
System dynamics
Encyclopedia
Complex system
A complex system is a system composed of interconnected parts that as a whole exhibit one or more properties not obvious from the properties of the individual parts....
s over time. It deals with internal feedback loops and time delays that affect the behaviour of the entire system. What makes using system dynamics different from other approaches to studying complex systems is the use of feedback
Feedback
Feedback describes the situation when output from an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or occurrences of the same Feedback describes the situation when output from (or information about the result of) an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or...
loops and stocks and flows
Stock and flow
Economics, business, accounting, and related fields often distinguish between quantities that are stocks and those that are flows. These differ in their units of measurement. A stock variable is measured at one specific time, and represents a quantity existing at that point in time , which may have...
. These elements help describe how even seemingly simple systems display baffling nonlinearity
Nonlinearity
In mathematics, a nonlinear system is one that does not satisfy the superposition principle, or one whose output is not directly proportional to its input; a linear system fulfills these conditions. In other words, a nonlinear system is any problem where the variable to be solved for cannot be...
.
Overview
System dynamics is a methodology and mathematical modeling technique for framing, understanding, and discussing complex issues and problems. Originally developed in the 1950s to help corporate managers improve their understanding of industrial processes, system dynamics is currently being used throughout the public and private sector for policy analysis and design.Convenient GUI
Graphical user interface
In computing, a graphical user interface is a type of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices with images rather than text commands. GUIs can be used in computers, hand-held devices such as MP3 players, portable media players or gaming devices, household appliances and...
system dynamics software developed into user friendly versions by the 1990s and have been applied to diverse systems. SD models solve the problem of simultaneity (mutual causation) by updating all variables in small time increments with positive and negative feedbacks and time delays structuring the interactions and control. The best known SD model is probably the 1972 The Limits to Growth. This model forecast that exponential growth would lead to economic collapse during the 21st century under a wide variety of growth scenarios.
System dynamics is an aspect of systems theory
Systems theory
Systems theory is the transdisciplinary study of systems in general, with the goal of elucidating principles that can be applied to all types of systems at all nesting levels in all fields of research...
as a method for understanding the dynamic behavior of complex systems. The basis of the method is the recognition that the structure of any system — the many circular, interlocking, sometimes time-delayed relationships among its components — is often just as important in determining its behavior as the individual components themselves. Examples are chaos theory
Chaos theory
Chaos theory is a field of study in mathematics, with applications in several disciplines including physics, economics, biology, and philosophy. Chaos theory studies the behavior of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions, an effect which is popularly referred to as the...
and social dynamics
Social dynamics
Social dynamics can refer to the behavior of groups that results from the interactions of individual group members as well to the study of the relationship between individual interactions and group level behaviors...
. It is also claimed that because there are often properties-of-the-whole which cannot be found among the properties-of-the-elements, in some cases the behavior of the whole cannot be explained in terms of the behavior of the parts.
History
System dynamics was created during the mid-1950s by Professor Jay Forrester of the Massachusetts Institute of TechnologyMassachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology is a private research university located in Cambridge, Massachusetts. MIT has five schools and one college, containing a total of 32 academic departments, with a strong emphasis on scientific and technological education and research.Founded in 1861 in...
. In 1956, Forrester accepted a professorship in the newly-formed MIT Sloan School of Management
MIT Sloan School of Management
The MIT Sloan School of Management is the business school of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, in Cambridge, Massachusetts....
. His initial goal was to determine how his background in science and engineering could be brought to bear, in some useful way, on the core issues that determine the success or failure of corporations. Forrester's insights into the common foundations that underlie engineering, which led to the creation of system dynamics, were triggered, to a large degree, by his involvement with managers at General Electric
General Electric
General Electric Company , or GE, is an American multinational conglomerate corporation incorporated in Schenectady, New York and headquartered in Fairfield, Connecticut, United States...
(GE) during the mid-1950s. At that time, the managers at GE were perplexed because employment at their appliance plants in Kentucky exhibited a significant three-year cycle. The business cycle
Business cycle
The term business cycle refers to economy-wide fluctuations in production or economic activity over several months or years...
was judged to be an insufficient explanation for the employment instability. From hand simulations (or calculations) of the stock-flow-feedback structure of the GE plants, which included the existing corporate decision-making structure for hiring and layoffs, Forrester was able to show how the instability in GE employment was due to the internal structure of the firm and not to an external force such as the business cycle. These hand simulations were the beginning of the field of system dynamics.
