, many different types of heat shock proteins are used in immune response signaling, but it appears that different proteins act and respond differently to other signaling molecules. HSP60 has been shown to be released from specific cells like peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) when there are lipopolysaccharides (LPS) or GroEL
present. This suggests that the cell has different receptors
and responses to human and bacterial HSP60 . In addition, it has been shown that HSP60 has the capability “of activating monocytes, macrophages and dendritic cells…and also of inducing secretion of a wide range of cytokines.” The fact that HSP60 responds to other signal molecules like LPS or GroEL and has the ability to activate certain types of cells supports the idea that HSP60 is part of a danger signal cascade which is involved in activating an immune response.
There is however, a twist in the immunological role of HSP60. As mentioned above, there are two different types of HSP60 proteins, bacterial as well as mammalian. Since they are very similar in sequence, bacterial HSP60 wouldn’t be expected to cause a large immune response in humans. The immune system is “designed to ignore ‘self’, that is, host constituents; however, paradoxically, this is not the case with chaperonins”. It has been found that many anti-chaperonin antibodies exist and are associated with many autoimmune diseases. According to Ranford, et al. experiments have been performed which have shown that antibodies which are “generated by a human host after exposure to bacterial chaperonin 60 proteins” can cross-react with human chaperonin 60 proteins. Bacterial HSP60 is causing the immune system to create anti-chaperonin antibodies, even though bacterial and human HSP60 have similar protein sequences. These new antibodies are then recognizing and attacking human HSP60 which causes an autoimmune disease. This suggests that HSP60 may play a role in autoimmunity
, however more research needs to be done in order to discover more completely its role in this disease.
and discovered significant upregulation of HSP60 expression in the mitochondria and HSP70
expression in the cytoplasm. Researchers concluded that the heat shock signal pathway serves as “the basic mechanism of defense against neurotoxicity elicited by free radical oxygen and nitrogen species produced in aging and neurodegenerative disorders” . Several studies have shown that HSP60 and other heat shock proteins are necessary for cellular survival under toxic or stressful circumstances.
 HSP60 has been shown to influence apoptosis
HSP60 has been shown to influence apoptosis
in tumor
cells which seems to be associated with a change in expression levels. There is some inconsistency in that some research shows a positive expression while other research shows a negative expression, and it seems to depend on the type of cancer. There are different hypotheses to explain the effects of positive versus negative expression. Positive expression seems to inhibit “apoptotic and necrotic cell death” while negative expression is thought to play a part “in activation of apoptosis”.
As well as influencing apoptosis, HSP60 changes in expression level have been shown to be “useful new biomarkers for diagnostic and prognostic purposes.” According to Lebret et al., a loss of HSP60 expression “indicates a poor prognosis and the risk of developing tumor infiltration” specifically with bladder
carcinomas, but that does not necessarily hold true for other types of cancers. For example, ovarian tumors research has shown that over expression is correlated with a better prognosis while a decreased expression is correlated with an aggressive tumor. All this research indicates that it may be possible for HSP60 expression to be used in predicting survival for certain types of cancer and therefore may be able to identify patients who could benefit from certain treatments.
Heat shock protein 60 (HSP60) is a mitochondrial chaperonin
Chaperonin
Chaperonins are proteins that fold and unfold other proteins. Newly made proteins usually must fold from a linear chain of amino acids into a three-dimensional form. Chaperonins belong to a large class of molecules that assist protein folding, called molecular chaperones...
that is typically held responsible for the transportation and refolding of proteins from the cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a small gel-like substance residing between the cell membrane holding all the cell's internal sub-structures , except for the nucleus. All the contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms are contained within the cytoplasm...
into the mitochondrial matrix
Mitochondrial matrix
In the mitochondrion, the matrix contains soluble enzymes that catalyze the oxidation of pyruvate and other small organic molecules.The mitochondrial matrix also contains the mitochondria's DNA and ribosomes. The word "matrix" stems from the fact that this space is viscous, compared to the...
. In addition to its role as a heat shock protein, HSP60 functions as a chaperonin to assist in folding linear amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
chains into their respective three-dimensional structure. Through the extensive study of groEL
GroEL
GroEL belongs to the chaperonin family of molecular chaperones, and is found in a large number of bacteria. It is required for the proper folding of many proteins. To function properly, GroEL requires the lid-like cochaperonin protein complex GroES...
