
Prague Orloj
Encyclopedia

Astronomical clock
An astronomical clock is a clock with special mechanisms and dials to display astronomical information, such as the relative positions of the sun, moon, zodiacal constellations, and sometimes major planets.-Definition:...
located in Prague
Prague
Prague is the capital and largest city of the Czech Republic. Situated in the north-west of the country on the Vltava river, the city is home to about 1.3 million people, while its metropolitan area is estimated to have a population of over 2.3 million...
, the capital of the Czech Republic
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Poland to the northeast, Slovakia to the east, Austria to the south, and Germany to the west and northwest....
, at 50°5′13.23"N 14°25′15.30"E. The clock was first installed in 1410, making it the third-oldest astronomical clock in the world and the oldest one still working.
Description
The Orloj is mounted on the southern wall of Old TownOld Town, Prague
Old Town is a medieval settlement of Prague, Czech Republic. It was separated from the outside by a semi-circular moat and wall, connected to the Vltava at both of its ends. The moat is now covered up by the streets Revolučni, na Příkopě, and Národni—which remain the official boundary of the...
City Hall in the Old Town Square. The clock mechanism itself is composed of three main components: the astronomical dial, representing the position of the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
and Moon
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
in the sky and displaying various astronomical details; "The Walk of the Apostles", a clockwork hourly show of figures of the Apostles and other moving sculptures—notably a figure of Death (represented by a skeleton) striking the time; and a calendar dial with medallions representing the months.
History

Mikulas of Kadan
Mikuláš of Kadaň was an Imperial clockmaker who designed the clock machine of Prague Orloj together with Jan Šindel around 1410 . The Orloj was modified by Master Hanuš who was mistaken to be the creator of the clock according to the legend recorded by Alois Jirásek....
and Jan Šindel
Jan Šindel
Jan Šindel was a professor at Charles University and became the rector of the University in 1410. He lectured on mathematics and astronomy....
, the latter a professor of mathematics and astronomy at Charles University.
Later, presumably around 1490, the calendar dial was added and clock facade decorated with gothic
Gothic architecture
Gothic architecture is a style of architecture that flourished during the high and late medieval period. It evolved from Romanesque architecture and was succeeded by Renaissance architecture....
sculptures.
In 1552 it was repaired by Jan Taborský, clock-master of Orloj, who also wrote a report on the clock where he mentioned Hanuš as maker of the clock.
The Orloj stopped working many times in the centuries after 1552, and was repaired many times. In the 17th century moving statues were added, and figures of the Apostles were added after major repair in 1865-1866.
The Orloj suffered heavy damage on May 7 and especially May 8, 1945, during the Prague Uprising
Prague uprising
The Prague uprising was an attempt by the Czech resistance to liberate the city of Prague from German occupation during World War II. Events began on May 5, 1945, in the last moments of the war in Europe...
, when Germans directed incendiary fire from several armored vehicles and an anti-aircraft gun to the south-west side of the Old Town Square in an effort to silence the provocative broadcasting initiated by the National Committee on May 5. The hall and nearby buildings burned along with the wooden sculptures on the Orloj and the calendar dial face made by Josef Mánes
Josef Mánes
Josef Mánes was a Czech painter.He was taught by his father, Antonín Mánes , who was a landscape painter and the professor of arts; in addition, he was the nephew of Václav Mánes, and brother of Quido Mánes and Amalie Mánesová, all of whom were also painters...
. The machinery was repaired, the wooden Apostles restored by Vojtěch Sucharda
Vojtech Sucharda
Vojtěch Sucharda ) was a Czech sculptor, woodcarver and puppeteer.Sucharda was the founder of Prague's Ríše Loutek Theater in 1920, and he is known for restoring the wooden figures of the apostles on the Prague Astronomical Clock, which had been heavily damaged by enemy fire in mid-May 1945...
, and the Orloj started working again in 1948, but only after significant effort.
Formerly, it was believed that the Orloj was constructed in 1490 by clockmaster Jan Růže (also called Hanuš); this is now known to be a historical mistake. A legend, recounted by Alois Jirásek
Alois Jirásek
Alois Jirásek was a Czech writer, author of historical novels and plays. Jirásek was a secondary-school teacher until his retirement in 1909. He wrote a series of historical novels imbued with faith in his nation and in progress toward freedom and justice...
, has it that the clockmaker Hanuš was blinded on the order of the Prague Councillors so that he could not repeat his work; in turn, he broke down the clock, and no one was able to repair it for the next hundred years.
According to local legend the city will suffer if the clock is neglected and its good operation is placed in jeopardy.
600th Anniversary
On October 9, 2010, the Clock's 600th anniversary was celebrated with a light show on the face of the clock tower. Two 2x ChristieChristie (company)
The Christie group of companies are part of the Ushio group of companies, the ultimate parent of which is Ushio Inc., a publicly traded Japanese company, Japan...
18K HD projectors, each with a 1920x1080 resolution, were used to project several animated videos on the clock. The videos showed it being built, torn down, rebuilt, and peeled away to show its internal mechanisms and the famous animated figures, as well as various events in the clock's history. The video interacted with the tower's architecture, such as rain rolling off the arch, and showing the passage of time with moving shadows. The show was developed over the course of four months by the macula, Duber Studio, and Michel Kotek, and was presented by AV Media.
