
Economy of Bangladesh
Encyclopedia
The economy
of Bangladesh
is a rapidly developing
market-based economy
. Its per capita income in 2010 was est. US$1,700 (adjusted by purchasing power parity
). According to the International Monetary Fund
, Bangladesh ranked as the 43rd largest economy in the world in 2010 in PPP terms and 57th largest in nominal terms, among the Next Eleven
or N-11
of Goldman Sachs
and D-8
economies, with a gross domestic product of US$269.3 billion in PPP terms and US$104.9 billion in nominal terms. The economy has grown at the rate of 6-7% p.a. over the past few years. More than half of the GDP belongs to the service sector, a major number of nearly half of Bangladeshis are employed in the agriculture sector, with RMG, textiles, leather, jute, fish, vegetables, leather and leather goods, ceramics, fruits as other important produce.
Remittances from Bangladeshis working overseas, mainly in the Middle East is the major source of foreign exchange earnings; exports of garments and textiles are the other main sources of foreign exchange earning. Ship building and cane cultivation have become a major force of growth. GDP's rapid growth due to sound financial control and regulations have also contributed to its growth. However, foreign direct investment
is yet to rise significantly. Bangladesh has made major strides in its human development index.
The land is devoted mainly to rice
and jute
cultivation as well as fruits and produce, although wheat
production has increased in recent years; the country is largely self-sufficient in rice production. Bangladesh's growth of its agro industries is due to its rich deltaic fertile land that depend on its six seasons and multiple harvests.
Improving at a very fast rate, infrastructure to support transportation, communications, power supply and water distribution are rapidly developing. Bangladesh is limited in its reserves of oil
, but recently there was huge development in gas
and coal mining
. The service sector has expanded rapidly during last two decades, the country's industrial base remains very positive. The country's main endowments include its vast human resource base, rich agricultural land, relatively abundant water, and substantial reserves of natural gas, with the blessing of possessing the worlds only natural sea ports in Mongla and Chittagong, in addition to being the only central port linking two large burgeoning economic hub groups SAARC and ASEAN.
, a region that is today Bangladesh—was a prosperous region of South Asia
until modern times. It had the advantages of a mild, almost tropical climate, fertile soil, ample water, and an abundance of fish, wildlife, and fruit. The standard of living compared favorably with other parts of South Asia. As early as the thirteenth century, the region was developing as an agrarian economy. It was not entirely without commercial centers, and Dhaka
in particular grew into an important entrepôt during the Mughal Empire
. The British, however, on their arrival in the late eighteenth(18th) century, chose to develop Calcutta, now the capital city of West Bengal
, as their commercial and administrative center in South Asia. The development of East Bengal was thereafter limited to agriculture. The administrative infrastructure of the late eighteenth and nineteenth centuries reinforced East Bengal's function as the primary agricultural producer—chiefly of rice, tea, teak, cotton, cane and jute—for processors and traders from around Asia and beyond.
After its independence from Pakistan, Bangladesh followed a socialist economy by nationalizing all industries, proving to be a critical blunder undertaken by Awami League's Mujib Government following India
's policy. Education policies of the British dating back from colonial era deprived education to millions of Bangla's Muslim peoples setting them back by decades. Some of the same factors that had made East Bengal a prosperous region became disadvantages during the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. As life expectancy increased, the limitations of land and the annual floods increasingly became constraints on economic growth. Preponderance on traditional agricultural methods became obstacles to the modernization of agriculture. Geography severely limited the development and maintenance of a modern transportation and communications system.
The partition of South Asia and the emergence of India
and Pakistan
in 1947 severely disrupted the economic system that had preserved East Bengal (now Bangladesh) as a producer of jute, rice and other agro commodities for the rest of India
. East Pakistan had to build a new industrial base and modernize agriculture in the midst of a population explosion. The united government of Pakistan expanded the cultivated area and some irrigation facilities, but the rural population generally became poorer between 1947 and 1971 because improvements did not keep pace with rural population increase. Pakistan's five-year plans opted for a development strategy based on industrialization, but the major share of the development budget went to West Pakistan, that is, contemporary Pakistan. The lack of natural resources meant that East Pakistan was heavily dependent on imports, creating a balance of payments problem. Without a substantial industrialization program or adequate agrarian expansion, the economy of East Pakistan steadily declined. Blame was placed by various observers, but especially those in East Pakistan, on the West Pakistani leaders who not only dominated the government but also most of the fledgling industries in East Pakistan.
Since Bangladesh followed a socialist economy by nationalizing all industries after its independence, it underwent a slow growth of producing experienced entrepreneurs, managers, administrators, engineers, and technicians. There were critical shortages of essential food grains and other staples because of wartime disruptions. External markets for jute had been lost because of the instability of supply and the increasing popularity of synthetic substitutes. Foreign exchange resources were minuscule, and the banking and monetary systems were unreliable. Although Bangladesh had a large work force, the vast reserves of under trained and underpaid workers were largely illiterate, unskilled, and underemployed. Commercially exploitable industrial resources, except for natural gas, were lacking. Inflation, especially for essential consumer goods, ran between 300 and 400 percent. The war of independence had crippled the transportation system. Hundreds of road and railroad bridges had been destroyed or damaged, and rolling stock was inadequate and in poor repair. The new country was still recovering from a severe cyclone that hit the area in 1970 and cause 250,000 deaths. India, by a heavily poor nation and without any ability of giving aid to other nations, let alone to its suffering masses, came forward immediately with critically measured economic assistance in the first months after Bangladesh achieved independence from Pakistan
. Between December 1971 and January 1972, India committed US$232 million in aid to Bangladesh from the politco-economic aid India received from the USA and USSR. Official amount of disbursement yet undisclosed.
After 1975, Bangladeshi leaders began to turn their attention to developing new industrial capacity and rehabilitating its economy. The static economic model adopted by these early leaders, however—including the nationalization of much of the industrial sector—resulted in inefficiency and economic stagnation. Beginning in late 1975, the government gradually gave greater scope to private sector participation in the economy, a pattern that has continued. Many state-owned enterprises have been privatized, like banking, telecommunication, aviation, media, and jute. Inefficiency in the public sector has been rising however at a gradual pace; external resistance to developing the country's richest natural resources is mounting; and power sectors including infrastructure have all contributed to slowing economic growth.
