Energy use in the United States
Encyclopedia
The United States
is the 2nd largest energy
consumer in terms of total use in 2010 . The U.S. ranks seventh in energy consumption per-capita after Canada and a number of small countries.
The majority of this energy is derived from fossil fuel
s: in 2009, EIA data showed 37% of the nation's energy came from petroleum
, 21% from coal
, and 25% from natural gas
. Nuclear power
supplied 9% and renewable energy
supplied 8%, which was mainly from hydroelectric dams although other renewables are included such as wind power
, geothermal
and solar energy. Energy consumption has increased at a faster rate than energy production over the last fifty years in the U.S.(when they were roughly equal). This difference is now largely met through imports.
According to the Energy Information Administration
's statistics, the per-capita energy consumption in the US has been somewhat consistent from the 1970s to today. The average has been 335.9 million British thermal unit
s (BTUs) per person from 1980 to 2006. One explanation suggested for this is that the energy required to produce the increase in US consumption of manufactured equipment, cars, and other goods has been shifted to other countries producing and transporting those goods to the US with a corresponding shift of green house gases and pollution. In comparison, the world average has increased from 63.7 in 1980 to 72.4 million BTU's per person in 2006. On the other hand, US "off-shoring" of manufacturing is sometimes exaggerated: US domestic manufacturing has grown by 50% since 1980.
The development of renewable energy and energy efficiency marks "a new era of energy exploration" in the United States, according to President Barack Obama
.
Primary energy use in the United States was 25,155 TWh and 82 TWh per million persons in 2009. Primary energy use was 1,100 TWh less in the US than in China in 2009. Same year the share of energy import in the US was 26 % of the primary energy use. The energy import declined ca 22 % and the annual CO2 emissions ca 10 % in 2009 compared to 2004.
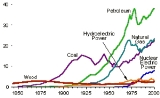
. Rapid industrialization of the economy, urbanization, and the growth of railroads led to increased use of coal
, and by 1885 it had eclipsed wood as the nation's primary energy source.
Coal remained dominant for the next 7 decades, but by 1950, it was surpassed in turn by both petroleum and natural gas. , coal consumption is the highest it has ever been, with coal mostly being used to generate electricity
. Natural gas, which is cleaner-burning and more easily transportable, has replaced coal as the preferred source of heating in homes, businesses and industrial furnaces. Although total energy use increased by approximately a factor of 50 between 1850 and 2000, energy use per capita increased only by a factor of four. As of 2009, United States per capita energy use had declined to 7075 more than 12% since 2000, and currently is at levels not seen since 1960s usage levels.
At the beginning of the 20th century, petroleum was a minor resource used to manufacture lubricants and fuel for kerosene
and oil lamps. One hundred years later it had become the preeminent energy source for the U.S. and the rest of the world. This rise closely paralleled the emergence of the automobile
as a major force in American culture and the economy.
While petroleum is also used as a source for plastics and other chemicals
, and powers various industrial processes, today two-thirds of oil consumption in the U.S. is in the form of its derived transportation fuels. Oil's unique qualities for transportation fuels in terms of energy content, cost of production, and speed of refueling have made it difficult to supplant with technological alternatives developed so far.
In June 2010, the American Energy Innovation Council, (which includes Bill Gates
, Microsoft; Jeffrey R. Immelt
, chief executive of General Electric; and John Doerr
) has urged the government to more than triple spending on energy research and development, to $16 billion a year. Mr. Gates endorsed the administration’s goal of reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 80 percent by 2050, but said that was not possible with today’s technology or politicism. He said that the only way to find such disruptive new technology was to pour large sums of money at the problem. The group notes that the federal government spends less than $5 billion a year on energy research and development, not counting one-time stimulus projects. About $30 billion is spent annually on health research and more than $80 billion on military R.& D. They advocate a jump in spending on basic energy research.
The breakdown of energy consumption by source is given here:
U.S, Primary Energy Consumption by Source and Sector in 2008 is tabled as following:
Note: Sum of components may not equal 100 percent due to independent rounding.
Total Primary Consumption Historical Evolution in U.S until 2009.
Total Consumption until 2009 in Mtoe :
CAGR = Compound Annual Growth Rate
Note: Total energy includes coal, gas, oil, electricity, heat and biomass.