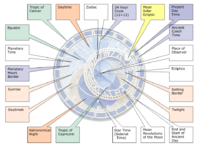
Astronomical dial
Astrolabe
An astrolabe is an elaborate inclinometer, historically used by astronomers, navigators, and astrologers. Its many uses include locating and predicting the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets, and stars, determining local time given local latitude and longitude, surveying, triangulation, and to...
, a device used in medieval astronomy
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
. Alternatively, one may consider the Orloj to be a primitive planetarium
Planetarium
A planetarium is a theatre built primarily for presenting educational and entertaining shows about astronomy and the night sky, or for training in celestial navigation...
, displaying the current state of the universe.
The astronomical dial has a background that represents the standing Earth and sky, and surrounding it operate four main moving components: the zodiacal ring, an outer rotating ring, an icon representing the Sun, and an icon representing the Moon.
Stationary background
The background represents the Earth and the local view of the sky. The blue circle directly in the center represents the Earth, and the upper blue is the portion of the sky which is above the horizonHorizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates earth from sky, the line that divides all visible directions into two categories: those that intersect the Earth's surface, and those that do not. At many locations, the true horizon is obscured by trees, buildings, mountains, etc., and the resulting...
. The red and black areas indicate portions of the sky below the horizon. During the daytime, the Sun sits over the blue part of the background and at night it sits over the black. During dawn or dusk, the mechanical sun is positioned over the red part of the background.
Written on the eastern (left) part of the horizon is aurora (dawn in Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
) and ortus (rising). On the western (right) part is occasus (sunset), and crepusculum (twilight).
Golden Roman numbers at the outer edge of blue circle are the timescale of a normal 24 hour day and indicate time in local Prague time, or Central European Time
Central European Time
Central European Time , used in most parts of the European Union, is a standard time that is 1 hour ahead of Coordinated Universal Time . The time offset from UTC can be written as +01:00...
. Curved golden lines dividing the blue part of dial into 12 parts are marks for unequal "hours". These hours are defined as 1/12 of the time between sunrise and sunset, and vary as the days grow longer or shorter during the year.
Zodiacal ring

Zodiac
In astronomy, the zodiac is a circle of twelve 30° divisions of celestial longitude which are centred upon the ecliptic: the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year...
which indicates the location of the Sun on the ecliptic
Ecliptic
The ecliptic is the plane of the earth's orbit around the sun. In more accurate terms, it is the intersection of the celestial sphere with the ecliptic plane, which is the geometric plane containing the mean orbit of the Earth around the Sun...
. The signs are shown in anticlockwise order. In the photographs accompanying this article, the Sun is currently in Aries
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac, located between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. Its name is Latin for ram, and its symbol is , representing a ram's horns...
, and will be moving anticlockwise into Taurus
Taurus (constellation)
Taurus is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is a Latin word meaning 'bull', and its astrological symbol is a stylized bull's head:...
next.
The displacement of the zodiac circle results from the use of a stereographic projection
Stereographic projection
The stereographic projection, in geometry, is a particular mapping that projects a sphere onto a plane. The projection is defined on the entire sphere, except at one point — the projection point. Where it is defined, the mapping is smooth and bijective. It is conformal, meaning that it...
of the ecliptic plane using the North pole as the basis of the projection. This is commonly seen in astronomical clock
Astronomical clock
An astronomical clock is a clock with special mechanisms and dials to display astronomical information, such as the relative positions of the sun, moon, zodiacal constellations, and sometimes major planets.-Definition:...
s of the period.
The small golden star shows the position of the vernal equinox, and sidereal time
Sidereal time
Sidereal time is a time-keeping system astronomers use to keep track of the direction to point their telescopes to view a given star in the night sky...
can be read on the scale with golden Roman with numerals. Zodiac is on the 366 teeth gear inside the machine. This gear is connect to the sun gear and the moon gear by 24 teeth gear.
Old Czech time scale
At the outer edge of the clock, golden SchwabacherSchwabacher
The German word Schwabacher refers to a specific blackletter typeface. The term derives from the town of Schwabach.-Characteristics:The small-letter g and the capital-letter H have particularly distinctive forms.-History:...
numerals are set on a black background. These numbers indicate Old Czech Time (or Italian hours), with 24 indicating the time of sunset, which varies during the year from as early as 16:00 in winter to 20:16 in summer. This ring moves back and forth during the year to coincide with the time of sunset.
Sun
The golden Sun moves around the zodiacal circle, thus showing its position on the eclipticEcliptic
The ecliptic is the plane of the earth's orbit around the sun. In more accurate terms, it is the intersection of the celestial sphere with the ecliptic plane, which is the geometric plane containing the mean orbit of the Earth around the Sun...
. The sun is attached to an arm with a golden hand, and together they show the time in three different ways:
- The position of the golden hand over the Roman numerals on the background indicates the time in local Prague time.
- The position of the Sun over the curved golden lines indicates the time in unequal hours.
