
Saint Isaac's Cathedral
Encyclopedia
Saint Isaac's Cathedral or Isaakievskiy Sobor in Saint Petersburg
, Russia
is the largest Russian Orthodox cathedral
(sobor
) in the city. It is dedicated to Saint Isaac of Dalmatia, a patron saint
of Peter the Great
who had been born on the feast day of that saint.
 The church on St Isaac's Square
The church on St Isaac's Square
was ordered by Tsar
Alexander I
, to replace an earlier Rinaldiesque structure, and was the fourth consecutive church standing at this place. A specially appointed commission examined several designs, including that of the French-born architect
Auguste de Montferrand
(1786–1858), who had studied in the atelier of Napoleon's designer, Charles Percier
. Montferrand's design was criticised by some members of the commission for the dry and allegedly boring rhythm of its four identical pedimented octastyle porticos. It was also suggested that despite gigantic dimensions, the edifice would look squat and not very impressive. The emperor, who favoured the ponderous Empire style
of architecture, had to step in and solve the dispute in Montferrand's favour.
The cathedral took 40 years to construct, under Montferrand's direction, from 1818 to 1858. Under the Soviet
government, the building was stripped of religious trappings. In 1931, it was turned into the Antireligious Museum, The dove sculpture was removed, and replaced by a Foucault pendulum
. On April 12, 1931, the first public demonstration of the Foucault pendulum was held to visualise the Copernicus’s theory. In 1937, the museum was transformed into the museum of the Cathedral, and former collections were transferred to the Museum of the History of Religion (located in the Kazan Cathedral).
During World War II
, the dome was painted over in gray to avoid attracting attention from enemy aircraft. On its top, in the skylight, a geodesical intersection point was placed, with the objective of aiding in the location of enemy cannon.
With the fall of communism, the museum was removed and regular worship activity has resumed in the cathedral, but only in the left-hand side chapel. The main body of the cathedral is used for services on feast days only.
exterior expresses a traditional Russian-Byzantine formula: a Greek-cross groundplan with a large central dome and four subsidiary domes. It is similar to Andrea Palladio
's Villa La Rotonda, with a full dome on a high drum substituted for the Villa's low central saucer dome. The design of the cathedral in general and the dome in particular later influenced the design of the United States Capitol
in Washington, D.C.
and the Cathedral
in Helsinki
.
The exterior, which barely hints at the riotously rich interior, is faced with gray and pink stone, and features a total of 112 red granite column
s with Corinthian
capitals, each hewn and erected as a single block: 48 at ground level, 24 on the rotunda of the uppermost dome, 8 on each of four side domes, and 2 framing each of four windows. The rotunda is encircled by a walkway accessible to tourists. 24 statues gaze down from the roof, and another 24 from the top of the rotunda.
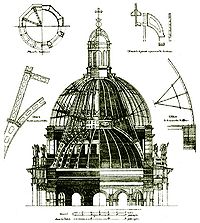 The cathedral's main dome
The cathedral's main dome
rises 101.5 metres (333 ft) and is plated
with pure gold. The dome is decorated with twelve statues
of angels by Josef Hermann. These angels were likely the first large sculptures produced by the then novel process of electrotyping
, which was an alternative to traditional bronze casting of sculptures. Montferrand's design of the dome is based on a supporting cast iron
structure. It was the third historical instance of cast iron cupola
after the Leaning Tower of Nevyansk
(1732) and Mainz Cathedral
(1826).
doors are covered in relief
s, patterned after the celebrated doors of the Battistero di San Giovanni (Florence)
in Florence
, designed by Lorenzo Ghiberti
. Suspended underneath the peak of the dome is a sculpted dove representing the Holy Spirit
. Internal features such as column
s, pilaster
s, floor, and statue of Montferrand are composed of multicolored granite
s and marble
s gathered from all parts of Russia. The iconostasis
is framed by eight columns of semiprecious stone: six of malachite
and two smaller ones of lazurite
. The four pediment
s are also richly sculpted.
