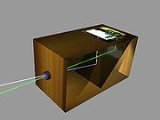
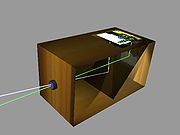
Camera obscura
Encyclopedia
Image
An image is an artifact, for example a two-dimensional picture, that has a similar appearance to some subject—usually a physical object or a person.-Characteristics:...
of its surroundings on a screen. It is used in drawing and for entertainment, and was one of the inventions that led to photography
Photography
Photography is the art, science and practice of creating durable images by recording light or other electromagnetic radiation, either electronically by means of an image sensor or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film...
. The device consists of a box or room with a hole in one side. Light from an external scene passes through the hole and strikes a surface inside where it is reproduced, upside-down, but with color and perspective
Perspective (graphical)
Perspective in the graphic arts, such as drawing, is an approximate representation, on a flat surface , of an image as it is seen by the eye...
preserved. The image can be projected onto paper, and can then be traced to produce a highly accurate representation.
Using mirrors, as in the 18th century overhead version (illustrated in the History section below), it is possible to project a right-side-up image. Another more portable type is a box with an angled mirror projecting onto tracing paper
Tracing paper
Tracing paper is a type of translucent paper. It is made by immersing uncut and unloaded paper of good quality in sulphuric acid for a few seconds. The acid converts some of the cellulose into amyloid form having a gelatinous and impermeable character. When the treated paper is thoroughly washed...
placed on the glass top, the image being upright as viewed from the back.
As a pinhole is made smaller, the image gets sharper, but the projected image becomes dimmer. With too small a pinhole the sharpness again becomes worse due to diffraction
Diffraction
Diffraction refers to various phenomena which occur when a wave encounters an obstacle. Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi coined the word "diffraction" and was the first to record accurate observations of the phenomenon in 1665...
. Some practical camera obscuras use a lens
Lens (optics)
A lens is an optical device with perfect or approximate axial symmetry which transmits and refracts light, converging or diverging the beam. A simple lens consists of a single optical element...
rather than a pinhole because it allows a larger aperture
F-number
In optics, the f-number of an optical system expresses the diameter of the entrance pupil in terms of the focal length of the lens; in simpler terms, the f-number is the focal length divided by the "effective" aperture diameter...
, giving a usable brightness while maintaining focus. (See pinhole camera
Pinhole camera
A pinhole camera is a simple camera without a lens and with a single small aperture – effectively a light-proof box with a small hole in one side. Light from a scene passes through this single point and projects an inverted image on the opposite side of the box...
for construction information.)
History

China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
philosopher and the founder of Mohism
Mohism
Mohism or Moism was a Chinese philosophy developed by the followers of Mozi , 470 BC–c.391 BC...
. Mo-Ti referred to this camera as a "collecting plate" or "locked treasure room". The Greek philosopher Aristotle
Aristotle
Aristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
(384 to 322 BC) understood the optical principle of the pinhole camera. He viewed the crescent shape of a partially eclipsed sun projected on the ground through the holes in a sieve, and the gaps between leaves of a plane tree.
The camera obscura was known to earlier scholars since the time of Mozi
Mozi
Mozi |Lat.]] as Micius, ca. 470 BC – ca. 391 BC), original name Mo Di , was a Chinese philosopher during the Hundred Schools of Thought period . Born in Tengzhou, Shandong Province, China, he founded the school of Mohism, and argued strongly against Confucianism and Daoism...
and Aristotle
Aristotle
Aristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
. Euclid
Euclid
Euclid , fl. 300 BC, also known as Euclid of Alexandria, was a Greek mathematician, often referred to as the "Father of Geometry". He was active in Alexandria during the reign of Ptolemy I...
's Optics (ca 300 BC), presupposed the camera obscura as a demonstration that light travels in straight lines.
In the 4th century BC, Aristotle
Aristotle
Aristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
noted that "sunlight travelling through small openings between the leaves of a tree, the holes of a sieve, the openings wickerwork, and even interlaced fingers will create circular patches of light on the ground." In the 4th century AD, Theon of Alexandria
Theon of Alexandria
Theon was a Greek scholar and mathematician who lived in Alexandria, Egypt. He edited and arranged Euclid's Elements and Ptolemy's Handy Tables, as well as writing various commentaries...
observed how "candlelight passing through a pinhole will create an illuminated spot on a screen that is directly in line with the aperture and the center of the candle." In the 9th century, Al-Kindi
Al-Kindi
' , known as "the Philosopher of the Arabs", was a Muslim Arab philosopher, mathematician, physician, and musician. Al-Kindi was the first of the Muslim peripatetic philosophers, and is unanimously hailed as the "father of Islamic or Arabic philosophy" for his synthesis, adaptation and promotion...
