
Space Interferometry Mission
Encyclopedia
The Space Interferometry Mission, or SIM, also known as SIM Lite (formerly known as SIM PlanetQuest), was a planned space telescope
developed by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), in conjunction with contractor Northrop Grumman
. One of the main goals of the mission was the hunt for Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of nearby stars other than the Sun. SIM was postponed several times and finally cancelled in 2010.
In addition to hunting for extrasolar planets, SIM would have helped astronomers construct a map of the Milky Way galaxy. Other important tasks would have included collecting data to help pinpoint stellar masses for specific types of star
s, assisting in the determination of the spatial distribution of dark matter
in the Milky Way and in the Local Group of galaxies and using the gravitational microlensing
effect to measure the mass of stars.
The spacecraft would have used optical interferometry
to accomplish these and other scientific goals. This technique collects light with multiple mirrors (in SIM’s case, two) which is combined to make an interference pattern which can be very precisely measured.
The initial contracts for SIM Lite were awarded in 1998, totaling US$
200 million. Work on the SIM project required scientists and engineers to move through eight specific new technology milestones, and by November 2006, all eight had been completed.
SIM Lite was originally scheduled for a 2005 launch, aboard an Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV). As a result of continued budget cuts, the launch date has been pushed back at least five times. NASA has set a preliminary launch date for 2015 and U.S. federal budget documents confirm that a launch date is expected "no earlier" than 2015. The budget cuts to SIM Lite are expected to continue through FY 2010. As of February 2007, many of the engineers working on the SIM program had moved on to other areas and projects, and NASA directed the project to allocate its resources toward engineering risk reduction. However, the preliminary budget for NASA for 2008 included zero dollars for SIM.
In December 2007, the Congress restored funding for fiscal year 2008 as part of an omnibus appropriations bill which the President later signed. At the same time the Congress directed NASA to move the mission forward to the development phase. As of the end of 2009, the project continues its risk reduction work while NASA’s decision on the project’s future awaits the findings and recommendations of the Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey
, Astro2010, performed by the National Academy of Sciences, due in the second half of 2010.
On August 13, 2010, the Astro2010 Decadal Report was released and did not recommend that NASA continue the development of the SIM Lite Astrometric Observatory. This prompted NASA Astronomy and Physics Director, Jon Morse, to issue a letter on September 24, 2010 to the SIM Lite project manager, informing him that NASA was discontinuing its sponsorship of the SIM Lite mission and directing the project to discontinue Phase B activities immediately or as soon as practical. Accordingly, all SIM Lite activities were closed down by the end of calendar year 2010.
 SIM Lite would have operated in an Earth-trailing heliocentric orbit
SIM Lite would have operated in an Earth-trailing heliocentric orbit
. The SIM would have drifted away from Earth at the rate of 0.1 AU
per year. At the end of the planned mission, it would have reached a distance of 82 million km from Earth. This would have taken approximately 5½ years. The Sun would have continuously shone on the spacecraft, allowing it to avoid the occultations of target stars and eclipses of the sun that would occur in an Earth orbit.
Had it been launched, SIM would have performed scientific research for five years.
hunting space telescope ever built. Through the technique of interferometry
the spacecraft would be able to detect Earth-sized planets. SIM Lite will perform its search for nearby, Earth-like planets by looking for the "wobble
" in the parent star's apparent motion as the planet orbits. The spacecraft will accomplish this task to an accuracy of one millionth of an arcsecond, or the thickness of a nickel viewed at the distance from Earth to the Moon
. Titled the Deep Search, the planet hunting program is intended to search approximately 60 nearby stars for terrestrial planets (like Earth
and Venus
) in the habitable zone (where liquid water can exist throughout a full revolution (one “year”) of the planet around its star). The Deep Search is the most demanding in terms of astrometric
accuracy, hence the name, Deep Search. This program will use the full capability of the SIM Lite spacecraft to make its measurements.
A flexible search strategy tunes SIM Lite's mass sensitivity at each star to a desired level in the habitable planet search. The value of ηEarth (Eta_Earth), the fraction of stars carrying Earth-analog planets, will be estimated by the Kepler Mission
some time before SIM Lite launches. One strategy for a habitable planet search is to do a 'deeper' search (i.e. to lower mass sensitivity in the habitable zone) of a smaller number of targets if Earth analogs are common. A 'shallower' search of a larger number of targets could be done if Earth analogs are rarer. For example, assuming that 40% of mission time is allocated for the planet search, SIM Lite could survey:
Aside from searching for Earth-sized planets SIM Lite was scheduled to perform what has been dubbed the "Broad Survey". The Broad Survey would have looked at approximately 1,500 stars to help determine the abundance of Neptune
-mass and larger planets around all star-types in Earth's sector of the Milky Way
.
 A third part of the planet finding mission was the search for Jupiter
A third part of the planet finding mission was the search for Jupiter
-mass planets around young stars. The survey would have helped scientists understand more about solar system formation, including the occurrence of hot Jupiters. This portion of the planet hunt is designed to study systems with one or more Jupiter mass planets before the system has reached long term equilibrium. Planet hunting techniques using a star’s radial velocity cannot measure the regular, tiny to-and-fro wobble motions induced by planets against the strong atmospheric activity of a youthful star. It is through the techniques pioneered by Albert Michelson that the SIM will be able to execute its three primary planet-finding missions.
The mission's planet finding component was set up to serve as an important complement to the future missions designed to image and measure terrestrial and other exoplanets. SIM Lite will perform an important task that these missions will not be capable of: determining planet masses. Another task that the SIM was envisioned to perform for the future missions will include providing the orbital characteristics of the planets. With this knowledge other missions can estimate the optimal times and projected star-planet separation angles for them to observe the terrestrial (and other) planets SIM has detected.
 Another key aspect of SIM Lite's future mission was determining the upper and lower limits of star's masses. Today, scientists understand that there are limits to the how small or large a star can be. Objects that are too small lack the internal pressure
Another key aspect of SIM Lite's future mission was determining the upper and lower limits of star's masses. Today, scientists understand that there are limits to the how small or large a star can be. Objects that are too small lack the internal pressure
to initiate thermonuclear fusion, which is what causes a star to shine. These objects are known as brown dwarf
s and represent the lower end of the stellar mass scale. Stars that are too large become unstable and explode in a supernova
.