 Household energy use varies significantly across the United States. An average home in the Pacific region (consisting of California
Household energy use varies significantly across the United States. An average home in the Pacific region (consisting of California
, Oregon
, and Washington) consumes 35% less energy than a home in the South Central region. Most of the regional differences can be explained by climate. The heavily populated coastal areas of the Pacific states experience generally mild winters and summers, reducing the need for both home heating and air conditioning
. The warm, humid climates of the South Central and South Atlantic regions lead to higher electricity usage, while the cold winters experienced in the Northeast and North Central regions result in much higher consumption of natural gas and heating oil
.
Another reason for regional differences is the variety of building codes and environmental regulations found at the local and state level. California has some of the strictest environmental laws and building codes in the country, which may contribute to the fact that its per-household energy consumption is lower than all other states except Hawaii.
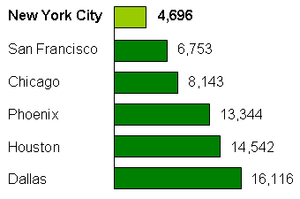
Major U.S. cities also show significant variation in per capita energy consumption. In addition to differences in regional climates and variations in building code standards, factors affecting energy use in cities include population density and building design. Townhouses are more energy efficient than single-family homes because less heat, for example, is wasted per person.
In 2010 2/3 of total petroleum consumption was for transportation.12321 Almost 2/3 of transportation consumption was gasoline
.
During the Carter
administration, in response to an energy crisis and hostile Iranian and Soviet Union relations, President Jimmy Carter announced the Carter Doctrine
which declared that any interference with U. S. interests in the Persian Gulf would be considered an attack on U.S. vital interests. This doctrine was expanded by Ronald Reagan
.
and other kinds of gas
powered plants.
From 1992 to 2005 some 270,000 MWe (Megawatt electric) of new gas-fired plant were built, but only 14,000 MWe of new nuclear and coal-fired capacity came on line, mostly coal, with 2,315 MWe of that being nuclear. Nuclear and coal
are considerably more capital intensive when compared to gas, and the great shift to gas plant construction is often attributed to deregulation and other political and economic factors.
the American Wind Energy Association
estimated that U.S. wind power
, capacity as 16,818 MW, sufficient to power 4.5 million homes. The largest wind facility in the U.S. and the world is in Roscoe Texas, costing more than $1 billion and providing 781.5 MW of power (enough for 230,000 homes throughout Texas, which has more wind power generation capacity than any other state and all but four countries.). Several solar thermal power stations, including the new 64 MW Nevada Solar One
, have also been built. The largest of these solar thermal power stations is the SEGS group of plants in the Mojave Desert with a total generating capacity of 354 MW, making the system the largest solar plant of any kind in the world.
In 2007, summer demand for electricity was 783 GW and 640 GW for winter. By 2017, North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) projects summer consumption to be 925GW for summer and 756 GW for winter.
as well as in all subsectors listed in the column entitled Major uses in the above tables. In 1999, a study by Mark. P. Mills of the Green Earth Society reported that computers consumed 13% of the entire US supply. Numerous researchers questioned Mills' methodology and it was later demonstrated that he was off by an order of magnitude; for example, Lawrence Berkeley Labs
concluded that the figure was nearer three percent of US electricity use. Although the Mills study was inaccurate, it helped drive the debate to the national level, and in 2006 the US Senate started a study of the energy consumption of Server farm
s.
and China's President Hu Jintao
announced on 2009-11-17 a far-reaching package of measures to strengthen cooperation between the United States and China on clean energy. The presidents began by establishing a U.S.-China Clean Energy Research Center to facilitate joint research and development of renewable energy technologies by scientists from both countries. The center will be supported by $150 million in public and private funds over the next five years, split evenly between the partners. Initial research priorities will be building energy efficiency and electric vehicle
s......
The two countries will also leverage private sector resources to develop clean energy projects in China through the U.S.-China Energy Cooperation Program (ECP). More than 22 companies are founding members of the program. The ECP will include collaborative projects involving renewable energy
, smart grids, electric vehicle
s, green building
s, combined heat and power
and energy efficiency.
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
is the 2nd largest energy
Energy development
Energy development is the effort to provide sufficient primary energy sources and secondary energy forms for supply, cost, impact on air pollution and water pollution, mitigation of climate change with renewable energy....
consumer in terms of total use in 2010 . The U.S. ranks seventh in energy consumption per-capita after Canada and a number of small countries.