The interior was originally decorated with scores of paintings by Carlo Brullo and other great Russian masters of the day. When these paintings began to deteriorate due to the cold, damp conditions inside the cathedral, Montferrand ordered them to be painstakingly reproduced as mosaic
s, a technique introduced in Russia by Mikhail Lomonosov
. This work was never completed.
and other engineers used many technological innovations in the construction of the building. The massive portico columns were raised with the use of enormous wooden frameworks before the walls were erected. The enormous building rests on 10,000 tree trunks that were sunk by an army of serfs into the marshy banks upon which the cathedral is situated. The dome was gilded by a technique similar to spraypainting; the solution used included toxic mercury
, the vapors of which caused the deaths of an unknown number of workers. A dozen gilded statues of angels, each six metres tall, face each other across the interior of the rotunda (see photo below). They were constructed using galvanoplastic technology, making them only millimeters thick and very lightweight. St. Isaac's Cathedral represents the first use of this technique in architecture.
The meticulous and painstakingly detailied work on constructing the St. Isaac's Cathedral took 40 years to complete. This left an expression in the Finnish language
rakentaa kuin Iisakin kirkkkoa (to build like St. Isaac's Church) for lengthy and never-ending megaproject
s.
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg is a city and a federal subject of Russia located on the Neva River at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea...
, Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
is the largest Russian Orthodox cathedral
Cathedral
A cathedral is a Christian church that contains the seat of a bishop...
(sobor
Sobor
A sobor is a council of bishops together with other clerical and lay delegates representing the church as a whole in matters of importance...
) in the city. It is dedicated to Saint Isaac of Dalmatia, a patron saint
Patron saint
A patron saint is a saint who is regarded as the intercessor and advocate in heaven of a nation, place, craft, activity, class, clan, family, or person...
of Peter the Great
Peter I of Russia
Peter the Great, Peter I or Pyotr Alexeyevich Romanov Dates indicated by the letters "O.S." are Old Style. All other dates in this article are New Style. ruled the Tsardom of Russia and later the Russian Empire from until his death, jointly ruling before 1696 with his half-brother, Ivan V...
who had been born on the feast day of that saint.
History

St Isaac's Square
Saint Isaac's Square or Isaakiyevskaya Ploshchad , known as Vorovsky Square between 1923 and 1944, in Saint Petersburg, Russia is a major city square sprawling between the Mariinsky Palace and Saint Isaac's Cathedral, which separates it from Senate Square...
was ordered by Tsar
Tsar
Tsar is a title used to designate certain European Slavic monarchs or supreme rulers. As a system of government in the Tsardom of Russia and Russian Empire, it is known as Tsarist autocracy, or Tsarism...
Alexander I
Alexander I of Russia
Alexander I of Russia , served as Emperor of Russia from 23 March 1801 to 1 December 1825 and the first Russian King of Poland from 1815 to 1825. He was also the first Russian Grand Duke of Finland and Lithuania....
, to replace an earlier Rinaldiesque structure, and was the fourth consecutive church standing at this place. A specially appointed commission examined several designs, including that of the French-born architect
Architect
An architect is a person trained in the planning, design and oversight of the construction of buildings. To practice architecture means to offer or render services in connection with the design and construction of a building, or group of buildings and the space within the site surrounding the...
Auguste de Montferrand
Auguste de Montferrand
Auguste de Montferrand was a French Neoclassical architect who worked primarily in Russia. His two best known works are the Saint Isaac's Cathedral and the Alexander Column in St. Petersburg.-Family:...
(1786–1858), who had studied in the atelier of Napoleon's designer, Charles Percier
Charles Percier
Charles Percier was a neoclassical French architect, interior decorator and designer, who worked in a close partnership with Pierre François Léonard Fontaine, originally his friend from student days...