(Alkindus) demonstrated that "light from the right side of the flame will pass through the aperture and end up on the left side of the screen, while light from the left side of the flame will pass through the aperture and end up on the right side of the screen."
In the 6th century, Byzantine mathematician and architect Anthemius of Tralles
Anthemius of Tralles
Anthemius of Tralles was a Greek professor of Geometry in Constantinople and architect, who collaborated with Isidore of Miletus to build the church of Hagia Sophia by the order of Justinian I. Anthemius came from an educated family, one of five sons of Stephanus of Tralles, a physician...
(most famous for designing the Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia is a former Orthodox patriarchal basilica, later a mosque, and now a museum in Istanbul, Turkey...
), used a type of camera obscura in his experiments.
The Song Dynasty
Song Dynasty
The Song Dynasty was a ruling dynasty in China between 960 and 1279; it succeeded the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period, and was followed by the Yuan Dynasty. It was the first government in world history to issue banknotes or paper money, and the first Chinese government to establish a...
Chinese
Chinese people
The term Chinese people may refer to any of the following:*People with Han Chinese ethnicity ....
scientist Shen Kuo
Shen Kuo
Shen Kuo or Shen Gua , style name Cunzhong and pseudonym Mengqi Weng , was a polymathic Chinese scientist and statesman of the Song Dynasty...
(1031–1095) experimented with a camera obscura, and was the first to apply geometrical and quantitative
Quantitative property
A quantitative property is one that exists in a range of magnitudes, and can therefore be measured with a number. Measurements of any particular quantitative property are expressed as a specific quantity, referred to as a unit, multiplied by a number. Examples of physical quantities are distance,...
attributes to it in his book of 1088 AD, the Dream Pool Essays
Dream Pool Essays
The Dream Pool Essays was an extensive book written by the polymath Chinese scientist and statesman Shen Kuo by 1088 AD, during the Song Dynasty of China...
. However, Shen Kuo alluded to the fact that the Miscellaneous Morsels from Youyang
Miscellaneous Morsels from Youyang
The Miscellaneous Morsels from Youyang is a miscellany of Chinese and foreign legends and hearsay, reports on natural phenomena, short anecdotes, and tales of the wondrous and mundane, as well as notes on such topics as medicinal herbs and tattoos....
written in about 840 AD by Duan Chengshi
Duan Chengshi
Duan Chengshi was an author and scholar of the Tang Dynasty in China. He was born to a wealthy family in present day Zibo, Shandong. A descendant of the early Tang official Duan Zhixuan 段志玄 , and the son of Duan Wenchang 段文昌, a high official under Tang Xuanzong, his family background enabled him...
(d. 863) during the Tang Dynasty
Tang Dynasty
The Tang Dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China preceded by the Sui Dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period. It was founded by the Li family, who seized power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire...
(618–907) mentioned inverting the image of a Chinese pagoda
Chinese pagoda
Chinese Pagodas are a traditional part of Chinese architecture. In addition to religious use, since ancient times Chinese pagodas have been praised for the spectacular views which they offer, and many famous poems in Chinese history attest to the joy of scaling pagodas.-History:The pagoda is...
tower beside a seashore. In fact, Shen makes no assertion that he was the first to experiment with such a device. Shen wrote of Cheng's book: "[Miscellaneous Morsels from Youyang] said that the image of the pagoda is inverted because it is beside the sea, and that the sea has that effect. This is nonsense. It is a normal principle that the image is inverted after passing through the small hole."
In 13th-century England Roger Bacon
Roger Bacon
Roger Bacon, O.F.M. , also known as Doctor Mirabilis , was an English philosopher and Franciscan friar who placed considerable emphasis on the study of nature through empirical methods...
described the use of a camera obscura for the safe observation of solar eclipses. Its potential as a drawing aid may have been familiar to artists by as early as the 15th century; Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci was an Italian Renaissance polymath: painter, sculptor, architect, musician, scientist, mathematician, engineer, inventor, anatomist, geologist, cartographer, botanist and writer whose genius, perhaps more than that of any other figure, epitomized the Renaissance...