During the late 1950s and early 1960s, Forrester and a team of graduate students moved the emerging field of system dynamics from the hand-simulation stage to the formal computer modeling stage. Richard Bennett
Richard Bennett
Richard Bennett may refer to:* Richard Bennett , film star and father of actresses Constance Bennett and Joan Bennett* Richard Bennett , English cricketer...
created the first system dynamics computer modeling language called SIMPLE (Simulation of Industrial Management Problems with Lots of Equations) in the spring of 1958. In 1959, Phyllis Fox
Phyllis Fox
Phyllis Fox is an American mathematician and computer scientist.She was part of the team that wrote DYNAMO for Jay Forrester's system dynamics research group...
and Alexander Pugh wrote the first version of
DYNAMO
DYNAMO (programming language)
DYNAMO was a simulation language and accompanying graphical notation developed within the system dynamics analytical framework...
(DYNAmic MOdels), an improved version of SIMPLE, and the system dynamics language became the industry standard for over thirty years. Forrester published the first, and still classic, book in the field titled Industrial Dynamics in 1961.
From the late 1950s to the late 1960s, system dynamics was applied almost exclusively to corporate/managerial problems. In 1968, however, an unexpected occurrence caused the field to broaden beyond corporate modeling. John Collins
John Collins
- Arts :*John Churton Collins , English literary critic*John Collins , bass guitarist for Powderfinger*John Collins , of The New Pornographers and The Smugglers...
, the former mayor of Boston, was appointed a visiting professor of Urban Affairs at MIT. The result of the Collins-Forrester collaboration was a book titled Urban Dynamics. The Urban Dynamics model presented in the book was the first major non-corporate application of system dynamics.
The second major noncorporate application of system dynamics came shortly after the first. In 1970, Jay Forrester was invited by the Club of Rome
Club of Rome
The Club of Rome is a global think tank that deals with a variety of international political issues. Founded in 1968 at Accademia dei Lincei in Rome, Italy, the CoR describes itself as "a group of world citizens, sharing a common concern for the future of humanity." It consists of current and...
to a meeting in Bern, Switzerland. The Club of Rome is an organization devoted to solving what its members describe as the "predicament of mankind" -- that is, the global crisis that may appear sometime in the future, due to the demands being placed on the Earth's carrying capacity (its sources of renewable and nonrenewable resources and its sinks for the disposal of pollutants) by the world's exponentially growing population. At the Bern meeting, Forrester was asked if system dynamics could be used to address the predicament of mankind. His answer, of course, was that it could. On the plane back from the Bern meeting, Forrester created the first draft of a system dynamics model of the world's socioeconomic system. He called this model WORLD1. Upon his return to the United States, Forrester refined WORLD1 in preparation for a visit to MIT by members of the Club of Rome. Forrester called the refined version of the model WORLD2. Forrester published WORLD2 in a book titled World Dynamics.
Topics in systems dynamics
The elements of system dynamics diagrams are feedback, accumulation of flows into stocks and time delays.As an illustration of the use of system dynamics, imagine an organisation that plans to introduce an innovative new durable consumer product. The organisation needs to understand the possible market dynamics in order to design marketing and production plans.
Causal loop diagrams
A causal loop diagram is a visual representation of the feedback loops in a system. The causal loop diagram of the new product introduction may look as follows: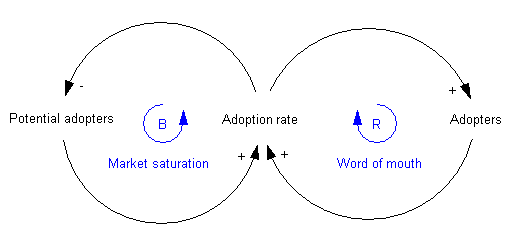
The second feedback loop on the left is negative reinforcement (or "balancing" and hence labeled B). Clearly growth can not continue forever, because as more and more people adopt, there remain fewer and fewer potential adopters.
Both feedback loops act simultaneously, but at different times they may have different strengths. Thus one would expect growing sales in the initial years, and then declining sales in the later years.

