
Tepper School of Business
Encyclopedia
The Tepper School of Business is a private business school
located on Carnegie Mellon University
’s 140 acre (0.5665604 km²) campus in Pittsburgh
, Pennsylvania
, USA
.
The school consistently ranks highly among the top business schools in the U.S., as well as in a wide range of specializations, such as finance
, entrepreneurship
, operations management
and information technology
. The school offers degrees from the undergraduate through doctoral levels, in addition to executive education
programs.
Prior to the founding of the Tepper School, management education typically used the case method
approach popularized at the Harvard Business School
, based upon widely accepted examples from successful companies and microeconomic theory. Although the Tepper School did not entirely abandon those traditional models and theories, it has focused on management science, or decision making
based on quantitative
models and an analytical
approach to decision making
and problem solving
. Today, the Tepper School is known for its strong emphasis on quantitative skills and its continued teaching of courses based upon the science of management. A number of Nobel Prize
winning economists have been affiliated with the school, including Herbert Simon
, Franco Modigliani
, Merton Miller
, Robert Lucas
, Edward Prescott, Finn Kydland, Oliver Williamson, and Dale Mortensen.
The Tepper School of Business was originally known as The Graduate School of Industrial Administration (GSIA), which was founded in 1949 by William Larimer Mellon
. In March 2004, the school received a record $55 million gift from alumnus David Tepper
. In recognition of this gift, the school was named the David A. Tepper School of Business at Carnegie Mellon.
 In 1946, economist George Bach was hired by the Carnegie Institute of Technology
In 1946, economist George Bach was hired by the Carnegie Institute of Technology
(predecessor of Carnegie Mellon University) to restart the school’s economics department. Bach had previously been working at the Federal Reserve during World War II
. He added William W. Cooper from the field of Operations Research
(which had increased its visibility during the war) and Herbert Simon
, a political scientist who was to direct the undergraduate business program. The beginnings of the Cold War
were applying pressure on the academic community to increase US managerial ability, and when William Larimer Mellon
gave a $6 million grant to found a school of industrial administration, Bach became the first dean, bringing along the entire economics department.
Under Bach’s leadership, the school was credited with several educational innovations that have now become standard at other prominent business schools. Specifically, in 1958, the school's Management Game was the first to use computer simulations for experiential learning of business roles; such simulations have subsequently been adopted by other institutions. Additionally, in 1989, the school's Financial Analysis and Security Trading Center (FAST) was the first educational institution to successfully replicate the live international data feeds and sophisticated software of Wall Street
trading firms.
Several faculty members have won acclaim for research in the areas of business and economics. As an example, the school has produced seven Nobel Prize
winners in Economics: Robert Lucas, Jr.
, Merton Miller
, Franco Modigliani
, Herb Simon, Oliver E. Williamson
, Edward Prescott and Finn Kydland. Lucas was awarded the prize for developing and applying the theory of rational expectations
, an econometric hypothesis that directly challenged Keynesian orthodoxy. Modigliani's prize recognized his life-cycle hypothesis, which attempts to explain the level of saving in the economy. Modigliani proposed that consumers would aim for a stable level of income throughout their lifetime, for example by saving during their working years and spending during their retirement. Miller's prize was awarded in recognition of his contributions to corporate finance. The results of his research—in collaboration with Franco Modigliani—are now taught in every business school in the country. Simon's prize was given for his development of the idea of bounded rationality
in economics, described as "pioneering research into the decision-making process within economic organizations". In 2004, Kydland and Prescott received the Nobel Prize for "their contributions to dynamic macroeconomics: the time consistency of economic policy and the driving forces behind business cycles".
It is also important to note that the school's impact has been so significant on Carnegie Mellon's campus that two other colleges: the School of Computer Science
and the Heinz College were actually spin-offs by business school's faculty.
 Undergraduate Business
Undergraduate Business
Tepper offers a traditional four-year undergraduate degree in business administration. The program's coursework has a global focus and places an emphasis on quantitative
decision making
and analytical problem solving
. The structure of the undergraduate program is distinctly different from the Master of Business Administration
(MBA) program, emphasizing that students receive breadth of academic experience over focused professionally oriented courses. Students major in business administration and choose one of the following tracks to specialize in:
For the academic year ending in May 2007, there were 475 total students enrolled in the undergraduate program.
Undergraduate Economics
The Undergraduate Economics Program is jointly administered by the Tepper School of Business and the Dietrich College of Humanities and Social Sciences. It has been designed to prepare students for careers as economic analysts in either the private or public sector, for advanced professional studies in business
, law
and public policy
, as well as for entry into PhD
programs in Economics
, Finance
, and related fields.
 MBA
MBA
The Tepper School's primary MBA degree is a two-year, full-time program, during which most students complete an internship in the summer between the first and second year of study. Students have the option of waiving the summer internship and taking classes, which allows full-time students to complete their studies in 16 months. Working professionals in the Pittsburgh area may also complete the MBA degree in the evening as members of the flex-time program.
The mini-semester system is half the length of a traditional academic semester, creating four mini-semesters per academic year. Each mini-semester is 7.5 weeks long, and students typically take 5 different courses each mini-semester. This system, which was pioneered by the Tepper School, allows students to take more than 32 different courses while enrolled in the MBA program. The Tepper School prefers this structure as students can gain exposure to a greater breadth of topics, as well as several electives.
The MBA curriculum is designed to increase in complexity and application throughout students' time at the Tepper School. The first year builds a fundamental skill set in the core disciplines, including Finance, Operations
, Marketing
, Strategy, Organizational Behavior and Technology. Year two advances the theories and analytical framework developed in the first year to provide breadth and depth in areas that support corporate strategy and general management as students complete three to four concentrations in specific functional areas. In lieu of selecting three to four general management concentrations, second year students may complete courses in satisfaction of specialized MBA Tracks.
The Don Jones Center for Entrepreneurship at Tepper holds an annual Venture Competition every spring in three tracks: Technology, Life Sciences, and Sustainable Technology. Teams from many universities and countries compete for cash prizes and venture startup assistance. Entrepreneurship education was pioneered at the school in the 1970s, under the leadership of Dr. Jack Thorne.
