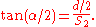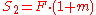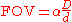Angle of view
Encyclopedia
Photography
Photography is the art, science and practice of creating durable images by recording light or other electromagnetic radiation, either electronically by means of an image sensor or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film...
, angle of view describes the angular
Angle
In geometry, an angle is the figure formed by two rays sharing a common endpoint, called the vertex of the angle.Angles are usually presumed to be in a Euclidean plane with the circle taken for standard with regard to direction. In fact, an angle is frequently viewed as a measure of an circular arc...
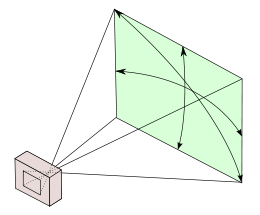
extent of a given scene that is imaged by a camera
Camera
A camera is a device that records and stores images. These images may be still photographs or moving images such as videos or movies. The term camera comes from the camera obscura , an early mechanism for projecting images...
. It is used interchangeably with the more general term field of view
Field of view
The field of view is the extent of the observable world that is seen at any given moment....
.
It is important to distinguish the angle of view from the angle of coverage, which describes the angle range that a lens can image. Typically the image circle
Image circle
The image circle, or circle of illumination, of a lens is the circular area in the image plane formed by the cone of light transmitted by the lens . Within this circle is the smaller circle for which image definition is acceptable, the circle of good definition ; however, some authors make no...
produced by a lens is large enough to cover the film or sensor completely, possibly including some vignetting
Vignetting
In photography and optics, vignetting is a reduction of an image's brightness or saturation at the periphery compared to the image center. The word vignette, from the same root as vine, originally referred to a decorative border in a book. Later, the word came to be used for a photographic...
toward the edge. If the angle of coverage of the lens does not fill the sensor, the image circle will be visible, typically with strong vignetting toward the edge, and the effective angle of view will be limited to the angle of coverage.

Calculating a camera's angle of view
For lenses projecting rectilinearRectilinear lens
In photography, a rectilinear lens is a photographic lens that yields images where straight features, such as the walls of buildings, appear with straight lines, as opposed to being curved. In other words, it is a lens with little or no barrel or pincushion distortion...
(non-spatially-distorted) images of distant objects, the effective focal length
Focal length
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light. For an optical system in air, it is the distance over which initially collimated rays are brought to a focus...
and the image format dimensions completely define the angle of view. Calculations for lenses producing non-rectilinear images are much more complex and in the end not very useful in most practical applications. (In the case of a lens with distortion, e.g., a fisheye lens
Fisheye lens
In photography, a fisheye lens is a wide-angle lens that takes in a broad, panoramic and hemispherical image. Originally developed for use in meteorology to study cloud formation and called "whole-sky lenses", fisheye lenses quickly became popular in general photography for their unique, distorted...
, a longer lens with distortion can have a wider angle of view than a shorter lens with low distortion)
Angle of view may be measured horizontally (from the left to right edge of the frame), vertically (from the top to bottom of the frame), or diagonally (from one corner of the frame to its opposite corner).
For a lens projecting a rectilinear image, the angle of view (α) can be calculated from the chosen dimension (d), and effective focal length (f) as follows:
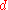 represents the size of the film (or sensor) in the direction measured. For example, for film that is 36 mm wide,
represents the size of the film (or sensor) in the direction measured. For example, for film that is 36 mm wide,  mm would be used to obtain the horizontal angle of view.
mm would be used to obtain the horizontal angle of view.Because this is a trigonometric function, the angle of view does not vary quite linearly with the reciprocal of the focal length. However, except for wide-angle lenses, it is reasonable to approximate
 radians or
radians or 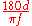 degrees.
degrees.The effective focal length is nearly equal to the stated focal length of the lens (F), except in macro photography
Macro photography
Macrophotography is close-up photography, usually of very small subjects. Classically a macrophotograph is one in which the size of the subject on the negative is greater than life size. However in modern use it refers to a finished photograph of a subject at greater than life size...