- step1 : (+) green arrows show that Adoption rate is function of Potential Adopters and Adopters
- step2 : (-) red arrow shows that Potential adopters decreases by Adoption rate
- step3 : (+) blue arrow shows that Adopters increases by Adoption rate
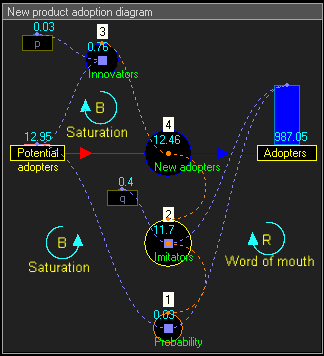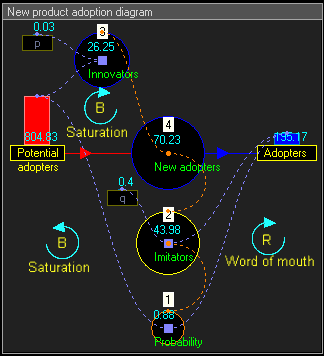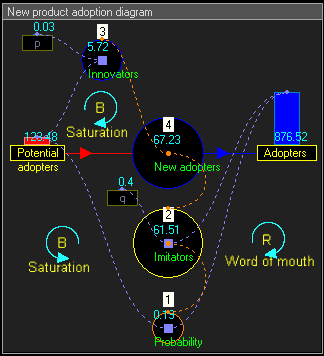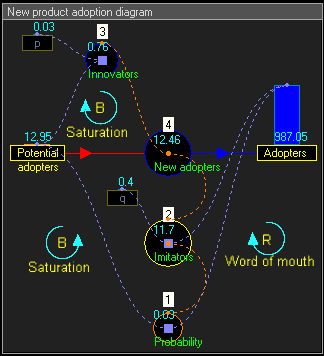
Stock and flow diagrams
The next step is to create what is termed a stock and flowStock and flow
Economics, business, accounting, and related fields often distinguish between quantities that are stocks and those that are flows. These differ in their units of measurement. A stock variable is measured at one specific time, and represents a quantity existing at that point in time , which may have...
diagram. A stock is the term for any entity that accumulates or depletes over time. A flow is the rate of change in a stock.
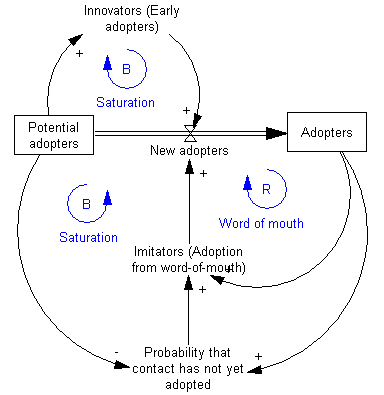
Equations
The real power of system dynamics is utilised through simulation. Although it is possible to perform the modeling in a spreadsheetSpreadsheet
A spreadsheet is a computer application that simulates a paper accounting worksheet. It displays multiple cells usually in a two-dimensional matrix or grid consisting of rows and columns. Each cell contains alphanumeric text, numeric values or formulas...
, there are a variety of software packages that have been optimised for this.
The steps involved in a simulation are:
- Define the problem boundary
- Identify the most important stocks and flows that change these stock levels
- Identify sources of information that impact the flows
- Identify the main feedback loops
- Draw a causal loop diagram that links the stocks, flows and sources of information
- Write the equations that determine the flows
- Estimate the parameters and initial conditions. These can be estimated using statistical methods, expert opinion, market research data or other relevant sources of information.
- Simulate the model and analyse results
In this example, the equations that change the two stocks via the flow are:


Equations in discrete time
List of all the equations in Discrete timeDiscrete time
Discrete time is the discontinuity of a function's time domain that results from sampling a variable at a finite interval. For example, consider a newspaper that reports the price of crude oil once every day at 6:00AM. The newspaper is described as sampling the cost at a frequency of once per 24...
, in their order of execution in each year, for years 1 to 15 :








Dynamic simulation results
The dynamic simulation results show that the behaviour of the system would be to have growth in Adopters that follows a classical s-curve shape.The increase in Adopters is very slow initially, then exponential growth for a period, followed ultimately by saturation.