, HSP60’s bacterial homolog, HSP60 has been deemed essential in the synthesis and transportation of essential mitochondrial proteins from the cell's cytoplasm into the mitochondrial matrix. Further studies have linked HSP60 to diabetes, stress
Stress (medicine)
Stress is a term in psychology and biology, borrowed from physics and engineering and first used in the biological context in the 1930s, which has in more recent decades become commonly used in popular parlance...
response, cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
and certain types of immunological disorders.
Discovery
Not much is known about the function of HSP60. MammalMammal
Mammals are members of a class of air-breathing vertebrate animals characterised by the possession of endothermy, hair, three middle ear bones, and mammary glands functional in mothers with young...
ian HSP60 was first reported as a mitochondrial P1 protein. It was subsequently cloned and sequenced by Radhey Gupta and coworkers. The amino acid sequence showed a strong homology to GroEL
GroEL
GroEL belongs to the chaperonin family of molecular chaperones, and is found in a large number of bacteria. It is required for the proper folding of many proteins. To function properly, GroEL requires the lid-like cochaperonin protein complex GroES...
. It was initially believed that HSP60 functioned only in the mitochondria and that there was no equivalent protein located in the cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a small gel-like substance residing between the cell membrane holding all the cell's internal sub-structures , except for the nucleus. All the contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms are contained within the cytoplasm...
. Recent discoveries have discredited this claim and have suggested that there is a recognizable difference between HSP60 in the mitochondria and in the cytoplasm. A similar protein structure exists in the chloroplast
Chloroplast
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and other eukaryotic organisms that conduct photosynthesis. Chloroplasts capture light energy to conserve free energy in the form of ATP and reduce NADP to NADPH through a complex set of processes called photosynthesis.Chloroplasts are green...
of certain plants. This protein presence provides evidence for the evolutionary relationship of the development of the mitochondria and the chloroplast by means of endosymbiosis.
Structure
Under normal physiological conditions, HSP60 is a 60 kilodalton oligomer composed of monomers that form a complex arranged as two stacked heptameric rings.. This double ring structure forms a large central cavity in which the unfolded protein binds via hydrophobic interactions. This structure is typically in equilibrium with each of its individual components: monomers, heptamers, and tetradeceamers. Recent studies have begun to suggest that in addition to its typical location in the mitochondria, HSP60 can also be found in the cytoplasm under normal physiological conditions.Each subunit of HSP60 has three domains
Protein domain
A protein domain is a part of protein sequence and structure that can evolve, function, and exist independently of the rest of the protein chain. Each domain forms a compact three-dimensional structure and often can be independently stable and folded. Many proteins consist of several structural...
: the apical domain, the equatorial domain, and the intermediate domain. The equatorial domain contains the binding site for ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
and for the other heptameric ring. The intermediate domain binds the equatorial domain and the apical domain together. The intermediate domain induces a conformational change when ATP is bound allowing for an alternation between the hydrophilic and hydrophobic substrate binding sites. In its inactive state, the protein is in a hydrophobic state. When activated by ATP, the intermediate domain undergoes a conformational change that exposes the hydrophilic region. This insures fidelity in protein binding. Chaperonin 10 aids HSP60 in folding by acting as a dome-like cover on the ATP active form of HSP60. This causes the central cavity to enlarge and aids in protein folding. See the above figure for further detail on the structure.

Sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an ordered list of objects . Like a set, it contains members , and the number of terms is called the length of the sequence. Unlike a set, order matters, and exactly the same elements can appear multiple times at different positions in the sequence...
contains a series of G repeats at the C-terminal. The structure and function of this sequence is not quite known. The N-terminal contains a leader sequence of hydroxylated amino acids, namely arginine
Arginine
Arginine is an α-amino acid. The L-form is one of the 20 most common natural amino acids. At the level of molecular genetics, in the structure of the messenger ribonucleic acid mRNA, CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG, AGA, and AGG, are the triplets of nucleotide bases or codons that codify for arginine during...
, lysine
Lysine
Lysine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCH4NH2. It is an essential amino acid, which means that the human body cannot synthesize it. Its codons are AAA and AAG....
, serine
Serine
Serine is an amino acid with the formula HO2CCHCH2OH. It is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. By virtue of the hydroxyl group, serine is classified as a polar amino acid.-Occurrence and biosynthesis:...
, and threonine
Threonine
Threonine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCHCH3. Its codons are ACU, ACA, ACC, and ACG. This essential amino acid is classified as polar...
, which serve as directors for the importation of the protein into the mitochondria.