In the mid-1980s, there were encouraging signs of progress. Economic policies aimed at encouraging private enterprise and investment, privatizing public industries, reinstating budgetary discipline, and liberalizing the import regime were accelerated. From 1991 to 1993, the government successfully followed an enhanced structural adjustment facility (ESAF) with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) but failed to follow through on reforms in large part because of preoccupation with the government's domestic political troubles. In the late 1990s the government's economic policies became more entrenched, and some of the early gains were lost, which was highlighted by a precipitous drop in foreign direct investment in 2000 and 2001. In June 2003 the IMF approved 3-year, $490-million plan as part of the Poverty Reduction and Growth Facility (PRGF) for Bangladesh that aimed to support the government's economic reform program up to 2006. Seventy million dollars was made available immediately. In the same vein the World Bank approved $536 million in interest-free loans.In the year 2010 Government of India extended a line of credit worth $ 1 billion to counter-balance China's close relationship with Bangladesh.
Bangladesh historically has run a large trade deficit, financed largely through aid receipts and remittances from workers overseas. Foreign reserves dropped markedly in 2001 but stabilized in the USD3 to USD4 billion range (or about 3 months' import cover). In January 2007, reserves stood at $3.74 billion, and then increased to $5.8 billion by January 2008, in November 2009 it surpassed $10.0 billion, and as of April 2011 it surpassed the US $12 billion according to the Bank of Bangladesh, the central bank. In addition imports and aid-dependence of the country has systematically been reduced since the beginning of 1990s.
Mean wages were $0.58 per manhour in 2009.
The IMF and World Bank predict GDP growth over the next 5 years will be about 6.5%, well short of the 9-10% needed to lift Bangladesh to Mid Income Nation level, within that time period. The initial impact of the end of quotas under the Multi-Fiber Arrangement has been positive for Bangladesh, with continuing investment in the ready-made garment sector, which has experienced annual export growth in excess of around 20%. Downward price pressure means Bangladesh must continue to cut final delivered costs if it is to remain competitive in the world market. Foreign investors in a broad range of sectors are increasingly frustrated with the politics of confrontation, the level of corruption, the slow pace of reform and privatization and deregulation of the public sector and the lack of basic infrastructure e.g. roads. While investors view favorably recent steps by the interim government to address corruption, governance, and infrastructure issues, most believe it is too early to assess the long-term impact of these developments.
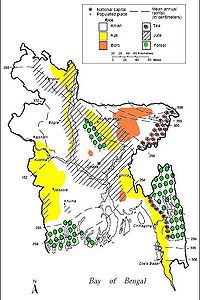 Most Bangladeshis earn their living from agriculture. Although rice and jute are the primary crops, maize and vegetables are assuming greater importance. Due to the expansion of irrigation networks, some wheat producers have switched to cultivation of maize which is used mostly as poultry feed. Tea is grown in the northeast. Because of Bangladesh's fertile soil and normally ample water supply, rice can be grown and harvested three times a year in many areas. Due to a number of factors, Bangladesh's labor-intensive agriculture has achieved steady increases in food grain production despite the often unfavorable weather conditions. These include better flood control and irrigation, a generally more efficient use of fertilizers, and the establishment of better distribution and rural credit networks. With 28.8 million metric tons produced in 2005-2006 (July–June), rice is Bangladesh's principal crop. By comparison, wheat output in 2005-2006 was 9 million metric tons. Population pressure continues to place a severe burden on productive capacity, creating a food deficit, especially of wheat. Foreign assistance and commercial imports fill the gap, but seasonal hunger ("monga") remains a problem. Underemployment remains a serious problem, and a growing concern for Bangladesh's agricultural sector will be its ability to absorb additional manpower. Finding alternative sources of employment will continue to be a daunting problem for future governments, particularly with the increasing numbers of landless peasants who already account for about half the rural labor force. Due to farmers' vulnerability to various risks, Bangladesh's poorest face numerous potential limitations on their ability to enhance agriculture production and their livelihoods. These include an actual and perceived risk to investing in new agricultural technologies and activities (despite their potential to increase income), a vulnerability to shocks and stresses and a limited ability to mitigate or cope with these and limited access to market information.
Most Bangladeshis earn their living from agriculture. Although rice and jute are the primary crops, maize and vegetables are assuming greater importance. Due to the expansion of irrigation networks, some wheat producers have switched to cultivation of maize which is used mostly as poultry feed. Tea is grown in the northeast. Because of Bangladesh's fertile soil and normally ample water supply, rice can be grown and harvested three times a year in many areas. Due to a number of factors, Bangladesh's labor-intensive agriculture has achieved steady increases in food grain production despite the often unfavorable weather conditions. These include better flood control and irrigation, a generally more efficient use of fertilizers, and the establishment of better distribution and rural credit networks. With 28.8 million metric tons produced in 2005-2006 (July–June), rice is Bangladesh's principal crop. By comparison, wheat output in 2005-2006 was 9 million metric tons. Population pressure continues to place a severe burden on productive capacity, creating a food deficit, especially of wheat. Foreign assistance and commercial imports fill the gap, but seasonal hunger ("monga") remains a problem. Underemployment remains a serious problem, and a growing concern for Bangladesh's agricultural sector will be its ability to absorb additional manpower. Finding alternative sources of employment will continue to be a daunting problem for future governments, particularly with the increasing numbers of landless peasants who already account for about half the rural labor force. Due to farmers' vulnerability to various risks, Bangladesh's poorest face numerous potential limitations on their ability to enhance agriculture production and their livelihoods. These include an actual and perceived risk to investing in new agricultural technologies and activities (despite their potential to increase income), a vulnerability to shocks and stresses and a limited ability to mitigate or cope with these and limited access to market information.
Eastern Bengal was known for its fine muslin and silk fabric before the British period. The dyes, yarn, and cloth were the envy of much of the premodern world. Bengali muslin, silk, and brocade were worn by the aristocracy of Asia and Europe. The introduction of machine-made textiles from England in the late eighteenth century spelled doom for the costly and time-consuming hand loom process. Cotton growing died out in East Bengal, and the textile industry became dependent on imported yarn. Those who had earned their living in the textile industry were forced to rely more completely on farming. Only the smallest vestiges of a once-thriving cottage industry survived.
Other industries which have shown very strong growth include the chemical industry, steel industry, mining industry and the paper and pulp industry.
Bangladesh is 3rd in world textile exports behind Turkey, another low volume exporter, and China which exported $120.1 billion worth of textiles in 2009. The industry employs nearly 3.5 million workers. Current exports have doubled since 2004. Wages in Bangladesh's textile industry were the lowest in the world as of 2010. The country was considered the most formidable rival to China where wages were rapidly rising and currency was appreciating.
After massive labor unrest in 2006 the government formed a Minimum Wage Board including business and worker representatives which in 2006 set a minimum wage equivalent to 1,662.50 taka, $24 a month, up from Tk950. In 2010, following widespread labor protests involving 100,000 workers in June, 2010, a controversial proposal was being considered by the Board which would raise the monthly minimum to the equivalent of $50 a month, still far below worker demands of 5,000 taka, $72, for entry level wages, but unacceptably high according to textile manufacturers who are asking for a wage below $30. On July 28, 2010 it was announced that the minimum entry level wage would be increased to 3,000 taka, about $43.