Part of the SIM's mission is to provide pinpoint measurements for the two extremes in stellar mass and evolution. The telescope will not be able to measure the mass of every star in the Galaxy, since there are over 200 billion, but instead, it will take a "population census." Through this technique, SIM will be able to output accurate masses for representative examples for nearly every star type, including brown dwarfs, hot white dwarf
s, red giant star
s, and elusive black hole
s. Current space telescopes, including NASA's Hubble Space Telescope
, can accurately measure mass for some types of stars, but not all. Estimates put the range for stellar mass somewhere between 8% the mass of the Sun
and in excess of 60 times the mass of the Sun. The entire study will be focused on binary star
systems, stars coupled through a mutual gravitational attraction.
 Interferometric measurements of stellar positions over the course of the mission will permit SIM to precisely measure the distances between stars throughout the Milky Way
Interferometric measurements of stellar positions over the course of the mission will permit SIM to precisely measure the distances between stars throughout the Milky Way
. This will allow astronomers to create a "roadmap" of the Galaxy which will answer many questions about its shape and size.
Currently, astronomers know little about the shape and size of our galaxy relative to what they know about other galaxies; it is difficult to observe the entire Milky Way from the inside. A good analogy is trying to observe a marching band as a member of the band. Observing other galaxies is much easier because humans are outside of those galaxies. Steven Majewski and his team plan to use SIM Lite to help determine not only the shape and size of the Galaxy but also the distribution of its mass and the motion of its stars.
SIM Lite measurements of Milky Way stars will yield data to understand four topics: fundamental Galactic parameters, the Oort Limit
, disk mass potential, and mass of the Galaxy to large radii. The first, fundamental Galactic parameters, is aimed at answering key questions about the size, shape and the rotation rate of the Milky Way. The team hopes to more accurately determine the distance from the Sun to the Galactic center
. The second topic, the Oort Limit, will attempt to determine the mass of the Galactic disk.
The third project topic is disk mass potential. This topic is designed to make measurements of the distances to disk stars as well as their proper motions. The results of the third topic of study will be combined with the results of the fundamental Galactic parameters portion of the study to determine the Solar System's position and velocity in the Galaxy. The final topic deals with dark matter distribution in the Milky Way. SIM data will be used to create a three-dimensional
model of mass distribution in the Galaxy, out to a radius of 270 kiloparsecs (kps). They will then use two different tests to determine the Galactic potential at large radii.
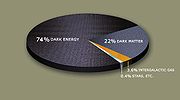 Dark matter is the matter in the universe that cannot be seen. Because of the gravitational effect it exerts on stars and galaxies, scientists know that approximately 80% of the matter in the universe is dark matter. The spatial distribution of dark matter
Dark matter is the matter in the universe that cannot be seen. Because of the gravitational effect it exerts on stars and galaxies, scientists know that approximately 80% of the matter in the universe is dark matter. The spatial distribution of dark matter
in the universe is largely unknown; SIM Lite will help scientists determine an answer to this question through another integral part of its mission.
The strongest evidence for dark matter comes from galactic motion. Galaxies rotate much faster than the amount of visible matter
suggests they should; the gravity from the ordinary matter is not enough to hold the galaxy together. Scientists theorize that the galaxy is held together by huge quantities of dark matter. Similarly, clusters of galaxies do not appear to have enough visible matter to gravitationally balance the high speed motions of their component galaxies.
Besides measuring stellar motions within the Milky Way, SIM Lite will measure the internal and average galactic motion of some of the neighboring galaxies near the Milky Way. Many of these measurements will be the first of their kind. The telescope's measurements will be used in conjunction with other, currently available, data to provide astronomers with the first total mass measurements of individual galaxies. These numbers will enable scientists to estimate the spatial distribution of dark matter in the Local Group of galaxies, and by extension throughout the universe.
and Hughes Danbury Optical Systems to conduct the study. In 1998, TRW Inc. was selected as the contractor for the SIM Lite project; Northrup Grumman acquired part of TRW in 2002 and took over the contract. Also selected was Lockheed Martin Missiles and Space
located in Sunnyvale, California
. The two contracts, which included the mission formulation and implementation phases, were announced in September 1998 and worth a total of over US$
200 million. The formulation phase of the mission included initial mission design and planning for the full scale implementation of the mission. At the time of the NASA announcement, launch was scheduled for 2005 and the mission was part of the Origins Program
, a series of missions designed to answer questions such as how and why humans are on Earth.
In August 2000, NASA asked project managers to consider looking at the Space Shuttle
, instead of the previously proposed EELV, as a launch vehicle. In late November 2000, NASA announced that the project's scientific team was selected. The group included notable names from the world of extrasolar planet
research including Geoffrey Marcy
. The entire group consisted of 10 principal investigators and five mission specialists. At the time of this NASA announcement launch was scheduled for 2009 and the mission was still part of the Origins Program.
 One of the new technologies developed for the mission were high-tech "rulers", capable of making measurements in increments a fraction of the width of a hydrogen
One of the new technologies developed for the mission were high-tech "rulers", capable of making measurements in increments a fraction of the width of a hydrogen
atom In addition, the rulers were developed to work as a network
. The mission team also created "shock absorber
s" to alleviate the effects of tiny vibrations in the spacecraft which would impede accurate measurements. Another one of the milestones involved combining the new "rulers" and "shock absorbers" to prove that the Space Interferometry Mission craft could detect the tiny wobbles in stars caused by Earth-sized planets. The fifth of the technology milestones required the demonstration of the Microarcsecond Metrology
Testbed
at a performance of 3,200 picometers over its wide angle field of regard. The wide angle measurements will be used to determine the fixed positions of stars each time they are measured. This level of performance demonstrated SIM Lite's ability to calculate the astrometric
grid. Another key development, known as gridless narrow-angle astrometry (GNAA), was the ability to apply the measurement capability worked out in the wide angle milestone and take it a step further, into narrow-angle measurements. Aiming to give an accuracy of 1 micro-arcsecond to the early stages of the SIM, the technique allows star positions to be measured without first setting up a grid of reference stars; instead, it sets up a reference frame using several reference stars and a target star observed from different locations, and star positions are calculated using delay measurements from the separate observations. The narrow angle field will be used by SIM to detect terrestrial planets; the team applied the same criteria to both the narrow and wide angle measurements. The final requirement before beginning work on flight controls was to make sure that all of the systems developed for the mission worked cohesively; this final NASA technology goal was completed last as it was dependent upon the others.