where the lens-to-object distance is comparable to the focal length. In this case, the magnification
Magnification
Magnification is the process of enlarging something only in appearance, not in physical size. This enlargement is quantified by a calculated number also called "magnification"...
factor (m) must be taken into account:
(In photography
 is usually defined to be positive, despite the inverted image.) For example, with a magnification ratio of 1:2, we find
is usually defined to be positive, despite the inverted image.) For example, with a magnification ratio of 1:2, we find  and thus the angle of view is reduced by 33% compared to focusing on a distant object with the same lens.
and thus the angle of view is reduced by 33% compared to focusing on a distant object with the same lens.A second effect which comes into play in macro photography
Macro photography
Macrophotography is close-up photography, usually of very small subjects. Classically a macrophotograph is one in which the size of the subject on the negative is greater than life size. However in modern use it refers to a finished photograph of a subject at greater than life size...
is lens asymmetry (an asymmetric lens is a lens where the aperture appears to have different dimensions when viewed from the front and from the back). The lens asymmetry causes an offset between the nodal plane and pupil positions. The effect can be quantified using the ratio (P) between apparent exit pupil diameter and entrance pupil diameter. The full formula for angle of view now becomes:
Angle of view can also be determined using FOV tables or paper or software lens calculators.
Example
Consider a 35 mm camera with a normal lensNormal lens
In photography and cinematography a normal lens, also called a standard lens, is a lens that reproduces perspective that generally looks "natural" to a human observer under normal viewing conditions, as compared with lenses with longer or shorter focal lengths which produce an expanded or...
having a focal length of . The dimensions of the 35 mm image format are 24 mm (vertically) × 36 mm (horizontal), giving a diagonal of about 43.3 mm.
At infinity focus, , and the angles of view are:
- horizontally,

- vertically,

- diagonally,
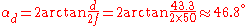
Derivation of the angle-of-view formula
Consider a rectilinear lens in a camera used to photograph an object at a distance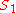 , and forming an image that just barely fits in the dimension,
, and forming an image that just barely fits in the dimension, 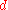 , of the frame (the film
, of the frame (the filmPhotographic film
Photographic film is a sheet of plastic coated with an emulsion containing light-sensitive silver halide salts with variable crystal sizes that determine the sensitivity, contrast and resolution of the film...
or image sensor
Image sensor
An image sensor is a device that converts an optical image into an electronic signal. It is used mostly in digital cameras and other imaging devices...
). Treat the lens as if it were a pinhole
Pinhole camera model
The pinhole camera model describes the mathematical relationship between the coordinates of a 3D point and its projection onto the image plane of an ideal pinhole camera, where the camera aperture is described as a point and no lenses are used to focus light...
at distance
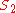 from the image plane (technically, the center of perspective of a rectilinear lens
from the image plane (technically, the center of perspective of a rectilinear lensRectilinear lens
In photography, a rectilinear lens is a photographic lens that yields images where straight features, such as the walls of buildings, appear with straight lines, as opposed to being curved. In other words, it is a lens with little or no barrel or pincushion distortion...
is at the center of its entrance pupil
Entrance pupil
In an optical system, the entrance pupil is the optical image of the physical aperture stop, as 'seen' through the front of the lens system. The corresponding image of the aperture as seen through the back of the lens system is called the exit pupil...