The government also seems to believe some change is necessary. On September 21, 2006 then ex-Prime Minister Khaleda Zia
called on textile firms to ensure the safety of workers by complying with international labor law at a speech inaugurating the Bangladesh Apparel & Textile Exposition (BATEXPO).
of the Dhaka Stock Exchange
in Bangladesh crossed $10 billion in November 2007 and the $30 billion dollar mark in 2009, and USD 50 billion in August 2010. Bangladesh had one of the best performing stock markets in the world during the recent global recession, due to relatively low correlations with developed country stock markets.
Major investment in real estate by domestic and foreign-resident Bangladeshis has led to a massive building boom in Dhaka and Chittagong.
Recent (2011) trends for investing in Bangladesh as Saudi Arabia trying to secure public and private investment in oil and gas, power and transportation projects, United Arab Emirates (UAE) is keen to invest in growing shipbuilding industry in Bangladesh encouraged by comparative cost advantage, Tata, an India-based leading industrial multinational to invest Taka 1500 crore to set up an automobile industry in Bangladesh, World Bank to invest in rural roads improving quality of live, the Rwandan entrepreneurs are keen to invest in Bangladesh's pharmaceuticals sector considering its potentiality in international market, Samsung sought to lease 500 industrial plots from the export zones authority to set up an electronics hub in Bangladesh with an investment of US$1.25 billion, National Board of Revenue (NBR) is set to withdraw tax rebate facilities on investment in the capital market by individual taxpayers from the fiscal 2011-12.
 The Bangladesh Garments Manufacturers and Exporters Association (BGMEA) has predicted textile exports will rise from US$7.90 billion earned in 2005-06 to US$15
The Bangladesh Garments Manufacturers and Exporters Association (BGMEA) has predicted textile exports will rise from US$7.90 billion earned in 2005-06 to US$15
billion by 2011. In part this optimism stems from how well the sector has fared since the end of textile and clothing quotas, under the Multifibre Agreement, in early 2005.
According to a United Nations Development Programme
report "Sewing Thoughts: How to Realize Human Development Gains in the Post-Quota World" Bangladesh has been able to offset a decline
in European sales by cultivating new markets in the United States.
"[In 2005] we had tremendous growth. The quota-free textile regime has proved to be a big boost for our factories," said BGMEA president S.M. Fazlul Hoque told reporters, after the
sector's 24 per cent growth rate was revealed.
Bangladesh Knitwear Manufacturers and Exporters Association (BKMEA) president Md Fazlul Hoque has also struck an optimistic tone. In an interview with United News Bangladesh he lauded the blistering growth rate, saying "The quality of our products and its competitiveness in terms of prices helped the sector achieve such... tremendous success."
Knitwear posted the strongest growth of all textile products in 2005-06, surging 35.38 per cent to US$2.82 billion. On the downside however, the sector's strong growth came amid sharp falls in prices for textile products on the world market, with growth subsequently dependent upon large increases in volume.
Bangladesh's quest to boost the quantity of textile trade was also helped by US and EU caps on Chinese textiles. The US cap restricts growth in imports of Chinese textiles to 12.5 per cent next year and between 15 and 16 per cent in 2008. The EU deal similarly manages import growth until 2008.
Bangladesh may continue to benefit from these restrictions over the next two years, however a climate of falling global textile prices forces wage rates the centre of the nation's efforts to increase market share.
Prior to the Wage Board's announcement of its recommended minimum wage of $24, Tk1,604, in 2006, the rate had remained unchanged at Tk950, about $15, for more than 12 years. Although the government may allow up to three years for the new wage to be implemented, and inevitably there will be compliance issues as manufacturers drag their feet, it seemed politically untenable for wages to remain at those levels given the unprecedented industrial unrest.
In response to the Wage Board's initial draft recommendation of a minimum wage of Tk1,604 to be increased to Tk1,800 after eight months, the BGMEA declared over 50 per cent of factories would be ruined within three months. While this claim is no doubt an exaggeration, the capacity of Bangladesh's textile industry to absorb a significant wage hike as margins become tighter is a key question which hangs over the future of the industry. Bangladesh's textile sector is concentrated in export processing zones in Dhaka and Chittagong. These zones, which are administered by the Bangladesh Export Processing Zone Authority, aim to offer "a congenial investment climate, free from cumbersome procedures"m according to Bangladesh Export Promotion Bureau's website.
They offer a range of incentives to potential investors including 10 year tax holidays, duty free import of capital goods, raw materials and building materials, exemptions on income tax on salaries paid to foreign nationals for three years and dividend tax exemptions for the period of the tax holiday.
All goods produced in the zones are able to be exported duty free, in addition to which Bangladesh benefits from the Generalised System of Preferences in US, European and Japanese markets and is also endowed with Most Favoured Nation status from the United States.
Furthermore, Bangladesh imposes no ceiling on investment in the EPZs and allows full repatriation of profits.
The formation of labour unions within the EPZs is prohibited as are strikes.
Bangladesh's exports to the U.S. surpassed $1.9 billion in 1999. Bangladesh also exports significant amounts of garments and knitwear to the EU market.
Bangladesh also has significant jute, leather
, shrimp
, pharmaceutical, and ceramic
s industries.
Bangladesh has been a world leader in its efforts to end the use of child labor in garment factories. On July 4, 1995, the Bangladesh Garment Manufacturers Export Association, International Labour Organization
, and UNICEF signed a memorandum of understanding on the elimination of child labor in the garment sector. Implementation of this pioneering agreement began in fall 1995, and by the end of 1999, child labor in the garment trade virtually had been eliminated. The labor-intensive process of ship breaking for scrap has developed to the point where it now meets most of Bangladesh's domestic steel
needs. Other industries include sugar
, tea, leather goods, newsprint
, pharmaceutical, and fertilizer
production.
The Bangladesh government continues to court foreign investment, something it has done fairly successfully in private power generation and gas exploration and production, as well as in other sectors such as cellular telephony, textiles, and pharmaceuticals. In 1989, the same year it signed a bilateral investment treaty with the United States, it established a Board of Investment to simplify approval and start-up procedures for foreign investors, although in practice the board has done little to increase investment. The government created the Bangladesh Export Processing Zone Authority
to manage the various export processing zones. The agency currently manages EPZs in Adamjee, Chittagong
, Comilla
, Dhaka
, Ishwardi, Karnaphuli, Mongla, and Uttara
. An EPZ has also been proposed for Sylhet
. The government has given the private sector permission to build and operate competing EPZs-initial construction on a Korea
n EPZ started in 1999. In June 1999, the AFL-CIO
petitioned the U.S. Government to deny Bangladesh access to U.S. markets under the Generalized System of Preferences
(GSP), citing the country's failure to meet promises made in 1992 to allow freedom of association in EPZs.