The project has been in Phase B since June 2003, (and that is still the case as of July 2010). Jet Propulsion Laboratory's "Phase B" is called the "Preliminary Design" phase. Phase B further develops the mission concept developed during Phase A to prepare the project for entry into the Implementation Phase of the project. Requirements are defined, schedules are determined, and specifications are prepared to initiate system design and development." In addition, as part of Phase B, the SIM Lite project will go through a number of reviews by NASA including System Requirements Review, System Design Review, and Non-Advocate Review. During this phase, experiments will be proposed, peer reviewed, and eventually selected by NASA's Office of Space Science. Experiment selections are based on scientific value, cost, management, engineering, and safety. The project has been in Phase B since June 2003.
 The launch date for the SIM Lite mission has been pushed back at least five times. At the program's outset, in 1998, the launch was scheduled for 2005. By 2000, the launch date had been delayed until 2009, a date that held through 2003; though some project scientists cited 2008 in late 2000. Between 2004 and 2006, contractor Northrop Grumman, the company designing and developing SIM, listed a launch date of 2011 on their website. With the release of the FY 2007 NASA budget, predictions changed again, this time to a date no earlier than 2015 or 2016. The delay of the launch date is primarily related to budget cuts made to the SIM Lite program. The 2007 change represented a difference of about three years from the 2006 launch date, outlined in NASA's FY 2006 budget as being two years behind 2005 budget predictions.
The launch date for the SIM Lite mission has been pushed back at least five times. At the program's outset, in 1998, the launch was scheduled for 2005. By 2000, the launch date had been delayed until 2009, a date that held through 2003; though some project scientists cited 2008 in late 2000. Between 2004 and 2006, contractor Northrop Grumman, the company designing and developing SIM, listed a launch date of 2011 on their website. With the release of the FY 2007 NASA budget, predictions changed again, this time to a date no earlier than 2015 or 2016. The delay of the launch date is primarily related to budget cuts made to the SIM Lite program. The 2007 change represented a difference of about three years from the 2006 launch date, outlined in NASA's FY 2006 budget as being two years behind 2005 budget predictions.
Other groups predict dates matching officially predicted launch dates; the NASA Exoplanet Science Institute (formerly the Michelson Science Center) at the California Institute of Technology
also sets the date at 2015. As of June 2008, NASA has postponed the launch date "indefinitely".
The launch date of the SIM mission cannot be predicted with any certainty. A May 2005 NASA operating plan put the mission into a replanning phase through the spring of 2006. No definitive mission schedule has been published on the SIM Lite website, maintained by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory
(JPL), as of April 2007, aside from the estimated launch date of 2015. When the launch does occur it is planned to be via an Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV), likely an Atlas V 521
or equivalent.
, the program is, "a coherent series of increasingly challenging projects, each complementary to the others and each mission building on the results and capabilities of those that preceded it as NASA searches for habitable planets outside of the solar system." The program, in addition to the Space Interferometry Mission, includes the Keck Interferometer and the Large Binocular Telescope
Interferometer. When originally approved in 1996, the mission was given a $700 million cap (in 1996 dollars) which included launch costs and five years of operation. The first contracts, for the preliminary architecture study, were worth $200,000 each.
 NASA's budget outlined plans for the three projects for fiscal year (FY) 2007. Of the three missions, SIM Lite was delayed further and the Keck Interferometer saw budget cuts. The 2007 NASA budget stipulated, "SIM Phase B activity will continue while new cost and schedule plans are developed, consistent with recent funding decisions." The funding decisions included a US$
NASA's budget outlined plans for the three projects for fiscal year (FY) 2007. Of the three missions, SIM Lite was delayed further and the Keck Interferometer saw budget cuts. The 2007 NASA budget stipulated, "SIM Phase B activity will continue while new cost and schedule plans are developed, consistent with recent funding decisions." The funding decisions included a US$
118.5 million cut over the FY 2006 NASA budget request for the Exoplanet Exploration Program. The budget also laid out projections for the program through the year 2010. Each year will have successive funding cuts, if compared to the 2006 request numbers. Starting with FY 2008, the Exoplanet Exploration Program will receive around $223.9 million less compared to 2006. The following years will have cuts of $155.2 million in 2009 and $172.5 million in 2010, compared to the 2006 request.
When SIM Lite entered what JPL terms "Phase B" in 2003 Fringes: Space Interferometry Mission Newsletter, called it a most important milestone on the way to a 2009 launch. The delays are budgetary in nature. In 2006, the mission received $117 million, an increase of $8.1 million over the previous year, but 2007 cuts amounted to $47.9 million less for the SIM program. In 2008, $128.7 million of the $223.9 million estimated to be cut from the Exoplanet Program budget will come from the SIM Lite mission. After an additional $51.9 million decrease in FY 2009, the program was reduced to $6 million in FY 2010 supplemented by substantial carryover from the previous year while awaiting the results of the Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey, Astro2010.
By February 2007 many of the budget cuts outlined in the FY 2007 budget were already being felt within the project. Engineers who worked on SIM were forced to find other areas to work in. A February 2007 editorial in the Space Interferometry Mission Newsletter described the situation as, "entirely due to budget pressures and priorities within the Science Mission Directorate at NASA (with) scientific motivation for the mission...as strong as ever." NASA, per the budget cuts, directed the SIM project to refocus its efforts toward engineering risk reduction
. As of the February 2007 newsletter the plans for the refocus were in the process of being completed.