The majority of this energy is derived from fossil fuel
Fossil fuel
Fossil fuels are fuels formed by natural processes such as anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms. The age of the organisms and their resulting fossil fuels is typically millions of years, and sometimes exceeds 650 million years...
s: in 2009, EIA data showed 37% of the nation's energy came from petroleum
Petroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
, 21% from coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
, and 25% from natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
. Nuclear power
Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
supplied 9% and renewable energy
Renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat, which are renewable . About 16% of global final energy consumption comes from renewables, with 10% coming from traditional biomass, which is mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from...
supplied 8%, which was mainly from hydroelectric dams although other renewables are included such as wind power
Wind power
Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into a useful form of energy, such as using wind turbines to make electricity, windmills for mechanical power, windpumps for water pumping or drainage, or sails to propel ships....
, geothermal
Geothermal
Geothermal is related to energy and may refer to:* The geothermal gradient and associated heat flows from within the Earth- Renewable technology :...
and solar energy. Energy consumption has increased at a faster rate than energy production over the last fifty years in the U.S.(when they were roughly equal). This difference is now largely met through imports.
According to the Energy Information Administration
Energy Information Administration
The U.S. Energy Information Administration is the statistical and analytical agency within the U.S. Department of Energy. EIA collects, analyzes, and disseminates independent and impartial energy information to promote sound policymaking, efficient markets, and public understanding of energy and...
's statistics, the per-capita energy consumption in the US has been somewhat consistent from the 1970s to today. The average has been 335.9 million British thermal unit
British thermal unit
The British thermal unit is a traditional unit of energy equal to about 1055 joules. It is approximately the amount of energy needed to heat of water, which is exactly one tenth of a UK gallon or about 0.1198 US gallons, from 39°F to 40°F...
s (BTUs) per person from 1980 to 2006. One explanation suggested for this is that the energy required to produce the increase in US consumption of manufactured equipment, cars, and other goods has been shifted to other countries producing and transporting those goods to the US with a corresponding shift of green house gases and pollution. In comparison, the world average has increased from 63.7 in 1980 to 72.4 million BTU's per person in 2006. On the other hand, US "off-shoring" of manufacturing is sometimes exaggerated: US domestic manufacturing has grown by 50% since 1980.
The development of renewable energy and energy efficiency marks "a new era of energy exploration" in the United States, according to President Barack Obama
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.Born in...
.
| Energy in the United States | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capita | Prim. energy | Production | Import | Electricity | CO2-emission | |
| Million | TWh | TWh | TWh | TWh | Mt | |
| 2004 | 294.0 | 27,050 | 19,085 | 8,310 | 3,921 | 5,800 |
| 2007 | 302.1 | 27,214 | 19,366 | 8,303 | 4,113 | 5,769 |
| 2008 | 304.5 | 26,560 | 19,841 | 7,379 | 4,156 | 5,596 |
| 2009 | 307.5 | 25,155 | 19,613 | 6,501 | 3,962 | 5,195 |
| Change 2004-2009 | 4.6 % | -7.0 % | 2.8 % | -21.8 % | 1.0 % | -10.4 % |
| Mtoe = 11.63 TWh. Primary energy includes energy losses that are 2/3 for nuclear power |
||||||
Primary energy use in the United States was 25,155 TWh and 82 TWh per million persons in 2009. Primary energy use was 1,100 TWh less in the US than in China in 2009. Same year the share of energy import in the US was 26 % of the primary energy use. The energy import declined ca 22 % and the annual CO2 emissions ca 10 % in 2009 compared to 2004.
History
From its founding until the late 18th century, the United States was a largely agrarian country with abundant forests. During this period, energy consumption overwhelmingly focused on readily available firewoodWood fuel
Wood fuel is wood used as fuel. The burning of wood is currently the largest use of energy derived from a solid fuel biomass. Wood fuel can be used for cooking and heating, and occasionally for fueling steam engines and steam turbines that generate electricity. Wood fuel may be available as...
. Rapid industrialization of the economy, urbanization, and the growth of railroads led to increased use of coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
, and by 1885 it had eclipsed wood as the nation's primary energy source.
Coal remained dominant for the next 7 decades, but by 1950, it was surpassed in turn by both petroleum and natural gas. , coal consumption is the highest it has ever been, with coal mostly being used to generate electricity
Electricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric energy from other forms of energy.The fundamental principles of electricity generation were discovered during the 1820s and early 1830s by the British scientist Michael Faraday...