Sylhet
is fast becoming a major center of retailing in Bangladesh, with many shopping centres being built by expatriates to serve fellow expatriates visiting Sylhet and the emerging middle class. Many of these developments hark back to Britain
.
Bangladesh has made significant strides in its economic sector performance since independence in 1971. Although the economy has improved vastly in the 1990s, Bangladesh still suffers in the area of foreign trade in South Asia
n region. Despite major impediments to growth like the inefficiency of state-owned enterprises, a rapidly growing labor force that cannot be absorbed by agriculture, inadequate power supplies, and slow implementation of economic reforms, Bangladesh has made some headway improving the climate for foreign investors
and liberalizing the capital market
s; for example, it has negotiated with foreign firms for oil and gas exploration, better countrywide distribution of cooking gas, and the construction of natural gas
pipelines
and power station
s. Progress on other economic reforms has been halting because of opposition from the bureaucracy, public sector unions, and other vested interest groups.
The especially severe floods of 1998 increased the flow of international aid. So far the global financial crisis has not had a major impact on the economy. The World Bank predicted economic growth of 6.5% for current year. Foreign aid has seen a decline of 10% over the last few months but economists see this as a good sign for self-reliance.There has been 18% growth in exports over the last 9 months and remittance inflow has increased at a remarkable 25% rate.
Economy
An economy consists of the economic system of a country or other area; the labor, capital and land resources; and the manufacturing, trade, distribution, and consumption of goods and services of that area...
of Bangladesh
Bangladesh
Bangladesh , officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh is a sovereign state located in South Asia. It is bordered by India on all sides except for a small border with Burma to the far southeast and by the Bay of Bengal to the south...
is a rapidly developing
Developing country
A developing country, also known as a less-developed country, is a nation with a low level of material well-being. Since no single definition of the term developing country is recognized internationally, the levels of development may vary widely within so-called developing countries...
market-based economy
Market economy
A market economy is an economy in which the prices of goods and services are determined in a free price system. This is often contrasted with a state-directed or planned economy. Market economies can range from hypothetically pure laissez-faire variants to an assortment of real-world mixed...
. Its per capita income in 2010 was est. US$1,700 (adjusted by purchasing power parity
Purchasing power parity
In economics, purchasing power parity is a condition between countries where an amount of money has the same purchasing power in different countries. The prices of the goods between the countries would only reflect the exchange rates...
). According to the International Monetary Fund
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
, Bangladesh ranked as the 43rd largest economy in the world in 2010 in PPP terms and 57th largest in nominal terms, among the Next Eleven
Next Eleven
The Next Eleven are eleven countries—Bangladesh, Egypt, Indonesia, Iran, Mexico, Nigeria, Pakistan, Philippines, South Korea, Turkey, and Vietnam — identified by Goldman Sachs investment bank and Jim O'Neill as having a high potential of becoming, along with the BRICS, the world's largest...
or N-11
Next Eleven
The Next Eleven are eleven countries—Bangladesh, Egypt, Indonesia, Iran, Mexico, Nigeria, Pakistan, Philippines, South Korea, Turkey, and Vietnam — identified by Goldman Sachs investment bank and Jim O'Neill as having a high potential of becoming, along with the BRICS, the world's largest...
of Goldman Sachs
Goldman Sachs
The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. is an American multinational bulge bracket investment banking and securities firm that engages in global investment banking, securities, investment management, and other financial services primarily with institutional clients...
and D-8
Developing 8 Countries
The Developing 8 are a group of developing countries with large Muslim populations that have formed an economic development alliance. It consists of Bangladesh, Egypt, Indonesia, Iran, Malaysia, Nigeria, Pakistan, and Turkey.-History:The D-8 was founded by Necmettin Erbakan, former Turkish Prime...
economies, with a gross domestic product of US$269.3 billion in PPP terms and US$104.9 billion in nominal terms. The economy has grown at the rate of 6-7% p.a. over the past few years. More than half of the GDP belongs to the service sector, a major number of nearly half of Bangladeshis are employed in the agriculture sector, with RMG, textiles, leather, jute, fish, vegetables, leather and leather goods, ceramics, fruits as other important produce.
Remittances from Bangladeshis working overseas, mainly in the Middle East is the major source of foreign exchange earnings; exports of garments and textiles are the other main sources of foreign exchange earning. Ship building and cane cultivation have become a major force of growth. GDP's rapid growth due to sound financial control and regulations have also contributed to its growth. However, foreign direct investment
Foreign direct investment
Foreign direct investment or foreign investment refers to the net inflows of investment to acquire a lasting management interest in an enterprise operating in an economy other than that of the investor.. It is the sum of equity capital,other long-term capital, and short-term capital as shown in...
is yet to rise significantly. Bangladesh has made major strides in its human development index.
The land is devoted mainly to rice
Rice
Rice is the seed of the monocot plants Oryza sativa or Oryza glaberrima . As a cereal grain, it is the most important staple food for a large part of the world's human population, especially in East Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, the Middle East, and the West Indies...
and jute
Jute
Jute is a long, soft, shiny vegetable fibre that can be spun into coarse, strong threads. It is produced from plants in the genus Corchorus, which has been classified in the family Tiliaceae, or more recently in Malvaceae....
cultivation as well as fruits and produce, although wheat
Wheat
Wheat is a cereal grain, originally from the Levant region of the Near East, but now cultivated worldwide. In 2007 world production of wheat was 607 million tons, making it the third most-produced cereal after maize and rice...
production has increased in recent years; the country is largely self-sufficient in rice production. Bangladesh's growth of its agro industries is due to its rich deltaic fertile land that depend on its six seasons and multiple harvests.
Improving at a very fast rate, infrastructure to support transportation, communications, power supply and water distribution are rapidly developing. Bangladesh is limited in its reserves of oil
Oil
An oil is any substance that is liquid at ambient temperatures and does not mix with water but may mix with other oils and organic solvents. This general definition includes vegetable oils, volatile essential oils, petrochemical oils, and synthetic oils....
, but recently there was huge development in gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
and coal mining
Coal mining
The goal of coal mining is to obtain coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content, and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron from iron ore and for cement production. In the United States,...
. The service sector has expanded rapidly during last two decades, the country's industrial base remains very positive. The country's main endowments include its vast human resource base, rich agricultural land, relatively abundant water, and substantial reserves of natural gas, with the blessing of possessing the worlds only natural sea ports in Mongla and Chittagong, in addition to being the only central port linking two large burgeoning economic hub groups SAARC and ASEAN.