The Management Game was first introduced by Carnegie Mellon in 1958 and has been adopted by many other leading business schools as an effective business simulation model. Tepper students work with an external board of directors
to manage a multinational corporation, guiding the organization through a wide range of issues including global expansion, labor negotiations, operations, market share
, shifting economies and financial performance. They also have a Capstone project, which is like a culmination of all the students work at Tepper. It is akin to a final year project where the students work with various firms on real world problems.
They also have a Capstone project, which is like a culmination of all the students work at Tepper. It is akin to a final year project where the students work with various firms on real world problems.
The General Management MBA Track, the Core MBA degree, serves as an umbrella academic option due to the flexibility associated with multiple concentrations. The General Management MBA Track complements the eight other Tepper MBA Tracks: Analytical Marketing Strategy, Biotechnology
, Entrepreneurship
in Organizations, Global Enterprise Management, Management of Innovation & Product Development, Technology Leadership, Operations Research
, and Investment Strategy
.
Tepper also offers the following joint and dual MBA degrees:
For the academic year ending in May 2007, there were 302 total students enrolled in the full time MBA program.
MS Computational Finance
Carnegie Mellon's intensive, Master of Science
in Computational Finance
(MSCF) is considered by many to be the top quantitative finance program in the country. The MSCF degree is primary granted through a sixteen month full-time program. The Tepper School also offers a thirty-three month part-time degree program and four non-degree certificate programs. Certificate students focus on one "stream" of the MSCF degree curriculum: Mathematics, Statistics or Financial Computing.
The MSCF degree was created in 1994 to fill a perceived gap in the market between traditional MBA students and PhDs. At the time of its creation, MBAs were perceived to have too little math skills, while the PhDs traditionally hired as quantitative analyst
s were deemed to have too little experience in finance. The purpose of the MSCF curriculum was to give students the correct balance of math and finance to enable them to fill the gap created in the market between MBAs and PhDs. The program is a collaboration between the Tepper School, the Heinz College, the Department of Statistics, and the Department of Mathematical Sciences.
The current curriculum consists of courses in finance, traditional finance theories of equity
and bond
portfolio management
, the stochastic calculus
models on which derivative
trading is based, the application of these models in both fixed income
markets and equity markets, computational methods including Monte Carlo simulation and finite difference approximations of partial differential equations, and statistical methodologies including regression and time series, culminating with courses on statistical arbitrage
, risk management
and dynamic asset management. Early in the program, students are taught C++
, which enables them to build the computational financial models necessary for their finance courses. The program's capstone is a sophisticated financial computing course.
Twenty full-time faculty instruct 40 full-time students in Pittsburgh and 51 full and part-time students in the financial district of New York City
. The primary method of instruction for the New York campus is live, interactive video. Lectures are recorded and made immediately available to students via the internet. Faculty teach twice every seven weeks in New York at which times the students are invited to join the professor for lunch after class.
MS Quantitative Economics
In the fall of 2003, the Quantitative Economics (MSQE) program began enrolling students. This degree is currently offered only to Carnegie Mellon undergraduates. The MSQE is designed to differ from a traditional M.A.
in Economics based upon the program's emphasis on rigorous analytical coursework. The Tepper School reports that the MSQE coursework is as advanced and as quantitative as any PhD. program in the United States
.
Doctoral Program
The doctoral degree is organized around a preliminary set of courses in the core disciplines of Economics, Organization Behavior and Theory, and Operations Research
. The foundational knowledge and methodologies that students in the doctoral program learn form the basis for further study and research either in one of the core disciplines, or in one (or more) of the remaining functional areas of business: Accounting, Financial Economics
, Information Systems
, Marketing
, or Manufacturing and Operating Systems.
The school also offers PhD degrees jointly with other colleges in the University:
All doctoral candidates receive full tuition, plus a stipend for three years, through the William Larimer Mellon
Fund.
Executive Education
In addition to customizable executive programs, the Tepper School offers three executive education events for the 2007 calendar year:
 The Tepper School places a strong emphasis on developing a sense of community and encourages students to get to know one another. There are dozens of student clubs organized around various aspects of business: functional, cultural and social. These clubs organize speakers, trips to various corporations and plants, as well as internal and external case competitions. Students participate in numerous case competitions and design case studies of their own. On the undergraduate level, there are various clubs and organizations that support the needs and interests of business administration students, including but not limited to the Undergraduate Marketing Organization (UMO), Financial Frontline Society (FFS), the Undergraduate Finance Association (UFA), Students in Free Enterprise (SIFE), the Carnegie Mellon Business Association (CMBA), the Undergraduate Consulting Club (UCC), and the Undergraduate Entrepreneurship Association (UEA). Students have also created and supported clubs that help with specific networking areas such as the Tepper Women in Business, the Black Business Association, the Asian Business Association and the Latin American Business Club.
The Tepper School places a strong emphasis on developing a sense of community and encourages students to get to know one another. There are dozens of student clubs organized around various aspects of business: functional, cultural and social. These clubs organize speakers, trips to various corporations and plants, as well as internal and external case competitions. Students participate in numerous case competitions and design case studies of their own. On the undergraduate level, there are various clubs and organizations that support the needs and interests of business administration students, including but not limited to the Undergraduate Marketing Organization (UMO), Financial Frontline Society (FFS), the Undergraduate Finance Association (UFA), Students in Free Enterprise (SIFE), the Carnegie Mellon Business Association (CMBA), the Undergraduate Consulting Club (UCC), and the Undergraduate Entrepreneurship Association (UEA). Students have also created and supported clubs that help with specific networking areas such as the Tepper Women in Business, the Black Business Association, the Asian Business Association and the Latin American Business Club.
The Tepper School has its own, irreverent, weekly student newspaper – Robber Barrons. Additionally, students gather every Friday at Posner Hall to socialize and discuss their experiences with classmates, significant others, faculty, administrators and occasionally alumni. School-related functions include the annual social, holiday parties, Pirate games and whitewater rafting. Others events are more functional, like business etiquette and leadership workshops.
Tepper School students have access to a variety of athletic facilities, including tennis courts near the school’s main entrance, the university gymnasium across the street from the business school and the University Center. Students organize intramural softball and volleyball teams and compete in basketball and golf tournaments with other business schools. In particular, MBA students are active participants in Duke's
MBA games.
The Carnegie Bosch Institute for Applied Studies in International Management (CBI) is an alliance between the Tepper School of Business at Carnegie Mellon and the Bosch Group, a leading German-based multinational corporation with long-standing operations in North America. The institute was founded in the summer of 1990 to form a link between management and academia in the field of international management research. The CBI was established through a donation made by the Robert Bosch Corporation.
