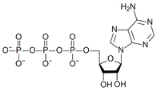
Adenosine triphosphate
Overview
Nucleoside triphosphate
Nucleoside triphosphate is a nucleoside with three phosphates. Natural nucleoside triphosphates include adenosine triphosphate , guanosine triphosphate , cytidine triphosphate , 5-methyluridine triphosphate , and uridine triphosphate . These terms refer to those nucleoside triphosphates that...
used in cells
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
unit of currency
Currency
In economics, currency refers to a generally accepted medium of exchange. These are usually the coins and banknotes of a particular government, which comprise the physical aspects of a nation's money supply...
" of intracellular energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
for metabolism
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
. It is produced by photophosphorylation
Photophosphorylation
The production of ATP using the energy of sunlight is called photophosphorylation. Only two sources of energy are available to living organisms: sunlight and reduction-oxidation reactions...
and cellular respiration
Cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate , and then release waste products. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions that involve...
and used by enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s and structural proteins
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a cellular "scaffolding" or "skeleton" contained within a cell's cytoplasm and is made out of protein. The cytoskeleton is present in all cells; it was once thought to be unique to eukaryotes, but recent research has identified the prokaryotic cytoskeleton...
in many cellular processes, including biosynthetic reactions
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is an enzyme-catalyzed process in cells of living organisms by which substrates are converted to more complex products. The biosynthesis process often consists of several enzymatic steps in which the product of one step is used as substrate in the following step...
, motility, and cell division
Cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells . Cell division is usually a small segment of a larger cell cycle. This type of cell division in eukaryotes is known as mitosis, and leaves the daughter cell capable of dividing again. The corresponding sort...
. One molecule of ATP contains three phosphate groups, and it is produced by ATP synthase
ATP synthase
right|thumb|300px|Molecular model of ATP synthase by X-ray diffraction methodATP synthase is an important enzyme that provides energy for the cell to use through the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate . ATP is the most commonly used "energy currency" of cells from most organisms...
from inorganic phosphate and adenosine diphosphate
Adenosine diphosphate
Adenosine diphosphate, abbreviated ADP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside adenosine. ADP consists of the pyrophosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine....
(ADP) or adenosine monophosphate
Adenosine monophosphate
Adenosine monophosphate , also known as 5'-adenylic acid, is a nucleotide that is used as a monomer in RNA. It is an ester of phosphoric acid and the nucleoside adenosine. AMP consists of a phosphate group, the sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine...
(AMP).
Metabolic processes that use ATP as an energy source convert it back into its precursors.
Unanswered Questions