Economic history
East Bengal—the eastern segment of BengalBengal
Bengal is a historical and geographical region in the northeast region of the Indian Subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. Today, it is mainly divided between the sovereign land of People's Republic of Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal, although some regions of the previous...
, a region that is today Bangladesh—was a prosperous region of South Asia
South Asia
South Asia, also known as Southern Asia, is the southern region of the Asian continent, which comprises the sub-Himalayan countries and, for some authorities , also includes the adjoining countries to the west and the east...
until modern times. It had the advantages of a mild, almost tropical climate, fertile soil, ample water, and an abundance of fish, wildlife, and fruit. The standard of living compared favorably with other parts of South Asia. As early as the thirteenth century, the region was developing as an agrarian economy. It was not entirely without commercial centers, and Dhaka
Dhaka
Dhaka is the capital of Bangladesh and the principal city of Dhaka Division. Dhaka is a megacity and one of the major cities of South Asia. Located on the banks of the Buriganga River, Dhaka, along with its metropolitan area, had a population of over 15 million in 2010, making it the largest city...
in particular grew into an important entrepôt during the Mughal Empire
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
. The British, however, on their arrival in the late eighteenth(18th) century, chose to develop Calcutta, now the capital city of West Bengal
West Bengal
West Bengal is a state in the eastern region of India and is the nation's fourth-most populous. It is also the seventh-most populous sub-national entity in the world, with over 91 million inhabitants. A major agricultural producer, West Bengal is the sixth-largest contributor to India's GDP...
, as their commercial and administrative center in South Asia. The development of East Bengal was thereafter limited to agriculture. The administrative infrastructure of the late eighteenth and nineteenth centuries reinforced East Bengal's function as the primary agricultural producer—chiefly of rice, tea, teak, cotton, cane and jute—for processors and traders from around Asia and beyond.
After its independence from Pakistan, Bangladesh followed a socialist economy by nationalizing all industries, proving to be a critical blunder undertaken by Awami League's Mujib Government following India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
's policy. Education policies of the British dating back from colonial era deprived education to millions of Bangla's Muslim peoples setting them back by decades. Some of the same factors that had made East Bengal a prosperous region became disadvantages during the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. As life expectancy increased, the limitations of land and the annual floods increasingly became constraints on economic growth. Preponderance on traditional agricultural methods became obstacles to the modernization of agriculture. Geography severely limited the development and maintenance of a modern transportation and communications system.
The partition of South Asia and the emergence of India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
in 1947 severely disrupted the economic system that had preserved East Bengal (now Bangladesh) as a producer of jute, rice and other agro commodities for the rest of India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
. East Pakistan had to build a new industrial base and modernize agriculture in the midst of a population explosion. The united government of Pakistan expanded the cultivated area and some irrigation facilities, but the rural population generally became poorer between 1947 and 1971 because improvements did not keep pace with rural population increase. Pakistan's five-year plans opted for a development strategy based on industrialization, but the major share of the development budget went to West Pakistan, that is, contemporary Pakistan. The lack of natural resources meant that East Pakistan was heavily dependent on imports, creating a balance of payments problem. Without a substantial industrialization program or adequate agrarian expansion, the economy of East Pakistan steadily declined. Blame was placed by various observers, but especially those in East Pakistan, on the West Pakistani leaders who not only dominated the government but also most of the fledgling industries in East Pakistan.
Since Bangladesh followed a socialist economy by nationalizing all industries after its independence, it underwent a slow growth of producing experienced entrepreneurs, managers, administrators, engineers, and technicians. There were critical shortages of essential food grains and other staples because of wartime disruptions. External markets for jute had been lost because of the instability of supply and the increasing popularity of synthetic substitutes. Foreign exchange resources were minuscule, and the banking and monetary systems were unreliable. Although Bangladesh had a large work force, the vast reserves of under trained and underpaid workers were largely illiterate, unskilled, and underemployed. Commercially exploitable industrial resources, except for natural gas, were lacking. Inflation, especially for essential consumer goods, ran between 300 and 400 percent. The war of independence had crippled the transportation system. Hundreds of road and railroad bridges had been destroyed or damaged, and rolling stock was inadequate and in poor repair. The new country was still recovering from a severe cyclone that hit the area in 1970 and cause 250,000 deaths. India, by a heavily poor nation and without any ability of giving aid to other nations, let alone to its suffering masses, came forward immediately with critically measured economic assistance in the first months after Bangladesh achieved independence from Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
. Between December 1971 and January 1972, India committed US$232 million in aid to Bangladesh from the politco-economic aid India received from the USA and USSR. Official amount of disbursement yet undisclosed.
After 1975, Bangladeshi leaders began to turn their attention to developing new industrial capacity and rehabilitating its economy. The static economic model adopted by these early leaders, however—including the nationalization of much of the industrial sector—resulted in inefficiency and economic stagnation. Beginning in late 1975, the government gradually gave greater scope to private sector participation in the economy, a pattern that has continued. Many state-owned enterprises have been privatized, like banking, telecommunication, aviation, media, and jute. Inefficiency in the public sector has been rising however at a gradual pace; external resistance to developing the country's richest natural resources is mounting; and power sectors including infrastructure have all contributed to slowing economic growth.
In the mid-1980s, there were encouraging signs of progress. Economic policies aimed at encouraging private enterprise and investment, privatizing public industries, reinstating budgetary discipline, and liberalizing the import regime were accelerated. From 1991 to 1993, the government successfully followed an enhanced structural adjustment facility (ESAF) with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) but failed to follow through on reforms in large part because of preoccupation with the government's domestic political troubles. In the late 1990s the government's economic policies became more entrenched, and some of the early gains were lost, which was highlighted by a precipitous drop in foreign direct investment in 2000 and 2001. In June 2003 the IMF approved 3-year, $490-million plan as part of the Poverty Reduction and Growth Facility (PRGF) for Bangladesh that aimed to support the government's economic reform program up to 2006. Seventy million dollars was made available immediately. In the same vein the World Bank approved $536 million in interest-free loans.In the year 2010 Government of India extended a line of credit worth $ 1 billion to counter-balance China's close relationship with Bangladesh.
Bangladesh historically has run a large trade deficit, financed largely through aid receipts and remittances from workers overseas. Foreign reserves dropped markedly in 2001 but stabilized in the USD3 to USD4 billion range (or about 3 months' import cover). In January 2007, reserves stood at $3.74 billion, and then increased to $5.8 billion by January 2008, in November 2009 it surpassed $10.0 billion, and as of April 2011 it surpassed the US $12 billion according to the Bank of Bangladesh, the central bank. In addition imports and aid-dependence of the country has systematically been reduced since the beginning of 1990s.