- The position of the golden hand over the outer ring indicates the hours passed after sunset in Old Czech Time.
Additionally, the distance of the Sun from the center of the dial shows the time of sunrise and sunset.
Sun and hand of the sun are at the 365 teeth gear inside the machine.
Moon
The movement of the Moon on the ecliptic is shown similarly to that of the Sun, although the speed is much faster (due to the Moon's own orbit around the Earth). The half-silvered sphere of the moon also shows the Lunar phaseLunar phase
A lunar phase or phase of the moon is the appearance of the illuminated portion of the Moon as seen by an observer, usually on Earth. The lunar phases change cyclically as the Moon orbits the Earth, according to the changing relative positions of the Earth, Moon, and Sun...
. Moon is on the 379 teeth gear inside the machine.
Computer Models of Prague Orloj
The movements of the various mechanical parts of the astronomical dial are too slow to appreciate in real time, but become easier to comprehend using a software model of the Orloj, in the form of an animation. One such animation can be found via the home page of "Prague à la carte", or directly by going here. An animated picture with explanations, and a spreadsheet that 'constructs' the clock for each moment in the year and at each place in the world is to see in a Didactic explanationThere are also at least three different application
Application software
Application software, also known as an application or an "app", is computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks. Examples include enterprise software, accounting software, office suites, graphics software and media players. Many application programs deal principally with...
s (apps) available for Windows Phone 7, the iPhone
IPhone
The iPhone is a line of Internet and multimedia-enabled smartphones marketed by Apple Inc. The first iPhone was unveiled by Steve Jobs, then CEO of Apple, on January 9, 2007, and released on June 29, 2007...
or iPad
IPad
The iPad is a line of tablet computers designed, developed and marketed by Apple Inc., primarily as a platform for audio-visual media including books, periodicals, movies, music, games, and web content. The iPad was introduced on January 27, 2010 by Apple's then-CEO Steve Jobs. Its size and...
that are based on the Orloj. They can be found via Zune Marketplace, the App Store or via the first of the two animations linked to in the previous paragraph.
Animated figures
 |
 |
 |
The four figures flanking the clock are set in motion at the hour, these represent four things that were despised at the time of the clock's making. From left to right in the photographs, the first is Vanity, represented by a figure admiring himself in a mirror. Next, a stereotypical Jew holding a bag of gold represents greed or usury. Across the clock stands Death, a skeleton that strikes the time upon the hour. Finally, the Turk tells pleasure and entertainment.
There is also a presentation of statues of the Apostles at the doorways above the clock, with all twelve presented every hour.
Calendar
 |
 |
The present-day calendar below the clock was added in 1870.
See also
- Antikythera mechanismAntikythera mechanismThe Antikythera mechanism is an ancient mechanical computer designed to calculate astronomical positions. It was recovered in 1900–1901 from the Antikythera wreck. Its significance and complexity were not understood until decades later. Its time of construction is now estimated between 150 and 100...
- Armillary sphereArmillary sphereAn armillary sphere is a model of objects in the sky , consisting of a spherical framework of rings, centred on Earth, that represent lines of celestial longitude and latitude and other astronomically important features such as the ecliptic...
- AstrolabeAstrolabeAn astrolabe is an elaborate inclinometer, historically used by astronomers, navigators, and astrologers. Its many uses include locating and predicting the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets, and stars, determining local time given local latitude and longitude, surveying, triangulation, and to...
- Astronomical clockAstronomical clockAn astronomical clock is a clock with special mechanisms and dials to display astronomical information, such as the relative positions of the sun, moon, zodiacal constellations, and sometimes major planets.-Definition:...
- Equation of TimeEquation of timeThe equation of time is the difference between apparent solar time and mean solar time. At any given instant, this difference will be the same for every observer...
- Geocentric modelGeocentric modelIn astronomy, the geocentric model , is the superseded theory that the Earth is the center of the universe, and that all other objects orbit around it. This geocentric model served as the predominant cosmological system in many ancient civilizations such as ancient Greece...
- HorologyHorologyHorology is the art or science of measuring time. Clocks, watches, clockwork, sundials, clepsydras, timers, time recorders and marine chronometers are all examples of instruments used to measure time.People interested in horology are called horologists...
- HourHourThe hour is a unit of measurement of time. In modern usage, an hour comprises 60 minutes, or 3,600 seconds...
- OrreryOrreryAn orrery is a mechanical device that illustrates the relative positions and motions of the planets and moons in the Solar System in a heliocentric model. Though the Greeks had working planetaria, the first orrery that was a planetarium of the modern era was produced in 1704, and one was presented...
- PlanetariumPlanetariumA planetarium is a theatre built primarily for presenting educational and entertaining shows about astronomy and the night sky, or for training in celestial navigation...
- PraguePraguePrague is the capital and largest city of the Czech Republic. Situated in the north-west of the country on the Vltava river, the city is home to about 1.3 million people, while its metropolitan area is estimated to have a population of over 2.3 million...
- TorquetumTorquetumThe torquetum or turquet is a medieval astronomical instrument designed to take and convert measurements made in three sets of coordinates: Horizon, equatorial, and ecliptic...