SIM Lite project status as of April 2009 and August 2009 can be found on the JPL SIM public web site in the form of two submissions to the National Research Council (NRC) Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey (Astro2010) Request for Information, Part 1 and Part 2. While these documents use a 2015 launch date for reference in communicating schedule and budget, NASA has not yet set a launch date for SIM Lite and will not do so until after the Astro2010 Decadal report is released in mid- to late 2010.
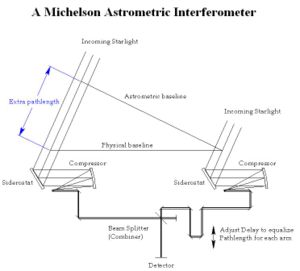 Interferometry is a technique pioneered by Albert Michelson in the 19th century. Optical interferometry, which has matured within the last two decades, combines the light of multiple telescopes so that exquisitely precise measurements can be made, akin to what might be accomplished with a single, much larger telescope. It is the interaction of light waves, called interference
Interferometry is a technique pioneered by Albert Michelson in the 19th century. Optical interferometry, which has matured within the last two decades, combines the light of multiple telescopes so that exquisitely precise measurements can be made, akin to what might be accomplished with a single, much larger telescope. It is the interaction of light waves, called interference
, that makes this possible. Interference can be used to cancel out the glare of bright stars or to measure distances and angles accurately. The construction of the word partially illustrates this: interfere + measure = interfer-o-metry. At radio wave
lengths of the electromagnetic spectrum
, interferometry has been used for more than 50 years to measure the structure of distant galaxies.
The SIM Lite telescope functions through optical interferometry
. SIM is composed of one science interferometer (50 cm collectors, 6 m separation [baseline]), a guide interferometer (30 cm collectors, 4.2 m baseline), and a guide telescope (30 cm aperture). The sophisticated guide telescope stabilizes instrument pointing in the third dimension. The spacecraft's operational limiting magnitude goes down to 20 at 20 millionths of an arcsecond (μas) and its planet-finding, astrometric accuracy of 1.12 µas is for single measurements. The accuracy of its global, all-sky astrometric grid is 4 µas.
SIM’s design since 2000 consists of two light collectors (strictly speaking, they are Mersenne telescopes) mounted on opposite ends of a six-meter structure. The observatory will be able to measure the small wobbles in stars and detect the planets causing them down to one Earth mass at distances up to 33 light years (10 parsecs) from the Sun.
Space observatory
A space observatory is any instrument in outer space which is used for observation of distant planets, galaxies, and other outer space objects...
developed by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), in conjunction with contractor Northrop Grumman
Northrop Grumman
Northrop Grumman Corporation is an American global aerospace and defense technology company formed by the 1994 purchase of Grumman by Northrop. The company was the fourth-largest defense contractor in the world as of 2010, and the largest builder of naval vessels. Northrop Grumman employs over...
. One of the main goals of the mission was the hunt for Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of nearby stars other than the Sun. SIM was postponed several times and finally cancelled in 2010.
In addition to hunting for extrasolar planets, SIM would have helped astronomers construct a map of the Milky Way galaxy. Other important tasks would have included collecting data to help pinpoint stellar masses for specific types of star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
s, assisting in the determination of the spatial distribution of dark matter
Dark matter
In astronomy and cosmology, dark matter is matter that neither emits nor scatters light or other electromagnetic radiation, and so cannot be directly detected via optical or radio astronomy...
in the Milky Way and in the Local Group of galaxies and using the gravitational microlensing
Gravitational microlensing
Gravitational microlensing is an astronomical phenomenon due to the gravitational lens effect. It can be used to detect objects ranging from the mass of a planet to the mass of a star, regardless of the light they emit. Typically, astronomers can only detect bright objects that emit lots of light ...
effect to measure the mass of stars.
The spacecraft would have used optical interferometry
Interferometry
Interferometry refers to a family of techniques in which electromagnetic waves are superimposed in order to extract information about the waves. An instrument used to interfere waves is called an interferometer. Interferometry is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy,...
to accomplish these and other scientific goals. This technique collects light with multiple mirrors (in SIM’s case, two) which is combined to make an interference pattern which can be very precisely measured.
The initial contracts for SIM Lite were awarded in 1998, totaling US$
United States dollar
The United States dollar , also referred to as the American dollar, is the official currency of the United States of America. It is divided into 100 smaller units called cents or pennies....
200 million. Work on the SIM project required scientists and engineers to move through eight specific new technology milestones, and by November 2006, all eight had been completed.
SIM Lite was originally scheduled for a 2005 launch, aboard an Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV). As a result of continued budget cuts, the launch date has been pushed back at least five times. NASA has set a preliminary launch date for 2015 and U.S. federal budget documents confirm that a launch date is expected "no earlier" than 2015. The budget cuts to SIM Lite are expected to continue through FY 2010. As of February 2007, many of the engineers working on the SIM program had moved on to other areas and projects, and NASA directed the project to allocate its resources toward engineering risk reduction. However, the preliminary budget for NASA for 2008 included zero dollars for SIM.
In December 2007, the Congress restored funding for fiscal year 2008 as part of an omnibus appropriations bill which the President later signed. At the same time the Congress directed NASA to move the mission forward to the development phase. As of the end of 2009, the project continues its risk reduction work while NASA’s decision on the project’s future awaits the findings and recommendations of the Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey
Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey
The Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey is a review of astronomy and astrophysics literature produced approximately every ten years by the National Research Council of the National Academy of Sciences in the United States. The report surveys the current state of the field, identifies research...
, Astro2010, performed by the National Academy of Sciences, due in the second half of 2010.
On August 13, 2010, the Astro2010 Decadal Report was released and did not recommend that NASA continue the development of the SIM Lite Astrometric Observatory. This prompted NASA Astronomy and Physics Director, Jon Morse, to issue a letter on September 24, 2010 to the SIM Lite project manager, informing him that NASA was discontinuing its sponsorship of the SIM Lite mission and directing the project to discontinue Phase B activities immediately or as soon as practical. Accordingly, all SIM Lite activities were closed down by the end of calendar year 2010.
