
Electronic filter topology
Encyclopedia
Electronic filter topology
defines electronic filter
circuits without taking note of the values of the components used but only the manner in which those components are connected.
Filter design
characterises filter circuits primarily by their transfer function
rather than their topology
. Transfer functions may be linear
or nonlinear. Common types of linear filter transfer function are; high-pass
, low-pass
, bandpass
, band-reject or notch
and all-pass
. Once the transfer function for a filter is chosen, the particular topology to implement such a prototype filter
can be selected so that, for example, one might choose to design a Butterworth filter
using the Sallen–Key topology.
Filter topologies may be divided into passive
and active
types. Passive topologies do not contain a generator of energy, either in reality or, due to non-linearity, in their equivalent circuit, but only capacitors, inductors and also, in some topologies, resistors: particularly, variable resistors are often included in order to control the depth of filtering. Active topologies include components that require power. Further, topologies may be implemented either in unbalanced
form or else in balanced
form when employed in balanced circuit
s. Implementations such as electronic mixer
s and stereo sound may require arrays of identical circuits.
. Most are built from simple two-port network
s called "sections". There is no formal definition of a section except that it must have at least one series component and one shunt component. Sections are invariably connected in a "cascade" or "daisy-chain"
topology, consisting of either repeats of the same section or of completely different sections. Impedance
would combine two sections consisting only of series components or shunt components into a single section.
Some passive filters, consisting of only one or two filter sections, are given special names including the L-section, T-section and Π-section, which are unbalanced filters, and the C-section, H-section and box-section, which are balanced. All are built upon a very simple "ladder" topology (see below). The chart at the bottom of the page shows these various topologies in terms of general constant k filter
s.
Filters designed using network synthesis
usually repeat the simplest form of L-section topology though component values may change in each section. Image designed filters, on the other hand, keep the same basic component values from section to section though the topology may vary and tend to make use of more complex sections.
L-sections are never symmetrical but two L-sections back-to-back form a symmetrical topology and many other sections are symmetrical in form.
(inventor of the Elliptical filter), was in fact first used by George Campbell
(inventor of the Constant k filter
). Campbell published in 1922 but had clearly been using the topology for some time before this. Cauer first picked up on ladders (published 1926) inspired by the work of Foster (1924). There are two forms of basic ladder topologies; unbalanced and balanced. Cauer topology is usually thought of as an unbalanced ladder topology.
A ladder network consists of cascaded asymmetrical L-sections (unbalanced) or C-sections (balanced). In low pass
form the topology would consist of series inductors and shunt capacitors. Other bandforms would have an equally simple topology transformed from the lowpass topology. The transformed network will have shunt admittances that are dual networks of the series impedances if they were duals in the starting network - which is the case with series inductors and shunt capacitors.
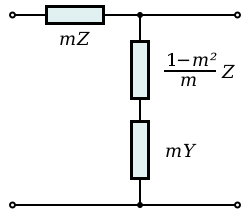 Image filter design commonly uses modifications of the basic ladder topology. These topologies, invented by Otto Zobel, have the same passband
Image filter design commonly uses modifications of the basic ladder topology. These topologies, invented by Otto Zobel, have the same passband
s as the ladder on which they are based but their transfer functions are modified to improve some parameter such as impedance matching
, stopband
rejection or passband-to-stopband transition steepness. Usually the design applies some transform to a simple ladder topology: the resulting topology is ladder-like but no longer obeys the rule that shunt admittances are the dual network of series impedances: it invariably becomes more complex with higher component count. Such topologies include;
The m-type (m-derived) filter is by far the most commonly used modified image ladder topology. There are two m-type topologies for each of the basic ladder topologies; the series-derived and shunt-derived topologies. These have identical transfer functions to each other but different image impedances. Where a filter is being designed with more than one passband, the m-type topology will result in a filter where each passband has an analogous frequency-domain response. It is possible to generalise the m-type topology for filters with more than one passband using parameters m1, m2, m3 etc., which are not equal to each other resulting in general mn-type filters which have bandforms that can differ in different parts of the frequency spectrum.
The mm'-type topology can be thought of as a double m-type design. Like the m-type it has the same bandform but offers further improved transfer characteristics. It is, however, a rarely used design due to increased component count and complexity as well as its normally requiring basic ladder and m-type sections in the same filter for impedance matching reasons. It is normally only found in a composite filter
.