(1452–1519 AD) described camera obscura in Codex Atlanticus
Codex Atlanticus
The Codex Atlanticus is a twelve-volume, bound set of drawings and writings by Leonardo da Vinci, the largest such set; its name indicates its atlas-like breadth. It comprises 1,119 leaves dating from 1478 to 1519, the contents covering a great variety of subjects, from flight to weaponry to...
. Johann Zahn's
Johann Zahn
Johann Zahn was the seventeenth-century German author of Oculus Artificialis Teledioptricus Sive Telescopium...
Oculus Artificialis Teledioptricus Sive Telescopium was published in 1685. This work contains many descriptions and diagrams, illustrations and sketches of both the camera obscura and of the magic lantern
Magic lantern
The magic lantern or Laterna Magica is an early type of image projector developed in the 17th century.-Operation:The magic lantern has a concave mirror in front of a light source that gathers light and projects it through a slide with an image scanned onto it. The light rays cross an aperture , and...
.

Johannes Vermeer
Johannes, Jan or Johan Vermeer was a Dutch painter who specialized in exquisite, domestic interior scenes of middle class life. Vermeer was a moderately successful provincial genre painter in his lifetime...
, who were hired as painters in the 17th century, were known for their magnificent attention to detail. It has been widely speculated that they made use of such a camera, but the extent of their use by artists at this period remains a matter of considerable controversy, recently revived by the Hockney-Falco thesis
Hockney-Falco thesis
The Hockney–Falco thesis is a controversial theory of art history, advanced by artist David Hockney and physicist Charles M. Falco, suggesting that advances in realism and accuracy in the history of Western art since the Renaissance were primarily the result of optical aids such as the camera...
. The term "camera obscura" was first used by the German astronomer Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler was a German mathematician, astronomer and astrologer. A key figure in the 17th century scientific revolution, he is best known for his eponymous laws of planetary motion, codified by later astronomers, based on his works Astronomia nova, Harmonices Mundi, and Epitome of Copernican...
in 1604. The English physician and author Sir Thomas Browne
Thomas Browne
Sir Thomas Browne was an English author of varied works which reveal his wide learning in diverse fields including medicine, religion, science and the esoteric....
speculated upon the inter-related workings of optics and the camera obscura in his 1658 Discourse The Garden of Cyrus
The Garden of Cyrus
The Garden of Cyrus or The Quincunciall Lozenge, or Network Plantations of the Ancients, naturally, artificially, mystically considered is a Discourse written by Sir Thomas Browne. It was first published in 1658, along with its diptych companion, Urn-Burial...
thus-
For at the eye the Pyramidal rayes from the object, receive a decussation, and so strike a second base upon the Retina or hinder coat, the proper organ of Vision; wherein the pictures from objects are represented, answerable to the paper, or wall in the dark chamber; after the decussation of the rayes at the hole of the hornycoat, and their refraction upon the Christalline humour, answering the foramen of the window, and the convex or burning-glasses, which refract the rayes that enter it.
Early models were large; comprising either a whole darkened room or a tent (as employed by Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler was a German mathematician, astronomer and astrologer. A key figure in the 17th century scientific revolution, he is best known for his eponymous laws of planetary motion, codified by later astronomers, based on his works Astronomia nova, Harmonices Mundi, and Epitome of Copernican...
). By the 18th century, following developments by Robert Boyle
Robert Boyle
Robert Boyle FRS was a 17th century natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, and inventor, also noted for his writings in theology. He has been variously described as English, Irish, or Anglo-Irish, his father having come to Ireland from England during the time of the English plantations of...
and Robert Hooke
Robert Hooke
Robert Hooke FRS was an English natural philosopher, architect and polymath.His adult life comprised three distinct periods: as a scientific inquirer lacking money; achieving great wealth and standing through his reputation for hard work and scrupulous honesty following the great fire of 1666, but...
, more easily portable models became available. These were extensively used by amateur artists while on their travels, but they were also employed by professionals, including Paul Sandby
Paul Sandby
Paul Sandby was an English map-maker turned landscape painter in watercolours, who, along with his older brother Thomas, became one of the founding members of the Royal Academy in 1768.-Life and work:...