The predicted structure of HSP60 includes several vertical sine waves, alpha helices, beta sheets, and 90 degree turns. There are regions of hydrophobicity where the protein presumably spans the membrane
Biological membrane
A biological membrane or biomembrane is an enclosing or separatingmembrane that acts as a selective barrier, within or around a cell. It consists of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins that may constitute close to 50% of membrane content...
. There are also three N-linked glycosylation sites at positions 104, 230, 436. The sequence and secondary structure for the mitochondrial protein are illustrated in the above image obtained from the Protein Data Bank.
Newer information has begun to suggest that the HSP60 found in the mitochondria differs from that of the cytoplasm. With respect to the amino acid sequence, the cytoplasmic HSP60 has an N-terminal sequence not found in the mitochondrial protein. In gel electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a method used in clinical chemistry to separate proteins by charge and or size and in biochemistry and molecular biology to separate a mixed population of DNA and RNA fragments by length, to estimate the size of DNA and RNA fragments or to separate proteins by charge...
analysis, significant differences were found in the migration of cytoplasmic and mitochondrial HSP60. The cytoplasmic HSP60 contains a signal sequence
Signal sequence
Signal sequence can refer to:*Protein targeting*Signal peptide*DNA uptake signal sequence...
of 26 amino acids on the N terminus. This sequence is highly degenerate and is capable of folding into amphiphilic helix. Antibodies against HSP60 targeted both the mitochondrial and cytoplasmic form. Nonetheless, antibodies against the signal sequence targeted only the cytoplasmic form. Under normal physiological condition, both are found in relatively equal concentrations. In times of stress or high need of HSP60 in either the cytoplasm or the mitochondria, the cell is capable for compensating by increasing the presence of HSP60 in one compartment and decreasing its concentration in the opposite compartment.
Common
Heat shock proteins are amongst the most evolutionarily conserved of proteinsProtein family
A protein family is a group of evolutionarily-related proteins, and is often nearly synonymous with gene family. The term protein family should not be confused with family as it is used in taxonomy....
. The significant function, structural, and sequential homology between HSP60 and its prokaryotic homolog, groEL, demonstrates this level of conservation. Moreover, HSP60’s amino acid sequence bears a similarity to its homolog in plants, bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
, and humans. Heat shock proteins are primarily responsible for maintaining the integrity of cellular proteins particularly in response to environmental changes. Stresses such as temperature, concentration imbalance, pH change, and toxins can all induce heat shock proteins to maintain the conformation of the cell’s proteins. HSP60 constitutes approximately 15-30% of all cellular proteins. In additional to HSP60’s typical role as a heat shock protein, studies have shown that HSP60 plays an important role in the transport
Transport
Transport or transportation is the movement of people, cattle, animals and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, rail, road, water, cable, pipeline, and space. The field can be divided into infrastructure, vehicles, and operations...
and maintenance of mitochondrial proteins as well as the transmission
Transmission (genetics)
Genetic transmission is the transfer of genetic information from genes to another generation , almost synonymous with heredity, or from one location in a cell to another....
and replication
Replication
Replication may refer to:Science* Replication is one of the main principles of the scientific method, a.k.a. reproducibility** Replication , the repetition of a test or complete experiment...
of mitochondrial DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
.
Mitochondrial protein transport
HSP60 possesses two main responsibilities with respect to mitochondrial protein transport. It functions to catalyze the folding of proteins destined for the matrix and maintains protein in an unfolded state for transport across the inner membrane of the mitochondria. Many proteins are targeted for processing in the matrix of the mitochondria but then are quickly exported to other parts of the cell. The hydrophobic portion HSP60 is responsible for maintaining the unfolded conformation of the protein for transmembrane transport. Studies have shown how HSP60 binds to incoming proteins and induces conformational and structural changes. Subsequent changes in ATP concentrations hydrolyze the bonds between the protein and HSP60 which signals the protein to exit the mitochondria. HSP60 is also capable of distinguishing between proteins designated for export and proteins destined to remain in the mitochondrial matrix by looking for an amphiphilic alpha-helix of 15-20 residues. The existence of this sequence signals that the protein is to be exported while the absence signals that the protein is to remain in the mitochondria. The precise mechanism is not yet entirely understood.DNA Metabolism
In addition to its critical role in protein folding, HSP60 is involved in the replication and transmission of mitochondrial DNAMitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA is the DNA located in organelles called mitochondria, structures within eukaryotic cells that convert the chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, adenosine triphosphate...