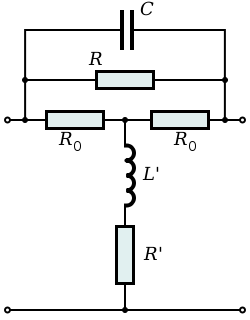 Zobel constant resistance filters use a topology that is somewhat different from other filter types, distinguished by having a constant input resistance at all frequencies and in that they use resistive components in the design of their sections. The higher component and section count of these designs usually limits their use to equalisation applications. Topologies usually associated with constant resistance filters are the bridged-T and its variants, all described in the Zobel network
Zobel constant resistance filters use a topology that is somewhat different from other filter types, distinguished by having a constant input resistance at all frequencies and in that they use resistive components in the design of their sections. The higher component and section count of these designs usually limits their use to equalisation applications. Topologies usually associated with constant resistance filters are the bridged-T and its variants, all described in the Zobel network
article;
The bridged-T topology is also used in sections intended to produce a signal delay but in this case no resistive components are used in the design.
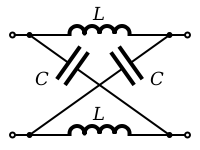 Both the T-section (from ladder topology) and the bridge-T (from Zobel topology) can be transformed into a lattice topology filter section but in both cases this results in high component count and complexity. The most common application of lattice filters (X-sections) is in all-pass filter
Both the T-section (from ladder topology) and the bridge-T (from Zobel topology) can be transformed into a lattice topology filter section but in both cases this results in high component count and complexity. The most common application of lattice filters (X-sections) is in all-pass filter
s used for phase equalisation
.
Although T and bridged-T sections can always be transformed into X-sections the reverse is not always possible because of the possibility of negative values of inductance and capacitance arising in the transform.
Lattice topology is identical to the more familiar bridge topology, the difference being merely the drawn representation on the page rather than any real difference in topology, cicuitry or function.
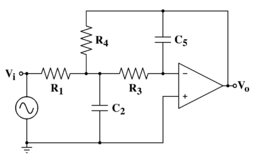 Multiple feedback topology is an electronic filter topology which is used to implement an electronic filter
Multiple feedback topology is an electronic filter topology which is used to implement an electronic filter
by adding two poles to the transfer function
. A diagram of the circuit topology for a second order low pass filter is shown in the figure on the right.
The transfer function of the multiple feedback topology circuit, like all second-order linear filter
s, is:
 .
.
In an MF filter,


 is the Q factor
is the Q factor
. is the DC voltage gain
is the DC voltage gain
 is the corner frequency
is the corner frequency
A biquad filter is a type of linear filter
that implements a transfer function
that is the ratio of two quadratic function
s. The name biquad is short for biquadratic.
Biquad filters are typically active
and implemented with a single-amplifier biquad (SAB) or two-integrator-loop topology.
The SAB topology is sensitive to component choice and can be more difficult to adjust. Hence, usually the term biquad refers to the two-integrator-loop state variable filter topology.
or bandpass
filter depending on where the output signal is taken from.
The second-order low-pass transfer function is given by

where low-pass gain . The second-order bandpass transfer function is given by
. The second-order bandpass transfer function is given by
 .
.
with bandpass gain . In both cases, the
. In both cases, the
The bandwidth is approximated by , and Q is sometimes expressed as a damping constant
, and Q is sometimes expressed as a damping constant  . If a noninverting low-pass filter is required, the output can be taken at the output of the second operational amplifier
. If a noninverting low-pass filter is required, the output can be taken at the output of the second operational amplifier
. If a noninverting bandpass filter is required, the order of the second integrator and the inverter can be switched, and the output taken at the output of the inverter's operational amplifier.
Topology (electronics)
The topology of an electronic circuit is the form taken by the network of interconnections of the circuit components. Different specific values or ratings of the components are regarded as being the same topology....
defines electronic filter
Electronic filter
Electronic filters are electronic circuits which perform signal processing functions, specifically to remove unwanted frequency components from the signal, to enhance wanted ones, or both...
circuits without taking note of the values of the components used but only the manner in which those components are connected.
Filter design
Filter design
Filter design is the process of designing a filter , often a linear shift-invariant filter, that satisfies a set of requirements, some of which are contradictory...
characterises filter circuits primarily by their transfer function
Transfer function
A transfer function is a mathematical representation, in terms of spatial or temporal frequency, of the relation between the input and output of a linear time-invariant system. With optical imaging devices, for example, it is the Fourier transform of the point spread function i.e...
rather than their topology
Topology
Topology is a major area of mathematics concerned with properties that are preserved under continuous deformations of objects, such as deformations that involve stretching, but no tearing or gluing...
