
Systems science
Encyclopedia
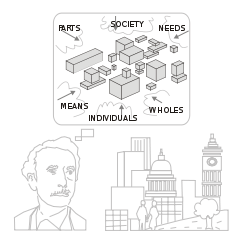
Complex system
A complex system is a system composed of interconnected parts that as a whole exhibit one or more properties not obvious from the properties of the individual parts....
s in nature
Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is equivalent to the natural world, physical world, or material world. "Nature" refers to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general...
, society
Society
A society, or a human society, is a group of people related to each other through persistent relations, or a large social grouping sharing the same geographical or virtual territory, subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations...
, and science
Science
Science is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe...
. It aims to develop interdisciplinary foundations, which are applicable in a variety of areas, such as engineering, biology, medicine and social sciences.
Systems sciences covers formal sciences fields like complex systems
Complex systems
Complex systems present problems in mathematical modelling.The equations from which complex system models are developed generally derive from statistical physics, information theory and non-linear dynamics, and represent organized but unpredictable behaviors of systems of nature that are considered...
, cybernetics
Cybernetics
Cybernetics is the interdisciplinary study of the structure of regulatory systems. Cybernetics is closely related to information theory, control theory and systems theory, at least in its first-order form...
, dynamical systems theory
Dynamical systems theory
Dynamical systems theory is an area of applied mathematics used to describe the behavior of complex dynamical systems, usually by employing differential equations or difference equations. When differential equations are employed, the theory is called continuous dynamical systems. When difference...
, and systems theory
Systems theory
Systems theory is the transdisciplinary study of systems in general, with the goal of elucidating principles that can be applied to all types of systems at all nesting levels in all fields of research...
, and applications in the field of the natural and social sciences and engineering, such as control theory
Control theory
Control theory is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering and mathematics that deals with the behavior of dynamical systems. The desired output of a system is called the reference...
, operations research
Operations research
Operations research is an interdisciplinary mathematical science that focuses on the effective use of technology by organizations...
, social systems theory, systems biology
Systems biology
Systems biology is a term used to describe a number of trends in bioscience research, and a movement which draws on those trends. Proponents describe systems biology as a biology-based inter-disciplinary study field that focuses on complex interactions in biological systems, claiming that it uses...
, systems dynamics, systems ecology
Systems ecology
Systems ecology is an interdisciplinary field of ecology, taking a holistic approach to the study of ecological systems, especially ecosystems. Systems ecology can be seen as an application of general systems theory to ecology. Central to the systems ecology approach is the idea that an ecosystem...
, systems engineering
Systems engineering
Systems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering that focuses on how complex engineering projects should be designed and managed over the life cycle of the project. Issues such as logistics, the coordination of different teams, and automatic control of machinery become more...
and systems psychology
Systems psychology
Systems psychology is a branch of applied psychology that studies human behaviour and experience in complex systems. It is inspired by systems theory and systems thinking, and based on the theoretical work of Roger Barker, Gregory Bateson, Humberto Maturana and others. It is an approach in...
.
Theories
Since the emergence of the General Systems Research in the 1950s systems thinkingSystems thinking
Systems thinking is the process of understanding how things influence one another within a whole. In nature, systems thinking examples include ecosystems in which various elements such as air, water, movement, plants, and animals work together to survive or perish...
and systems science have been developed into many theoretical frameworks. The following overview will only show the most basic types.

- Systems analysisSystems analysisSystems analysis is the study of sets of interacting entities, including computer systems analysis. This field is closely related to requirements analysis or operations research...
is the interdisciplinary branch of science, dealing with analysis of systemSystemSystem is a set of interacting or interdependent components forming an integrated whole....
s, often prior to their automation as computer systems, and the interactions within those systems. This field is closely related to operations researchOperations researchOperations research is an interdisciplinary mathematical science that focuses on the effective use of technology by organizations...
.
