Seyferth-Gilbert homologation
Encyclopedia
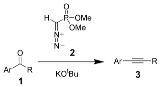
The Seyferth–Gilbert homologation is a the chemical reaction
of an aryl
ketone
1 (or aldehyde
) with dimethyl (diazomethyl)phosphonate 2 and potassium tert-butoxide
to give substituted alkyne
s 3. Dimethyl (diazomethyl)phosphonate 2 is often called the Seyferth–Gilbert reagent.
 This reaction is called a homologation because the product has exactly one additional carbon
This reaction is called a homologation because the product has exactly one additional carbon
more than the starting material.
diazo
-intermediate Fa and Fb. The generation of nitrogen
gas gives a vinyl
carbene
G, which via a 1,2-migration
forms the desired alkyne H.
and potassium carbonate
. Reaction of Bestmann's reagent with aldehydes gives terminal alkynes often in very high yield.
 The use of the milder potassium carbonate makes this procedure much more compatible with a wide variety of functional group
The use of the milder potassium carbonate makes this procedure much more compatible with a wide variety of functional group
s.
Another modification for less reactive aldehydes is made by replacement of potassium carbonate with caesium carbonate
in MeOH and results in a drastic yield increase.
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
of an aryl
Aryl
In the context of organic molecules, aryl refers to any functional group or substituent derived from an aromatic ring, be it phenyl, naphthyl, thienyl, indolyl, etc....
ketone
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
1 (or aldehyde
Aldehyde
An aldehyde is an organic compound containing a formyl group. This functional group, with the structure R-CHO, consists of a carbonyl center bonded to hydrogen and an R group....
) with dimethyl (diazomethyl)phosphonate 2 and potassium tert-butoxide
Potassium tert-butoxide
Potassium tert-butoxide is the chemical compound with the formula 3COK. This colourless solid is a strong base useful in organic synthesis. It exists as a tetrameric cubane-like cluster...
to give substituted alkyne
Alkyne
Alkynes are hydrocarbons that have a triple bond between two carbon atoms, with the formula CnH2n-2. Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name acetylene also refers specifically to C2H2, known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature...
s 3. Dimethyl (diazomethyl)phosphonate 2 is often called the Seyferth–Gilbert reagent.

Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
more than the starting material.
Reaction mechanism
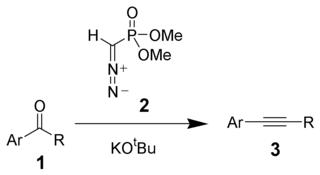
Deprotonation of the Seyferth–Gilbert reagent A gives an anion B, which reacts with the ketone to form the oxaphosphatane D. Elimination of dimethylphosphate E gives the vinylVinyl
A vinyl compound is any organic compound that contains a vinyl group ,which are derivatives of ethene, CH2=CH2, with one hydrogen atom replaced with some other group...
diazo
Diazo
Diazo refers to a type of organic compound called diazo compound that has two linked nitrogen atoms as a terminal functional group. The general formula is R2C=N2. The simplest example of a diazo compound is diazomethane...
-intermediate Fa and Fb. The generation of nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
gas gives a vinyl
Vinyl
A vinyl compound is any organic compound that contains a vinyl group ,which are derivatives of ethene, CH2=CH2, with one hydrogen atom replaced with some other group...
carbene
Carbene
In chemistry, a carbene is a molecule containing a neutral carbon atom with a valence of two and two unshared valence electrons. The general formula is RR'C:, but the carbon can instead be double-bonded to one group. The term "carbene" may also merely refer to the compound H2C:, also called...
G, which via a 1,2-migration
1,2-rearrangement
A 1,2-rearrangement or 1,2-migration or 1,2-shift or Whitmore 1,2-shift is an organic reaction where a substituent moves from one atom to another atom in a chemical compound. In a 1,2 shift the movement involves two adjacent atoms but moves over larger distances are possible...
forms the desired alkyne H.

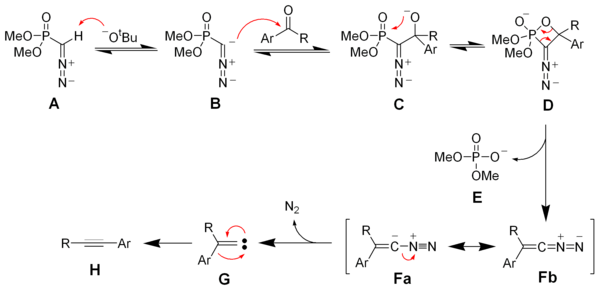
Bestmann modification
Dimethyl (diazomethyl)phosphonate can be generated in situ from dimethyl-1-diazo-2-oxopropylphosphonate (also called Bestmann's reagent) by reaction with methanolMethanol
Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol, wood alcohol, wood naphtha or wood spirits, is a chemical with the formula CH3OH . It is the simplest alcohol, and is a light, volatile, colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive odor very similar to, but slightly sweeter than, ethanol...
and potassium carbonate
Potassium carbonate
Potassium carbonate is a white salt, soluble in water , which forms a strongly alkaline solution. It can be made as the product of potassium hydroxide's absorbent reaction with carbon dioxide. It is deliquescent, often appearing a damp or wet solid...
. Reaction of Bestmann's reagent with aldehydes gives terminal alkynes often in very high yield.

Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
s.
Another modification for less reactive aldehydes is made by replacement of potassium carbonate with caesium carbonate
Caesium carbonate
Caesium carbonate is a white crystalline solid of formula Cs2CO3. It is more soluble in organic solvents than many other carbonates such as potassium carbonate, and therefore finds use as a base in organic chemistry....
in MeOH and results in a drastic yield increase.
See also
- Corey-Fuchs reactionCorey-Fuchs reactionThe Corey–Fuchs reaction, also known as the Ramirez–Corey–Fuchs reaction, is a series of chemical reactions designed to transform an aldehyde into an alkyne. The formation of the 1,1-dibromoolefins via phosphine-dibromomethylenes was originally discovered by Desai, McKelvie and Ramirez...
- Horner-Wadsworth-Emmons reactionHorner-Wadsworth-Emmons reactionThe Horner-Wadsworth-Emmons reaction is the chemical reaction of stabilized phosphonate carbanions with aldehydes to produce predominantly E-alkenes....
- Wittig reactionWittig reactionThe Wittig reaction is a chemical reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a triphenyl phosphonium ylide to give an alkene and triphenylphosphine oxide....