. In extensive studies of HSP60 activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, scientists have proposed that HSP60 binds preferentially to the single stranded template DNA strand in a tetradecamer like complex
This tetradecamer complex interacts with other transcriptional elements to serve as a regulatory mechanism for the replication and transmission of mitochondrial DNA. Mutagenic studies have further supported HSP60 regulatory involvement in the replication and transmission of mitochondrial DNA. Mutations in HSP60 increase the levels of mitochondrial DNA and result in subsequent transmission defects.
Cytoplasmic vs mitochondrial HSP60
In addition to the already illustrated structural differences between cytoplasmic and mitochondrial HSP60, there are marked functional differences. Studies have suggested that HSP60 plays a key role in preventing apoptosisApoptosis
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
in the cytoplasm. The cytoplasmic HSP60 forms a complex with proteins responsible for apoptosis and regulates the activity of these proteins. The cytoplasmic version is also involved in immune response and cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
. These two aspects will be elaborated on later. Extremely recent investigations have begun to suggest a regulatory correlation between HSP60 and the glycolytic
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+...
enzyme, 6-phosphofructokinase-1. Although not much information is available, cytoplasmic HSP60 concentrations have influenced the expression of 6-phosphofructokinase in glycolysis
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+...
. Despite these marked differences between the cytoplasmic and mitochondrial form, experimental analysis has shown that the cell is quickly capable of moving cytoplasmic HSP60 into the mitochondria if environmental conditions demand a higher presence of mitochondrial HSP60.
Synthesis and assembly
HSP60 is typically found in the mitochondria and has been found in organelles of endosymbiotic origin. HSP60 monomers form two heptameric rings that bind to the surface of linear proteins and catalyze their folding in an ATP dependent process. HSP60 subunits are encoded by nuclear genesGênes
Gênes is the name of a département of the First French Empire in present Italy, named after the city of Genoa. It was formed in 1805, when Napoleon Bonaparte occupied the Republic of Genoa. Its capital was Genoa, and it was divided in the arrondissements of Genoa, Bobbio, Novi Ligure, Tortona and...
and translated into the cytosol. These subunits then move into the mitochondria where they are processed by other HSP60 molecules. Several studies have shown how HSP60 proteins must be present in the mitochondria for the synthesis and assembly of additional HSP60 components. There is a direct positive correlation between the presence of HSP60 proteins in the mitochondria and the production of additional HSP60 protein complexes.
The kinetics
Enzyme kinetics
Enzyme kinetics is the study of the chemical reactions that are catalysed by enzymes. In enzyme kinetics, the reaction rate is measured and the effects of varying the conditions of the reaction investigated...
of assembly of HSP60 subunits into the 2-hepatmeric rings takes two minutes. The subsequent protease
Protease
A protease is any enzyme that conducts proteolysis, that is, begins protein catabolism by hydrolysis of the peptide bonds that link amino acids together in the polypeptide chain forming the protein....
-resistant HSP60 is formed in a half-time of 5–10 minutes. This rapid synthesis indicates that there is an ATP-dependent interaction where the formed HSP60 complex stabilizes the intermediate of the HSP60 assembly complex, effectively serving as a catalyst. The necessity of preexisting HSP60 in order to synthesize additional HSP60 molecules supports the endosymbiotic theory
Endosymbiotic theory
The endosymbiotic theory concerns the mitochondria, plastids , and possibly other organelles of eukaryotic cells. According to this theory, certain organelles originated as free-living bacteria that were taken inside another cell as endosymbionts...
of the origin of mitochondria. There must have been a rudimentary prokaryotic homologous protein that was capable of similar self-assembly.
Immunological role
As discussed above, HSP60 has generally been known as a chaperonin which assists in protein folding in mitochondria. However, some new research has indicated that HSP60 possibly plays a role in a “danger signal cascade” immune response. There is also mounting evidence that it plays a role in autoimmune disease.Infection
Infection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
and disease
Disease
A disease is an abnormal condition affecting the body of an organism. It is often construed to be a medical condition associated with specific symptoms and signs. It may be caused by external factors, such as infectious disease, or it may be caused by internal dysfunctions, such as autoimmune...
are extremely stressful on the cell. When a cell is under stress, it naturally increases the production of stress proteins, including heat shock proteins such as HSP60. In order for HSP60 to act as a signal it must be present in the extracellular
Extracellular
In cell biology, molecular biology and related fields, the word extracellular means "outside the cell". This space is usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid...
