
Free surface
Encyclopedia

Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, a free surface is the surface of a fluid that is subject to constant perpendicular normal stress
Stress (physics)
In continuum mechanics, stress is a measure of the internal forces acting within a deformable body. Quantitatively, it is a measure of the average force per unit area of a surface within the body on which internal forces act. These internal forces are a reaction to external forces applied on the body...
and zero parallel shear stress
Shear stress
A shear stress, denoted \tau\, , is defined as the component of stress coplanar with a material cross section. Shear stress arises from the force vector component parallel to the cross section...
,
such as the boundary between two homogenous fluid
Fluid
In physics, a fluid is a substance that continually deforms under an applied shear stress. Fluids are a subset of the phases of matter and include liquids, gases, plasmas and, to some extent, plastic solids....
s,
for example liquid water and the air in the Earth's atmosphere
Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention , and reducing temperature extremes between day and night...
. Unlike liquid
Liquid
Liquid is one of the three classical states of matter . Like a gas, a liquid is able to flow and take the shape of a container. Some liquids resist compression, while others can be compressed. Unlike a gas, a liquid does not disperse to fill every space of a container, and maintains a fairly...
s, gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
es cannot form a free surface on their own.
A liquid in a gravitational field
Gravitational field
The gravitational field is a model used in physics to explain the existence of gravity. In its original concept, gravity was a force between point masses...
will form a free surface if unconfined from above.
Under mechanical equilibrium
Mechanical equilibrium
A standard definition of static equilibrium is:This is a strict definition, and often the term "static equilibrium" is used in a more relaxed manner interchangeably with "mechanical equilibrium", as defined next....
this free surface must be perpendicular to the forces acting on the liquid; if not there would be a force along the surface, and the liquid would flow in that direction. Thus, on the surface of the Earth, all free surfaces of liquids are horizontal
Horizontal plane
In geometry, physics, astronomy, geography, and related sciences, a plane is said to be horizontal at a given point if it is perpendicular to the gradient of the gravity field at that point— in other words, if apparent gravity makes a plumb bob hang perpendicular to the plane at that point.In...
unless disturbed (except near solids dipping into them, where surface tension
Surface tension
Surface tension is a property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force. It is revealed, for example, in floating of some objects on the surface of water, even though they are denser than water, and in the ability of some insects to run on the water surface...
distorts the surface in a region called the meniscus
Meniscus
The meniscus is the curve in the upper surface of a liquid close to the surface of the container or another object, caused by surface tension. It can be either convex or concave. A convex meniscus occurs when the molecules have a stronger attraction to each other than to the material of the...
).
In a free liquid that is not affected by outside forces such as a gravitational field, internal attractive forces only play a role (e.g. Van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonds). Its free surface will assume the shape with the least surface area for its volume: a perfect sphere
Sphere
A sphere is a perfectly round geometrical object in three-dimensional space, such as the shape of a round ball. Like a circle in two dimensions, a perfect sphere is completely symmetrical around its center, with all points on the surface lying the same distance r from the center point...
. Such behaviour can be expressed in terms of surface tension
Surface tension
Surface tension is a property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force. It is revealed, for example, in floating of some objects on the surface of water, even though they are denser than water, and in the ability of some insects to run on the water surface...
. It can be demonstrated experimentally by observing a large globule of oil placed below the surface of a mixture of water and alcohol having the same density
Density
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
so the oil has neutral buoyancy
Buoyancy
In physics, buoyancy is a force exerted by a fluid that opposes an object's weight. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus a column of fluid, or an object submerged in the fluid, experiences greater pressure at the bottom of the...
.
Waves
If the free surface of a liquid is disturbed, wavesWAVES
The WAVES were a World War II-era division of the U.S. Navy that consisted entirely of women. The name of this group is an acronym for "Women Accepted for Volunteer Emergency Service" ; the word "emergency" implied that the acceptance of women was due to the unusual circumstances of the war and...
are produced on the surface. These waves are not elastic waves due to any elastic force
Elasticity (physics)
In physics, elasticity is the physical property of a material that returns to its original shape after the stress that made it deform or distort is removed. The relative amount of deformation is called the strain....
; they are gravity wave
Gravity wave
In fluid dynamics, gravity waves are waves generated in a fluid medium or at the interface between two media which has the restoring force of gravity or buoyancy....
s caused by the force of gravity tending to bring the surface of the disturbed liquid back to its horizontal level. Momentum
Momentum
In classical mechanics, linear momentum or translational momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object...
causes the wave to overshoot
Overshoot
Overshoot may refer to:* Overshoot , when a signal exceeds its steady state value* Overshoot , when a population exceeds the environment's carrying capacity* Overshoot , an aborted landing...
, thus oscillating and spreading the disturbance to the neighboring portions of the surface. The velocity of the surface waves varies as the square root of the wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
if the liquid is deep; therefore long waves
Swell (ocean)
A swell, in the context of an ocean, sea or lake, is a series surface gravity waves that is not generated by the local wind. Swell waves often have a long wavelength but this varies with the size of the water body, e.g. rarely more than 150 m in the Mediterranean, and from event to event, with...
on the sea go faster than short ones. Very minute waves or ripples are not due to gravity but to capillary action
Capillary action
Capillary action, or capilarity, is the ability of a liquid to flow against gravity where liquid spontanously rise in a narrow space such as between the hair of a paint-brush, in a thin tube, or in porous material such as paper or in some non-porous material such as liquified carbon fiber, or in a...