Systems design
- In computing systems designSystems designSystems design is the process of defining the architecture, components, modules, interfaces, and data for a system to satisfy specified requirements. One could see it as the application of systems theory to product development...
is the process or art of defining the hardwareComputer hardwarePersonal computer hardware are component devices which are typically installed into or peripheral to a computer case to create a personal computer upon which system software is installed including a firmware interface such as a BIOS and an operating system which supports application software that...
and software architecture, components, modules, interfaces, and dataDataThe term data refers to qualitative or quantitative attributes of a variable or set of variables. Data are typically the results of measurements and can be the basis of graphs, images, or observations of a set of variables. Data are often viewed as the lowest level of abstraction from which...
for a computer system to satisfy specified requirementRequirementIn engineering, a requirement is a singular documented physical and functional need that a particular product or service must be or perform. It is most commonly used in a formal sense in systems engineering, software engineering, or enterprise engineering...
s. One could see it as the application of systems theory to computingComputingComputing is usually defined as the activity of using and improving computer hardware and software. It is the computer-specific part of information technology...
. Some overlap with the discipline of systems analysis appears inevitable.
System dynamics
- System dynamicsSystem dynamicsSystem dynamics is an approach to understanding the behaviour of complex systems over time. It deals with internal feedback loops and time delays that affect the behaviour of the entire system. What makes using system dynamics different from other approaches to studying complex systems is the use...
is an approach to understanding the behaviour of complex systemComplex systemA complex system is a system composed of interconnected parts that as a whole exhibit one or more properties not obvious from the properties of the individual parts....
s over time. It deals with internal feedback loops and time delays that affect the behaviour of the entire system. What makes using system dynamics different from other approaches to studying complex systems is the use of feedbackFeedbackFeedback describes the situation when output from an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or occurrences of the same Feedback describes the situation when output from (or information about the result of) an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or...
loops and stocks and flowsStock and flowEconomics, business, accounting, and related fields often distinguish between quantities that are stocks and those that are flows. These differ in their units of measurement. A stock variable is measured at one specific time, and represents a quantity existing at that point in time , which may have...
. These elements help describe how even seemingly simple systems display baffling nonlinearityNonlinearityIn mathematics, a nonlinear system is one that does not satisfy the superposition principle, or one whose output is not directly proportional to its input; a linear system fulfills these conditions. In other words, a nonlinear system is any problem where the variable to be solved for cannot be...
.
Systems engineering
- Systems engineeringSystems engineeringSystems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering that focuses on how complex engineering projects should be designed and managed over the life cycle of the project. Issues such as logistics, the coordination of different teams, and automatic control of machinery become more...
(SE) is an interdisciplinary field of engineeringEngineeringEngineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
, that focuses on the development and organization of complex artificial systemSystemSystem is a set of interacting or interdependent components forming an integrated whole....
s. Systems engineering has emerged into all kinds of sciences, and universities nowadays offer all kinds of specialized academic programs.
Systems Methodologies
- There are several types of Systems Methodologies, that is, disciplines for analysis of systems. For example:
- Soft Systems Methodology (SSM) : in the field of organizational studies is an approach to organisational process modelling and it can be used both for general problemProblemA problem is an obstacle, impediment, difficulty or challenge, or any situation that invites resolution; the resolution of which is recognized as a solution or contribution toward a known purpose or goal...
solving and in the management of change. It was developed in EnglandEnglandEngland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
by academics at the University of Lancaster Systems Department through a ten year Action Research programme. - System Development Methodology (SDM) in the field of IT development is a general term applied to a variety of structured, organized processes for developing information technology and embedded software systems.
- Viable systems approachViable systems approachThe Viable Systems Approach is a system theory in which the observed entities and their environment are interpreted through a systemic viewpoint, starting with the analysis of fundamental elements and finally considering more complex related systems...
(vSa) is a methodology usesful for the understanding and governance of complex phenomena; it has been successfully proposed in the field of management, decision making, marketing and service.
- Soft Systems Methodology (SSM) : in the field of organizational studies is an approach to organisational process modelling and it can be used both for general problem
Systems theories
- Systems theorySystems theorySystems theory is the transdisciplinary study of systems in general, with the goal of elucidating principles that can be applied to all types of systems at all nesting levels in all fields of research...
is an interdisciplinary field of scienceScienceScience is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe...
. It studies the nature of complex systemComplex systemA complex system is a system composed of interconnected parts that as a whole exhibit one or more properties not obvious from the properties of the individual parts....
s in natureNatureNature, in the broadest sense, is equivalent to the natural world, physical world, or material world. "Nature" refers to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general...
, societySocietyA society, or a human society, is a group of people related to each other through persistent relations, or a large social grouping sharing the same geographical or virtual territory, subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations...
, and scienceScienceScience is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe...
. More specificially, it is a framework by which one can analyze and/or describe any group of objects that work in concert to produce some result.