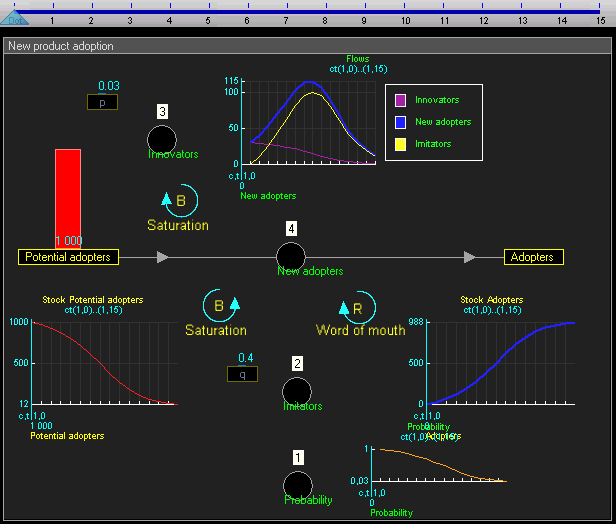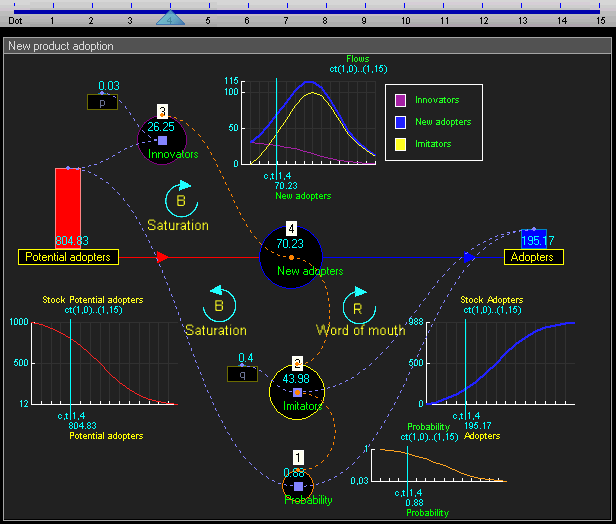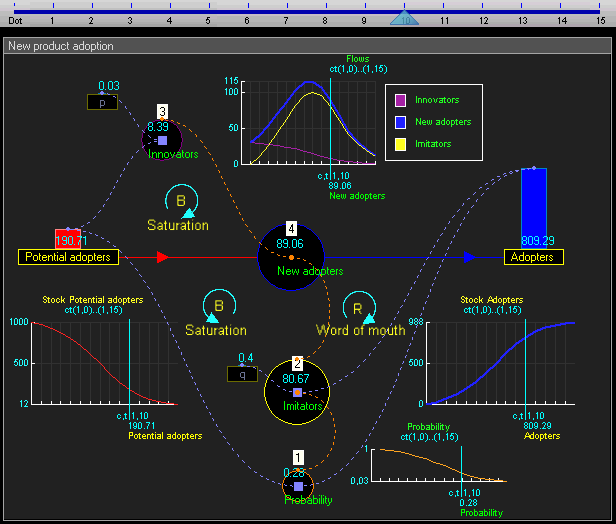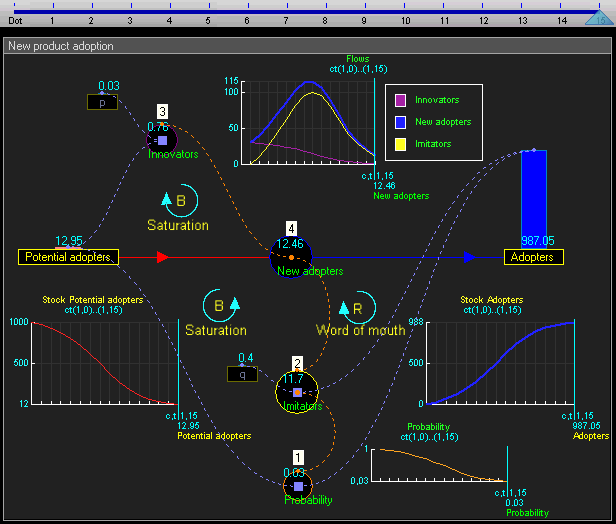
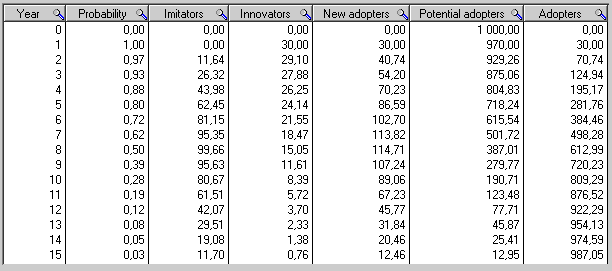
Equations in continuous time
To get intermediate values and better accuracy, the model can run in continuous time : we multiply the number of units of time and we proportionally divide values that change stock levels. In this example we multiply the 15 years by 4 to obtain 60 trimesters, and we divide the value of the flow by 4.Dividing the value is the simplest of the Euler method, we can use too other methods such Runge–Kutta methods
Runge–Kutta methods
In numerical analysis, the Runge–Kutta methods are an important family of implicit and explicit iterative methods for the approximation of solutions of ordinary differential equations. These techniques were developed around 1900 by the German mathematicians C. Runge and M.W. Kutta.See the article...