Mission

Heliocentric orbit
A heliocentric orbit is an orbit around the Sun. All planets, comets, and asteroids in our Solar System are in such orbits, as are many artificial probes and pieces of debris. The moons of planets in the Solar System, by contrast, are not in heliocentric orbits as they orbit their respective planet...
. The SIM would have drifted away from Earth at the rate of 0.1 AU
Astronomical unit
An astronomical unit is a unit of length equal to about or approximately the mean Earth–Sun distance....
per year. At the end of the planned mission, it would have reached a distance of 82 million km from Earth. This would have taken approximately 5½ years. The Sun would have continuously shone on the spacecraft, allowing it to avoid the occultations of target stars and eclipses of the sun that would occur in an Earth orbit.
Had it been launched, SIM would have performed scientific research for five years.
Planet hunting
SIM Lite, when completed, will be the most powerful extrasolar planetExtrasolar planet
An extrasolar planet, or exoplanet, is a planet outside the Solar System. A total of such planets have been identified as of . It is now known that a substantial fraction of stars have planets, including perhaps half of all Sun-like stars...
hunting space telescope ever built. Through the technique of interferometry
Interferometry
Interferometry refers to a family of techniques in which electromagnetic waves are superimposed in order to extract information about the waves. An instrument used to interfere waves is called an interferometer. Interferometry is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy,...
the spacecraft would be able to detect Earth-sized planets. SIM Lite will perform its search for nearby, Earth-like planets by looking for the "wobble
Methods of detecting extrasolar planets
Any planet is an extremely faint light source compared to its parent star. In addition to the intrinsic difficulty of detecting such a faint light source, the light from the parent star causes a glare that washes it out...
" in the parent star's apparent motion as the planet orbits. The spacecraft will accomplish this task to an accuracy of one millionth of an arcsecond, or the thickness of a nickel viewed at the distance from Earth to the Moon
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
. Titled the Deep Search, the planet hunting program is intended to search approximately 60 nearby stars for terrestrial planets (like Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
and Venus
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun, orbiting it every 224.7 Earth days. The planet is named after Venus, the Roman goddess of love and beauty. After the Moon, it is the brightest natural object in the night sky, reaching an apparent magnitude of −4.6, bright enough to cast shadows...
) in the habitable zone (where liquid water can exist throughout a full revolution (one “year”) of the planet around its star). The Deep Search is the most demanding in terms of astrometric
Astrometry
Astrometry is the branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements of the positions and movements of stars and other celestial bodies. The information obtained by astrometric measurements provides information on the kinematics and physical origin of our Solar System and our Galaxy, the Milky...
accuracy, hence the name, Deep Search. This program will use the full capability of the SIM Lite spacecraft to make its measurements.
A flexible search strategy tunes SIM Lite's mass sensitivity at each star to a desired level in the habitable planet search. The value of ηEarth (Eta_Earth), the fraction of stars carrying Earth-analog planets, will be estimated by the Kepler Mission
Kepler Mission
The Kepler spacecraft is an American space observatory, the space-based portion of NASA's Kepler Mission to discover Earth-like planets orbiting other stars. The spacecraft is named in honor of the 17th-century German astronomer Johannes Kepler...
some time before SIM Lite launches. One strategy for a habitable planet search is to do a 'deeper' search (i.e. to lower mass sensitivity in the habitable zone) of a smaller number of targets if Earth analogs are common. A 'shallower' search of a larger number of targets could be done if Earth analogs are rarer. For example, assuming that 40% of mission time is allocated for the planet search, SIM Lite could survey:
- 65 stars for planets down to one Earth mass, in scaled 1 AU orbits, OR
- 149 stars for planets down to two Earth masses, in scaled 1 AU orbits, OR
- 239 stars for planets down to three Earth masses, in scaled 1 AU orbits.
Aside from searching for Earth-sized planets SIM Lite was scheduled to perform what has been dubbed the "Broad Survey". The Broad Survey would have looked at approximately 1,500 stars to help determine the abundance of Neptune
Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest planet from the Sun in the Solar System. Named for the Roman god of the sea, it is the fourth-largest planet by diameter and the third largest by mass. Neptune is 17 times the mass of Earth and is slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus, which is 15 times...
-mass and larger planets around all star-types in Earth's sector of the Milky Way
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
.

Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet within the Solar System. It is a gas giant with mass one-thousandth that of the Sun but is two and a half times the mass of all the other planets in our Solar System combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn,...
-mass planets around young stars. The survey would have helped scientists understand more about solar system formation, including the occurrence of hot Jupiters. This portion of the planet hunt is designed to study systems with one or more Jupiter mass planets before the system has reached long term equilibrium. Planet hunting techniques using a star’s radial velocity cannot measure the regular, tiny to-and-fro wobble motions induced by planets against the strong atmospheric activity of a youthful star. It is through the techniques pioneered by Albert Michelson that the SIM will be able to execute its three primary planet-finding missions.
The mission's planet finding component was set up to serve as an important complement to the future missions designed to image and measure terrestrial and other exoplanets. SIM Lite will perform an important task that these missions will not be capable of: determining planet masses. Another task that the SIM was envisioned to perform for the future missions will include providing the orbital characteristics of the planets. With this knowledge other missions can estimate the optimal times and projected star-planet separation angles for them to observe the terrestrial (and other) planets SIM has detected.
Stellar mass

Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
to initiate thermonuclear fusion, which is what causes a star to shine. These objects are known as brown dwarf
Brown dwarf
Brown dwarfs are sub-stellar objects which are too low in mass to sustain hydrogen-1 fusion reactions in their cores, which is characteristic of stars on the main sequence. Brown dwarfs have fully convective surfaces and interiors, with no chemical differentiation by depth...
s and represent the lower end of the stellar mass scale. Stars that are too large become unstable and explode in a supernova
Supernova
A supernova is a stellar explosion that is more energetic than a nova. It is pronounced with the plural supernovae or supernovas. Supernovae are extremely luminous and cause a burst of radiation that often briefly outshines an entire galaxy, before fading from view over several weeks or months...