. Transfer functions may be linear
Linear filter
Linear filters in the time domain process time-varying input signals to produce output signals, subject to the constraint of linearity.This results from systems composed solely of components classified as having a linear response....
or nonlinear. Common types of linear filter transfer function are; high-pass
High-pass filter
A high-pass filter is a device that passes high frequencies and attenuates frequencies lower than its cutoff frequency. A high-pass filter is usually modeled as a linear time-invariant system...
, low-pass
Low-pass filter
A low-pass filter is an electronic filter that passes low-frequency signals but attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The actual amount of attenuation for each frequency varies from filter to filter. It is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble cut filter...
, bandpass
Band-pass filter
A band-pass filter is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects frequencies outside that range.Optical band-pass filters are of common usage....
, band-reject or notch
Band-stop filter
In signal processing, a band-stop filter or band-rejection filter is a filter that passes most frequencies unaltered, but attenuates those in a specific range to very low levels. It is the opposite of a band-pass filter...
and all-pass
All-pass filter
An all-pass filter is a signal processing filter that passes all frequencies equally, but changes the phase relationship between various frequencies. It does this by varying its propagation delay with frequency...
. Once the transfer function for a filter is chosen, the particular topology to implement such a prototype filter
Prototype filter
Prototype filters are electronic filter designs that are used as a template to produce a modified filter design for a particular application. They are an example of a nondimensionalised design from which the desired filter can be scaled or transformed. They are most often seen in regards to...
can be selected so that, for example, one might choose to design a Butterworth filter
Butterworth filter
The Butterworth filter is a type of signal processing filter designed to have as flat a frequency response as possible in the passband so that it is also termed a maximally flat magnitude filter...
using the Sallen–Key topology.
Filter topologies may be divided into passive
Passivity (engineering)
Passivity is a property of engineering systems, used in a variety of engineering disciplines, but most commonly found in analog electronics and control systems...
and active
Active filter
An active filter is a type of analog electronic filter that uses an amplifier stage. Amplifiers included in a filter design can be used to improve the performance, stability and predictability of a filter. An amplifier prevents the impedance of source or load stages from affecting the...
types. Passive topologies do not contain a generator of energy, either in reality or, due to non-linearity, in their equivalent circuit, but only capacitors, inductors and also, in some topologies, resistors: particularly, variable resistors are often included in order to control the depth of filtering. Active topologies include components that require power. Further, topologies may be implemented either in unbalanced
Unbalanced line
In Electrical engineering, an unbalanced line is a transmission line, usually coaxial cable, whose conductors have unequal impedances with respect to ground; as opposed to a balanced line.Microstrip and single-wire lines are also unbalanced lines....
form or else in balanced
Balanced line
In telecommunications and professional audio, a balanced line or balanced signal pair is a transmission line consisting of two conductors of the same type, each of which have equal impedances along their lengths and equal impedances to ground and to other circuits. The chief advantage of the...
form when employed in balanced circuit
Balanced circuit
A balanced circuit is circuitry for use with a balanced line or the balanced line itself. Balanced lines are a common method of transmitting many types of electrical communication signals between two points on two wires...
s. Implementations such as electronic mixer
Electronic mixer
An electronic mixer is a device that combines two or more electrical or electronic signals into one or two composite output signals. There are two basic circuits that both use the term mixer, but they are very different types of circuits: additive mixers and multiplying mixers...
s and stereo sound may require arrays of identical circuits.
Passive topologies
Passive filters have been long in development and usePassive analogue filter development
Analogue filters are a basic building block of signal processing much used in electronics. Amongst their many applications are the separation of an audio signal before application to bass, mid-range and tweeter loudspeakers; the combining and later separation of multiple telephone conversations...
. Most are built from simple two-port network
Two-port network
A two-port network is an electrical circuit or device with two pairs of terminals connected together internally by an electrical network...
s called "sections". There is no formal definition of a section except that it must have at least one series component and one shunt component. Sections are invariably connected in a "cascade" or "daisy-chain"
Daisy chain (electrical engineering)
In electrical and electronic engineering a daisy chain is a wiring scheme in which multiple devices are wired together in sequence or in a ring...
topology, consisting of either repeats of the same section or of completely different sections. Impedance
Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
would combine two sections consisting only of series components or shunt components into a single section.