.
List of the équations in continuous time for trimesters = 1 to 60 :
- They are the same equations as in the section Equation in discrete time above, except equations 4.1 and 4.2 replaced by following :




- In the below stock and flow diagram, the intermediate flow 'Rate New adopters' calculates the equation :

Application
System dynamics has found application in a wide range of areas, for example populationPopulation dynamics
Population dynamics is the branch of life sciences that studies short-term and long-term changes in the size and age composition of populations, and the biological and environmental processes influencing those changes...
, ecological
Ecology
Ecology is the scientific study of the relations that living organisms have with respect to each other and their natural environment. Variables of interest to ecologists include the composition, distribution, amount , number, and changing states of organisms within and among ecosystems...
and economic
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
systems, which usually interact strongly with each other.
System dynamics have various "back of the envelope" management applications. They are a potent tool to:
- Teach system thinking reflexes to persons being coached
- Analyze and compare assumptions and mental models about the way things work
- Gain qualitative insight into the workings of a system or the consequences of a decision
- Recognize archetypes of dysfunctional systems in everyday practice
Computer software is used to simulate
Computer simulation
A computer simulation, a computer model, or a computational model is a computer program, or network of computers, that attempts to simulate an abstract model of a particular system...
a system dynamics model of the situation being studied. Running "what if" simulations to test certain policies on such a model can greatly aid in understanding how the system changes over time. System dynamics is very similar to systems thinking
Systems thinking
Systems thinking is the process of understanding how things influence one another within a whole. In nature, systems thinking examples include ecosystems in which various elements such as air, water, movement, plants, and animals work together to survive or perish...
and constructs the same causal loop diagram
Causal loop diagram
A causal loop diagram is a causal diagram that aids in visualizing how interrelated variables affect one another. The diagram consists of a set of nodes representing the variables connected together...
s of systems with feedback. However, system dynamics typically goes further and utilises simulation to study the behaviour of systems and the impact of alternative policies.
System dynamics has been used to investigate resource dependencies, and resulting problems, in product development.
Example
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
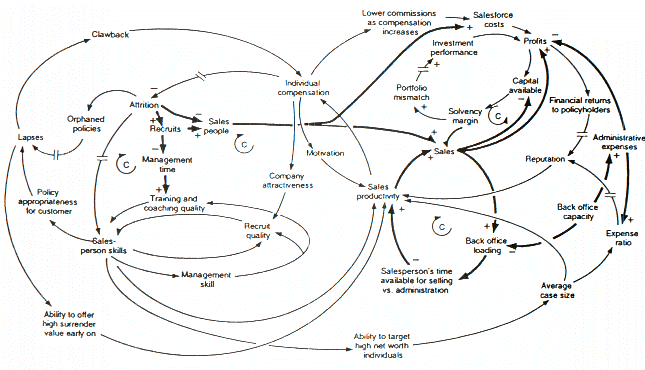
. A number of this figure's features are worth mentioning. The first is that the model's negative feedback loops are identified by "C's," which stand for "Counteracting" loops. The second is that double slashes are used to indicate places where there is a significant delay between causes (i.e., variables at the tails of arrows) and effects (i.e., variables at the heads of arrows). This is a common causal loop diagramming convention in system dynamics. Third, is that thicker lines are used to identify the feedback loops and links that author wishes the audience to focus on. This is also a common system dynamics diagramming convention. Last, it is clear that a decision maker would find it impossible to think through the dynamic behavior inherent in the model, from inspection of the figure alone.
Example of piston motion
- 1.Objective : study of a crank-connecting rod system.
We want to model a crank-connecting rod system through a system dynamic model. Two different full descriptions of the physical system with related systems of equations can be found hereafter and hereafter : they give the same results. In this example, the crank, with variable radius and angular frequency, will drive a piston with a variable connecting rod length.
- 2.System dynamic modeling : the system is now modelled, according to a stock and flow system dynamic logic.
Below figure shows stock and flow diagram :
- 3.Simulation : the behavior of the crank-connecting rod dynamic system can then be simulated.