):

Now
 is the angle between the optical axis
is the angle between the optical axisOptical axis
An optical axis is a line along which there is some degree of rotational symmetry in an optical system such as a camera lens or microscope.The optical axis is an imaginary line that defines the path along which light propagates through the system...
of the lens and the ray joining its optical center to the edge of the film. Here
 is defined to be the angle-of-view, since it is the angle enclosing the largest object whose image can fit on the film. We want to find the relationship between:
is defined to be the angle-of-view, since it is the angle enclosing the largest object whose image can fit on the film. We want to find the relationship between:
-
- the angle

- the "opposite" side of the right triangle,
 (half the film-format dimension)
(half the film-format dimension) - the "adjacent" side,
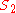 (distance from the lens to the image plane)
(distance from the lens to the image plane)
- the angle
Using basic trigonometry, we find:
which we can solve for α, giving:
To project a sharp image of distant objects,
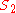 needs to be equal to the focal length
needs to be equal to the focal lengthFocal length
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light. For an optical system in air, it is the distance over which initially collimated rays are brought to a focus...
,
 , which is attained by setting the lens for infinity focus
, which is attained by setting the lens for infinity focusInfinity focus
In optics and photography, infinity focus is the state where a lens or other optical system forms an image of an object an infinite distance away. This corresponds to the point of focus for parallel rays. The image is formed at the focal point of the lens....
. Then the angle of view is given by:
-
 where
where 
Macro photography
For macro photography, we cannot neglect the difference between and
and 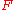 . From the thin lens formula,
. From the thin lens formula,-
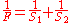 .
.
We substitute for the magnification
Magnification
Magnification is the process of enlarging something only in appearance, not in physical size. This enlargement is quantified by a calculated number also called "magnification"...
,
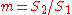 , and with some algebra find:
, and with some algebra find:
Defining
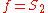 as the "effective focal length", we get the formula presented above:
as the "effective focal length", we get the formula presented above:-
 where
where 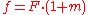 .
.
A second effect which comes into play in macro photography is lens asymmetry (an asymmetric lens is a lens where the aperture appears to have different dimensions when viewed from the front and from the back). The lens asymmetry causes an offset between the nodal plane and pupil positions. The effect can be quantified using the ratio (P) between apparent exit pupil diameter and entrance pupil diameter. The full formula for angle of view now becomes:
Measuring a camera's field of view
In the optical instrumentation industry the term field of view (FOV) is most often used, though the measurements are still expressed as angles. Optical tests are commonly used for measuring the FOV of UV, visibleVisible spectrum
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called visible light or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 390 to 750 nm. In terms of...
, and infrared
Infrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
(wavelengths about 0.1–20 µm in the electromagnetic spectrum
Electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. The "electromagnetic spectrum" of an object is the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by that particular object....
) sensors and cameras.
The purpose of this test is to measure the horizontal and vertical FOV of a lens and sensor used in an imaging system, when the lens focal length or sensor size is not known (that is, when the calculation above is not immediately applicable). Although this is one typical method that the optics
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
industry uses to measure the FOV, there exist many other possible methods.
UV/visible light from an integrating sphere
Integrating sphere
An Integrating sphere is an optical component consisting of a hollow cavity with its interior coated for high diffuse reflectivity , having relatively small holes as needed for entrance and exit ports....
(and/or other source such as a black body
Black body
A black body is an idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation. Because of this perfect absorptivity at all wavelengths, a black body is also the best possible emitter of thermal radiation, which it radiates incandescently in a characteristic, continuous spectrum...
) is focused onto a square test target at the focal plane of a collimator
Collimator
A collimator is a device that narrows a beam of particles or waves. To "narrow" can mean either to cause the directions of motion to become more aligned in a specific direction or to cause the spatial cross section of the beam to become smaller.- Optical collimators :In optics, a collimator may...
(the mirrors in the diagram), such that a virtual image of the test target will be seen infinitely far away by the camera under test. The camera under test senses a real image of the virtual image of the target, and the sensed image is displayed on a monitor.
The sensed image, which includes the target, is displayed on a monitor, where it can be measured. Dimensions of the full image display and of the portion of the image that is the target are determined by inspection (measurements are typically in pixels, but can just as well be inches or cm).
