
General mn-type image filters
Encyclopedia
These filters are electrical wave filters designed using the image method
. They are an invention of Otto Zobel at AT&T Corp.. They are a generalisation of the m-type filter in that a transform is applied that modifies the transfer function while keeping the image impedance unchanged. For filters that have only one stopband
there is no distinction with the m-type filter. However, for a filter that has multiple stopbands, there is the possibility that the form of the transfer function in each stopband can be different. For instance, it may be required to filter one band with the sharpest possible cut-off, but in another to minimise phase distortion while still achieving some attenuation. If the form is identical at each transition from passband to stopband the filter will be the same as an m-type filter (k-type filter in the limiting case of m=1). If they are different, then the general case described here pertains.
The k-type filter acts as a prototype
for producing the general mn designs. For any given desired bandform there are two classes of mn transformation that can be applied, namely, the mid-series and mid-shunt derived sections; this terminology being more fully explained in the m-derived filter
article. Another feature of m-type filters that also applies in the general case is that a half section will have the original k-type image impedance on one side only. The other port will present a new image impedance. The two transformations have equivalent transfer functions but different image impedances and circuit topology.
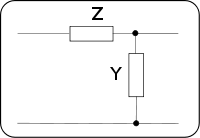 If Z and Y are the series impedance and shunt admittance of a constant k half section and;
If Z and Y are the series impedance and shunt admittance of a constant k half section and;
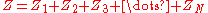
the transformed series impedance for a mid-series derived filter becomes;
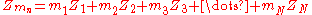
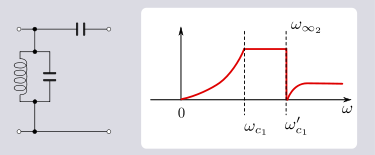
Where the mn are arbitrary positive coefficients. For an invariant image impedance ZiT and invariant bandform (that is, invariant cut-off frequencies ωc) the transformed shunt admittance, expressed in terms of Zmn, is given by;

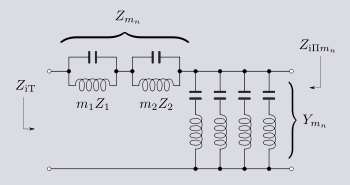 A result of this relationship is that the N antiresonators in Zmn will transform into 2N resonators in Ymn. The coefficients mn can be adjusted by the designer to set the frequency of one of the two poles of attenuation, ω∞, in each stopband. The second pole of attenuation is dependant and cannot be set separately.
A result of this relationship is that the N antiresonators in Zmn will transform into 2N resonators in Ymn. The coefficients mn can be adjusted by the designer to set the frequency of one of the two poles of attenuation, ω∞, in each stopband. The second pole of attenuation is dependant and cannot be set separately.
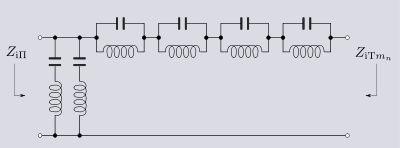 By dual analogy, the shunt derived filter starts from;
By dual analogy, the shunt derived filter starts from;