.
Part of the SIM's mission is to provide pinpoint measurements for the two extremes in stellar mass and evolution. The telescope will not be able to measure the mass of every star in the Galaxy, since there are over 200 billion, but instead, it will take a "population census." Through this technique, SIM will be able to output accurate masses for representative examples for nearly every star type, including brown dwarfs, hot white dwarf
White dwarf
A white dwarf, also called a degenerate dwarf, is a small star composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. They are very dense; a white dwarf's mass is comparable to that of the Sun and its volume is comparable to that of the Earth. Its faint luminosity comes from the emission of stored...
s, red giant star
Red giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass in a late phase of stellar evolution. The outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius immense and the surface temperature low, somewhere from 5,000 K and lower...
s, and elusive black hole
Black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime from which nothing, not even light, can escape. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass will deform spacetime to form a black hole. Around a black hole there is a mathematically defined surface called an event horizon that...
s. Current space telescopes, including NASA's Hubble Space Telescope
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was carried into orbit by a Space Shuttle in 1990 and remains in operation. A 2.4 meter aperture telescope in low Earth orbit, Hubble's four main instruments observe in the near ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared...
, can accurately measure mass for some types of stars, but not all. Estimates put the range for stellar mass somewhere between 8% the mass of the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
and in excess of 60 times the mass of the Sun. The entire study will be focused on binary star
Binary star
A binary star is a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common center of mass. The brighter star is called the primary and the other is its companion star, comes, or secondary...
systems, stars coupled through a mutual gravitational attraction.
Galactic mapping

Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
. This will allow astronomers to create a "roadmap" of the Galaxy which will answer many questions about its shape and size.
Currently, astronomers know little about the shape and size of our galaxy relative to what they know about other galaxies; it is difficult to observe the entire Milky Way from the inside. A good analogy is trying to observe a marching band as a member of the band. Observing other galaxies is much easier because humans are outside of those galaxies. Steven Majewski and his team plan to use SIM Lite to help determine not only the shape and size of the Galaxy but also the distribution of its mass and the motion of its stars.
SIM Lite measurements of Milky Way stars will yield data to understand four topics: fundamental Galactic parameters, the Oort Limit
Oort Limit
There are two definitions of the Oort limit:* the outer boundary of the Oort cloud. The current estimate is about 100,000 astronomical units from the Sun, which is approximately 1/3 of the distance to the nearest star .* the estimate of the local density of matter in the Sun's vicinity.-...
, disk mass potential, and mass of the Galaxy to large radii. The first, fundamental Galactic parameters, is aimed at answering key questions about the size, shape and the rotation rate of the Milky Way. The team hopes to more accurately determine the distance from the Sun to the Galactic center
Galactic Center
The Galactic Center is the rotational center of the Milky Way galaxy. It is located at a distance of 8.33±0.35 kpc from the Earth in the direction of the constellations Sagittarius, Ophiuchus, and Scorpius where the Milky Way appears brightest...
. The second topic, the Oort Limit, will attempt to determine the mass of the Galactic disk.
The third project topic is disk mass potential. This topic is designed to make measurements of the distances to disk stars as well as their proper motions. The results of the third topic of study will be combined with the results of the fundamental Galactic parameters portion of the study to determine the Solar System's position and velocity in the Galaxy. The final topic deals with dark matter distribution in the Milky Way. SIM data will be used to create a three-dimensional
Three-dimensional space
Three-dimensional space is a geometric 3-parameters model of the physical universe in which we live. These three dimensions are commonly called length, width, and depth , although any three directions can be chosen, provided that they do not lie in the same plane.In physics and mathematics, a...
model of mass distribution in the Galaxy, out to a radius of 270 kiloparsecs (kps). They will then use two different tests to determine the Galactic potential at large radii.
Dark matter

Dark matter
In astronomy and cosmology, dark matter is matter that neither emits nor scatters light or other electromagnetic radiation, and so cannot be directly detected via optical or radio astronomy...
in the universe is largely unknown; SIM Lite will help scientists determine an answer to this question through another integral part of its mission.
The strongest evidence for dark matter comes from galactic motion. Galaxies rotate much faster than the amount of visible matter
Matter
Matter is a general term for the substance of which all physical objects consist. Typically, matter includes atoms and other particles which have mass. A common way of defining matter is as anything that has mass and occupies volume...
suggests they should; the gravity from the ordinary matter is not enough to hold the galaxy together. Scientists theorize that the galaxy is held together by huge quantities of dark matter. Similarly, clusters of galaxies do not appear to have enough visible matter to gravitationally balance the high speed motions of their component galaxies.
Besides measuring stellar motions within the Milky Way, SIM Lite will measure the internal and average galactic motion of some of the neighboring galaxies near the Milky Way. Many of these measurements will be the first of their kind. The telescope's measurements will be used in conjunction with other, currently available, data to provide astronomers with the first total mass measurements of individual galaxies. These numbers will enable scientists to estimate the spatial distribution of dark matter in the Local Group of galaxies, and by extension throughout the universe.
Beginnings
The Space Interferometry Mission began as a four-month preliminary architecture study in March 1997. NASA selected TRW's Space & Electronics Group, Eastman KodakEastman Kodak
Eastman Kodak Company is a multinational imaging and photographic equipment, materials and services company headquarted in Rochester, New York, United States. It was founded by George Eastman in 1892....
and Hughes Danbury Optical Systems to conduct the study. In 1998, TRW Inc. was selected as the contractor for the SIM Lite project; Northrup Grumman acquired part of TRW in 2002 and took over the contract. Also selected was Lockheed Martin Missiles and Space
Lockheed Martin
Lockheed Martin is an American global aerospace, defense, security, and advanced technology company with worldwide interests. It was formed by the merger of Lockheed Corporation with Martin Marietta in March 1995. It is headquartered in Bethesda, Maryland, in the Washington Metropolitan Area....
located in Sunnyvale, California
Sunnyvale, California
Sunnyvale is a city in Santa Clara County, California, United States. It is one of the major cities that make up the Silicon Valley located in the San Francisco Bay Area...