Global Study Abroad
The International Management MBA Track features an eight-week global experience in which students travel to Western and Eastern Europe to study emerging, transitional and competitive economies. During study abroad, students experience real-world aspects of classroom work through manufacturing tours, presentations at financial institutions, meetings with government and non-governmental organizations as well as the experience of living in an international setting. This program operates in partnership with the WHU-Otto Beisheim School of Management
.
Undergraduate business students are also encouraged to explore opportunities to learn about different cultures in which to live and work. Each year students travel abroad as part of a capstone educational experience.
at Carnegie Mellon University
who displays the best work in the field of economic theory. A large proportion of the winners of the award has later made contributions to economics that have changed the practice of the field. Since its inception, four recipients have already been awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics. Among the deceased award winners are John Muth
, known as "the father of the rational expectations revolution"; Albert Ando
, among the very pioneers of overlapping-generations models
; and Jan Mossin
who derived the Capital Asset Pricing Model
.
) score can reasonably duplicate the top 20 list of the national publications. The study concluded that a truly objective ranking would be individualized to the needs of each prospective student.
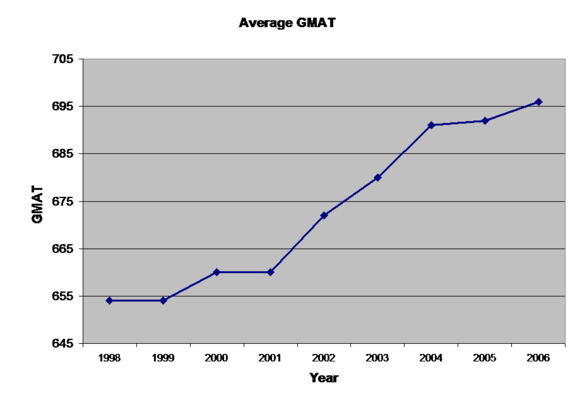
Below are the most recent Tepper School rankings for undergraduate and MBA programs. As MBA rankings are driven largely from average GMAT scores and starting salaries, these statistics are provided for the past 9 years.
 Wall Street Journal Rankings - 2007
Wall Street Journal Rankings - 2007
Business Week Graduate Rankings – 2010
Business Week Undergraduate Rankings – 2011
U.S. News & World Report
- 2012 (Graduate)
U.S. News & World Report
- 2011 (Undergraduate)
Forbes
– 2005
Financial Times
– 2010
Business school
A business school is a university-level institution that confers degrees in Business Administration. It teaches topics such as accounting, administration, economics, entrepreneurship, finance, information systems, marketing, organizational behavior, public relations, strategy, human resource...
located on Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University is a private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States....
’s 140 acre (0.5665604 km²) campus in Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
Pittsburgh is the second-largest city in the US Commonwealth of Pennsylvania and the county seat of Allegheny County. Regionally, it anchors the largest urban area of Appalachia and the Ohio River Valley, and nationally, it is the 22nd-largest urban area in the United States...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
, USA
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
.
The school consistently ranks highly among the top business schools in the U.S., as well as in a wide range of specializations, such as finance
Finance
"Finance" is often defined simply as the management of money or “funds” management Modern finance, however, is a family of business activity that includes the origination, marketing, and management of cash and money surrogates through a variety of capital accounts, instruments, and markets created...
, entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship is the act of being an entrepreneur, which can be defined as "one who undertakes innovations, finance and business acumen in an effort to transform innovations into economic goods". This may result in new organizations or may be part of revitalizing mature organizations in response...
, operations management
Operations management
Operations management is an area of management concerned with overseeing, designing, and redesigning business operations in the production of goods and/or services. It involves the responsibility of ensuring that business operations are efficient in terms of using as little resources as needed, and...
and information technology
Information technology
Information technology is the acquisition, processing, storage and dissemination of vocal, pictorial, textual and numerical information by a microelectronics-based combination of computing and telecommunications...
. The school offers degrees from the undergraduate through doctoral levels, in addition to executive education
Executive Education
Executive Education refers to academic programs at leading graduate-level business schools worldwide for executives, business leaders and functional managers. These programs are non-credit and non-degree granting...
programs.
Prior to the founding of the Tepper School, management education typically used the case method
Case method
The case method is a teaching approach that consists in presenting the students with a case, putting them in the role of a decision maker facing a problem...
approach popularized at the Harvard Business School
Harvard Business School
Harvard Business School is the graduate business school of Harvard University in Boston, Massachusetts, United States and is widely recognized as one of the top business schools in the world. The school offers the world's largest full-time MBA program, doctoral programs, and many executive...
, based upon widely accepted examples from successful companies and microeconomic theory. Although the Tepper School did not entirely abandon those traditional models and theories, it has focused on management science, or decision making
Decision making
Decision making can be regarded as the mental processes resulting in the selection of a course of action among several alternative scenarios. Every decision making process produces a final choice. The output can be an action or an opinion of choice.- Overview :Human performance in decision terms...
based on quantitative
Quantitative
A quantitative property is one that exists in a range of magnitudes, and can therefore be measured with a number. Measurements of any particular quantitative property are expressed as a specific quantity, referred to as a unit, multiplied by a number. Examples of physical quantities are distance,...
models and an analytical
Analytical skill
Analytical skill is the ability to visualize, articulate, and solve both complex and uncomplicated problems and concepts, and make decisions that make sense based on available information...
approach to decision making
Decision making
Decision making can be regarded as the mental processes resulting in the selection of a course of action among several alternative scenarios. Every decision making process produces a final choice. The output can be an action or an opinion of choice.- Overview :Human performance in decision terms...
and problem solving
Problem solving
Problem solving is a mental process and is part of the larger problem process that includes problem finding and problem shaping. Consideredthe most complex of all intellectual functions, problem solving has been defined as higher-order cognitive process that requires the modulation and control of...
. Today, the Tepper School is known for its strong emphasis on quantitative skills and its continued teaching of courses based upon the science of management. A number of Nobel Prize
Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes are annual international awards bestowed by Scandinavian committees in recognition of cultural and scientific advances. The will of the Swedish chemist Alfred Nobel, the inventor of dynamite, established the prizes in 1895...
winning economists have been affiliated with the school, including Herbert Simon
Herbert Simon
Herbert Alexander Simon was an American political scientist, economist, sociologist, and psychologist, and professor—most notably at Carnegie Mellon University—whose research ranged across the fields of cognitive psychology, cognitive science, computer science, public administration, economics,...