. Natural gas, which is cleaner-burning and more easily transportable, has replaced coal as the preferred source of heating in homes, businesses and industrial furnaces. Although total energy use increased by approximately a factor of 50 between 1850 and 2000, energy use per capita increased only by a factor of four. As of 2009, United States per capita energy use had declined to 7075 more than 12% since 2000, and currently is at levels not seen since 1960s usage levels.
At the beginning of the 20th century, petroleum was a minor resource used to manufacture lubricants and fuel for kerosene
Kerosene lamp
The kerosene lamp is a type of lighting device that uses kerosene as a fuel. This article refers to kerosene lamps that have a wick and a tall glass chimney. Kerosene lanterns that have a wick and a glass globe are related to kerosene lamps and are included here as well...
and oil lamps. One hundred years later it had become the preeminent energy source for the U.S. and the rest of the world. This rise closely paralleled the emergence of the automobile
Automobile
An automobile, autocar, motor car or car is a wheeled motor vehicle used for transporting passengers, which also carries its own engine or motor...
as a major force in American culture and the economy.
While petroleum is also used as a source for plastics and other chemicals
Petrochemical
Petrochemicals are chemical products derived from petroleum. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable sources such as corn or sugar cane....
, and powers various industrial processes, today two-thirds of oil consumption in the U.S. is in the form of its derived transportation fuels. Oil's unique qualities for transportation fuels in terms of energy content, cost of production, and speed of refueling have made it difficult to supplant with technological alternatives developed so far.
In June 2010, the American Energy Innovation Council, (which includes Bill Gates
Bill Gates
William Henry "Bill" Gates III is an American business magnate, investor, philanthropist, and author. Gates is the former CEO and current chairman of Microsoft, the software company he founded with Paul Allen...
, Microsoft; Jeffrey R. Immelt
Jeffrey R. Immelt
Jeffrey Robert "Jeff" Immelt is an American business executive. He is currently the chairman of the board and chief executive officer of the U.S.-based conglomerate General Electric. He was selected by GE's Board of Directors in 2000 to replace Jack Welch following his retirement...
, chief executive of General Electric; and John Doerr
John Doerr
L. John Doerr is an American venture capitalist at Kleiner Perkins Caufield & Byers in Menlo Park, California, in Silicon Valley. In February 2009, Doerr was appointed as a member of the President's Economic Recovery Advisory Board to provide the president and his administration with advice and...
) has urged the government to more than triple spending on energy research and development, to $16 billion a year. Mr. Gates endorsed the administration’s goal of reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 80 percent by 2050, but said that was not possible with today’s technology or politicism. He said that the only way to find such disruptive new technology was to pour large sums of money at the problem. The group notes that the federal government spends less than $5 billion a year on energy research and development, not counting one-time stimulus projects. About $30 billion is spent annually on health research and more than $80 billion on military R.& D. They advocate a jump in spending on basic energy research.
Current consumption
The U.S. Department of Energy tracks national energy consumption in four broad sectors: industrial, transportation, residential, and commercial. The industrial sector has long been the country's largest energy user, currently representing about 33% of the total. Next in importance is the transportation sector, followed by the residential and commercial sectors.| Sector Name | Description | Major uses |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial | Facilities and equipment used for producing and processing goods. | 22% chemical production 16% petroleum refining 14% metal smelting/refining |
| Transportation | Vehicles which transport people/goods on ground, air or water. | 61% gasoline fuel 21% diesel fuel 12% aviation |
| Residential | Living quarters for private households. | 32% space heating 13% water heating 12% lighting 11% air conditioning 8% refrigeration 5% electronics 5% wet-clean (mostly clothes dryers) |
| Commercial | Service-providing facilities and equipment (businesses, government, other institutions). | 25% lighting 13% heating 11% cooling 6% refrigeration 6% water heating 6% ventilation 6% electronics |
The breakdown of energy consumption by source is given here:
| Fuel type | 2006 US consumption in PWh | 2006 World consumption in PWh |
| Oil | 11.71 | 50.33 |
| Gas | 6.50 | 31.65 |
| Coal | 6.60 | 37.38 |
| Hydroelectric | 0.84 | 8.71 |
| Nuclear | 2.41 | 8.14 |
| Geothermal, wind, solar, wood, waste |
0.95 | 1.38 |
| Total | 29.26 | 138.41 |
U.S, Primary Energy Consumption by Source and Sector in 2008 is tabled as following:
| Supply Sources | Percent of Source | Demand Sectors | Percent of Sector |
|---|---|---|---|
| Petroleum 37.1% |
71% Transportation 23% Industrial 5% Residential and Commercial 1% Electric Power |
Transportation 27.8% |
95% Petroleum 2% Natural Gas 3% Renewable Energy |
| Natural Gas 23.8% |
3% Transportation 34% Industrial 34% Residential and Commercial 29% Electric Power |
Industrial 20.6% |
42% Petroleum 40% Natural Gas 9% Coal 10% Renewable Energy |
| Coal 22.5% |
8% Industrial <1% Residential and Commercial 91% Electric Power |
Residential and Commercial 10.8% |
16% Petroleum 76% Natural Gas 1% Coal 1% Renewable Energy |
| Renewable Energy 7.3% |
11% Transportation 28% Industrial 10% Residential and Commercial 51% Electric Power |
Electric Power 40.1% |
1% Petroleum 17% Natural Gas 51% Coal 9% Renewable Energy 21% Nuclear Electric Power |
| Nuclear Electric Power 8.5% (30% ) |
100% Electric Power |
Note: Sum of components may not equal 100 percent due to independent rounding.