. The two contracts, which included the mission formulation and implementation phases, were announced in September 1998 and worth a total of over US$
United States dollar
The United States dollar , also referred to as the American dollar, is the official currency of the United States of America. It is divided into 100 smaller units called cents or pennies....
200 million. The formulation phase of the mission included initial mission design and planning for the full scale implementation of the mission. At the time of the NASA announcement, launch was scheduled for 2005 and the mission was part of the Origins Program
Origins Program
NASA's Origins program is a decades-long study addressing the origins of the universe, various astronomical bodies, and life. The Origins program was started in the 1990s.So far, it consists of the following missions:* Hubble Space Telescope*...
, a series of missions designed to answer questions such as how and why humans are on Earth.
In August 2000, NASA asked project managers to consider looking at the Space Shuttle
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle was a manned orbital rocket and spacecraft system operated by NASA on 135 missions from 1981 to 2011. The system combined rocket launch, orbital spacecraft, and re-entry spaceplane with modular add-ons...
, instead of the previously proposed EELV, as a launch vehicle. In late November 2000, NASA announced that the project's scientific team was selected. The group included notable names from the world of extrasolar planet
Extrasolar planet
An extrasolar planet, or exoplanet, is a planet outside the Solar System. A total of such planets have been identified as of . It is now known that a substantial fraction of stars have planets, including perhaps half of all Sun-like stars...
research including Geoffrey Marcy
Geoffrey Marcy
Geoffrey W. Marcy is an American astronomer, who is currently Professor of Astronomy at the University of California, Berkeley, famous for discovering more extrasolar planets than anyone else, 70 out of the first 100 to be discovered, along with R...
. The entire group consisted of 10 principal investigators and five mission specialists. At the time of this NASA announcement launch was scheduled for 2009 and the mission was still part of the Origins Program.
New technologies
SIM's new technology is meant to lead to the development of telescopes powerful enough to take images of Earth-like extrasolar planets orbiting distant stars and to determine whether those planets are able to sustain life. NASA has already started developing future missions that will build on SIM's technological legacy. The technological development phase of the mission was completed in November 2006 with the announcement that the eight, mission-technology-milestones set by NASA were reached. The milestones were necessary steps in the technological development before flight control instruments could begin to be designed. The completion of each milestone meant that new systems had to be developed for nanometer control as well as picometer knowledge technology; these systems enable the telescope to make its accurate measurements with such extreme accuracy.
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
atom In addition, the rulers were developed to work as a network
Network analysis (electrical circuits)
A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are a number of different techniques for achieving this...
. The mission team also created "shock absorber
Shock absorber
A shock absorber is a mechanical device designed to smooth out or damp shock impulse, and dissipate kinetic energy. It is a type of dashpot.-Nomenclature:...
s" to alleviate the effects of tiny vibrations in the spacecraft which would impede accurate measurements. Another one of the milestones involved combining the new "rulers" and "shock absorbers" to prove that the Space Interferometry Mission craft could detect the tiny wobbles in stars caused by Earth-sized planets. The fifth of the technology milestones required the demonstration of the Microarcsecond Metrology
Metrology
Metrology is the science of measurement. Metrology includes all theoretical and practical aspects of measurement. The word comes from Greek μέτρον , "measure" + "λόγος" , amongst others meaning "speech, oration, discourse, quote, study, calculation, reason"...
Testbed
Testbed
A testbed is a platform for experimentation of large development projects. Testbeds allow for rigorous, transparent, and replicable testing of scientific theories, computational tools, and new technologies.The term is used across many disciplines to describe a development environment that is...
at a performance of 3,200 picometers over its wide angle field of regard. The wide angle measurements will be used to determine the fixed positions of stars each time they are measured. This level of performance demonstrated SIM Lite's ability to calculate the astrometric
Astrometry
Astrometry is the branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements of the positions and movements of stars and other celestial bodies. The information obtained by astrometric measurements provides information on the kinematics and physical origin of our Solar System and our Galaxy, the Milky...
grid. Another key development, known as gridless narrow-angle astrometry (GNAA), was the ability to apply the measurement capability worked out in the wide angle milestone and take it a step further, into narrow-angle measurements. Aiming to give an accuracy of 1 micro-arcsecond to the early stages of the SIM, the technique allows star positions to be measured without first setting up a grid of reference stars; instead, it sets up a reference frame using several reference stars and a target star observed from different locations, and star positions are calculated using delay measurements from the separate observations. The narrow angle field will be used by SIM to detect terrestrial planets; the team applied the same criteria to both the narrow and wide angle measurements. The final requirement before beginning work on flight controls was to make sure that all of the systems developed for the mission worked cohesively; this final NASA technology goal was completed last as it was dependent upon the others.
Status after 2006
Between the end of April and June 2006 the project completed three engineering milestones and from November 2–November 8, 2006 SIM completed a "Spacecraft Internal Design Review." As of June 2008, all of the eight engineering milestones have been successfully completed.The project has been in Phase B since June 2003, (and that is still the case as of July 2010). Jet Propulsion Laboratory's "Phase B" is called the "Preliminary Design" phase. Phase B further develops the mission concept developed during Phase A to prepare the project for entry into the Implementation Phase of the project. Requirements are defined, schedules are determined, and specifications are prepared to initiate system design and development." In addition, as part of Phase B, the SIM Lite project will go through a number of reviews by NASA including System Requirements Review, System Design Review, and Non-Advocate Review. During this phase, experiments will be proposed, peer reviewed, and eventually selected by NASA's Office of Space Science. Experiment selections are based on scientific value, cost, management, engineering, and safety. The project has been in Phase B since June 2003.
Planned launch

Other groups predict dates matching officially predicted launch dates; the NASA Exoplanet Science Institute (formerly the Michelson Science Center) at the California Institute of Technology
California Institute of Technology
The California Institute of Technology is a private research university located in Pasadena, California, United States. Caltech has six academic divisions with strong emphases on science and engineering...
also sets the date at 2015. As of June 2008, NASA has postponed the launch date "indefinitely".