environment. In recent research “it has emerged that…chaperonin 60 can be found on the surface of various prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, and can even be released from cells”. According to recent research, many different types of heat shock proteins are used in immune response signaling, but it appears that different proteins act and respond differently to other signaling molecules. HSP60 has been shown to be released from specific cells like peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) when there are lipopolysaccharides (LPS) or GroEL
GroEL
GroEL belongs to the chaperonin family of molecular chaperones, and is found in a large number of bacteria. It is required for the proper folding of many proteins. To function properly, GroEL requires the lid-like cochaperonin protein complex GroES...
present. This suggests that the cell has different receptors
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a receptor is a molecule found on the surface of a cell, which receives specific chemical signals from neighbouring cells or the wider environment within an organism...
and responses to human and bacterial HSP60 . In addition, it has been shown that HSP60 has the capability “of activating monocytes, macrophages and dendritic cells…and also of inducing secretion of a wide range of cytokines.” The fact that HSP60 responds to other signal molecules like LPS or GroEL and has the ability to activate certain types of cells supports the idea that HSP60 is part of a danger signal cascade which is involved in activating an immune response.
There is however, a twist in the immunological role of HSP60. As mentioned above, there are two different types of HSP60 proteins, bacterial as well as mammalian. Since they are very similar in sequence, bacterial HSP60 wouldn’t be expected to cause a large immune response in humans. The immune system is “designed to ignore ‘self’, that is, host constituents; however, paradoxically, this is not the case with chaperonins”. It has been found that many anti-chaperonin antibodies exist and are associated with many autoimmune diseases. According to Ranford, et al. experiments have been performed which have shown that antibodies which are “generated by a human host after exposure to bacterial chaperonin 60 proteins” can cross-react with human chaperonin 60 proteins. Bacterial HSP60 is causing the immune system to create anti-chaperonin antibodies, even though bacterial and human HSP60 have similar protein sequences. These new antibodies are then recognizing and attacking human HSP60 which causes an autoimmune disease. This suggests that HSP60 may play a role in autoimmunity
Autoimmunity
Autoimmunity is the failure of an organism to recognize its own constituent parts as self, which allows an immune response against its own cells and tissues. Any disease that results from such an aberrant immune response is termed an autoimmune disease...
, however more research needs to be done in order to discover more completely its role in this disease.
Stress response
HSP60, as a mitochondrial protein, has been shown to be involved in stress response as well. The heat shock response is a homeostatic mechanism that that protects cell from damage by upregulating the expression of genes that code for HSP60. The upregulation of HSP60 production allows for the maintenance of other cellular processes occurring in the cell, especially during stressful times. In one experiment, investigators treated various mice with DOPADopa
Dopa or DOPA can refer to:* L-DOPA , used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease* D-DOPA, a chemical compound related to L-DOPA* Dopa, an angel in Enochian* Deleting Online Predators Act of 2006...
and discovered significant upregulation of HSP60 expression in the mitochondria and HSP70
Hsp70
The 70 kilodalton heat shock proteins are a family of ubiquitously expressed heat shock proteins. Proteins with similar structure exist in virtually all living organisms...
expression in the cytoplasm. Researchers concluded that the heat shock signal pathway serves as “the basic mechanism of defense against neurotoxicity elicited by free radical oxygen and nitrogen species produced in aging and neurodegenerative disorders” . Several studies have shown that HSP60 and other heat shock proteins are necessary for cellular survival under toxic or stressful circumstances.
Relationship to cancer

Apoptosis
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
in tumor
Tumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
cells which seems to be associated with a change in expression levels. There is some inconsistency in that some research shows a positive expression while other research shows a negative expression, and it seems to depend on the type of cancer. There are different hypotheses to explain the effects of positive versus negative expression. Positive expression seems to inhibit “apoptotic and necrotic cell death” while negative expression is thought to play a part “in activation of apoptosis”.
As well as influencing apoptosis, HSP60 changes in expression level have been shown to be “useful new biomarkers for diagnostic and prognostic purposes.” According to Lebret et al., a loss of HSP60 expression “indicates a poor prognosis and the risk of developing tumor infiltration” specifically with bladder
Urinary bladder
The urinary bladder is the organ that collects urine excreted by the kidneys before disposal by urination. A hollow muscular, and distensible organ, the bladder sits on the pelvic floor...
carcinomas, but that does not necessarily hold true for other types of cancers. For example, ovarian tumors research has shown that over expression is correlated with a better prognosis while a decreased expression is correlated with an aggressive tumor. All this research indicates that it may be possible for HSP60 expression to be used in predicting survival for certain types of cancer and therefore may be able to identify patients who could benefit from certain treatments.