Macro-economic trend
This is a chart of trend of gross domestic product of Bangladesh at market prices estimated by the International Monetary Fund with figures in millions of Bangladeshi Taka. However, this reflects only the formal sector of the economy.| Year | Gross Domestic Product | US Dollar Exchange | Inflation Index (2000=100) |
Per Capita Income (as % of USA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 250,300 | 16.10 Taka | 20 | 1.79 |
| 1985 | 597,318 | 31.00 Taka | 36 | 1.19 |
| 1990 | 1,054,234 | 35.79 Taka | 58 | 1.16 |
| 1995 | 1,594,210 | 40.27 Taka | 78 | 1.12 |
| 2000 | 2,453,160 | 52.14 Taka | 100 | 0.97 |
| 2005 | 3,913,334 | 63.92 Taka | 126 | 0.95 |
| 2008 | 5,003,438 | 68.65 Taka | 147 |
Mean wages were $0.58 per manhour in 2009.
Economic outlook
Efforts to achieve Bangladesh's macroeconomic goals have been problematic mostly due to various factors including the country's large population, corruption within the government, power shortages etc. The privatization of public sector industries has proceeded at a slow pace—due in part to worker unrest in affected industries—although on June 30, 2010, the government took a bold step as it closed down the Adamjee Jute Mill, the country's largest and most costly state-owned enterprise. The government also has proven unable to resist demands for wage hikes in government-owned industries. Access to capital is impeded. State-owned banks, which control about three-fourths of deposits and loans, carry classified loan burdens of about 50%.The IMF and World Bank predict GDP growth over the next 5 years will be about 6.5%, well short of the 9-10% needed to lift Bangladesh to Mid Income Nation level, within that time period. The initial impact of the end of quotas under the Multi-Fiber Arrangement has been positive for Bangladesh, with continuing investment in the ready-made garment sector, which has experienced annual export growth in excess of around 20%. Downward price pressure means Bangladesh must continue to cut final delivered costs if it is to remain competitive in the world market. Foreign investors in a broad range of sectors are increasingly frustrated with the politics of confrontation, the level of corruption, the slow pace of reform and privatization and deregulation of the public sector and the lack of basic infrastructure e.g. roads. While investors view favorably recent steps by the interim government to address corruption, governance, and infrastructure issues, most believe it is too early to assess the long-term impact of these developments.
Agriculture

Manufacturing & Industry
Many new jobs - mostly for women - have been created by the country's dynamic private ready-made garment industry, which grew at double-digit rates through most of the 1990s. By the late 1990s, about 1.5 million people, mostly women, were employed in the garments sector as well as Leather products specially Footwear (Shoe manufacturing unit). During 2001-2002, export earnings from ready-made garments reached $3,125 million, representing 52% of Bangladesh's total exports. Bangladesh has overtaken India in apparel exports in 2009, its exports stood at 2.66 billion US dollar, ahead of India's 2.27 billion US dollar.Eastern Bengal was known for its fine muslin and silk fabric before the British period. The dyes, yarn, and cloth were the envy of much of the premodern world. Bengali muslin, silk, and brocade were worn by the aristocracy of Asia and Europe. The introduction of machine-made textiles from England in the late eighteenth century spelled doom for the costly and time-consuming hand loom process. Cotton growing died out in East Bengal, and the textile industry became dependent on imported yarn. Those who had earned their living in the textile industry were forced to rely more completely on farming. Only the smallest vestiges of a once-thriving cottage industry survived.
Other industries which have shown very strong growth include the chemical industry, steel industry, mining industry and the paper and pulp industry.
Textile sector
Bangladesh's textile industry, which includes knitwear and ready-made garments along with specialized textile products, is the nation's number one export earner, accounting for 80% of Bangladesh's exports of $15.56 billion in 2009.Bangladesh is 3rd in world textile exports behind Turkey, another low volume exporter, and China which exported $120.1 billion worth of textiles in 2009. The industry employs nearly 3.5 million workers. Current exports have doubled since 2004. Wages in Bangladesh's textile industry were the lowest in the world as of 2010. The country was considered the most formidable rival to China where wages were rapidly rising and currency was appreciating.
After massive labor unrest in 2006 the government formed a Minimum Wage Board including business and worker representatives which in 2006 set a minimum wage equivalent to 1,662.50 taka, $24 a month, up from Tk950. In 2010, following widespread labor protests involving 100,000 workers in June, 2010, a controversial proposal was being considered by the Board which would raise the monthly minimum to the equivalent of $50 a month, still far below worker demands of 5,000 taka, $72, for entry level wages, but unacceptably high according to textile manufacturers who are asking for a wage below $30. On July 28, 2010 it was announced that the minimum entry level wage would be increased to 3,000 taka, about $43.
The government also seems to believe some change is necessary. On September 21, 2006 then ex-Prime Minister Khaleda Zia
Khaleda Zia
Begum Khaleda Zia is the former First Lady of Bangladesh , and then Prime Minister of Bangladesh, having served from 1991 to 1996, becoming the first woman in the country's history and second in the Muslim world to head a democratic government as prime minister. She served again from 2001 until...
called on textile firms to ensure the safety of workers by complying with international labor law at a speech inaugurating the Bangladesh Apparel & Textile Exposition (BATEXPO).
Investment
The stock market capitalizationMarket capitalization
Market capitalization is a measurement of the value of the ownership interest that shareholders hold in a business enterprise. It is equal to the share price times the number of shares outstanding of a publicly traded company...
of the Dhaka Stock Exchange
Dhaka Stock Exchange
Dhaka Stock Exchange is the main stock exchange of Bangladesh. It is located in Motijheel at the heart of the Dhaka city. It was incorporated in 1954. Dhaka stock exchange is the first stock exchange of the country...
in Bangladesh crossed $10 billion in November 2007 and the $30 billion dollar mark in 2009, and USD 50 billion in August 2010. Bangladesh had one of the best performing stock markets in the world during the recent global recession, due to relatively low correlations with developed country stock markets.
Major investment in real estate by domestic and foreign-resident Bangladeshis has led to a massive building boom in Dhaka and Chittagong.
Recent (2011) trends for investing in Bangladesh as Saudi Arabia trying to secure public and private investment in oil and gas, power and transportation projects, United Arab Emirates (UAE) is keen to invest in growing shipbuilding industry in Bangladesh encouraged by comparative cost advantage, Tata, an India-based leading industrial multinational to invest Taka 1500 crore to set up an automobile industry in Bangladesh, World Bank to invest in rural roads improving quality of live, the Rwandan entrepreneurs are keen to invest in Bangladesh's pharmaceuticals sector considering its potentiality in international market, Samsung sought to lease 500 industrial plots from the export zones authority to set up an electronics hub in Bangladesh with an investment of US$1.25 billion, National Board of Revenue (NBR) is set to withdraw tax rebate facilities on investment in the capital market by individual taxpayers from the fiscal 2011-12.