The launch date of the SIM mission cannot be predicted with any certainty. A May 2005 NASA operating plan put the mission into a replanning phase through the spring of 2006. No definitive mission schedule has been published on the SIM Lite website, maintained by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory
Jet Propulsion Laboratory
Jet Propulsion Laboratory is a federally funded research and development center and NASA field center located in the San Gabriel Valley area of Los Angeles County, California, United States. The facility is headquartered in the city of Pasadena on the border of La Cañada Flintridge and Pasadena...
(JPL), as of April 2007, aside from the estimated launch date of 2015. When the launch does occur it is planned to be via an Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV), likely an Atlas V 521
Atlas V
Atlas V is an active expendable launch system in the Atlas rocket family. Atlas V was formerly operated by Lockheed Martin, and is now operated by the Lockheed Martin-Boeing joint venture United Launch Alliance...
or equivalent.
Budget
SIM Lite is considered the flagship mission of NASA's Exoplanet Exploration Program (formerly known as the Navigator Program). According to the 2007 Presidential Budget for NASANASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
, the program is, "a coherent series of increasingly challenging projects, each complementary to the others and each mission building on the results and capabilities of those that preceded it as NASA searches for habitable planets outside of the solar system." The program, in addition to the Space Interferometry Mission, includes the Keck Interferometer and the Large Binocular Telescope
Large Binocular Telescope
Large Binocular Telescope is an optical telescope for astronomy located on Mount Graham in the Pinaleno Mountains of southeastern Arizona, and is a part of the Mount Graham International Observatory...
Interferometer. When originally approved in 1996, the mission was given a $700 million cap (in 1996 dollars) which included launch costs and five years of operation. The first contracts, for the preliminary architecture study, were worth $200,000 each.

United States dollar
The United States dollar , also referred to as the American dollar, is the official currency of the United States of America. It is divided into 100 smaller units called cents or pennies....
118.5 million cut over the FY 2006 NASA budget request for the Exoplanet Exploration Program. The budget also laid out projections for the program through the year 2010. Each year will have successive funding cuts, if compared to the 2006 request numbers. Starting with FY 2008, the Exoplanet Exploration Program will receive around $223.9 million less compared to 2006. The following years will have cuts of $155.2 million in 2009 and $172.5 million in 2010, compared to the 2006 request.
When SIM Lite entered what JPL terms "Phase B" in 2003 Fringes: Space Interferometry Mission Newsletter, called it a most important milestone on the way to a 2009 launch. The delays are budgetary in nature. In 2006, the mission received $117 million, an increase of $8.1 million over the previous year, but 2007 cuts amounted to $47.9 million less for the SIM program. In 2008, $128.7 million of the $223.9 million estimated to be cut from the Exoplanet Program budget will come from the SIM Lite mission. After an additional $51.9 million decrease in FY 2009, the program was reduced to $6 million in FY 2010 supplemented by substantial carryover from the previous year while awaiting the results of the Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey, Astro2010.
By February 2007 many of the budget cuts outlined in the FY 2007 budget were already being felt within the project. Engineers who worked on SIM were forced to find other areas to work in. A February 2007 editorial in the Space Interferometry Mission Newsletter described the situation as, "entirely due to budget pressures and priorities within the Science Mission Directorate at NASA (with) scientific motivation for the mission...as strong as ever." NASA, per the budget cuts, directed the SIM project to refocus its efforts toward engineering risk reduction
Risk reduction
Risk reduction may refer to:* Absolute risk reduction or Relative risk reduction, statistical descriptors of an intervention.* Risk management* Safety Integrity Level* Hedge...
. As of the February 2007 newsletter the plans for the refocus were in the process of being completed.
SIM Lite project status as of April 2009 and August 2009 can be found on the JPL SIM public web site in the form of two submissions to the National Research Council (NRC) Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey (Astro2010) Request for Information, Part 1 and Part 2. While these documents use a 2015 launch date for reference in communicating schedule and budget, NASA has not yet set a launch date for SIM Lite and will not do so until after the Astro2010 Decadal report is released in mid- to late 2010.
Optical interferometry

Electromagnetic interference
Electromagnetic interference is disturbance that affects an electrical circuit due to either electromagnetic induction or electromagnetic radiation emitted from an external source. The disturbance may interrupt, obstruct, or otherwise degrade or limit the effective performance of the circuit...
, that makes this possible. Interference can be used to cancel out the glare of bright stars or to measure distances and angles accurately. The construction of the word partially illustrates this: interfere + measure = interfer-o-metry. At radio wave
Radio Wave
Radio Wave may refer to:*Radio frequency*Radio Wave 96.5, a radio station in Blackpool, UK...
lengths of the electromagnetic spectrum
Electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. The "electromagnetic spectrum" of an object is the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by that particular object....
, interferometry has been used for more than 50 years to measure the structure of distant galaxies.
The SIM Lite telescope functions through optical interferometry
Optical interferometry
Optical interferometry combines two or more light waves in an opticalinstrument in such a way that interference occurs between them.Early interferometers used white light sources and also monochromatic light from atomic sources...
. SIM is composed of one science interferometer (50 cm collectors, 6 m separation [baseline]), a guide interferometer (30 cm collectors, 4.2 m baseline), and a guide telescope (30 cm aperture). The sophisticated guide telescope stabilizes instrument pointing in the third dimension. The spacecraft's operational limiting magnitude goes down to 20 at 20 millionths of an arcsecond (μas) and its planet-finding, astrometric accuracy of 1.12 µas is for single measurements. The accuracy of its global, all-sky astrometric grid is 4 µas.
SIM’s design since 2000 consists of two light collectors (strictly speaking, they are Mersenne telescopes) mounted on opposite ends of a six-meter structure. The observatory will be able to measure the small wobbles in stars and detect the planets causing them down to one Earth mass at distances up to 33 light years (10 parsecs) from the Sun.