Some passive filters, consisting of only one or two filter sections, are given special names including the L-section, T-section and Π-section, which are unbalanced filters, and the C-section, H-section and box-section, which are balanced. All are built upon a very simple "ladder" topology (see below). The chart at the bottom of the page shows these various topologies in terms of general constant k filter
Constant k filter
Constant k filters, also k-type filters, are a type of electronic filter designed using the image method. They are the original and simplest filters produced by this methodology and consist of a ladder network of identical sections of passive components...
s.
Filters designed using network synthesis
Network synthesis filters
Network synthesis is a method of designing signal processing filters. It has produced several important classes of filter including the Butterworth filter, the Chebyshev filter and the Elliptic filter. It was originally intended to be applied to the design of passive linear analogue filters but...
usually repeat the simplest form of L-section topology though component values may change in each section. Image designed filters, on the other hand, keep the same basic component values from section to section though the topology may vary and tend to make use of more complex sections.
L-sections are never symmetrical but two L-sections back-to-back form a symmetrical topology and many other sections are symmetrical in form.
Ladder topologies
Ladder topology, often called Cauer topology after Wilhelm CauerWilhelm Cauer
Wilhelm Cauer was a German mathematician and scientist. He is most noted for his work on the analysis and synthesis of electrical filters and his work marked the beginning of the field of network synthesis...
(inventor of the Elliptical filter), was in fact first used by George Campbell
George Ashley Campbell
George Ashley Campbell was a pioneer in developing and applying quantitative mathematical methods to the problems of long-distance telegraphy and telephony. His most important contributions were to the theory and implementation of the use of loading coils and the first wave filters designed to...
(inventor of the Constant k filter
Constant k filter
Constant k filters, also k-type filters, are a type of electronic filter designed using the image method. They are the original and simplest filters produced by this methodology and consist of a ladder network of identical sections of passive components...
). Campbell published in 1922 but had clearly been using the topology for some time before this. Cauer first picked up on ladders (published 1926) inspired by the work of Foster (1924). There are two forms of basic ladder topologies; unbalanced and balanced. Cauer topology is usually thought of as an unbalanced ladder topology.
A ladder network consists of cascaded asymmetrical L-sections (unbalanced) or C-sections (balanced). In low pass
Low pass
Low Pass may refer to*Low Pass, Oregon*Low-pass filter* Low Pass in Mountain passes in Montana...
form the topology would consist of series inductors and shunt capacitors. Other bandforms would have an equally simple topology transformed from the lowpass topology. The transformed network will have shunt admittances that are dual networks of the series impedances if they were duals in the starting network - which is the case with series inductors and shunt capacitors.
Modified ladder topologies
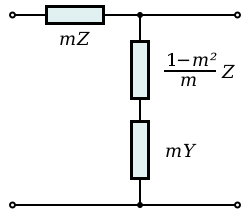
Passband
A passband is the range of frequencies or wavelengths that can pass through a filter without being attenuated.A bandpass filtered signal , is known as a bandpass signal, as opposed to a baseband signal....
s as the ladder on which they are based but their transfer functions are modified to improve some parameter such as impedance matching
Impedance matching
In electronics, impedance matching is the practice of designing the input impedance of an electrical load to maximize the power transfer and/or minimize reflections from the load....
, stopband
Stopband
A stopband is a band of frequencies, between specified limits, through which a circuit, such as a filter or telephone circuit, does not allow signals to pass, or the attenuation is above the required stopband attenuation level...
rejection or passband-to-stopband transition steepness. Usually the design applies some transform to a simple ladder topology: the resulting topology is ladder-like but no longer obeys the rule that shunt admittances are the dual network of series impedances: it invariably becomes more complex with higher component count. Such topologies include;
- m-derived filterM-derived filterm-derived filters or m-type filters are a type of electronic filter designed using the image method. They were invented by Otto Zobel in the early 1920s. This filter type was originally intended for use with telephone multiplexing and was an improvement on the existing constant k type filter...
- mm'-type filterMm'-type filtermm'-type filters, also called double-m-derived filters, are a type of electronic filter designed using the image method. They were patented by Otto Zobel in 1932...
- General mn-type filterGeneral mn-type image filtersThese filters are electrical wave filters designed using the image method. They are an invention of Otto Zobel at AT&T Corp.. They are a generalisation of the m-type filter in that a transform is applied that modifies the transfer function while keeping the image impedance unchanged. For filters...