, Franco Modigliani
Franco Modigliani
Franco Modigliani was an Italian economist at the MIT Sloan School of Management and MIT Department of Economics, and winner of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics in 1985.-Life and career:...
, Merton Miller
Merton Miller
Merton Howard Miller was the co-author of the Modigliani-Miller theorem which proposed the irrelevance of debt-equity structure. He shared the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1990, along with Harry Markowitz and William Sharpe...
, Robert Lucas
Robert Lucas
Robert Lucas may refer to:* Rob Lucas , Liberal member of the South Australian Legislative Council* Robert Lucas, 3rd Baron Lucas* Robert Lucas, Jr. , economist...
, Edward Prescott, Finn Kydland, Oliver Williamson, and Dale Mortensen.
The Tepper School of Business was originally known as The Graduate School of Industrial Administration (GSIA), which was founded in 1949 by William Larimer Mellon
William Larimer Mellon
William Larimer Mellon, Sr. , sometimes referred to as W. L., was a founder of Gulf Oil.-Biography:Born in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania on June 1, 1868 to James Ross Mellon, eldest son of Judge Thomas Mellon, and Rachel Larimer Mellon, daughter of railroad and land baron William Larimer, Jr...
. In March 2004, the school received a record $55 million gift from alumnus David Tepper
David Tepper
David Alan Tepper is an American hedge fund manager and the founder of Appaloosa Management. His investment specialty is distressed companies....
. In recognition of this gift, the school was named the David A. Tepper School of Business at Carnegie Mellon.
History

Carnegie Institute of Technology
The Carnegie Institute of Technology , is the name for Carnegie Mellon University’s College of Engineering. It was first called the Carnegie Technical Schools, or Carnegie Tech, when it was founded in 1900 by Andrew Carnegie who intended to build a “first class technical school” in Pittsburgh,...
(predecessor of Carnegie Mellon University) to restart the school’s economics department. Bach had previously been working at the Federal Reserve during World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
. He added William W. Cooper from the field of Operations Research
Operations research
Operations research is an interdisciplinary mathematical science that focuses on the effective use of technology by organizations...
(which had increased its visibility during the war) and Herbert Simon
Herbert Simon
Herbert Alexander Simon was an American political scientist, economist, sociologist, and psychologist, and professor—most notably at Carnegie Mellon University—whose research ranged across the fields of cognitive psychology, cognitive science, computer science, public administration, economics,...
, a political scientist who was to direct the undergraduate business program. The beginnings of the Cold War
Cold War
The Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
were applying pressure on the academic community to increase US managerial ability, and when William Larimer Mellon
William Larimer Mellon
William Larimer Mellon, Sr. , sometimes referred to as W. L., was a founder of Gulf Oil.-Biography:Born in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania on June 1, 1868 to James Ross Mellon, eldest son of Judge Thomas Mellon, and Rachel Larimer Mellon, daughter of railroad and land baron William Larimer, Jr...
gave a $6 million grant to found a school of industrial administration, Bach became the first dean, bringing along the entire economics department.
Under Bach’s leadership, the school was credited with several educational innovations that have now become standard at other prominent business schools. Specifically, in 1958, the school's Management Game was the first to use computer simulations for experiential learning of business roles; such simulations have subsequently been adopted by other institutions. Additionally, in 1989, the school's Financial Analysis and Security Trading Center (FAST) was the first educational institution to successfully replicate the live international data feeds and sophisticated software of Wall Street
Wall Street
Wall Street refers to the financial district of New York City, named after and centered on the eight-block-long street running from Broadway to South Street on the East River in Lower Manhattan. Over time, the term has become a metonym for the financial markets of the United States as a whole, or...
trading firms.
Several faculty members have won acclaim for research in the areas of business and economics. As an example, the school has produced seven Nobel Prize
Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes are annual international awards bestowed by Scandinavian committees in recognition of cultural and scientific advances. The will of the Swedish chemist Alfred Nobel, the inventor of dynamite, established the prizes in 1895...
winners in Economics: Robert Lucas, Jr.
Robert Lucas, Jr.
Robert Emerson Lucas, Jr. is an American economist at the University of Chicago. He received the Nobel Prize in Economics in 1995 and is consistently indexed among the top 10 economists in the Research Papers in Economics rankings. He is married to economist Nancy Stokey.He received his B.A. in...
, Merton Miller
Merton Miller
Merton Howard Miller was the co-author of the Modigliani-Miller theorem which proposed the irrelevance of debt-equity structure. He shared the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1990, along with Harry Markowitz and William Sharpe...
, Franco Modigliani
Franco Modigliani
Franco Modigliani was an Italian economist at the MIT Sloan School of Management and MIT Department of Economics, and winner of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics in 1985.-Life and career:...
, Herb Simon, Oliver E. Williamson
Oliver E. Williamson
Oliver Eaton Williamson is an American economist, professor at the University of California, Berkeley and recipient of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences....
, Edward Prescott and Finn Kydland. Lucas was awarded the prize for developing and applying the theory of rational expectations
Rational expectations
Rational expectations is a hypothesis in economics which states that agents' predictions of the future value of economically relevant variables are not systematically wrong in that all errors are random. An alternative formulation is that rational expectations are model-consistent expectations, in...
, an econometric hypothesis that directly challenged Keynesian orthodoxy. Modigliani's prize recognized his life-cycle hypothesis, which attempts to explain the level of saving in the economy. Modigliani proposed that consumers would aim for a stable level of income throughout their lifetime, for example by saving during their working years and spending during their retirement. Miller's prize was awarded in recognition of his contributions to corporate finance. The results of his research—in collaboration with Franco Modigliani—are now taught in every business school in the country. Simon's prize was given for his development of the idea of bounded rationality
Bounded rationality
Bounded rationality is the idea that in decision making, rationality of individuals is limited by the information they have, the cognitive limitations of their minds, and the finite amount of time they have to make a decision...
in economics, described as "pioneering research into the decision-making process within economic organizations". In 2004, Kydland and Prescott received the Nobel Prize for "their contributions to dynamic macroeconomics: the time consistency of economic policy and the driving forces behind business cycles".