2010-11 market crash
The bullish capital market turned bearish during 2010, with the exchange losing 1,800 points between December 2010 and January 2011. Millions of investors have been rendered bankrupt as a result of the market crash. The crash is believed to be caused artificially to benefit a handful of players at the expense of the big players.External trade

billion by 2011. In part this optimism stems from how well the sector has fared since the end of textile and clothing quotas, under the Multifibre Agreement, in early 2005.
According to a United Nations Development Programme
United Nations Development Programme
The United Nations Development Programme is the United Nations' global development network. It advocates for change and connects countries to knowledge, experience and resources to help people build a better life. UNDP operates in 177 countries, working with nations on their own solutions to...
report "Sewing Thoughts: How to Realize Human Development Gains in the Post-Quota World" Bangladesh has been able to offset a decline
in European sales by cultivating new markets in the United States.
"[In 2005] we had tremendous growth. The quota-free textile regime has proved to be a big boost for our factories," said BGMEA president S.M. Fazlul Hoque told reporters, after the
sector's 24 per cent growth rate was revealed.
Bangladesh Knitwear Manufacturers and Exporters Association (BKMEA) president Md Fazlul Hoque has also struck an optimistic tone. In an interview with United News Bangladesh he lauded the blistering growth rate, saying "The quality of our products and its competitiveness in terms of prices helped the sector achieve such... tremendous success."
Knitwear posted the strongest growth of all textile products in 2005-06, surging 35.38 per cent to US$2.82 billion. On the downside however, the sector's strong growth came amid sharp falls in prices for textile products on the world market, with growth subsequently dependent upon large increases in volume.
Bangladesh's quest to boost the quantity of textile trade was also helped by US and EU caps on Chinese textiles. The US cap restricts growth in imports of Chinese textiles to 12.5 per cent next year and between 15 and 16 per cent in 2008. The EU deal similarly manages import growth until 2008.
Bangladesh may continue to benefit from these restrictions over the next two years, however a climate of falling global textile prices forces wage rates the centre of the nation's efforts to increase market share.
Prior to the Wage Board's announcement of its recommended minimum wage of $24, Tk1,604, in 2006, the rate had remained unchanged at Tk950, about $15, for more than 12 years. Although the government may allow up to three years for the new wage to be implemented, and inevitably there will be compliance issues as manufacturers drag their feet, it seemed politically untenable for wages to remain at those levels given the unprecedented industrial unrest.
In response to the Wage Board's initial draft recommendation of a minimum wage of Tk1,604 to be increased to Tk1,800 after eight months, the BGMEA declared over 50 per cent of factories would be ruined within three months. While this claim is no doubt an exaggeration, the capacity of Bangladesh's textile industry to absorb a significant wage hike as margins become tighter is a key question which hangs over the future of the industry. Bangladesh's textile sector is concentrated in export processing zones in Dhaka and Chittagong. These zones, which are administered by the Bangladesh Export Processing Zone Authority, aim to offer "a congenial investment climate, free from cumbersome procedures"m according to Bangladesh Export Promotion Bureau's website.
They offer a range of incentives to potential investors including 10 year tax holidays, duty free import of capital goods, raw materials and building materials, exemptions on income tax on salaries paid to foreign nationals for three years and dividend tax exemptions for the period of the tax holiday.
All goods produced in the zones are able to be exported duty free, in addition to which Bangladesh benefits from the Generalised System of Preferences in US, European and Japanese markets and is also endowed with Most Favoured Nation status from the United States.
Furthermore, Bangladesh imposes no ceiling on investment in the EPZs and allows full repatriation of profits.
The formation of labour unions within the EPZs is prohibited as are strikes.
Bangladesh's exports to the U.S. surpassed $1.9 billion in 1999. Bangladesh also exports significant amounts of garments and knitwear to the EU market.
Bangladesh also has significant jute, leather
Leather
Leather is a durable and flexible material created via the tanning of putrescible animal rawhide and skin, primarily cattlehide. It can be produced through different manufacturing processes, ranging from cottage industry to heavy industry.-Forms:...
, shrimp
Shrimp
Shrimp are swimming, decapod crustaceans classified in the infraorder Caridea, found widely around the world in both fresh and salt water. Adult shrimp are filter feeding benthic animals living close to the bottom. They can live in schools and can swim rapidly backwards. Shrimp are an important...
, pharmaceutical, and ceramic
Ceramic
A ceramic is an inorganic, nonmetallic solid prepared by the action of heat and subsequent cooling. Ceramic materials may have a crystalline or partly crystalline structure, or may be amorphous...
s industries.
Bangladesh has been a world leader in its efforts to end the use of child labor in garment factories. On July 4, 1995, the Bangladesh Garment Manufacturers Export Association, International Labour Organization
International Labour Organization
The International Labour Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that deals with labour issues pertaining to international labour standards. Its headquarters are in Geneva, Switzerland. Its secretariat — the people who are employed by it throughout the world — is known as the...
, and UNICEF signed a memorandum of understanding on the elimination of child labor in the garment sector. Implementation of this pioneering agreement began in fall 1995, and by the end of 1999, child labor in the garment trade virtually had been eliminated. The labor-intensive process of ship breaking for scrap has developed to the point where it now meets most of Bangladesh's domestic steel
Steel
Steel is an alloy that consists mostly of iron and has a carbon content between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight, depending on the grade. Carbon is the most common alloying material for iron, but various other alloying elements are used, such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten...
needs. Other industries include sugar
Sugar
Sugar is a class of edible crystalline carbohydrates, mainly sucrose, lactose, and fructose, characterized by a sweet flavor.Sucrose in its refined form primarily comes from sugar cane and sugar beet...
, tea, leather goods, newsprint
Newsprint
Newsprint is a low-cost, non-archival paper most commonly used to print newspapers, and other publications and advertising material. It usually has an off-white cast and distinctive feel. It is designed for use in printing presses that employ a long web of paper rather than individual sheets of...
, pharmaceutical, and fertilizer
Fertilizer
Fertilizer is any organic or inorganic material of natural or synthetic origin that is added to a soil to supply one or more plant nutrients essential to the growth of plants. A recent assessment found that about 40 to 60% of crop yields are attributable to commercial fertilizer use...
production.
The Bangladesh government continues to court foreign investment, something it has done fairly successfully in private power generation and gas exploration and production, as well as in other sectors such as cellular telephony, textiles, and pharmaceuticals. In 1989, the same year it signed a bilateral investment treaty with the United States, it established a Board of Investment to simplify approval and start-up procedures for foreign investors, although in practice the board has done little to increase investment. The government created the Bangladesh Export Processing Zone Authority
Bangladesh Export Processing Zone Authority
The Bangladesh Export Processing Zone Authority is an agency of the Government of Bangladesh and is administered out of the Prime Minister's Office. Its objective is to manage the various export processing zones in Bangladesh. BEPZA currently oversees the operations of five export processing zones...
to manage the various export processing zones. The agency currently manages EPZs in Adamjee, Chittagong
Chittagong
Chittagong ) is a city in southeastern Bangladesh and the capital of an eponymous district and division. Built on the banks of the Karnaphuli River, the city is home to Bangladesh's busiest seaport and has a population of over 4.5 million, making it the second largest city in the country.A trading...