Systems science
- Systems sciences are scientific disciplines partly based on systems thinking such as Chaos theoryChaos theoryChaos theory is a field of study in mathematics, with applications in several disciplines including physics, economics, biology, and philosophy. Chaos theory studies the behavior of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions, an effect which is popularly referred to as the...
, Complex systemsComplex systemsComplex systems present problems in mathematical modelling.The equations from which complex system models are developed generally derive from statistical physics, information theory and non-linear dynamics, and represent organized but unpredictable behaviors of systems of nature that are considered...
, Control theoryControl theoryControl theory is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering and mathematics that deals with the behavior of dynamical systems. The desired output of a system is called the reference...
, CyberneticsCyberneticsCybernetics is the interdisciplinary study of the structure of regulatory systems. Cybernetics is closely related to information theory, control theory and systems theory, at least in its first-order form...
, Sociotechnical systems theory, Systems biologySystems biologySystems biology is a term used to describe a number of trends in bioscience research, and a movement which draws on those trends. Proponents describe systems biology as a biology-based inter-disciplinary study field that focuses on complex interactions in biological systems, claiming that it uses...
, Systems ecologySystems ecologySystems ecology is an interdisciplinary field of ecology, taking a holistic approach to the study of ecological systems, especially ecosystems. Systems ecology can be seen as an application of general systems theory to ecology. Central to the systems ecology approach is the idea that an ecosystem...
, Systems psychologySystems psychologySystems psychology is a branch of applied psychology that studies human behaviour and experience in complex systems. It is inspired by systems theory and systems thinking, and based on the theoretical work of Roger Barker, Gregory Bateson, Humberto Maturana and others. It is an approach in...
and the already mentioned Systems dynamics, Systems engineering and Systems theory.
Fields
Systems sciences covers formal sciences fields like dynamical systems theoryDynamical systems theory
Dynamical systems theory is an area of applied mathematics used to describe the behavior of complex dynamical systems, usually by employing differential equations or difference equations. When differential equations are employed, the theory is called continuous dynamical systems. When difference...
and applications in the field of the natural and social sciences and engineering, such as social systems theory and systems dynamics.
- Chaos theoryChaos theoryChaos theory is a field of study in mathematics, with applications in several disciplines including physics, economics, biology, and philosophy. Chaos theory studies the behavior of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions, an effect which is popularly referred to as the...
- Complex systemsComplex systemsComplex systems present problems in mathematical modelling.The equations from which complex system models are developed generally derive from statistical physics, information theory and non-linear dynamics, and represent organized but unpredictable behaviors of systems of nature that are considered...
- Complex systemComplex systemA complex system is a system composed of interconnected parts that as a whole exhibit one or more properties not obvious from the properties of the individual parts....
- CyberneticsCyberneticsCybernetics is the interdisciplinary study of the structure of regulatory systems. Cybernetics is closely related to information theory, control theory and systems theory, at least in its first-order form...
- BiocyberneticsBiocyberneticsBiocybernetics is the application of cybernetics to biological science, composed of biological disciplines that benefit from the application of cybernetics: neurology, multicellular systems and others...
- Engineering cyberneticsEngineering cyberneticsEngineering cybernetics or technical cybernetics, established by H.S. Tsien, is a field of cybernetics, which deals with the question of control engineering of mechatronic systems as well as chemical or biological systems...
- Management cyberneticsManagement cyberneticsManagement cybernetics is the field of cybernetics concerned with management and organizations. The notion of cybernetics and management was first introduced by Stafford Beer in the late 1950s-Cybernetics and Complexity:...
- Medical cyberneticsMedical cyberneticsMedical Cybernetics is a branch of cybernetics which has been heavily affected by the development of the computer, which applies the concepts of cybernetics to medical research and practice...
- New CyberneticsNew CyberneticsNew Cybernetics is a study of self-organizing systems according to Peter Harries-Jones , "looking beyond the issues of the "first", "old" or "original" cybernetics and their politics and sciences of control, to the autonomy and self-organization capabilities of complex systems"...
- Second-order cyberneticsSecond-order cyberneticsSecond-order cybernetics, also known as the cybernetics of cybernetics, investigates the construction of models of cybernetic systems. It investigates cybernetics with awareness that the investigators are part of the system, and of the importance of self-referentiality, self-organizing, the...
- Biocybernetics
- Control theoryControl theoryControl theory is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering and mathematics that deals with the behavior of dynamical systems. The desired output of a system is called the reference...