It is also important to note that the school's impact has been so significant on Carnegie Mellon's campus that two other colleges: the School of Computer Science
Carnegie Mellon School of Computer Science
The School of Computer Science at Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA is a leading private school for computer science established in 1965. It has been consistently ranked among the top computer science programs over the decades. U.S...
and the Heinz College were actually spin-offs by business school's faculty.
Programs

Tepper offers a traditional four-year undergraduate degree in business administration. The program's coursework has a global focus and places an emphasis on quantitative
Quantitative
A quantitative property is one that exists in a range of magnitudes, and can therefore be measured with a number. Measurements of any particular quantitative property are expressed as a specific quantity, referred to as a unit, multiplied by a number. Examples of physical quantities are distance,...
decision making
Decision making
Decision making can be regarded as the mental processes resulting in the selection of a course of action among several alternative scenarios. Every decision making process produces a final choice. The output can be an action or an opinion of choice.- Overview :Human performance in decision terms...
and analytical problem solving
Problem solving
Problem solving is a mental process and is part of the larger problem process that includes problem finding and problem shaping. Consideredthe most complex of all intellectual functions, problem solving has been defined as higher-order cognitive process that requires the modulation and control of...
. The structure of the undergraduate program is distinctly different from the Master of Business Administration
Master of Business Administration
The Master of Business Administration is a :master's degree in business administration, which attracts people from a wide range of academic disciplines. The MBA designation originated in the United States, emerging from the late 19th century as the country industrialized and companies sought out...
(MBA) program, emphasizing that students receive breadth of academic experience over focused professionally oriented courses. Students major in business administration and choose one of the following tracks to specialize in:
|
Management consulting Management consulting indicates both the industry and practice of helping organizations improve their performance primarily through the analysis of existing organizational problems and development of plans for improvement.... Marketing Marketing is the process used to determine what products or services may be of interest to customers, and the strategy to use in sales, communications and business development. It generates the strategy that underlies sales techniques, business communication, and business developments... Entrepreneurship Entrepreneurship is the act of being an entrepreneur, which can be defined as "one who undertakes innovations, finance and business acumen in an effort to transform innovations into economic goods". This may result in new organizations or may be part of revitalizing mature organizations in response... |
For the academic year ending in May 2007, there were 475 total students enrolled in the undergraduate program.
Undergraduate Economics
The Undergraduate Economics Program is jointly administered by the Tepper School of Business and the Dietrich College of Humanities and Social Sciences. It has been designed to prepare students for careers as economic analysts in either the private or public sector, for advanced professional studies in business
Business
A business is an organization engaged in the trade of goods, services, or both to consumers. Businesses are predominant in capitalist economies, where most of them are privately owned and administered to earn profit to increase the wealth of their owners. Businesses may also be not-for-profit...
, law
Law
Law is a system of rules and guidelines which are enforced through social institutions to govern behavior, wherever possible. It shapes politics, economics and society in numerous ways and serves as a social mediator of relations between people. Contract law regulates everything from buying a bus...
and public policy
Public policy
Public policy as government action is generally the principled guide to action taken by the administrative or executive branches of the state with regard to a class of issues in a manner consistent with law and institutional customs. In general, the foundation is the pertinent national and...
, as well as for entry into PhD
PHD
PHD may refer to:*Ph.D., a doctorate of philosophy*Ph.D. , a 1980s British group*PHD finger, a protein sequence*PHD Mountain Software, an outdoor clothing and equipment company*PhD Docbook renderer, an XML renderer...
programs in Economics
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
, Finance
Finance
"Finance" is often defined simply as the management of money or “funds” management Modern finance, however, is a family of business activity that includes the origination, marketing, and management of cash and money surrogates through a variety of capital accounts, instruments, and markets created...
, and related fields.

The Tepper School's primary MBA degree is a two-year, full-time program, during which most students complete an internship in the summer between the first and second year of study. Students have the option of waiving the summer internship and taking classes, which allows full-time students to complete their studies in 16 months. Working professionals in the Pittsburgh area may also complete the MBA degree in the evening as members of the flex-time program.
The mini-semester system is half the length of a traditional academic semester, creating four mini-semesters per academic year. Each mini-semester is 7.5 weeks long, and students typically take 5 different courses each mini-semester. This system, which was pioneered by the Tepper School, allows students to take more than 32 different courses while enrolled in the MBA program. The Tepper School prefers this structure as students can gain exposure to a greater breadth of topics, as well as several electives.
The MBA curriculum is designed to increase in complexity and application throughout students' time at the Tepper School. The first year builds a fundamental skill set in the core disciplines, including Finance, Operations
Business operations
Business operations are those ongoing recurring activities involved in the running of a business for the purpose of producing value for the stakeholders...
, Marketing
Marketing
Marketing is the process used to determine what products or services may be of interest to customers, and the strategy to use in sales, communications and business development. It generates the strategy that underlies sales techniques, business communication, and business developments...
, Strategy, Organizational Behavior and Technology. Year two advances the theories and analytical framework developed in the first year to provide breadth and depth in areas that support corporate strategy and general management as students complete three to four concentrations in specific functional areas. In lieu of selecting three to four general management concentrations, second year students may complete courses in satisfaction of specialized MBA Tracks.
The Don Jones Center for Entrepreneurship at Tepper holds an annual Venture Competition every spring in three tracks: Technology, Life Sciences, and Sustainable Technology. Teams from many universities and countries compete for cash prizes and venture startup assistance. Entrepreneurship education was pioneered at the school in the 1970s, under the leadership of Dr. Jack Thorne.
The Management Game was first introduced by Carnegie Mellon in 1958 and has been adopted by many other leading business schools as an effective business simulation model. Tepper students work with an external board of directors
Board of directors
A board of directors is a body of elected or appointed members who jointly oversee the activities of a company or organization. Other names include board of governors, board of managers, board of regents, board of trustees, and board of visitors...
to manage a multinational corporation, guiding the organization through a wide range of issues including global expansion, labor negotiations, operations, market share
Market share
Market share is the percentage of a market accounted for by a specific entity. In a survey of nearly 200 senior marketing managers, 67 percent responded that they found the "dollar market share" metric very useful, while 61% found "unit market share" very useful.Marketers need to be able to...
, shifting economies and financial performance.

