
Rapid prototyping
Encyclopedia

Additive manufacturing
Additive manufacturing is defined by ASTM as the "process of joining materials to make objects from 3D model data, usually layer upon layer, as opposed to subtractive manufacturing methodologies, such as traditional machining...
technology. The first techniques for rapid prototyping became available in the late 1980s and were used to produce model
Model (physical)
A physical model is a smaller or larger physical copy of an object...
s and prototype
Prototype
A prototype is an early sample or model built to test a concept or process or to act as a thing to be replicated or learned from.The word prototype derives from the Greek πρωτότυπον , "primitive form", neutral of πρωτότυπος , "original, primitive", from πρῶτος , "first" and τύπος ,...
parts. Today, they are used for a much wider range of applications and are even used to manufacture production-quality parts in relatively small numbers. Some sculptors use the technology to produce exhibition
Exhibition
An exhibition, in the most general sense, is an organized presentation and display of a selection of items. In practice, exhibitions usually occur within museums, galleries and exhibition halls, and World's Fairs...
s.
Details
Animation
Animation is the rapid display of a sequence of images of 2-D or 3-D artwork or model positions in order to create an illusion of movement. The effect is an optical illusion of motion due to the phenomenon of persistence of vision, and can be created and demonstrated in several ways...
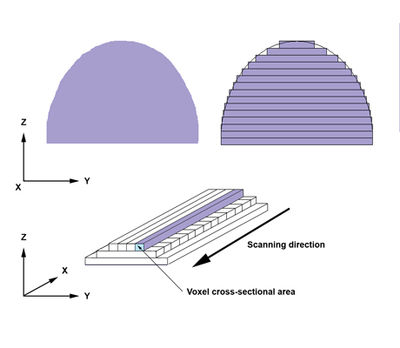
modeling software, transforms them into thin, virtual, horizontal cross-sections and then creates successive layers until the model is complete. It is a WYSIWYG
WYSIWYG
WYSIWYG is an acronym for What You See Is What You Get. The term is used in computing to describe a system in which content displayed onscreen during editing appears in a form closely corresponding to its appearance when printed or displayed as a finished product...
process where the virtual model and the physical model are almost identical.
With additive manufacturing, the machine reads in data from a CAD drawing and lays down successive layers of liquid, powder, or sheet material, and in this way builds up the model from a series of cross sections. These layers, which correspond to the virtual cross section from the CAD model, are joined together or fused automatically to create the final shape. The primary advantage to additive fabrication is its ability to create almost any shape or geometric feature.
The standard data interface
Interface (computer science)
In the field of computer science, an interface is a tool and concept that refers to a point of interaction between components, and is applicable at the level of both hardware and software...
between CAD software and the machines is the STL file format
STL (file format)
STL is a file format native to the stereolithography CAD software created by 3D Systems. This file format is supported by many other software packages; it is widely used for rapid prototyping and computer-aided manufacturing. STL files describe only the surface geometry of a three dimensional...
. An STL file approximates the shape of a part or assembly using triangular facets. Smaller facets produce a higher quality surface.
The word "rapid" is relative: construction of a model with contemporary methods can take from several hours to several days, depending on the method used and the size and complexity of the model. Additive systems for rapid prototyping can typically produce models in a few hours, although it can vary widely depending on the type of machine being used and the size and number of models being produced simultaneously.
Some solid freeform fabrication techniques use two materials in the course of constructing parts. The first material is the part material and the second is the support material (to support overhanging features during construction). The support material is later removed by heat or dissolved away with a solvent or water.
Traditional injection molding
Injection molding
Injection molding is a manufacturing process for producing parts from both thermoplastic and thermosetting plastic materials. Material is fed into a heated barrel, mixed, and forced into a mold cavity where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity...
can be less expensive for manufacturing polymer products in high quantities, but additive fabrication can be faster and less expensive when producing relatively small quantities of parts. 3D printers give designers and concept development teams the ability to produce parts and concept models using a desktop size printer.
Rapid prototyping is now entering the field of rapid manufacturing and it is believed by many experts that this is a "next level" technology.
Technologies

Selective laser sintering
Selective laser sintering is an additive manufacturing technique that uses a high power laser to fuse small particles of plastic, metal , ceramic, or glass powders into a mass that has a desired 3-dimensional shape...
, FDM
Fused deposition modeling
Fused deposition modeling is an additive manufacturing technology commonly used for modeling, prototyping, and production applications. The technology was developed by S...
) where others are laying liquid materials thermosets that are cured
Curing (chemistry)
Curing is a term in polymer chemistry and process engineering that refers to the toughening or hardening of a polymer material by cross-linking of polymer chains, brought about by chemical additives, ultraviolet radiation, electron beam or heat...
with different technologies. In the case of lamination systems, thin layers are cut to shape and joined together.