Total Primary Consumption Historical Evolution in U.S until 2009.
Total Consumption until 2009 in Mtoe :
| 1990 | 1991 | 1992 | 1993 | 1994 | 1995 | 1996 | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2008-2009 | CAGR 2000-09 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1914 | 1929,6 | 1967,5 | 2000,9 | 2041,3 | 2067,3 | 2118,4 | 2140,7 | 2167,2 | 2215,9 | 2279,6 | 2235,8 | 2270,6 | 2265,2 | 2311 | 2324,6 | 2304,5 | 2340,4 | 2301,4 | 2201,4 | -4,3% | 0,4% |
CAGR = Compound Annual Growth Rate
Note: Total energy includes coal, gas, oil, electricity, heat and biomass.
Regional variation

California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
, Oregon
Oregon
Oregon is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is located on the Pacific coast, with Washington to the north, California to the south, Nevada on the southeast and Idaho to the east. The Columbia and Snake rivers delineate much of Oregon's northern and eastern...
, and Washington) consumes 35% less energy than a home in the South Central region. Most of the regional differences can be explained by climate. The heavily populated coastal areas of the Pacific states experience generally mild winters and summers, reducing the need for both home heating and air conditioning
Air conditioning
An air conditioner is a home appliance, system, or mechanism designed to dehumidify and extract heat from an area. The cooling is done using a simple refrigeration cycle...
. The warm, humid climates of the South Central and South Atlantic regions lead to higher electricity usage, while the cold winters experienced in the Northeast and North Central regions result in much higher consumption of natural gas and heating oil
Heating oil
Heating oil, or oil heat, is a low viscosity, flammable liquid petroleum product used as a fuel for furnaces or boilers in buildings. Home heating oil is often abbreviated as HHO...
.
Another reason for regional differences is the variety of building codes and environmental regulations found at the local and state level. California has some of the strictest environmental laws and building codes in the country, which may contribute to the fact that its per-household energy consumption is lower than all other states except Hawaii.
Major U.S. cities also show significant variation in per capita energy consumption. In addition to differences in regional climates and variations in building code standards, factors affecting energy use in cities include population density and building design. Townhouses are more energy efficient than single-family homes because less heat, for example, is wasted per person.
Oil consumption
During the 1990s, the United States imported over two-thirds of its oil. , this has fallen; less than half of US oil consumption is now imported.In 2010 2/3 of total petroleum consumption was for transportation.12321 Almost 2/3 of transportation consumption was gasoline
Gasoline
Gasoline , or petrol , is a toxic, translucent, petroleum-derived liquid that is primarily used as a fuel in internal combustion engines. It consists mostly of organic compounds obtained by the fractional distillation of petroleum, enhanced with a variety of additives. Some gasolines also contain...
.
During the Carter
Jimmy Carter
James Earl "Jimmy" Carter, Jr. is an American politician who served as the 39th President of the United States and was the recipient of the 2002 Nobel Peace Prize, the only U.S. President to have received the Prize after leaving office...
administration, in response to an energy crisis and hostile Iranian and Soviet Union relations, President Jimmy Carter announced the Carter Doctrine
Carter Doctrine
The Carter Doctrine was a policy proclaimed by President of the United States Jimmy Carter in his State of the Union Address on January 23, 1980, which stated that the United States would use military force if necessary to defend its national interests in the Persian Gulf region...
which declared that any interference with U. S. interests in the Persian Gulf would be considered an attack on U.S. vital interests. This doctrine was expanded by Ronald Reagan
Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan was the 40th President of the United States , the 33rd Governor of California and, prior to that, a radio, film and television actor....