. Montferrand's design was criticised by some members of the commission for the dry and allegedly boring rhythm of its four identical pedimented octastyle porticos. It was also suggested that despite gigantic dimensions, the edifice would look squat and not very impressive. The emperor, who favoured the ponderous Empire style
Neoclassicism
Neoclassicism is the name given to Western movements in the decorative and visual arts, literature, theatre, music, and architecture that draw inspiration from the "classical" art and culture of Ancient Greece or Ancient Rome...
of architecture, had to step in and solve the dispute in Montferrand's favour.
The cathedral took 40 years to construct, under Montferrand's direction, from 1818 to 1858. Under the Soviet
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
government, the building was stripped of religious trappings. In 1931, it was turned into the Antireligious Museum, The dove sculpture was removed, and replaced by a Foucault pendulum
Foucault pendulum
The Foucault pendulum , or Foucault's pendulum, named after the French physicist Léon Foucault, is a simple device conceived as an experiment to demonstrate the rotation of the Earth. While it had long been known that the Earth rotated, the introduction of the Foucault pendulum in 1851 was the...
. On April 12, 1931, the first public demonstration of the Foucault pendulum was held to visualise the Copernicus’s theory. In 1937, the museum was transformed into the museum of the Cathedral, and former collections were transferred to the Museum of the History of Religion (located in the Kazan Cathedral).
During World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, the dome was painted over in gray to avoid attracting attention from enemy aircraft. On its top, in the skylight, a geodesical intersection point was placed, with the objective of aiding in the location of enemy cannon.
With the fall of communism, the museum was removed and regular worship activity has resumed in the cathedral, but only in the left-hand side chapel. The main body of the cathedral is used for services on feast days only.
Exterior
The severe neoclassicalNeoclassicism
Neoclassicism is the name given to Western movements in the decorative and visual arts, literature, theatre, music, and architecture that draw inspiration from the "classical" art and culture of Ancient Greece or Ancient Rome...
exterior expresses a traditional Russian-Byzantine formula: a Greek-cross groundplan with a large central dome and four subsidiary domes. It is similar to Andrea Palladio
Andrea Palladio
Andrea Palladio was an architect active in the Republic of Venice. Palladio, influenced by Roman and Greek architecture, primarily by Vitruvius, is widely considered the most influential individual in the history of Western architecture...
's Villa La Rotonda, with a full dome on a high drum substituted for the Villa's low central saucer dome. The design of the cathedral in general and the dome in particular later influenced the design of the United States Capitol
United States Capitol
The United States Capitol is the meeting place of the United States Congress, the legislature of the federal government of the United States. Located in Washington, D.C., it sits atop Capitol Hill at the eastern end of the National Mall...
in Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution....
and the Cathedral
Helsinki Cathedral
Helsinki Cathedral is an Evangelical Lutheran cathedral of the Diocese of Helsinki, located in the centre of Helsinki, Finland. The church was originally built as a tribute to the Grand Duke, Nicholas I, the Tsar of Russia and until the independence of Finland in 1917, it was called St...
in Helsinki
Helsinki
Helsinki is the capital and largest city in Finland. It is in the region of Uusimaa, located in southern Finland, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, an arm of the Baltic Sea. The population of the city of Helsinki is , making it by far the most populous municipality in Finland. Helsinki is...
.
The exterior, which barely hints at the riotously rich interior, is faced with gray and pink stone, and features a total of 112 red granite column
Column
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a vertical structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. For the purpose of wind or earthquake engineering, columns may be designed to resist lateral forces...
s with Corinthian
Corinthian order
The Corinthian order is one of the three principal classical orders of ancient Greek and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric and Ionic. When classical architecture was revived during the Renaissance, two more orders were added to the canon, the Tuscan order and the Composite order...
capitals, each hewn and erected as a single block: 48 at ground level, 24 on the rotunda of the uppermost dome, 8 on each of four side domes, and 2 framing each of four windows. The rotunda is encircled by a walkway accessible to tourists. 24 statues gaze down from the roof, and another 24 from the top of the rotunda.