-
 = dimension of full image
= dimension of full image = dimension of image of target
= dimension of image of target
The collimator's distant virtual image of the target subtends a certain angle, referred to as the angular extent of the target, that depends on the collimator focal length and the target size. Assuming the sensed image includes the whole target, the angle seen by the camera, its FOV, is this angular extent of the target times the ratio of full image size to target image size.
The target's angular extent is:
-
- where
 is the dimension of the target and
is the dimension of the target and 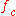 is the focal length of collimator.
is the focal length of collimator.
- where
The total field of view is then approximately:
or more precisely, if the imaging system is rectilinear
Rectilinear lens
In photography, a rectilinear lens is a photographic lens that yields images where straight features, such as the walls of buildings, appear with straight lines, as opposed to being curved. In other words, it is a lens with little or no barrel or pincushion distortion...
:
This calculation could be a horizontal or a vertical FOV, depending on how the target and image are measured.
Focal length

- fisheye lensFisheye lensIn photography, a fisheye lens is a wide-angle lens that takes in a broad, panoramic and hemispherical image. Originally developed for use in meteorology to study cloud formation and called "whole-sky lenses", fisheye lenses quickly became popular in general photography for their unique, distorted...
es, typical focal lengths are between 8 mm and 10 mm for circular images, and 15–16 mm for full-frame images. Up to 180° and beyond.- A circular fisheye lens (as opposed to a full-frame fisheye) is an example of a lens where the angle of coverage is less than the angle of view. The image projected onto the film is circular because the diameter of the image projected is narrower than that needed to cover the widest portion of the film.
- Ultra wide angle lensUltra wide angle lensAn ultra wide-angle lens is a lens whose focal length is shorter than the short side of film or sensor.Thus the term denotes a different range of lenses, relative to the size of the sensor in the camera in question....
is a rectilinearRectilinear lensIn photography, a rectilinear lens is a photographic lens that yields images where straight features, such as the walls of buildings, appear with straight lines, as opposed to being curved. In other words, it is a lens with little or no barrel or pincushion distortion...
which is less than 24mm of focal lengthFocal lengthThe focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light. For an optical system in air, it is the distance over which initially collimated rays are brought to a focus...
in 35mm film format, here 14mm is 114° and 24mm is 84° . - Wide-angle lensWide-angle lensFrom a design perspective, a wide angle lens is one that projects a substantially larger image circle than would be typical for a standard design lens of the same focal length; this enables either large tilt & shift movements with a view camera, or lenses with wide fields of view.More informally,...
es (24–35mm in 35mm film format) cover between 84° and 64° - Normal, or Standard lensesNormal lensIn photography and cinematography a normal lens, also called a standard lens, is a lens that reproduces perspective that generally looks "natural" to a human observer under normal viewing conditions, as compared with lenses with longer or shorter focal lengths which produce an expanded or...
(36–60mm in 35mm film format) cover between 62° and 40° - Long focus lenses (any lens with a focal length greater than the diagonal of the film or sensor used) generally have an angle of view of 35° or less. Since photographers usually only encounter the telephoto lensTelephoto lensIn photography and cinematography, a telephoto lens is a specific type of a long-focus lens in which the physical length of the lens is shorter than the focal length. This is achieved by incorporating a special lens group known as a telephoto group that extends the light path to create a long-focus...
sub-type, they are referred to in common photographic parlance as: - "Medium telephoto", a focal length of 85mm to 135mm in 35mm film format covering between 30° and 10°
- "Super telephoto" (over 300mm in 35mm film format) generally cover between 8° through less than 1°
Zoom lens
Zoom lens
A zoom lens is a mechanical assembly of lens elements for which the focal length can be varied, as opposed to a fixed focal length lens...
es are a special case wherein the focal length, and hence angle of view, of the lens can be altered mechanically without removing the lens from the camera.
Characteristics
For a given camera–subject distance, longer lenses magnify the subject more. For a given subject magnification (and thus different camera–subject distances), longer lenses have less depth of fieldDepth of field
In optics, particularly as it relates to film and photography, depth of field is the distance between the nearest and farthest objects in a scene that appear acceptably sharp in an image...