.
Electricity production
That United States has and continues to get most of its electrical production from conventional thermal power plants. Most of these are coal; however, the 1990s and 2000s have seen a significant increase in natural gasNatural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
and other kinds of gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
powered plants.
From 1992 to 2005 some 270,000 MWe (Megawatt electric) of new gas-fired plant were built, but only 14,000 MWe of new nuclear and coal-fired capacity came on line, mostly coal, with 2,315 MWe of that being nuclear. Nuclear and coal
Coal power in the United States
Coal power in the United States accounts for 46% of the country's electricity production. Utilities buy more than 90 percent of the coal mined in the United States....
are considerably more capital intensive when compared to gas, and the great shift to gas plant construction is often attributed to deregulation and other political and economic factors.
the American Wind Energy Association
American Wind Energy Association
Formed in 1974, the American Wind Energy Association is a Washington, D.C.-based national trade association representing wind power project developers, equipment suppliers, service providers, parts manufacturers, utilities, researchers, and others involved in the wind industry.With over 2,500...
estimated that U.S. wind power
Wind power in the United States
As of the third quarter of 2011, the cumulative installed capacity of wind power in the United States was 43,461 megawatts , making it second in the world, behind China. In 2010 wind power accounted for 2.3% of the electricity generated in the United States...
, capacity as 16,818 MW, sufficient to power 4.5 million homes. The largest wind facility in the U.S. and the world is in Roscoe Texas, costing more than $1 billion and providing 781.5 MW of power (enough for 230,000 homes throughout Texas, which has more wind power generation capacity than any other state and all but four countries.). Several solar thermal power stations, including the new 64 MW Nevada Solar One
Nevada Solar One
Nevada Solar One is a concentrated solar power plant, with a nominal capacity of 64 MW and maximum capacity of 75 MW spread over an area of 400 Acres. The projected CO2 emissions avoided is equivalent to taking approximately 20,000 cars off the road annually. The project required an investment of...
, have also been built. The largest of these solar thermal power stations is the SEGS group of plants in the Mojave Desert with a total generating capacity of 354 MW, making the system the largest solar plant of any kind in the world.
In 2007, summer demand for electricity was 783 GW and 640 GW for winter. By 2017, North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) projects summer consumption to be 925GW for summer and 756 GW for winter.
| Power Source | Units in Operation | Total Nameplate Capacity (MW) | % of total Capacity | Annual Production (billion kWh) | % of annual production |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Petroleum Coke Petroleum coke Petroleum coke is a carbonaceous solid derived from oil refinery coker units or other cracking processes. Other coke has traditionally been derived from coal.... Fueled Boiler Boiler A boiler is a closed vessel in which water or other fluid is heated. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications.-Materials:... |
|||||
| Oil Fired Oil An oil is any substance that is liquid at ambient temperatures and does not mix with water but may mix with other oils and organic solvents. This general definition includes vegetable oils, volatile essential oils, petrochemical oils, and synthetic oils.... Boiler Boiler A boiler is a closed vessel in which water or other fluid is heated. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications.-Materials:... |
|||||
| Nuclear Power Nuclear power Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity... |
|||||
| Natural Gas Natural gas Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural... Fueled Boiler Boiler A boiler is a closed vessel in which water or other fluid is heated. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications.-Materials:... |
|||||
| Diesel Generators Diesel engine A diesel engine is an internal combustion engine that uses the heat of compression to initiate ignition to burn the fuel, which is injected into the combustion chamber... |
|||||
| Incinerators | |||||
| Hydroelectric | |||||
| Geothermal | |||||
| Fuel Oil Fuel oil Fuel oil is a fraction obtained from petroleum distillation, either as a distillate or a residue. Broadly speaking, fuel oil is any liquid petroleum product that is burned in a furnace or boiler for the generation of heat or used in an engine for the generation of power, except oils having a flash... |
|||||
| Combustion Turbine Generators Gas turbine A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of internal combustion engine. It has an upstream rotating compressor coupled to a downstream turbine, and a combustion chamber in-between.... |
|||||
| Combined Cycle Natural Gas | |||||
| Coal Fired Boilers Coal Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure... |
|||||
| Biomass Biomass Biomass, as a renewable energy source, is biological material from living, or recently living organisms. As an energy source, biomass can either be used directly, or converted into other energy products such as biofuel.... |
|||||
| Wind Power Wind power Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into a useful form of energy, such as using wind turbines to make electricity, windmills for mechanical power, windpumps for water pumping or drainage, or sails to propel ships.... |