Next figure is a 3D simulation, created using the Procedural animation
Procedural animation
A procedural animation is a type of computer animation, used to automatically generate animation in real-time to allow for a more diverse series of actions than could otherwise be created using predefined animations....
technic. Variables of the model animate all parts of this animation : crank, radius, angular frequency, rod length, piston position.
See also
Related subjects- Causal loop diagramCausal loop diagramA causal loop diagram is a causal diagram that aids in visualizing how interrelated variables affect one another. The diagram consists of a set of nodes representing the variables connected together...
- Ecosystem modelEcosystem modelAn ecosystem model is an abstract, usually mathematical, representation of an ecological system , which is studied to gain a deeper understanding of the real system.Ecosystem models are formed by combining known ecological relations An ecosystem model is an abstract, usually mathematical,...
- Plateau PrinciplePlateau principleThe plateau principle is a mathematical model or scientific law originally developed to explain the time course of drug action The principle has wide applicability in pharmacology, physiology, nutrition, biochemistry and system dynamics...
- System ArchetypesSystem ArchetypesSystem Archetypes are patterns of behavior of a system. Systems expressed by circles of causality have therefore similar structure. Identifying a system archetype and finding the leverage enables efficient changes in a system...
- System Dynamics SocietySystem Dynamics SocietyThe System Dynamics Society is a not-for-profit organization based in Albany, New York, USA, whose mission is to further research into system dynamics and systems thinking.- Economics Chapter :...
- Twelve leverage pointsTwelve leverage pointsThe twelve leverage points to intervene in a system were proposed by Donella Meadows, a scientist and system analyst focused on environmental limits to economic growth...
- Wicked problems
- World3World3The World3 model was a computer simulation of interactions between population, industrial growth, food production and limits in the ecosystems of the Earth. It was originally produced and used by a Club of Rome study that produced the model and the book The Limits to Growth...
- Population dynamicsPopulation dynamicsPopulation dynamics is the branch of life sciences that studies short-term and long-term changes in the size and age composition of populations, and the biological and environmental processes influencing those changes...
- Predator-prey interaction
Related fields
- Dynamical systems theoryDynamical systems theoryDynamical systems theory is an area of applied mathematics used to describe the behavior of complex dynamical systems, usually by employing differential equations or difference equations. When differential equations are employed, the theory is called continuous dynamical systems. When difference...
- Operations researchOperations researchOperations research is an interdisciplinary mathematical science that focuses on the effective use of technology by organizations...
- Social dynamicsSocial dynamicsSocial dynamics can refer to the behavior of groups that results from the interactions of individual group members as well to the study of the relationship between individual interactions and group level behaviors...
- Systems theorySystems theorySystems theory is the transdisciplinary study of systems in general, with the goal of elucidating principles that can be applied to all types of systems at all nesting levels in all fields of research...
- Systems thinkingSystems thinkingSystems thinking is the process of understanding how things influence one another within a whole. In nature, systems thinking examples include ecosystems in which various elements such as air, water, movement, plants, and animals work together to survive or perish...
- TRIZTRIZTRIZ is "a problem-solving, analysis and forecasting tool derived from the study of patterns of invention in the global patent literature". It was developed by the Soviet inventor and science fiction author Genrich Altshuller and his colleagues, beginning in 1946...
Related scientists
- Jay Forrester
- Dennis MeadowsDennis MeadowsDennis L. Meadows is an American scientist and Emeritus Professor of Systems Management, and former director of the Institute for Policy and Social Science Research at the University of New Hampshire...
- Donella MeadowsDonella MeadowsDonella H. "Dana" Meadows was a pioneering American environmental scientist, teacher and writer. She is best known as lead author of the influential book The Limits to Growth, which made headlines around the world.- Life :Born in Elgin, Illinois, Meadows was educated in science, receiving a B.A...
- Peter SengePeter SengePeter Michael Senge is an American scientist and director of the Center for Organizational Learning at the MIT Sloan School of Management. He is known as author of the book The Fifth Discipline: The art and practice of the learning organization from 1990...
- John StermanJohn StermanJohn David Sterman is the Jay W. Forrester Professor of Management, and the current director of the MIT System Dynamics Group at the MIT Sloan School of Management. He is also co-faculty at the New England Complex Systems Institute. He is mostly considered as the current leader of the System...
External links
- Study Prepared for the U.S. Department of Energy's Introducing System Dynamics -
- Desert Island Dynamics "An Annotated Survey of the Essential System Dynamics Literature"