Dome

Dome
A dome is a structural element of architecture that resembles the hollow upper half of a sphere. Dome structures made of various materials have a long architectural lineage extending into prehistory....
rises 101.5 metres (333 ft) and is plated
Plating
Plating is a surface covering in which a metal is deposited on a conductive surface. Plating has been done for hundreds of years, but it is also critical for modern technology...
with pure gold. The dome is decorated with twelve statues
Statues
Statues is a popular children's game, often played in Australia but with versions throughout the world.-General rules:# A person starts out as the "Curator" and stands at the end of a field. Everyone else playing stands at the far end...
of angels by Josef Hermann. These angels were likely the first large sculptures produced by the then novel process of electrotyping
Electrotyping
Electrotyping is a chemical method for forming metal parts that exactly reproduce a model. The method was invented by Moritz von Jacobi in Russia in 1838, and was immediately adopted for applications in printing and several other fields...
, which was an alternative to traditional bronze casting of sculptures. Montferrand's design of the dome is based on a supporting cast iron
Cast iron
Cast iron is derived from pig iron, and while it usually refers to gray iron, it also identifies a large group of ferrous alloys which solidify with a eutectic. The color of a fractured surface can be used to identify an alloy. White cast iron is named after its white surface when fractured, due...
structure. It was the third historical instance of cast iron cupola
Cupola
In architecture, a cupola is a small, most-often dome-like, structure on top of a building. Often used to provide a lookout or to admit light and air, it usually crowns a larger roof or dome....
after the Leaning Tower of Nevyansk
Leaning Tower of Nevyansk
The Leaning Tower of Nevyansk is a tower in the town of Nevyansk in Sverdlovsk Oblast, Russia, built in the 18th century. Its construction was funded by Peter the Great’s associate and a famous Russian manufacturer Akinfiy Demidov .The height of the tower is 57.5 m from the ground and the...
(1732) and Mainz Cathedral
Mainz Cathedral
Mainz Cathedral or St. Martin's Cathedral is located near the historical center and pedestrianized market square of the city of Mainz, Germany...
(1826).
Interior
The cathedral's bronzeBronze
Bronze is a metal alloy consisting primarily of copper, usually with tin as the main additive. It is hard and brittle, and it was particularly significant in antiquity, so much so that the Bronze Age was named after the metal...
doors are covered in relief
Relief
Relief is a sculptural technique. The term relief is from the Latin verb levo, to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is thus to give the impression that the sculpted material has been raised above the background plane...
s, patterned after the celebrated doors of the Battistero di San Giovanni (Florence)
Battistero di San Giovanni (Florence)
The Florence Baptistry or Battistero di San Giovanni is a religious building in Florence , Italy, which has the status of a minor basilica....
in Florence
Florence
Florence is the capital city of the Italian region of Tuscany and of the province of Florence. It is the most populous city in Tuscany, with approximately 370,000 inhabitants, expanding to over 1.5 million in the metropolitan area....
, designed by Lorenzo Ghiberti
Lorenzo Ghiberti
Lorenzo Ghiberti , born Lorenzo di Bartolo, was an Italian artist of the early Renaissance best known for works in sculpture and metalworking.-Early life:...
. Suspended underneath the peak of the dome is a sculpted dove representing the Holy Spirit
Holy Spirit
Holy Spirit is a term introduced in English translations of the Hebrew Bible, but understood differently in the main Abrahamic religions.While the general concept of a "Spirit" that permeates the cosmos has been used in various religions Holy Spirit is a term introduced in English translations of...
. Internal features such as column
Column
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a vertical structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. For the purpose of wind or earthquake engineering, columns may be designed to resist lateral forces...
s, pilaster
Pilaster
A pilaster is a slightly-projecting column built into or applied to the face of a wall. Most commonly flattened or rectangular in form, pilasters can also take a half-round form or the shape of any type of column, including tortile....
s, floor, and statue of Montferrand are composed of multicolored granite
Granite
Granite is a common and widely occurring type of intrusive, felsic, igneous rock. Granite usually has a medium- to coarse-grained texture. Occasionally some individual crystals are larger than the groundmass, in which case the texture is known as porphyritic. A granitic rock with a porphyritic...