, and appear to compress distance; wider lenses appear to expand the distance between objects.
Another result of using a wide angle lens is a greater apparent perspective distortion
Perspective distortion (photography)
In photography and cinematography, perspective distortion is a warping or transformation of an object and its surrounding area that differs significantly from what the object would look like with a normal focal length, due to the relative scale of nearby and distant features...
when the camera is not aligned perpendicularly to the subject: parallel lines converge at the same rate as with a normal lens
Normal lens
In photography and cinematography a normal lens, also called a standard lens, is a lens that reproduces perspective that generally looks "natural" to a human observer under normal viewing conditions, as compared with lenses with longer or shorter focal lengths which produce an expanded or...
, but converge more due to the wider total field. For example, buildings appear to be falling backwards much more severely when the camera is pointed upward from ground level than they would if photographed with a normal lens at the same distance from the subject, because more of the subject building is visible in the wide-angle shot.
Because different lenses generally require a different camera–subject distance to preserve the size of a subject, changing the angle of view can indirectly distort
Perspective distortion (photography)
In photography and cinematography, perspective distortion is a warping or transformation of an object and its surrounding area that differs significantly from what the object would look like with a normal focal length, due to the relative scale of nearby and distant features...
perspective, changing the apparent relative size of the subject and foreground.
If the subject image size remains the same, then at any given aperture all lenses, wide angle and long lenses, will give the same depth of field.
Examples
An example of how lens choice affects angle of view. The photos below were taken by a 35 mm135 film
The term 135 was introduced by Kodak in 1934 as a designation for cartridge film wide, specifically for still photography. It quickly grew in popularity, surpassing 120 film by the late 1960s to become the most popular photographic film format...
still camera at a constant distance from the subject:
 |
 |
 |
 |
Common lens angles of view
This table shows the diagonal, horizontal, and vertical angles of view, in degrees, for lenses producing rectilinear images, when used with 36 mm × 24 mm format (that is, 135 film135 film
The term 135 was introduced by Kodak in 1934 as a designation for cartridge film wide, specifically for still photography. It quickly grew in popularity, surpassing 120 film by the late 1960s to become the most popular photographic film format...
or full-frame 35mm digital using width 36 mm, height 24 mm, and diagonal 43.3 mm for d in the formula above). Digital compact cameras sometimes state the focal lengths of their lenses in 35mm equivalents, which can be used in this table.
| Focal Length (mm) | 13 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 28 | 35 | 43.3 | 50 | 70 | 85 | 105 | 135 | 180 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 800 | 1200 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diagonal (°) | 118 | 111 | 100 | 91.7 | 84.1 | 75.4 | 63.4 | 53.1 | 46.8 | 34.4 | 28.6 | 23.3 | 18.2 | 13.7 | 12.4 | 8.25 | 6.19 | 4.96 | 4.13 | 3.10 | 2.07 |
| Vertical (°) | 85.4 | 77.3 | 67.4 | 59.5 | 53.1 | 46.4 | 37.8 | 31.0 | 27.0 | 19.5 | 16.1 | 13.0 | 10.2 | 7.63 | 6.87 | 4.58 | 3.44 | 2.75 | 2.29 | 1.72 | 1.15 |
| Horizontal (°) | 108 | 100.4 | 90.0 | 81.2 | 73.7 | 65.5 | 54.4 | 45.1 | 39.6 | 28.8 | 23.9 | 19.5 | 15.2 | 11.4 | 10.3 | 6.87 | 5.15 | 4.12 | 3.44 | 2.58 | 1.72 |
Three-dimensional digital art
Displaying 3d graphics as 3d projection3D projection
3D projection is any method of mapping three-dimensional points to a two-dimensional plane. As most current methods for displaying graphical data are based on planar two-dimensional media, the use of this type of projection is widespread, especially in computer graphics, engineering and drafting.-...
of the models onto a 2d surface uses a series of mathematical calculations to render the scene. The angle of view of the scene is thus readily set and changed; some renderers even measure the angle of view as the focal length of an imaginary lens. The angle of view can also be projected onto the surface at an angle greater than 90°, effectively creating a fish eye lens effect.