|||||
| Solar Energy | |||||
| Generator Type | 0-50MW | 50-100MW | 100-250MW | 250-500MW | 500-750MW | 750-1,000MW | 1000-1250MW | 1250MW + |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Petroleum Coke Petroleum coke Petroleum coke is a carbonaceous solid derived from oil refinery coker units or other cracking processes. Other coke has traditionally been derived from coal.... Fueled Boiler Boiler A boiler is a closed vessel in which water or other fluid is heated. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications.-Materials:... |
||||||||
| Oil Fired Oil An oil is any substance that is liquid at ambient temperatures and does not mix with water but may mix with other oils and organic solvents. This general definition includes vegetable oils, volatile essential oils, petrochemical oils, and synthetic oils.... Boiler Boiler A boiler is a closed vessel in which water or other fluid is heated. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications.-Materials:... |
||||||||
| Nuclear Power Nuclear power Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity... |
||||||||
| Natural Gas Natural gas Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural... Fueled Boiler Boiler A boiler is a closed vessel in which water or other fluid is heated. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications.-Materials:... |
||||||||
| Diesel Generators Diesel engine A diesel engine is an internal combustion engine that uses the heat of compression to initiate ignition to burn the fuel, which is injected into the combustion chamber... |
||||||||
| Incinerators | ||||||||
| Hydroelectric | ||||||||
| Geothermal | ||||||||
| Fuel Oil Fuel oil Fuel oil is a fraction obtained from petroleum distillation, either as a distillate or a residue. Broadly speaking, fuel oil is any liquid petroleum product that is burned in a furnace or boiler for the generation of heat or used in an engine for the generation of power, except oils having a flash... |
||||||||
| Combustion Turbine Generators Gas turbine A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of internal combustion engine. It has an upstream rotating compressor coupled to a downstream turbine, and a combustion chamber in-between.... |
||||||||
| Combined Cycle Natural Gas | ||||||||
| Coal Fired Boilers Coal Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure... |
||||||||
| Biomass Biomass Biomass, as a renewable energy source, is biological material from living, or recently living organisms. As an energy source, biomass can either be used directly, or converted into other energy products such as biofuel.... |
||||||||
| Wind Power Wind power Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into a useful form of energy, such as using wind turbines to make electricity, windmills for mechanical power, windpumps for water pumping or drainage, or sails to propel ships.... |
||||||||
| Solar Energy | ||||||||
Energy consumption of computers in the USA
Visible or embedded (i. e. hidden) computers are found everywhere: in all sectors listed in the above chapter,as well as in all subsectors listed in the column entitled Major uses in the above tables. In 1999, a study by Mark. P. Mills of the Green Earth Society reported that computers consumed 13% of the entire US supply. Numerous researchers questioned Mills' methodology and it was later demonstrated that he was off by an order of magnitude; for example, Lawrence Berkeley Labs
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
The Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory , is a U.S. Department of Energy national laboratory conducting unclassified scientific research. It is located on the grounds of the University of California, Berkeley, in the Berkeley Hills above the central campus...
concluded that the figure was nearer three percent of US electricity use. Although the Mills study was inaccurate, it helped drive the debate to the national level, and in 2006 the US Senate started a study of the energy consumption of Server farm
Server farm
A server farm or server cluster is a collection of computer servers usually maintained by an enterprise to accomplish server needs far beyond the capability of one machine. Server farms often have backup servers, which can take over the function of primary servers in the event of a primary server...
s.
International Cooperation
President Barack ObamaBarack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.Born in...
and China's President Hu Jintao
Hu Jintao
Hu Jintao is the current Paramount Leader of the People's Republic of China. He has held the titles of General Secretary of the Communist Party of China since 2002, President of the People's Republic of China since 2003, and Chairman of the Central Military Commission since 2004, succeeding Jiang...
announced on 2009-11-17 a far-reaching package of measures to strengthen cooperation between the United States and China on clean energy. The presidents began by establishing a U.S.-China Clean Energy Research Center to facilitate joint research and development of renewable energy technologies by scientists from both countries. The center will be supported by $150 million in public and private funds over the next five years, split evenly between the partners. Initial research priorities will be building energy efficiency and electric vehicle
Electric vehicle
An electric vehicle , also referred to as an electric drive vehicle, uses one or more electric motors or traction motors for propulsion...
s......