The m-type (m-derived) filter is by far the most commonly used modified image ladder topology. There are two m-type topologies for each of the basic ladder topologies; the series-derived and shunt-derived topologies. These have identical transfer functions to each other but different image impedances. Where a filter is being designed with more than one passband, the m-type topology will result in a filter where each passband has an analogous frequency-domain response. It is possible to generalise the m-type topology for filters with more than one passband using parameters m1, m2, m3 etc., which are not equal to each other resulting in general mn-type filters which have bandforms that can differ in different parts of the frequency spectrum.
The mm'-type topology can be thought of as a double m-type design. Like the m-type it has the same bandform but offers further improved transfer characteristics. It is, however, a rarely used design due to increased component count and complexity as well as its normally requiring basic ladder and m-type sections in the same filter for impedance matching reasons. It is normally only found in a composite filter
Composite image filter
A composite image filter is an electronic filter consisting of multiple image filter sections of two or more different types.The image method of filter design determines the properties of filter sections by calculating the properties they have in an infinite chain of such sections. In this, the...
.
Bridged-T topologies
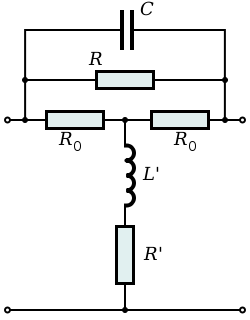
Zobel network
Zobel networks are a type of filter section based on the image impedance design principle. They are named after Otto Zobel of Bell Labs who published a much referenced paper on image filters in 1923. The distinguishing feature of Zobel networks is that the input impedance is fixed in the design...
article;
- Bridged-T topology
- Balanced bridged-T topology
- Open-circuit L-section topology
- Short-circuit L-section topology
- Balanced open-circuit C-section topology
- Balanced short-circuit C-section topology
The bridged-T topology is also used in sections intended to produce a signal delay but in this case no resistive components are used in the design.
Lattice topology

All-pass filter
An all-pass filter is a signal processing filter that passes all frequencies equally, but changes the phase relationship between various frequencies. It does this by varying its propagation delay with frequency...
s used for phase equalisation
Lattice phase equaliser
A lattice phase equaliser or lattice filter is an example of an all-pass filter. That is, the attenuation of the filter is constant at all frequencies but the relative phase between input and output varies with frequency...
.
Although T and bridged-T sections can always be transformed into X-sections the reverse is not always possible because of the possibility of negative values of inductance and capacitance arising in the transform.
Lattice topology is identical to the more familiar bridge topology, the difference being merely the drawn representation on the page rather than any real difference in topology, cicuitry or function.
Multiple feedback topology

Electronic filter
Electronic filters are electronic circuits which perform signal processing functions, specifically to remove unwanted frequency components from the signal, to enhance wanted ones, or both...
by adding two poles to the transfer function
Transfer function
A transfer function is a mathematical representation, in terms of spatial or temporal frequency, of the relation between the input and output of a linear time-invariant system. With optical imaging devices, for example, it is the Fourier transform of the point spread function i.e...
. A diagram of the circuit topology for a second order low pass filter is shown in the figure on the right.
The transfer function of the multiple feedback topology circuit, like all second-order linear filter
Linear filter
Linear filters in the time domain process time-varying input signals to produce output signals, subject to the constraint of linearity.This results from systems composed solely of components classified as having a linear response....
s, is:
 .
.In an MF filter,



 is the Q factor
is the Q factorQ factor
In physics and engineering the quality factor or Q factor is a dimensionless parameter that describes how under-damped an oscillator or resonator is, or equivalently, characterizes a resonator's bandwidth relative to its center frequency....
.
 is the DC voltage gain
is the DC voltage gainGain
In electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a circuit to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output. It is usually defined as the mean ratio of the signal output of a system to the signal input of the same system. It may also be defined on a logarithmic scale,...
 is the corner frequency
is the corner frequencyBiquad filter
For the digital implementation of a biquad filter, check digital biquad filter.A biquad filter is a type of linear filter
Linear filter
Linear filters in the time domain process time-varying input signals to produce output signals, subject to the constraint of linearity.This results from systems composed solely of components classified as having a linear response....
that implements a transfer function
Transfer function
A transfer function is a mathematical representation, in terms of spatial or temporal frequency, of the relation between the input and output of a linear time-invariant system. With optical imaging devices, for example, it is the Fourier transform of the point spread function i.e...
that is the ratio of two quadratic function
Quadratic function
A quadratic function, in mathematics, is a polynomial function of the formf=ax^2+bx+c,\quad a \ne 0.The graph of a quadratic function is a parabola whose axis of symmetry is parallel to the y-axis....
s. The name biquad is short for biquadratic.