, Canaletto
Canaletto
Giovanni Antonio Canal better known as Canaletto , was a Venetian painter famous for his landscapes, or vedute, of Venice. He was also an important printmaker in etching.- Early career :...
and Joshua Reynolds
Joshua Reynolds
Sir Joshua Reynolds RA FRS FRSA was an influential 18th-century English painter, specialising in portraits and promoting the "Grand Style" in painting which depended on idealization of the imperfect. He was one of the founders and first President of the Royal Academy...
, whose camera (disguised as a book) is now in the Science Museum (London)
Science Museum (London)
The Science Museum is one of the three major museums on Exhibition Road, South Kensington, London in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea. It is part of the National Museum of Science and Industry. The museum is a major London tourist attraction....
. Such cameras were later adapted by Joseph Nicephore Niepce, Louis Daguerre
Louis Daguerre
Louis-Jacques-Mandé Daguerre was a French artist and physicist, recognized for his invention of the daguerreotype process of photography.- Biography :...
and William Fox Talbot
William Fox Talbot
William Henry Fox Talbot was a British inventor and a pioneer of photography. He was the inventor of calotype process, the precursor to most photographic processes of the 19th and 20th centuries. He was also a noted photographer who made major contributions to the development of photography as an...
for creating the first photographs.
See also
- Bristol ObservatoryObservatory, BristolThe Observatory is a former mill, now used as an observatory, located on Clifton Down, close to the Clifton Suspension Bridge, Bristol, England...
- Black mirrorClaude glassA Claude glass is a small mirror, slightly convex in shape, with its surface tinted a dark colour. Bound up like a pocket-book or in a carrying case, black mirrors were used by artists, travellers and connoisseurs of landscape and landscape painting...
- Camera lucidaCamera lucidaA camera lucida is an optical device used as a drawing aid by artists.The camera lucida performs an optical superimposition of the subject being viewed upon the surface upon which the artist is drawing. The artist sees both scene and drawing surface simultaneously, as in a photographic double...
- Cameras
- History of cinema
- Hockney-Falco thesisHockney-Falco thesisThe Hockney–Falco thesis is a controversial theory of art history, advanced by artist David Hockney and physicist Charles M. Falco, suggesting that advances in realism and accuracy in the history of Western art since the Renaissance were primarily the result of optical aids such as the camera...
- Magic lanternMagic lanternThe magic lantern or Laterna Magica is an early type of image projector developed in the 17th century.-Operation:The magic lantern has a concave mirror in front of a light source that gathers light and projects it through a slide with an image scanned onto it. The light rays cross an aperture , and...
- OpticsOpticsOptics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
External links
- An Appreciation of the Camera Obscura
- The Camera Obscura in San Francisco—The Giant Camera of San Francisco at Ocean Beach, added to the National Register of Historic PlacesNational Register of Historic PlacesThe National Register of Historic Places is the United States government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures, and objects deemed worthy of preservation...
in 2001 - Camera Obscura and World of Illusions, EdinburghEdinburghEdinburgh is the capital city of Scotland, the second largest city in Scotland, and the eighth most populous in the United Kingdom. The City of Edinburgh Council governs one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas. The council area includes urban Edinburgh and a rural area...
- Dumfries Museum & Camera Obscura, Dumfries, Scotland
- Vermeer and the Camera Obscura by Philip Steadman
- Paleo-camera – The camera obscura and the origins of art
- List of all known Camera Obscura
- Willett & Patteson Camera Obscura hire and Creation.
- Camera Obscura and Outlook Tower, Edinburgh, Scotland
- Cameraobscuras.com George T Keene builds custom camera obscuras like the Griffith ObservatoryGriffith ObservatoryGriffith Observatory is in Los Angeles, California, United States. Sitting on the south-facing slope of Mount Hollywood in L.A.'s Griffith Park, it commands a view of the Los Angeles Basin, including downtown Los Angeles to the southeast, Hollywood to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest...
CO in Los Angeles. - Camera obscura in Trondheim, Norway, built by students of architecture and engineering from Norwegian University of Science and TechnologyNorwegian University of Science and TechnologyThe Norwegian University of Science and Technology , commonly known as NTNU, is located in Trondheim. NTNU is the second largest of the eight universities in Norway, and, as its name suggests, has the main national responsibility for higher education in engineering and technology...
(NTNU)