, Comilla
Comilla
Comilla is a city in south-eastern Bangladesh, located along the Dhaka-Chittagong Highway. It is the administrative center of the Comilla District, part of the Chittagong Division. The Eastern Wing of Bangladesh Highway Police is located in Comilla....
, Dhaka
Dhaka
Dhaka is the capital of Bangladesh and the principal city of Dhaka Division. Dhaka is a megacity and one of the major cities of South Asia. Located on the banks of the Buriganga River, Dhaka, along with its metropolitan area, had a population of over 15 million in 2010, making it the largest city...
, Ishwardi, Karnaphuli, Mongla, and Uttara
Uttara
Uttara, which means "north" in Hindi, may refer to:* In the Hindu epic Mahabharata** Uttara , the son of King Virata who went into battle with Arjuna, disguised as his charioteer....
. An EPZ has also been proposed for Sylhet
Sylhet
Sylhet , is a major city in north-eastern Bangladesh. It is the main city of Sylhet Division and Sylhet District, and was granted metropolitan city status in March 2009. Sylhet is located on the banks of the Surma Valley and is surrounded by the Jaintia, Khasi and Tripura hills...
. The government has given the private sector permission to build and operate competing EPZs-initial construction on a Korea
Korea
Korea ) is an East Asian geographic region that is currently divided into two separate sovereign states — North Korea and South Korea. Located on the Korean Peninsula, Korea is bordered by the People's Republic of China to the northwest, Russia to the northeast, and is separated from Japan to the...
n EPZ started in 1999. In June 1999, the AFL-CIO
AFL-CIO
The American Federation of Labor and Congress of Industrial Organizations, commonly AFL–CIO, is a national trade union center, the largest federation of unions in the United States, made up of 56 national and international unions, together representing more than 11 million workers...
petitioned the U.S. Government to deny Bangladesh access to U.S. markets under the Generalized System of Preferences
Generalized System of Preferences
The Generalized System of Preferences, or GSP, is a formal system of exemption from the more general rules of the World Trade Organization ,...
(GSP), citing the country's failure to meet promises made in 1992 to allow freedom of association in EPZs.
Sylhet
Sylhet
Sylhet , is a major city in north-eastern Bangladesh. It is the main city of Sylhet Division and Sylhet District, and was granted metropolitan city status in March 2009. Sylhet is located on the banks of the Surma Valley and is surrounded by the Jaintia, Khasi and Tripura hills...
is fast becoming a major center of retailing in Bangladesh, with many shopping centres being built by expatriates to serve fellow expatriates visiting Sylhet and the emerging middle class. Many of these developments hark back to Britain
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
.
Overview
Bangladesh has made significant strides in its economic sector performance since independence in 1971. Although the economy has improved vastly in the 1990s, Bangladesh still suffers in the area of foreign trade in South Asia
South Asia
South Asia, also known as Southern Asia, is the southern region of the Asian continent, which comprises the sub-Himalayan countries and, for some authorities , also includes the adjoining countries to the west and the east...
n region. Despite major impediments to growth like the inefficiency of state-owned enterprises, a rapidly growing labor force that cannot be absorbed by agriculture, inadequate power supplies, and slow implementation of economic reforms, Bangladesh has made some headway improving the climate for foreign investors
Investment
Investment has different meanings in finance and economics. Finance investment is putting money into something with the expectation of gain, that upon thorough analysis, has a high degree of security for the principal amount, as well as security of return, within an expected period of time...
and liberalizing the capital market
Capital market
A capital market is a market for securities , where business enterprises and governments can raise long-term funds. It is defined as a market in which money is provided for periods longer than a year, as the raising of short-term funds takes place on other markets...
s; for example, it has negotiated with foreign firms for oil and gas exploration, better countrywide distribution of cooking gas, and the construction of natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
pipelines
Pipeline transport
Pipeline transport is the transportation of goods through a pipe. Most commonly, liquids and gases are sent, but pneumatic tubes that transport solid capsules using compressed air are also used....
and power station
Power station
A power station is an industrial facility for the generation of electric energy....
s. Progress on other economic reforms has been halting because of opposition from the bureaucracy, public sector unions, and other vested interest groups.
The especially severe floods of 1998 increased the flow of international aid. So far the global financial crisis has not had a major impact on the economy. The World Bank predicted economic growth of 6.5% for current year. Foreign aid has seen a decline of 10% over the last few months but economists see this as a good sign for self-reliance.There has been 18% growth in exports over the last 9 months and remittance inflow has increased at a remarkable 25% rate.
| Fiscal Year | Total Export | Total Import | Foreign Remittance Earnings |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2007–2008 | $14.11b | $25.205b | $8.9b |
| 2008–2009 | $15.56b | $22.00b+ | $9.68b |
| 2009-2010 | $16.7b | ~$24b | $10.87b |
| 2010-2011 | $22.93b | $32b | $11.65b |
See also
- Bangladesh Academy for Rural Development
- Bangladesh textile industry
- Child labor in BangladeshChild labor in BangladeshBangladesh ratified both the Minimum Age Convention of the International Labour Organization , and the ILO Worst Forms of Child Labour Convention . In addition, the country also ratified the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child....
- Chittagong Stock ExchangeChittagong Stock ExchangeChittagong Stock Exchange is a stock exchange located in the port city of Chittagong in southeastern Bangladesh. It was established in 1995 as the second stock exchange of the country. The exchange is located in the Agrabad commercial area of the city...
- Dhaka Stock ExchangeDhaka Stock ExchangeDhaka Stock Exchange is the main stock exchange of Bangladesh. It is located in Motijheel at the heart of the Dhaka city. It was incorporated in 1954. Dhaka stock exchange is the first stock exchange of the country...
- List of companies of Bangladesh
- Next ElevenNext ElevenThe Next Eleven are eleven countries—Bangladesh, Egypt, Indonesia, Iran, Mexico, Nigeria, Pakistan, Philippines, South Korea, Turkey, and Vietnam — identified by Goldman Sachs investment bank and Jim O'Neill as having a high potential of becoming, along with the BRICS, the world's largest...
- 3G (countries)3G (countries)3G countries or Global Growth Generators countries are 11 countries economies which have been identified as sources of growth potential and of profitable investment opportunities.-Background:...