, and have properties different from those of the longer ocean surface waves,
because the surface is increased in area by the ripples and the capillary forces are in this case large compared with the gravitational forces.
Capillary ripples are damped both by sub-surface viscosity
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
and by surface rheology
Surface rheology
Surface rheology is a description of the rheological properties of a free surface. When perfectly pure, the interface between fluids usually displays only surface tension...
Rotation
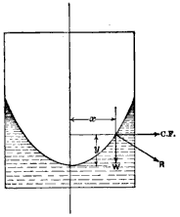
Surface of revolution
A surface of revolution is a surface in Euclidean space created by rotating a curve around a straight line in its plane ....
known as a paraboloid
Paraboloid
In mathematics, a paraboloid is a quadric surface of special kind. There are two kinds of paraboloids: elliptic and hyperbolic. The elliptic paraboloid is shaped like an oval cup and can have a maximum or minimum point....
. The free surface at each point is at a right angle to the force acting at it, which is the resultant of the force of gravity and the centrifugal force from the motion of each point in a circle. Since the main mirror in a telescope must be parabolic, this principle is used to create liquid mirror
Liquid mirror
Liquid mirror telescopes are telescopes made with a reflective liquid. The most common liquid used is mercury, but other liquids will work as well . The container for the liquid is rotating so that the liquid assumes a paraboloidal shape. A paraboloidal shape is precisely the shape needed for the...
telescopes.
If a free liquid is rotating about an axis, the free surface will take the shape of an oblate spheroid: the approximate shape of the Earth due to its equatorial bulge
Equatorial bulge
An equatorial bulge is a difference between the equatorial and polar diameters of a planet, due to the centrifugal force of its rotation. A rotating body tends to form an oblate spheroid rather than a sphere...
.
Related terms
- In hydrodynamics, the free surface is defined mathematically by the free-surface condition:
-
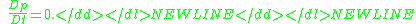
- In fluid dynamicsFluid dynamicsIn physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
, a free-surface vortexVortexA vortex is a spinning, often turbulent,flow of fluid. Any spiral motion with closed streamlines is vortex flow. The motion of the fluid swirling rapidly around a center is called a vortex...
, also known as a potential vortex or whirlpool, forms in an irrotational flow, for example when a bathtub is drained.
- In naval architectureNaval architectureNaval architecture is an engineering discipline dealing with the design, construction, maintenance and operation of marine vessels and structures. Naval architecture involves basic and applied research, design, development, design evaluation and calculations during all stages of the life of a...
and marine safety, the free surface effectFree Surface EffectThe free surface effect is one of several mechanisms which can cause a craft to become unstable and roll over . It refers to the tendency of liquids — and of aggregates of small solid objects, like seeds, gravel, or crushed ore which can act as liquids — to slosh about: to move in response to...
occurs when liquids or granular materials under a free surface in partially filled tanks or holds shift when the vessel heels.
- In hydraulic engineeringHydraulic engineeringThis article is about civil engineering. For the mechanical engineering discipline see Hydraulic machineryHydraulic engineering as a sub-discipline of civil engineering is concerned with the flow and conveyance of fluids, principally water and sewage. One feature of these systems is the extensive...
a free-surface jetJet (fluid)A jet is an efflux of fluid that is projected into a surrounding medium, usually from some kind of a nozzle, aperture or orifice. Jets can travel long distances without dissipating...
is one where the entrainment of the fluid outside the jet is minimal, as opposed to submerged jet where the entrainment effect is significant. A liquid jet in air approximates a free surface jet.
- In fluid mechanicsFluid mechanicsFluid mechanics is the study of fluids and the forces on them. Fluid mechanics can be divided into fluid statics, the study of fluids at rest; fluid kinematics, the study of fluids in motion; and fluid dynamics, the study of the effect of forces on fluid motion...
a free surface flow, also called open channel flow, is the gravity driven flow of a fluid under a free surface, typically water flowing under air in the atmosphere.
See also
- Free surface effectFree Surface EffectThe free surface effect is one of several mechanisms which can cause a craft to become unstable and roll over . It refers to the tendency of liquids — and of aggregates of small solid objects, like seeds, gravel, or crushed ore which can act as liquids — to slosh about: to move in response to...
- Surface tensionSurface tensionSurface tension is a property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force. It is revealed, for example, in floating of some objects on the surface of water, even though they are denser than water, and in the ability of some insects to run on the water surface...
- Laser-heated pedestal growthLaser-heated pedestal growthLaser-heated pedestal growth is a crystal growth technique. The technique can be viewed as a miniature floating zone, where the heat source is replaced by a powerful CO2 or YAG laser...
- Splash (fluid mechanics)Splash (fluid mechanics)In fluid mechanics, a splash is a sudden disturbance to the otherwise quiescent free surface of a liquid . The disturbance is typically caused by a solid object suddenly hitting the surface, although splashes can occur in which moving liquid supplies the energy...
- Slosh dynamicsSlosh dynamicsIn fluid dynamics, slosh refers to the movement of liquid inside another object . Strictly speaking, the liquid must have a free surface to constitute a slosh dynamics problem, where the dynamics of the liquid can interact with the container to alter the system dynamics significantly...
- Riabouchinsky solidRiabouchinsky solidIn fluid mechanics a Riabouchinsky solid is a technique used for approximating boundary layer separation from a bluff body using potential flow...
- In fluid dynamics