The General Management MBA Track, the Core MBA degree, serves as an umbrella academic option due to the flexibility associated with multiple concentrations. The General Management MBA Track complements the eight other Tepper MBA Tracks: Analytical Marketing Strategy, Biotechnology
Biotechnology
Biotechnology is a field of applied biology that involves the use of living organisms and bioprocesses in engineering, technology, medicine and other fields requiring bioproducts. Biotechnology also utilizes these products for manufacturing purpose...
, Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship is the act of being an entrepreneur, which can be defined as "one who undertakes innovations, finance and business acumen in an effort to transform innovations into economic goods". This may result in new organizations or may be part of revitalizing mature organizations in response...
in Organizations, Global Enterprise Management, Management of Innovation & Product Development, Technology Leadership, Operations Research
Operations research
Operations research is an interdisciplinary mathematical science that focuses on the effective use of technology by organizations...
, and Investment Strategy
Investment strategy
In finance, an investment strategy is a set of rules, behaviors or procedures, designed to guide an investor's selection of an investment portfolio...
.
Tepper also offers the following joint and dual MBA degrees:
|
Juris Doctor Juris Doctor is a professional doctorate and first professional graduate degree in law.The degree was first awarded by Harvard University in the United States in the late 19th century and was created as a modern version of the old European doctor of law degree Juris Doctor (see etymology and... University of Pittsburgh The University of Pittsburgh, commonly referred to as Pitt, is a state-related research university located in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. Founded as Pittsburgh Academy in 1787 on what was then the American frontier, Pitt is one of the oldest continuously chartered institutions of... |
For the academic year ending in May 2007, there were 302 total students enrolled in the full time MBA program.
MS Computational Finance
Carnegie Mellon's intensive, Master of Science
Master of Science
A Master of Science is a postgraduate academic master's degree awarded by universities in many countries. The degree is typically studied for in the sciences including the social sciences.-Brazil, Argentina and Uruguay:...
in Computational Finance
Computational finance
Computational finance, also called financial engineering, is a cross-disciplinary field which relies on computational intelligence, mathematical finance, numerical methods and computer simulations to make trading, hedging and investment decisions, as well as facilitating the risk management of...
(MSCF) is considered by many to be the top quantitative finance program in the country. The MSCF degree is primary granted through a sixteen month full-time program. The Tepper School also offers a thirty-three month part-time degree program and four non-degree certificate programs. Certificate students focus on one "stream" of the MSCF degree curriculum: Mathematics, Statistics or Financial Computing.
The MSCF degree was created in 1994 to fill a perceived gap in the market between traditional MBA students and PhDs. At the time of its creation, MBAs were perceived to have too little math skills, while the PhDs traditionally hired as quantitative analyst
Quantitative analyst
A quantitative analyst is a person who works in finance using numerical or quantitative techniques. Similar work is done in most other modern industries, but the work is not always called quantitative analysis...
s were deemed to have too little experience in finance. The purpose of the MSCF curriculum was to give students the correct balance of math and finance to enable them to fill the gap created in the market between MBAs and PhDs. The program is a collaboration between the Tepper School, the Heinz College, the Department of Statistics, and the Department of Mathematical Sciences.
The current curriculum consists of courses in finance, traditional finance theories of equity
Equity (finance)
In accounting and finance, equity is the residual claim or interest of the most junior class of investors in assets, after all liabilities are paid. If liability exceeds assets, negative equity exists...
and bond
Bond (finance)
In finance, a bond is a debt security, in which the authorized issuer owes the holders a debt and, depending on the terms of the bond, is obliged to pay interest to use and/or to repay the principal at a later date, termed maturity...
portfolio management
Investment management
Investment management is the professional management of various securities and assets in order to meet specified investment goals for the benefit of the investors...
, the stochastic calculus
Stochastic calculus
Stochastic calculus is a branch of mathematics that operates on stochastic processes. It allows a consistent theory of integration to be defined for integrals of stochastic processes with respect to stochastic processes...
models on which derivative
Derivative (finance)
A derivative instrument is a contract between two parties that specifies conditions—in particular, dates and the resulting values of the underlying variables—under which payments, or payoffs, are to be made between the parties.Under U.S...
trading is based, the application of these models in both fixed income
Fixed income
Fixed income refers to any type of investment that is not equity, which obligates the borrower/issuer to make payments on a fixed schedule, even if the number of the payments may be variable....
markets and equity markets, computational methods including Monte Carlo simulation and finite difference approximations of partial differential equations, and statistical methodologies including regression and time series, culminating with courses on statistical arbitrage
Statistical arbitrage
In the world of finance and investments, statistical arbitrage is used in two related but distinct ways:* In academic literature, "statistical arbitrage" is opposed to arbitrage. In deterministic arbitrage, a sure profit can be obtained from being long some securities and short others...
, risk management
Risk management
Risk management is the identification, assessment, and prioritization of risks followed by coordinated and economical application of resources to minimize, monitor, and control the probability and/or impact of unfortunate events or to maximize the realization of opportunities...
and dynamic asset management. Early in the program, students are taught C++
C++
C++ is a statically typed, free-form, multi-paradigm, compiled, general-purpose programming language. It is regarded as an intermediate-level language, as it comprises a combination of both high-level and low-level language features. It was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup starting in 1979 at Bell...
, which enables them to build the computational financial models necessary for their finance courses. The program's capstone is a sophisticated financial computing course.
Twenty full-time faculty instruct 40 full-time students in Pittsburgh and 51 full and part-time students in the financial district of New York City
New York City
New York is the most populous city in the United States and the center of the New York Metropolitan Area, one of the most populous metropolitan areas in the world. New York exerts a significant impact upon global commerce, finance, media, art, fashion, research, technology, education, and...
. The primary method of instruction for the New York campus is live, interactive video. Lectures are recorded and made immediately available to students via the internet. Faculty teach twice every seven weeks in New York at which times the students are invited to join the professor for lunch after class.
MS Quantitative Economics
In the fall of 2003, the Quantitative Economics (MSQE) program began enrolling students. This degree is currently offered only to Carnegie Mellon undergraduates. The MSQE is designed to differ from a traditional M.A.
Master of Arts (postgraduate)
A Master of Arts from the Latin Magister Artium, is a type of Master's degree awarded by universities in many countries. The M.A. is usually contrasted with the M.S. or M.Sc. degrees...
in Economics based upon the program's emphasis on rigorous analytical coursework. The Tepper School reports that the MSQE coursework is as advanced and as quantitative as any PhD. program in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
.