For an invariant image admittance YiΠ and invariant bandform the transformed series impedance is given by;
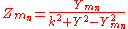
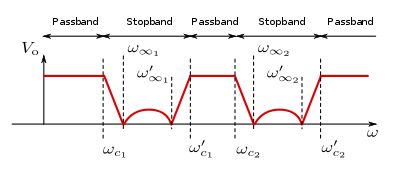
 The bandpass filter can be characterised as a 2-bandstop filter with ωc = 0 for the lower critical frequency of the lower band and ωc = ∞ for the upper critical frequency of the upper band. The two resonators reduce to an inductor and a capacitor respectively. The number of antiresonators reduces to two.
The bandpass filter can be characterised as a 2-bandstop filter with ωc = 0 for the lower critical frequency of the lower band and ωc = ∞ for the upper critical frequency of the upper band. The two resonators reduce to an inductor and a capacitor respectively. The number of antiresonators reduces to two.
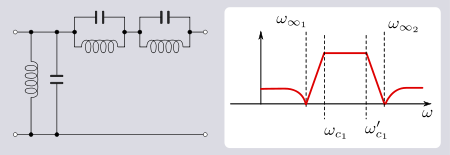
If, however, ω∞1 is set to zero (that is, there is no pole of attenuation in the lower stopband) and ω∞2 is set to correspond to the upper critical frequency ω' c1, then a particularly simple form of the bandpass filter is obtained consisting of just antiresonators coupled by capacitors. This was a popular topology for multi-section band-pass filters due its low component count, particularly of inductors. Many other such reduced forms are possible by setting one of the poles of attenuation to correspond to one of the critical frequencies for various classes of basic filter.
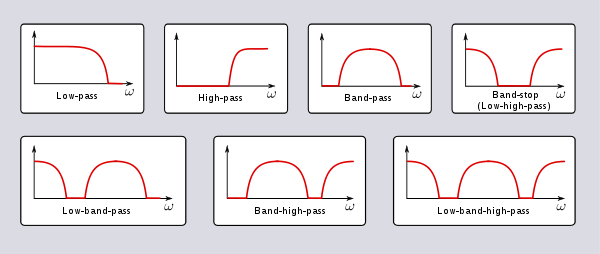
Image impedance
Image impedance is a concept used in electronic network design and analysis and most especially in filter design. The term image impedance applies to the impedance seen looking in to the ports of a network. Usually a two-port network is implied but the concept is capable of being extended to...
. They are an invention of Otto Zobel at AT&T Corp.. They are a generalisation of the m-type filter in that a transform is applied that modifies the transfer function while keeping the image impedance unchanged. For filters that have only one stopband
Stopband
A stopband is a band of frequencies, between specified limits, through which a circuit, such as a filter or telephone circuit, does not allow signals to pass, or the attenuation is above the required stopband attenuation level...
there is no distinction with the m-type filter. However, for a filter that has multiple stopbands, there is the possibility that the form of the transfer function in each stopband can be different. For instance, it may be required to filter one band with the sharpest possible cut-off, but in another to minimise phase distortion while still achieving some attenuation. If the form is identical at each transition from passband to stopband the filter will be the same as an m-type filter (k-type filter in the limiting case of m=1). If they are different, then the general case described here pertains.
The k-type filter acts as a prototype
Prototype filter
Prototype filters are electronic filter designs that are used as a template to produce a modified filter design for a particular application. They are an example of a nondimensionalised design from which the desired filter can be scaled or transformed. They are most often seen in regards to...
for producing the general mn designs. For any given desired bandform there are two classes of mn transformation that can be applied, namely, the mid-series and mid-shunt derived sections; this terminology being more fully explained in the m-derived filter
M-derived filter
m-derived filters or m-type filters are a type of electronic filter designed using the image method. They were invented by Otto Zobel in the early 1920s. This filter type was originally intended for use with telephone multiplexing and was an improvement on the existing constant k type filter...
article. Another feature of m-type filters that also applies in the general case is that a half section will have the original k-type image impedance on one side only. The other port will present a new image impedance. The two transformations have equivalent transfer functions but different image impedances and circuit topology.
 |
Mid-series multiple stopband

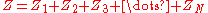
- where Z1, Z2 etc are a cascade of antiresonators,
the transformed series impedance for a mid-series derived filter becomes;
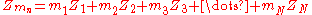
Where the mn are arbitrary positive coefficients. For an invariant image impedance ZiT and invariant bandform (that is, invariant cut-off frequencies ωc) the transformed shunt admittance, expressed in terms of Zmn, is given by;

- where
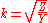 and is a constant by definition. When the mn are all equal this reduces to the expression for an m-type filter and where they are all equal to one it reduces further to the k-type filter.
and is a constant by definition. When the mn are all equal this reduces to the expression for an m-type filter and where they are all equal to one it reduces further to the k-type filter.

Special cases
In the case of a filter with a stopband extending to zero frequency, one of the antiresonators in Z will reduce to a single inductor. In this case the resonators in Ymn are reduced by one to 2N-1. Similarly, for a filter with a stopband extending to infinity, one antiresonator will reduce to a single capacitor and the resonators will again be reduced by one. In a filter where both conditions pertain, the number of resonators will be 2N-2. For these end stopbands, there is only one pole of attenuation in each, as would be expected from the reduced number of resonators. These forms are the maximum allowable complexity while maintaining invariance of bandform and one image impedance.Mid-shunt multiple stopband


For an invariant image admittance YiΠ and invariant bandform the transformed series impedance is given by;
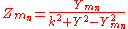
Simple bandpass section


If, however, ω∞1 is set to zero (that is, there is no pole of attenuation in the lower stopband) and ω∞2 is set to correspond to the upper critical frequency ω
See also

- Image impedanceImage impedanceImage impedance is a concept used in electronic network design and analysis and most especially in filter design. The term image impedance applies to the impedance seen looking in to the ports of a network. Usually a two-port network is implied but the concept is capable of being extended to...
- Constant k filterConstant k filterConstant k filters, also k-type filters, are a type of electronic filter designed using the image method. They are the original and simplest filters produced by this methodology and consist of a ladder network of identical sections of passive components...
- m-derived filterM-derived filterm-derived filters or m-type filters are a type of electronic filter designed using the image method. They were invented by Otto Zobel in the early 1920s. This filter type was originally intended for use with telephone multiplexing and was an improvement on the existing constant k type filter...
- mm'-type filterMm'-type filtermm'-type filters, also called double-m-derived filters, are a type of electronic filter designed using the image method. They were patented by Otto Zobel in 1932...
- Composite image filterComposite image filterA composite image filter is an electronic filter consisting of multiple image filter sections of two or more different types.The image method of filter design determines the properties of filter sections by calculating the properties they have in an infinite chain of such sections. In this, the...