As of 2005, conventional rapid prototype machines cost around £25,000.
| Prototyping technologies | Base materials |
|---|---|
| Selective laser sintering Selective laser sintering Selective laser sintering is an additive manufacturing technique that uses a high power laser to fuse small particles of plastic, metal , ceramic, or glass powders into a mass that has a desired 3-dimensional shape... (SLS) |
Thermoplastics, metals powders |
| Direct metal laser sintering Direct metal laser sintering Direct metal laser sintering is an additive metal fabrication technology developed by EOS out of Munich, Germany, sometimes also referred to by the terms selective laser sintering or selective laser melting . The process involves use of a 3D CAD model whereby a .stl file is created and sent to... (DMLS) |
Almost any alloy Alloy An alloy is a mixture or metallic solid solution composed of two or more elements. Complete solid solution alloys give single solid phase microstructure, while partial solutions give two or more phases that may or may not be homogeneous in distribution, depending on thermal history... metal Metal A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light... |
| Fused deposition modeling Fused deposition modeling Fused deposition modeling is an additive manufacturing technology commonly used for modeling, prototyping, and production applications. The technology was developed by S... (FDM) |
Thermoplastics, eutectic metals |
| Stereolithography Stereolithography Stereolithography is an additive manufacturing technology for producing models, prototypes, patterns, and in some cases, production parts.-Technology description:... (SLA) |
photopolymer Photopolymer A photopolymer is a polymer that changes its properties when exposed to light, often in the ultraviolet spectrum. These polymers are useful in dentistry for fillings and in rapid prototyping in the stereolithography and 3D printing processes. This material is also used in the creation of ADA... |
| Laminated object manufacturing Laminated object manufacturing Laminated object manufacturing is a rapid prototyping system developed by Helisys Inc. In it, layers of adhesive-coated paper, plastic, or metal laminates are successively glued together and cut to shape with a knife or laser cutter.The process is performed as follows:# Sheet is adhered to a... (LOM) |
Paper Paper Paper is a thin material mainly used for writing upon, printing upon, drawing or for packaging. It is produced by pressing together moist fibers, typically cellulose pulp derived from wood, rags or grasses, and drying them into flexible sheets.... |
| Electron beam melting Electron Beam Melting Electron beam melting is a type of additive manufacturing for metal parts. It is often classified as a rapid manufacturing method. The technology manufactures parts by melting metal powder layer per layer with an electron beam in a high vacuum... (EBM) |
Titanium alloy Titanium alloy Titanium alloys are metallic materials which contain a mixture of titanium and other chemical elements. Such alloys have very high tensile strength and toughness , light weight, extraordinary corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures... s |
| 3D printing 3D printing 3D printing is a form of additive manufacturing technology where a three dimensional object is created by laying down successive layers of material. 3D printers are generally faster, more affordable, and easier to use than other additive manufacturing technologies. However, the term 3D printing is... (3DP) |
Various materials |
See also
- 3D printing3D printing3D printing is a form of additive manufacturing technology where a three dimensional object is created by laying down successive layers of material. 3D printers are generally faster, more affordable, and easier to use than other additive manufacturing technologies. However, the term 3D printing is...
- Additive manufacturingAdditive manufacturingAdditive manufacturing is defined by ASTM as the "process of joining materials to make objects from 3D model data, usually layer upon layer, as opposed to subtractive manufacturing methodologies, such as traditional machining...
- Additive Manufacturing File FormatAdditive Manufacturing File FormatAdditive Manufacturing File Format is an open standard for describing objects for additive manufacturing processes such as 3D printing. The official ASTM F2915standard is an XML-based format designed to allow any computer-aided design software to describe the shape and composition of any 3D object...
- Direct metal laser sinteringDirect metal laser sinteringDirect metal laser sintering is an additive metal fabrication technology developed by EOS out of Munich, Germany, sometimes also referred to by the terms selective laser sintering or selective laser melting . The process involves use of a 3D CAD model whereby a .stl file is created and sent to...
- Fab labFab labA fab lab is a small-scale workshop offering digital fabrication.A fab lab is generally equipped with an array of flexible computer controlled tools that cover several different length scales and various materials, with the aim to make "almost anything"...
- Fused deposition modelingFused deposition modelingFused deposition modeling is an additive manufacturing technology commonly used for modeling, prototyping, and production applications. The technology was developed by S...
- Laser engineered net shapingLaser engineered net shapingLaser engineered net shaping or LENS is a technology developed by Sandia National Laboratories for fabricating metal parts directly from a computer-aided design solid model by using a metal powder injected into a molten pool created by a focused, high-powered laser beam.A high power laser is used...
- Cladding (metalworking)Cladding (metalworking)Cladding is the bonding together of dissimilar metals. It is distinct from welding or gluing as a method to fasten the metals together. Cladding is often achieved by extruding two metals through a die as well as pressing or rolling sheets together under high pressure.The United States Mint uses...
- MeshLabMeshLabMeshLab, is a free 3D mesh processing software program; MeshLab, started in late 2005, is an open-source general-purpose system aimed to help the processing of the typical not-so-small unstructured 3D models that arise in the pipeline of processing of the data coming from 3D scanning...
- RepRap
- Selective laser sinteringSelective laser sinteringSelective laser sintering is an additive manufacturing technique that uses a high power laser to fuse small particles of plastic, metal , ceramic, or glass powders into a mass that has a desired 3-dimensional shape...
- StereolithographyStereolithographyStereolithography is an additive manufacturing technology for producing models, prototypes, patterns, and in some cases, production parts.-Technology description:...
- Von Neumann universal constructorVon Neumann universal constructorJohn von Neumann's Universal Constructor is a self-replicating machine in a cellular automata environment. It was designed in the 1940s, without the use of a computer. The fundamental details of the machine were published in von Neumann's book Theory of Self-Reproducing Automata, completed in...