- Affect control theoryAffect control theoryIn control theory affect control theory proposes that individuals maintain affective meanings through their actions and interpretations of events...
- Control engineeringControl engineeringControl engineering or Control systems engineering is the engineering discipline that applies control theory to design systems with predictable behaviors...
- Control systems
- Dynamical systems
- Perceptual control theoryPerceptual control theoryPerceptual control theory is a model of the psychological and behavioral processes occurring within living beings, including humans. It demonstrates that animals are goal-driven, purposeful entities rather than automata repeating conditioned responses to external stimuli or computers planning...
- Affect control theory
- Operations researchOperations researchOperations research is an interdisciplinary mathematical science that focuses on the effective use of technology by organizations...
- Systems biologySystems biologySystems biology is a term used to describe a number of trends in bioscience research, and a movement which draws on those trends. Proponents describe systems biology as a biology-based inter-disciplinary study field that focuses on complex interactions in biological systems, claiming that it uses...
- Computational systems biologyComputational systems biologyModeling biological systems is a significant task of systems biology and mathematical biology.Computational systems biology aims to develop and use efficient algorithms, data structures, visualization and communication tools with the goal of computer modeling of biological systems...
- Synthetic biologySynthetic biologySynthetic biology is a new area of biological research that combines science and engineering. It encompasses a variety of different approaches, methodologies, and disciplines with a variety of definitions...
- Systems immunologySystems immunologySystems immunology is a recent research field that, under the larger umbrella of systems biology, aims to study the immune system in the more integrated perspective on how entities and players participate at different system levels to the immune function....
- Computational systems biology
- System dynamicsSystem dynamicsSystem dynamics is an approach to understanding the behaviour of complex systems over time. It deals with internal feedback loops and time delays that affect the behaviour of the entire system. What makes using system dynamics different from other approaches to studying complex systems is the use...
- Social dynamicsSocial dynamicsSocial dynamics can refer to the behavior of groups that results from the interactions of individual group members as well to the study of the relationship between individual interactions and group level behaviors...
- Social dynamics
- Systems ecologySystems ecologySystems ecology is an interdisciplinary field of ecology, taking a holistic approach to the study of ecological systems, especially ecosystems. Systems ecology can be seen as an application of general systems theory to ecology. Central to the systems ecology approach is the idea that an ecosystem...
- Ecosystem ecologyEcosystem ecologyEcosystem ecology is the integrated study of biotic and abiotic components of ecosystems and their interactions within an ecosystem framework. This science examines how ecosystems work and relates this to their components such as chemicals, bedrock, soil, plants, and animals.Ecosystem ecology...
- Ecosystem ecology
- Systems engineeringSystems engineeringSystems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering that focuses on how complex engineering projects should be designed and managed over the life cycle of the project. Issues such as logistics, the coordination of different teams, and automatic control of machinery become more...
- Biological systems engineeringBiological systems engineeringBiological Systems Engineering is a broad-based engineering discipline with particular emphasis on biology and chemistry. It can be thought of as a subset of the broader notion of Biological Engineering. It is not to be confused with Biomedical Engineering as it tends to focus less on medical...
- Earth systems engineering and managementEarth systems engineering and managementEarth systems engineering and management is a discipline used to analyze, design, engineer and manage complex environmental systems. It entails a wide range of subject areas including anthropology, engineering, environmental science, ethics and philosophy...
- Enterprise systems engineeringEnterprise systems engineeringEnterprise systems engineering is a emerging discipline of engineering that focuses on integration of many engineering sub-systems and principles into a complete system....
- Systems analysisSystems analysisSystems analysis is the study of sets of interacting entities, including computer systems analysis. This field is closely related to requirements analysis or operations research...
- Biological systems engineering
- Systems theory in anthropologySystems theory in anthropologySystems Theory in Anthropology is an interdisciplinary, non-representative, non-referential, and non-Cartesian approach that brings together natural and social sciences to understand society in its complexity. The basic idea of a system theory in social science is to solve the classical problem of...
- Systems psychologySystems psychologySystems psychology is a branch of applied psychology that studies human behaviour and experience in complex systems. It is inspired by systems theory and systems thinking, and based on the theoretical work of Roger Barker, Gregory Bateson, Humberto Maturana and others. It is an approach in...