Doctoral Program
The doctoral degree is organized around a preliminary set of courses in the core disciplines of Economics, Organization Behavior and Theory, and Operations Research
Operations research
Operations research is an interdisciplinary mathematical science that focuses on the effective use of technology by organizations...
. The foundational knowledge and methodologies that students in the doctoral program learn form the basis for further study and research either in one of the core disciplines, or in one (or more) of the remaining functional areas of business: Accounting, Financial Economics
Financial economics
Financial Economics is the branch of economics concerned with "the allocation and deployment of economic resources, both spatially and across time, in an uncertain environment"....
, Information Systems
Information systems
Information Systems is an academic/professional discipline bridging the business field and the well-defined computer science field that is evolving toward a new scientific area of study...
, Marketing
Marketing
Marketing is the process used to determine what products or services may be of interest to customers, and the strategy to use in sales, communications and business development. It generates the strategy that underlies sales techniques, business communication, and business developments...
, or Manufacturing and Operating Systems.
The school also offers PhD degrees jointly with other colleges in the University:
- Algorithms, CombinatoricsCombinatoricsCombinatorics is a branch of mathematics concerning the study of finite or countable discrete structures. Aspects of combinatorics include counting the structures of a given kind and size , deciding when certain criteria can be met, and constructing and analyzing objects meeting the criteria ,...
, and OptimizationOptimization (mathematics)In mathematics, computational science, or management science, mathematical optimization refers to the selection of a best element from some set of available alternatives....
(joint with MathematicsMathematicsMathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
and Computer ScienceComputer scienceComputer science or computing science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and of practical techniques for their implementation and application in computer systems...
)
- EconomicsEconomicsEconomics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
and Public PolicyPublic policyPublic policy as government action is generally the principled guide to action taken by the administrative or executive branches of the state with regard to a class of issues in a manner consistent with law and institutional customs. In general, the foundation is the pertinent national and...
(joint with the Heinz College) - Management of Manufacturing and Automation (joint with the Robotics Institute)
- Mathematical FinanceMathematical financeMathematical finance is a field of applied mathematics, concerned with financial markets. The subject has a close relationship with the discipline of financial economics, which is concerned with much of the underlying theory. Generally, mathematical finance will derive and extend the mathematical...
(joint with Mathematics)
All doctoral candidates receive full tuition, plus a stipend for three years, through the William Larimer Mellon
William Larimer Mellon
William Larimer Mellon, Sr. , sometimes referred to as W. L., was a founder of Gulf Oil.-Biography:Born in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania on June 1, 1868 to James Ross Mellon, eldest son of Judge Thomas Mellon, and Rachel Larimer Mellon, daughter of railroad and land baron William Larimer, Jr...
Fund.
Executive Education
In addition to customizable executive programs, the Tepper School offers three executive education events for the 2007 calendar year:
- The Operations Executive Series is three focused executive education programs that offer coverage of the people, process and technology management capabilities that drive effective operations.
- Global Leadership Executive Summer Forum, offered in conjunction with the Carnegie Bosch Institute, is a four week program addressing issues of strategy and leadership while also presenting topics of broad economic and international scope.
- Management in Technology Organizations teaches best practices in managing technology professionals, enhancing leadership skills and driving innovation.
Student life

The Tepper School has its own, irreverent, weekly student newspaper – Robber Barrons. Additionally, students gather every Friday at Posner Hall to socialize and discuss their experiences with classmates, significant others, faculty, administrators and occasionally alumni. School-related functions include the annual social, holiday parties, Pirate games and whitewater rafting. Others events are more functional, like business etiquette and leadership workshops.
Tepper School students have access to a variety of athletic facilities, including tennis courts near the school’s main entrance, the university gymnasium across the street from the business school and the University Center. Students organize intramural softball and volleyball teams and compete in basketball and golf tournaments with other business schools. In particular, MBA students are active participants in Duke's
Fuqua School of Business
The Fuqua School of Business is the business school of Duke University in Durham, North Carolina, United States. It currently enrolls 1,340 students in degree-seeking programs...
MBA games.
Career development
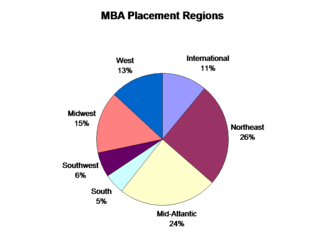
The Tepper School facilitates their students' employment through the Career Opportunities Center (COC). The COC provides assistance during the employment search through workshops, employment "treks", career fairs, and corporate presentations. They also provide individualized training for resume presentation and interviewing skills."Top Hiring Employers (MBA)
|  |  |
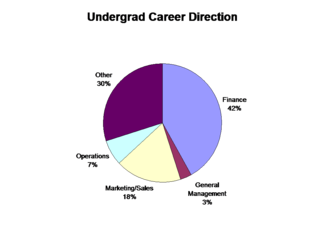
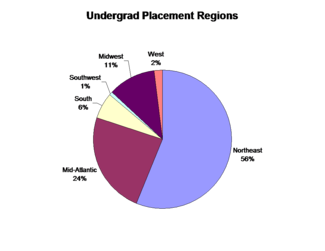
Top Hiring Employers (Undergraduate)
|  |  |
International study
Carnegie Bosch InstituteThe Carnegie Bosch Institute for Applied Studies in International Management (CBI) is an alliance between the Tepper School of Business at Carnegie Mellon and the Bosch Group, a leading German-based multinational corporation with long-standing operations in North America. The institute was founded in the summer of 1990 to form a link between management and academia in the field of international management research. The CBI was established through a donation made by the Robert Bosch Corporation.
Global Study Abroad
The International Management MBA Track features an eight-week global experience in which students travel to Western and Eastern Europe to study emerging, transitional and competitive economies. During study abroad, students experience real-world aspects of classroom work through manufacturing tours, presentations at financial institutions, meetings with government and non-governmental organizations as well as the experience of living in an international setting. This program operates in partnership with the WHU-Otto Beisheim School of Management
WHU-Otto Beisheim School of Management
WHU – Otto Beisheim School of Management is a German business school. The privately financed school was founded in 1984 by the Koblenz chamber of commerce and is located in Vallendar near Koblenz...
.