Cinematography and video gaming
Modifying the angle of view over time, or zooming, is a frequently used cinematic techniqueCinematic techniques
- Basic Definitions of Terms :Aerial Shot:A shot taken from a crane, plane, or helicopter. Not necessarily a moving shot.Backlighting:The main source of light is behind the subject, silhouetting it, and directed toward the camera....
.
For a visual effect, some first person video games (especially racing game
Racing game
A racing video game is a genre of video games, either in the first-person or third-person perspective, in which the player partakes in a racing competition with any type of land, air, or sea vehicles. They may be based on anything from real-world racing leagues to entirely fantastical settings...
s), widen the angle of view beyond 90° to exaggerate the distance the player is travelling, thus exaggerating the player's perceived speed and giving a tunnel
Tunnel
A tunnel is an underground passageway, completely enclosed except for openings for egress, commonly at each end.A tunnel may be for foot or vehicular road traffic, for rail traffic, or for a canal. Some tunnels are aqueducts to supply water for consumption or for hydroelectric stations or are sewers...
effect (like pincushion distortion). Narrowing the view angle gives a zoom in
Zoom lens
A zoom lens is a mechanical assembly of lens elements for which the focal length can be varied, as opposed to a fixed focal length lens...
effect. Also see Field of view in video games
Field of view in video games
Field of view in video games is the extent of the observable game world that is seen on the display at any given moment....
.
See also
- 35 mm equivalent focal length35 mm equivalent focal lengthIn photography, the 35 mm equivalent focal length is a measure that indicates the angle of view of a particular combination of a camera lens and film or sensor size...
- Camera angleCamera angleThe camera angle marks the specific location at which a camera is placed to take a shot. A scene may be shot from several camera angles. This will give different experience and sometimes emotion. the different camera angles will have different effects on the viewer and how they perceive the scene...
- Camera coverageCamera coverageCamera coverage, in filmmaking and video production, is the amount of footage shot and different camera angles used to capture a scene. When in the post-production process, the more camera coverage means that there is more footage for the film editor to work with in assembling the final cut.-See...
- Camera operatorCamera operatorA camera operator or cameraman is a professional operator of a film or video camera. In filmmaking, the leading cameraman is usually called a cinematographer, while a cameraman in a video production may be known as a television camera operator, video camera operator, or videographer, depending on...
- Cinematic techniquesCinematic techniques- Basic Definitions of Terms :Aerial Shot:A shot taken from a crane, plane, or helicopter. Not necessarily a moving shot.Backlighting:The main source of light is behind the subject, silhouetting it, and directed toward the camera....
- Field of viewField of viewThe field of view is the extent of the observable world that is seen at any given moment....
- FilmmakingFilmmakingFilmmaking is the process of making a film, from an initial story, idea, or commission, through scriptwriting, casting, shooting, directing, editing, and screening the finished product before an audience that may result in a theatrical release or television program...
- Multiple-camera setupMultiple-camera setupThe multiple-camera setup, multiple-camera mode of production, or multicam is a method of filmmaking and video production. Several cameras—either film or professional video cameras—are employed on the set and simultaneously record or broadcast a scene...
- Single-camera setupSingle-camera setupThe single-camera setup, or single-camera mode of production, is a method of filmmaking and video production. A single camera—either motion picture camera or professional video camera—is employed on the set and each shot to make up a scene is taken individually...
- Video productionVideo productionVideo production is videography, the process of capturing moving images on electronic media even streaming media. The term includes methods of production and post-production...