- ErgonomicsErgonomicsErgonomics is the study of designing equipment and devices that fit the human body, its movements, and its cognitive abilities.The International Ergonomics Association defines ergonomics as follows:...
- Family systems theory
- Systemic therapySystemic TherapySystemic therapy is a form of psychotherapy which seeks to address people not on individual level, as had been the focus of earlier forms of therapy, but as people in relationship, dealing with the interactions of groups and their interactional patterns and dynamics.- History :Systemic therapy has...
- Ergonomics
- Systems theorySystems theorySystems theory is the transdisciplinary study of systems in general, with the goal of elucidating principles that can be applied to all types of systems at all nesting levels in all fields of research...
- Biochemical systems theoryBiochemical systems theoryBiochemical systems theory is a mathematical modelling framework for biochemical systems, based on ordinary differential equations , in which biochemical processes are represented using power-law expansions in the variables of the system....
- Ecological systems theoryEcological Systems TheoryEcological systems theory, also called development in context or human ecology theory, specifies four types of nested environmental systems, with bi-directional influences within and between the systems.- Overview :...
- Developmental systems theoryDevelopmental systems theoryIn developmental psychology, developmental systems theory is an overarching theoretical perspective on biological development, heredity, and evolution . It emphasizes the equal contributions of genes, environment, and epigenetic factors on developmental processes...
- General systems theory
- Living systems theory
- LTI system theoryLTI system theoryLinear time-invariant system theory, commonly known as LTI system theory, comes from applied mathematics and has direct applications in NMR spectroscopy, seismology, circuits, signal processing, control theory, and other technical areas. It investigates the response of a linear and time-invariant...
- Sociotechnical systems theory
- Mathematical system theory
- World-systems theory
- Biochemical systems theory
- Systems theory in sociology
- Talcott ParsonsTalcott ParsonsTalcott Parsons was an American sociologist who served on the faculty of Harvard University from 1927 to 1973....
- Niklas LuhmannNiklas LuhmannNiklas Luhmann was a German sociologist, and a prominent thinker in sociological systems theory.-Biography:...
- Talcott Parsons
Systems scientists
General systems scientists can be divided into different generations. The founders of the systems movement like Ludwig von BertalanffyLudwig von Bertalanffy
Karl Ludwig von Bertalanffy was an Austrian-born biologist known as one of the founders of general systems theory . GST is an interdisciplinary practice that describes systems with interacting components, applicable to biology, cybernetics, and other fields...
, Kenneth Boulding, Ralph Gerard, James Grier Miller
James Grier Miller
James Grier Miller was an American biologist, a pioneer of systems science, who originated the modern use of the term "behavioral science", founded and directed the multi-disciplinary Mental Health Research Institute at the University of Michigan, and originated the living systems theory.-...
, George J. Klir,and Anatol Rapoport
Anatol Rapoport
Anatol Rapoport was a Russian-born American Jewish mathematical psychologist. He contributed to general systems theory, mathematical biology and to the mathematical modeling of social interaction and stochastic models of contagion.-Biography:...
were all born between 1900 and 1920. They all came from different natural and social science disciplines and joined forces in the 1950s to established the general systems theory paradigm
Paradigm
The word paradigm has been used in science to describe distinct concepts. It comes from Greek "παράδειγμα" , "pattern, example, sample" from the verb "παραδείκνυμι" , "exhibit, represent, expose" and that from "παρά" , "beside, beyond" + "δείκνυμι" , "to show, to point out".The original Greek...
. Along with the organization of their efforts a first generation of systems scientists rose.
Among them were other scientists like Ackoff, Ashby and Churchman, who popularized the systems concept in the 1950s and 1960s. These scientists inspired and educated a second generation with more notable scientist like Ervin Laszlo
Ervin László
Ervin László is a Hungarian philosopher of science, systems theorist, integral theorist, originally a classical pianist. He has published about 75 books and over 400 papers, and is editor of World Futures: The Journal of General Evolution...
(1932) and Fritjof Capra
Fritjof Capra
Fritjof Capra is an Austrian-born American physicist. He is a founding director of the Center for Ecoliteracy in Berkeley, California, and is on the faculty of Schumacher College....
(1939), who wrote about systems theory in the 1970s and 1980s. Others got acquainted and started studying these works in the 1980s and started writing about it since the 1990s. Debora Hammond
Debora Hammond
Debora Hammond is an American historian of science, Provost and Professor Interdisciplinary Studies of the Hutchins School of Liberal Studies at the Sonoma State University...
can be seen as a typical representative of these third generation of general systems scientists.