s and marble
Marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite.Geologists use the term "marble" to refer to metamorphosed limestone; however stonemasons use the term more broadly to encompass unmetamorphosed limestone.Marble is commonly used for...
s gathered from all parts of Russia. The iconostasis
Iconostasis
In Eastern Christianity an iconostasis is a wall of icons and religious paintings, separating the nave from the sanctuary in a church. Iconostasis also refers to a portable icon stand that can be placed anywhere within a church...
is framed by eight columns of semiprecious stone: six of malachite
Malachite
Malachite is a copper carbonate mineral, with the formula Cu2CO32. This green-colored mineral crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system, and most often forms botryoidal, fibrous, or stalagmitic masses. Individual crystals are rare but do occur as slender to acicular prisms...
and two smaller ones of lazurite
Lazurite
Lazurite is a tectosilicate mineral with sulfate, sulfur and chloride with formula: 8[2|]. It is a feldspathoid and a member of the sodalite group. Lazurite crystallizes in the isometric system although well formed crystals are rare. It is usually massive and forms the bulk of the gemstone lapis...
. The four pediment
Pediment
A pediment is a classical architectural element consisting of the triangular section found above the horizontal structure , typically supported by columns. The gable end of the pediment is surrounded by the cornice moulding...
s are also richly sculpted.
The interior was originally decorated with scores of paintings by Carlo Brullo and other great Russian masters of the day. When these paintings began to deteriorate due to the cold, damp conditions inside the cathedral, Montferrand ordered them to be painstakingly reproduced as mosaic
Mosaic
Mosaic is the art of creating images with an assemblage of small pieces of colored glass, stone, or other materials. It may be a technique of decorative art, an aspect of interior decoration, or of cultural and spiritual significance as in a cathedral...
s, a technique introduced in Russia by Mikhail Lomonosov
Mikhail Lomonosov
Mikhail Vasilyevich Lomonosov was a Russian polymath, scientist and writer, who made important contributions to literature, education, and science. Among his discoveries was the atmosphere of Venus. His spheres of science were natural science, chemistry, physics, mineralogy, history, art,...
. This work was never completed.
Technologies
William HandysideWilliam Handyside
William Handyside was a Scottish engineer who was involved in several important construction projects in St. Petersburg.-Biography:...
and other engineers used many technological innovations in the construction of the building. The massive portico columns were raised with the use of enormous wooden frameworks before the walls were erected. The enormous building rests on 10,000 tree trunks that were sunk by an army of serfs into the marshy banks upon which the cathedral is situated. The dome was gilded by a technique similar to spraypainting; the solution used included toxic mercury
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum...
, the vapors of which caused the deaths of an unknown number of workers. A dozen gilded statues of angels, each six metres tall, face each other across the interior of the rotunda (see photo below). They were constructed using galvanoplastic technology, making them only millimeters thick and very lightweight. St. Isaac's Cathedral represents the first use of this technique in architecture.
The meticulous and painstakingly detailied work on constructing the St. Isaac's Cathedral took 40 years to complete. This left an expression in the Finnish language
Finnish language
Finnish is the language spoken by the majority of the population in Finland Primarily for use by restaurant menus and by ethnic Finns outside Finland. It is one of the two official languages of Finland and an official minority language in Sweden. In Sweden, both standard Finnish and Meänkieli, a...
rakentaa kuin Iisakin kirkkkoa (to build like St. Isaac's Church) for lengthy and never-ending megaproject
Megaproject
A megaproject is an extremely large-scale investment project. Megaprojects are typically defined as costing more than US$1 billion and attracting a lot of public attention because of substantial impacts on communities, environment, and budgets. Megaprojects can also be defined as "initiatives that...
s.
External links
- The Main Cathedral of the Russian Empire Official website of the State Monument Museum
- St Isaac's Cathedral
- St Isaac's Cathedral guide, a large photo collection
- St Isaac's Cathedral WebCam