Undergraduate business students are also encouraged to explore opportunities to learn about different cultures in which to live and work. Each year students travel abroad as part of a capstone educational experience.
Research centers
From its outset, academic research has been one of the primary focuses of the Tepper School. When speaking of the school's founders, one author stated "Research was their fundamental engine of progress". The Tepper School has established 16 different research centers to continue the emphasis on research established at the school's founding.- Carnegie Bosch Institute for Applied Studies in International Management
- The Carnegie Mellon Electricity Industry Center
- Center for Analytical Research in Technology
- Center for Behavioral Decision Research
- Center for Business Communication
- Center for Business Solutions
- Center for E-Business Innovation
- Center for Financial Markets
- Center for Interdisciplinary Research on Teams
- Center for International Corporate Responsibility
- Center for the Management of Technology
- Center for Organizational Learning, Innovation and Performance
- Donald H. Jones Center for Entrepreneurship
- The Gailliot Center for Public Policy
- Green Design Institute
- Teaching Innovation Center
Alexander Henderson Award
The Alexander Henderson Award is presented to the student at the Tepper School of BusinessTepper School of Business
The Tepper School of Business is a private business school located on Carnegie Mellon University’s campus in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA.The school consistently ranks highly among the top business schools in the U.S., as well as in a wide range of specializations, such as finance,...
at Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University is a private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States....
who displays the best work in the field of economic theory. A large proportion of the winners of the award has later made contributions to economics that have changed the practice of the field. Since its inception, four recipients have already been awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics. Among the deceased award winners are John Muth
John Muth
-Legacy:It has hard to point to one substantial area of economic research into dynamic problems which has not changed as a result of the publication of Muth's works at GSIA. Almost paradoxically, the only viable alternative to Muth's hypothesis is the research agenda put forward by Herb Simon and...
, known as "the father of the rational expectations revolution"; Albert Ando
Albert Ando
Albert K. Ando was a Japanese-born economist.He came to the United States after World War II. He received his B.S. in economics from the University of Seattle in 1951, his M.A. in economics from St. Louis University in 1953, and an M.S. in economics in 1956 and a Ph.D...
, among the very pioneers of overlapping-generations models
Intertemporal consumption
Economic theories of intertemporal consumption seek to explain people's preferences in relation to consumption and saving over the course of their life...
; and Jan Mossin
Jan Mossin
Jan Mossin was a Norwegian economist. Born in Oslo, he graduated with a siv.øk. degree from the Norwegian School of Economics in 1959...
who derived the Capital Asset Pricing Model
Capital asset pricing model
In finance, the capital asset pricing model is used to determine a theoretically appropriate required rate of return of an asset, if that asset is to be added to an already well-diversified portfolio, given that asset's non-diversifiable risk...
.
Rankings
The ranking of MBA programs has been discussed in articles and on academic Web sites. One study found that objectively ranking MBA programs by a combination of graduates' starting salaries and average student Graduate Management Admissions Test (GMATGraduate Management Admission Test
The Graduate Management Admission Test is a computer-adaptive standardized test in mathematics and the English language for measuring aptitude to succeed academically in graduate business studies. Business schools use the test as a criterion for admission into graduate business administration...
) score can reasonably duplicate the top 20 list of the national publications. The study concluded that a truly objective ranking would be individualized to the needs of each prospective student.
Below are the most recent Tepper School rankings for undergraduate and MBA programs. As MBA rankings are driven largely from average GMAT scores and starting salaries, these statistics are provided for the past 9 years.


# 5 Business School (MBA) National# 2 Top School - Operations Management# 2 Top School - Information Technology# 4 Top School - Finance# 6 Top School - Entrepreneurship# 6 Top School - Strategy# 9 Top School - General Management# 8 Top School - For Recruiting Minorities# 9 Top School - For Recruiting MBAs With High Ethical Standards# 5 Management Consulting Industry Ranking# 6 Health Care Products and Services Industry Ranking# 7 Energy and Industrial Products and Services Industry Ranking# 8 Technology/Telecommunications/Internet Industry Ranking
Business Week Graduate Rankings – 2010
# 7 MBA - Part-Time MBA# 15 MBA - Overall National Ranking
Business Week Undergraduate Rankings – 2011
# 3 Starting Salaries# 4 Academic Quality# 9 MBA Feeder School# 21 Undergraduate Business Program
U.S. News & World Report
U.S. News & World Report
U.S. News & World Report is an American news magazine published from Washington, D.C. Along with Time and Newsweek it was for many years a leading news weekly, focusing more than its counterparts on political, economic, health and education stories...
- 2012 (Graduate)
# 2 Top School - Information Systems# 2 Top School - Production/Operations Management# 3 Top School - Supply Chain/Logistics# 7 Top School - Part-Time MBA# 13 Top School - Finance# 18 Graduate Business School (MBA)# 19 Economics (PhD)
U.S. News & World Report
U.S. News & World Report
U.S. News & World Report is an American news magazine published from Washington, D.C. Along with Time and Newsweek it was for many years a leading news weekly, focusing more than its counterparts on political, economic, health and education stories...
- 2011 (Undergraduate)
# 2 Management Information Systems# 2 Quantitative Analysis# 2 Production/Operations Management# 5 Supply Chain Management/Logistics# 5 Supply Chain Management/Logistics# 7 Undergraduate Business School# 9 Finance# 18 Entrepreneurship# 24 Management
Forbes
Forbes
Forbes is an American publishing and media company. Its flagship publication, the Forbes magazine, is published biweekly. Its primary competitors in the national business magazine category are Fortune, which is also published biweekly, and Business Week...
– 2005
# 8 Part-time MBA# 16 Business School (Full-Time MBA)
Financial Times
Financial Times
The Financial Times is an international business newspaper. It is a morning daily newspaper published in London and printed in 24 cities around the world. Its primary rival is the Wall Street Journal, published in New York City....
– 2010
# 10 International Doctoral Program# 19 Business School in the U.S. (MBA)# 32 Research (MBA)# 43 International Business School(MBA)
See also
- List of United States business school rankings
- List of business schools in the United States
- List of Carnegie Mellon University people
- Business SchoolBusiness schoolA business school is a university-level institution that confers degrees in Business Administration. It teaches topics such as accounting, administration, economics, entrepreneurship, finance, information systems, marketing, organizational behavior, public relations, strategy, human resource...