Organizations
The International Society for the Systems SciencesInternational Society for the Systems Sciences
The International Society for the Systems Sciences is a world-wide organization for systems sciences.- Overview :The initial purpose of the society was "to encourage the development of theoretical systems which are applicable to more than one of the traditional departments of knowledge."The idea...
(ISSS) is an organisation for interdisciplinary collaboration and synthesis of systems sciences. The ISSS is unique among systems-oriented institutions in terms of the breadth of its scope, bringing together scholars and practitioners from academic, business, government, and non-profit organizations. Based on fifty years of tremendous interdisciplinary research from the scientific study of complex systems to interactive approaches in management and community development. This society was initially conceived in 1954 at the Stanford Center for Advanced Study in the Behavioral Sciences
Center for Advanced Study in the Behavioral Sciences
The Center for Advanced Study in the Behavioral Sciences is an American interdisciplinary research body in Stanford, California focusing on the social sciences and humanities . Fellows are elected in a closed process, to spend a period of residence at the Center, released from other duties...
by Ludwig von Bertalanffy
Ludwig von Bertalanffy
Karl Ludwig von Bertalanffy was an Austrian-born biologist known as one of the founders of general systems theory . GST is an interdisciplinary practice that describes systems with interacting components, applicable to biology, cybernetics, and other fields...
, Kenneth Boulding, Ralph Gerard, and Anatol Rapoport
Anatol Rapoport
Anatol Rapoport was a Russian-born American Jewish mathematical psychologist. He contributed to general systems theory, mathematical biology and to the mathematical modeling of social interaction and stochastic models of contagion.-Biography:...
.
In the field of systems science the International Federation for Systems Research
International Federation for Systems Research
The International Federation for Systems Research is an international federation for global and local societies in the field of systems science...
(IFSR) is an international federation for global and local societies in the field of systems science. This federation is a non-profit, scientific and educational agency
Non-profit organization
Nonprofit organization is neither a legal nor technical definition but generally refers to an organization that uses surplus revenues to achieve its goals, rather than distributing them as profit or dividends...
founded in 1981, and constituted of some thirty member organizations from various countries. The overall purpose of this Federation is to advance cybernetic and systems research and systems applications and to serve the international systems community.
The best known research institute in the field is the Santa Fe Institute
Santa Fe Institute
The Santa Fe Institute is an independent, nonprofit theoretical research institute located in Santa Fe and dedicated to the multidisciplinary study of the fundamental principles of complex adaptive systems, including physical, computational, biological, and social systems.The Institute houses a...
(SFI) located in Santa Fe, New Mexico, United States, dedicated to the study of complex systems
Complex systems
Complex systems present problems in mathematical modelling.The equations from which complex system models are developed generally derive from statistical physics, information theory and non-linear dynamics, and represent organized but unpredictable behaviors of systems of nature that are considered...
. This institute was founded in 1984 by George Cowan
George Cowan
George A. Cowan is an American physical chemist, a businessman and philanthropist. He conducted early research in the Manhattan Project. George served 39 years at Los Alamos National Laboratory as director of chemistry, associate director of research and senior laboratory fellow. He participated...
, David Pines
David Pines
David Pines is the Founding Director of the Institute for Complex Adaptive Matter and the International Institute for Complex Adaptive Matter , Distinguished Professor of Physics, UC Davis, Research Professor of Physics and Professor...
, Stirling Colgate
Stirling Colgate
Stirling Colgate is an American physicist at Los Alamos National Laboratory and a professor emeritus of physics at the New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology . He was America's premier diagnostician of thermonuclear weapons during the early years at the Lawrence Livermore National...
, Murray Gell-Mann
Murray Gell-Mann
Murray Gell-Mann is an American physicist and linguist who received the 1969 Nobel Prize in physics for his work on the theory of elementary particles...
, Nick Metropolis, Herb Anderson, Peter A. Carruthers, and Richard Slansky. All but Pines and Gell-Mann were scientists with Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory, managed and operated by Los Alamos National Security , located in Los Alamos, New Mexico...
. SFI's original mission was to disseminate the notion of a separate interdisciplinary research area, complexity theory
Complex adaptive system
Complex adaptive systems are special cases of complex systems. They are complex in that they are dynamic networks of interactions and relationships not aggregations of static entities...
referred to at SFI as complexity science.