The two countries will also leverage private sector resources to develop clean energy projects in China through the U.S.-China Energy Cooperation Program (ECP). More than 22 companies are founding members of the program. The ECP will include collaborative projects involving renewable energy
Renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat, which are renewable . About 16% of global final energy consumption comes from renewables, with 10% coming from traditional biomass, which is mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from...
, smart grids, electric vehicle
Electric vehicle
An electric vehicle , also referred to as an electric drive vehicle, uses one or more electric motors or traction motors for propulsion...
s, green building
Green building
Green building refers to a structure and using process that is environmentally responsible and resource-efficient throughout a building's life-cycle: from siting to design, construction, operation, maintenance, renovation, and demolition...
s, combined heat and power
Combined Heat and Power
Combined Heat and Power may refer to:* Cogeneration* Combined Heat and Power Solar...
and energy efficiency.
See also
- Carter DoctrineCarter DoctrineThe Carter Doctrine was a policy proclaimed by President of the United States Jimmy Carter in his State of the Union Address on January 23, 1980, which stated that the United States would use military force if necessary to defend its national interests in the Persian Gulf region...
- The Climate RegistryThe Climate RegistryThe Climate Registry is a nonprofit collaboration between North American states, provinces, territories, and Native Sovereign Nations to record and track the greenhouse gas emissions of businesses, municipalities and other organisations...
- Efficient energy useEfficient energy useEfficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the goal of efforts to reduce the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a home allows a building to use less heating and cooling energy to achieve and maintain a comfortable temperature...
- Energy conservationEnergy conservationEnergy conservation refers to efforts made to reduce energy consumption. Energy conservation can be achieved through increased efficient energy use, in conjunction with decreased energy consumption and/or reduced consumption from conventional energy sources...
- Energy developmentEnergy developmentEnergy development is the effort to provide sufficient primary energy sources and secondary energy forms for supply, cost, impact on air pollution and water pollution, mitigation of climate change with renewable energy....
- Energy conservation in the United StatesEnergy conservation in the United StatesThe United States is currently the second largest single consumer of energy. The U.S. Department of Energy categorizes national energy use in four broad sectors: transportation, residential, commercial, and industrial....
- Energy policy of the United StatesEnergy policy of the United StatesThe energy policy of the United States is determined by federal, state and local public entities in the United States, which address issues of energy production, distribution, and consumption, such as building codes and gas mileage standards...
- Energy securityEnergy securityEnergy security is a term for an association between national security and the availability of natural resources for energy consumption. Access to cheap energy has become essential to the functioning of modern economies. However, the uneven distribution of energy supplies among countries has led...
- World energy resources and consumptionWorld energy resources and consumption]World energy consumption in 2010: over 5% growthEnergy markets have combined crisis recovery and strong industry dynamism. Energy consumption in the G20 soared by more than 5% in 2010, after the slight decrease of 2009. This strong increase is the result of two converging trends...
- List of countries by energy consumption and production
- Petroleum in the United StatesPetroleum in the United StatesPetroleum in the United States has been a major industry since shortly after the oil discovery in the Oil Creek area of Titusville, Pennsylvania in 1859. As of 2008, the US was the world's third-largest oil producer , producing 8.5 million barrels of oil and natural gas liquids per day...
- Renewable energy in the United StatesRenewable energy in the United StatesRenewable energy accounted for 14.3 percent of the domestically produced electricity in the United States in the first six months of 2011. Hydroelectricity is the largest producer of renewable power in the United States. In 2009, the U.S...
- Individual states:
- Energy in VermontEnergy in VermontVermont energy needs are served by over twenty utilities. The largest are Central Vermont Public Service and Green Mountain Power. Together they represent 70% of the customers. The state is a very small electricity consumer compared with other states. Its electricity sector has the lowest carbon...
- Energy in Vermont
External links
- Energy Information Administration - Official Energy Statistics from the U.S. Government
- Biomass Energy Data Book
- Buildings Energy Data Book
- Power Technologies Energy Data Book (renewables)
- Transportation Energy Data Book
- Interactive United States Energy Comparisons
- Renewable Energy Tops 10% of U.S. Energy Production
- World Energy Lighting