Biquad filters are typically active
Active filter
An active filter is a type of analog electronic filter that uses an amplifier stage. Amplifiers included in a filter design can be used to improve the performance, stability and predictability of a filter. An amplifier prevents the impedance of source or load stages from affecting the...
and implemented with a single-amplifier biquad (SAB) or two-integrator-loop topology.
- The SAB topology uses feedback to generate complexComplex numberA complex number is a number consisting of a real part and an imaginary part. Complex numbers extend the idea of the one-dimensional number line to the two-dimensional complex plane by using the number line for the real part and adding a vertical axis to plot the imaginary part...
poles and possibly complex zeroZero (complex analysis)In complex analysis, a zero of a holomorphic function f is a complex number a such that f = 0.-Multiplicity of a zero:A complex number a is a simple zero of f, or a zero of multiplicity 1 of f, if f can be written asf=g\,where g is a holomorphic function g such that g is not zero.Generally, the...
s. In particular, the feedback moves the realReal numberIn mathematics, a real number is a value that represents a quantity along a continuum, such as -5 , 4/3 , 8.6 , √2 and π...
poles of an RC circuitRC circuitA resistor–capacitor circuit ', or RC filter or RC network, is an electric circuit composed of resistors and capacitors driven by a voltage or current source...
in order to generate the proper filter characteristics. - The two-integrator-loop topology is derived from rearranging a biquadratic transfer function. The rearrangement will equate one signal with the sum of another signal, its integral, and the integral's integral. In other words, the rearrangement reveals a state variable filterState variable filterA state variable filter is a type of active filter. It consists of one or more integrators, connected in some feedback configuration. Any LTI system can be described as a state-space model, with n state variables for an nth-order system. A state variable filter realizes the state-space model directly...
structure. By using different states as outputs, any kind of second-order filter can be implemented.
The SAB topology is sensitive to component choice and can be more difficult to adjust. Hence, usually the term biquad refers to the two-integrator-loop state variable filter topology.
Tow-Thomas Biquad Example
For example, the basic configuration in Figure 1 can be used as either a low-passLow-pass filter
A low-pass filter is an electronic filter that passes low-frequency signals but attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The actual amount of attenuation for each frequency varies from filter to filter. It is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble cut filter...
or bandpass
Band-pass filter
A band-pass filter is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects frequencies outside that range.Optical band-pass filters are of common usage....
filter depending on where the output signal is taken from.
The second-order low-pass transfer function is given by

where low-pass gain
 . The second-order bandpass transfer function is given by
. The second-order bandpass transfer function is given by .
.with bandpass gain
 . In both cases, the
. In both cases, the
- Natural frequency is
 .
. - Quality factor is
 .
.
The bandwidth is approximated by
 , and Q is sometimes expressed as a damping constant
, and Q is sometimes expressed as a damping constant  . If a noninverting low-pass filter is required, the output can be taken at the output of the second operational amplifier
. If a noninverting low-pass filter is required, the output can be taken at the output of the second operational amplifierOperational amplifier
An operational amplifier is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output...
. If a noninverting bandpass filter is required, the order of the second integrator and the inverter can be switched, and the output taken at the output of the inverter's operational amplifier.
See also
- Prototype filterPrototype filterPrototype filters are electronic filter designs that are used as a template to produce a modified filter design for a particular application. They are an example of a nondimensionalised design from which the desired filter can be scaled or transformed. They are most often seen in regards to...
- Topology (electronics)Topology (electronics)The topology of an electronic circuit is the form taken by the network of interconnections of the circuit components. Different specific values or ratings of the components are regarded as being the same topology....
- Linear filterLinear filterLinear filters in the time domain process time-varying input signals to produce output signals, subject to the constraint of linearity.This results from systems composed solely of components classified as having a linear response....
- State variable filterState variable filterA state variable filter is a type of active filter. It consists of one or more integrators, connected in some feedback configuration. Any LTI system can be described as a state-space model, with n state variables for an nth-order system. A state variable filter realizes the state-space model directly...