See also
- List of systems sciences organizations
- List of systems scientists
- Principia CyberneticaPrincipia CyberneticaPrincipia Cybernetica is an international cooperation of scientists in the field of cybernetics and systems science, especially known for their Principia Cybernetica Web website...
- System engineering
- SystemicsSystemicsIn the context of systems science and systems philosophy, the term systemics refers to an initiative to study systems from a holistic point of view...
- Systems theorySystems theorySystems theory is the transdisciplinary study of systems in general, with the goal of elucidating principles that can be applied to all types of systems at all nesting levels in all fields of research...
- Systems theory in archaeologySystems theory in archaeologySystems theory in archaeology is the application of systems theory and systems thinking in archaeology. It originated with the work of Ludwig von Bertalanffy in the 1950s, and is introduced in archaeology in the 1960s with the work of Sally R. Binford & Lewis Binford's "New Perspectives in...
- Systems theory in anthropologySystems theory in anthropologySystems Theory in Anthropology is an interdisciplinary, non-representative, non-referential, and non-Cartesian approach that brings together natural and social sciences to understand society in its complexity. The basic idea of a system theory in social science is to solve the classical problem of...
- Systems theory in political scienceSystems theory in political scienceSystems theory in political science is a highly abstract, partly holistic view of politics, influenced by cybernetics. The adaptation of system theory to political science was first conceived by David Easton in 1953.-Overview:...
- World-systems theory
- System equivalenceSystem equivalenceIn the systems sciences the term system equivalence is the notion that a parameter or component of a system behaves in a similar way as a parameter or component of a different system. Similarity means that mathematically the parameters/components will be indistinguishable from each other...
- AntireductionismAntireductionismAntireductionism is a reaction against reductionism, which instead advocates holism. Although "breaking complex phenomena into parts, is a key method in science," there are those complex phenomena where some resistance to or rebellion against this approach arises, primarily due to the perceived...
- EGangesEGangeseGanges is an expert system shell, mainly for the domains of law, quality control management, and education. It represents and processes systems of mixed hypothetical and categorical syllogisms, no matter how large and complex...
Further reading
- B. A. Bayraktar, Education in Systems Science, 1979, 369 pp.
- Kenneth D. BaileyKenneth D. BaileyMajor Kenneth Dillon Bailey was a United States Marine Corps officer who posthumously received the Medal of Honor for heroic conduct during action during the Battle of Guadalcanal in the Solomon Islands...
, "Fifty Years of Systems Science:Further Reflections", Systems Research and Behavioral Science, 22, 2005, pp. 355–361. - Robert L. FloodRobert L. FloodRobert Louis Flood , British organizational scientist, and Professor of Management Sciences at the University of Hull, UK. He is a recognized authority on applied systemic thinking in the areas of strategic management, organizational behavior and organizational improvement.- Biography :Flood...
, Ewart R Carson, Dealing with Complexity: An Introduction to the Theory and Application of Systems Science, 1988. - George J. Klir, Facets of Systems Science, Plenum Press, 1991.
- Ervin LászlóErvin LászlóErvin László is a Hungarian philosopher of science, systems theorist, integral theorist, originally a classical pianist. He has published about 75 books and over 400 papers, and is editor of World Futures: The Journal of General Evolution...
, Systems Science and World Order: Selected Studies, 1983. - Anatol RapoportAnatol RapoportAnatol Rapoport was a Russian-born American Jewish mathematical psychologist. He contributed to general systems theory, mathematical biology and to the mathematical modeling of social interaction and stochastic models of contagion.-Biography:...
(ed.), General Systems: Yearbook of the Society for the Advancement of General Systems Theory, Society for General Systems Research, Vol 1., 1956. - Li D. Xu, "The contributions of Systems Science to Information Systems Research", Systems Research and Behavioral Science, 17, 2000, pp. 105–116.
- Graeme Donald Snooks, "A general theory of complex living systems: Exploring the demand side of dynamics", Complexity, vol. 13, no. 6, July/August 2008.
- John N. WarfieldJohn N. WarfieldJohn Nelson Warfield is an American systems scientist, who was professor and director of the Institute for Advanced Study in the Integrative Sciences at George Mason University.- Biography :...
, "A proposal for Systems Science", Systems Research and Behavioral Science, 20, 2003, pp. 507–520.

