
Poverty in Canada
Encyclopedia
Poverty in Canada
remains prevalent with some segments of society. The measurement of poverty
has been a challenge as there is no official government measure. There is an ongoing debate in Canada about whether a relative measure of poverty, or absolute measure of poverty, is more valid. The new 2011 book Poverty in Canada: Implications for Health and Quality of Life provides an overview of the Canadian scene.http://www.cspi.org/books/poverty_canada
Currently, an income inequality measure known low income cut-off published by Statistics Canada
is frequently used as a poverty rate and is 10.8% as of 2005. It is used by statistics collators like the Central Intelligence Agency
in lieu of an official measure, noting that a relative measure results in a higher poverty figure than an absolute one. The Fraser Institute, a conservative think-tank, alleges that the federal Canadian government exaggerates poverty rates, and publishes their own measure, known as the basic needs poverty measure. According to this measure, poverty has declined significantly over the past 60 years and is 4.9% as of 2004. Statistics Canada has refused to endorse any metric as a measure of poverty, including the low-income cut off it publishes, without a mandate to do so from the federal government.
Some elements that work towards reducing poverty in Canada include Canada's strong economic growth, government transfers to persons of $164 billion per annum as of 2008, universal medical
and public education
systems, a progressive income tax system
, and minimum wage
laws in each of the provinces and territories of Canada
.
In recent times, after a spike in poverty and low-income rates around the 1996 recession, relative poverty has continued to decline. Certain groups experience higher low-income rates. These include children , families with single-parent mothers, aboriginals, the mentally ill, the physically handicapped, recent immigrants, and students.
and recession
, and an evolving response of government intervention to assist low-income Canadians.
Reflecting the practice in the British Isles
, organized assistance to the poor was largely the realm of churches. In the early 20th century, the Catholic Encyclopedia
reported that there were eighty-seven hospitals in Canada under the control and direction of various Catholic religious communities.
After the Great Depression
, Bennett and Mackenzie King spurred the first stages of Canada's welfare state, and the size and role of the government began to grow immensely over the next decades. Many social programs developed during this time designed to increase the Canadian citizen's quality of life.
At the end of the Sixties, Statistics Canada
estimated that the number of Canadians living in poverty (using measurements drawn up by Jenny Podoluk) had fallen from about 25% of the population in 1961 to about 18% in 1969.
In recent years, newly arrived immigrants have higher than average low-income rates, although each immigrant arrival cohort year experiences a declining low-income rate over time.
Some researchers and governments instead use multiple measures to measure the depth and extent of poverty in Canada.
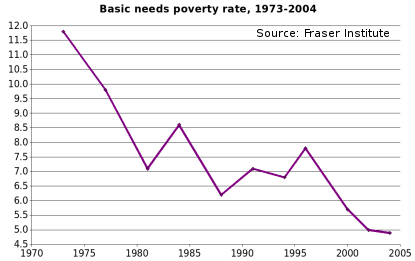 The basic needs poverty measure is designed to be a poverty threshold
The basic needs poverty measure is designed to be a poverty threshold
measure. It was developed in 1992 under the auspices of the conservative and libertarian Fraser Institute by economist Chris Sarlo. According to the latest update "the basic-needs approach is partly absolute (the list [of necessities] is limited to items required for long-term physical well-being) and partly relative, reflecting the standards that apply in the individual's own society at the present time."
The measure is based on various data sources including Statistics Canada's databases (for example Survey of Household Spending) and CMHC housing information to determine the cost of a list of household necessities (food
, shelter, clothing
, health care
, personal care
, essential furnishings
, transportation and communication
, laundry
, home insurance
, and miscellaneous) for various communities across Canada and then, based on family size, determines how many households have insufficient income to afford those necessities. Before 2004, the determination of the poverty rate was based on pre-tax income inclusive of government social program income such as welfare, employment insurance, and old-age pensions. Taxes were not particularly relevant as households at or beneath the poverty rate would pay little or no income tax. More recently, the after-tax incomes have been used as the indicator of household well-being. Like most measures, it is based on reported income and is therefore subject to error related to unreported employment
and the underground economy
.
The measure is based on various sources of historical income data. The basic needs poverty rate has fallen dramatically over the past 51 years, and as of 2004, was 4.9%, representing 1.6 million Canadians.
constructed their own absolute measure through the creation the Market Basket Measure (MBM) in 2003. The MBM costs a broader range of essential goods and services than the Fraser Institute measure. MBM thresholds take into account community size, location and household and composition, estimating the disposable income required to meet basic needs. Forty eight Canadian communities have been included in the measure.
The government of Newfoundland and Labrador are now developing a market basket measure which is more granular, costing out a set of basic goods in over 400 communities in the province.
In lieu of an official poverty measure, the LICO is regarded as a poverty measure by various groups. It has been referred to as "the most accepted measure" of poverty. Internationally, the Low Income Measure and the Gini coefficient are a prominent income distribution metrics.
 Low-income cut-off (LICO) rates are often quoted by the media as a measure of poverty even though Statistics Canada has stated it is not a poverty measure. It is also used by statistics collators like the Central Intelligence Agency
Low-income cut-off (LICO) rates are often quoted by the media as a measure of poverty even though Statistics Canada has stated it is not a poverty measure. It is also used by statistics collators like the Central Intelligence Agency
in lieu of an official measure, although the CIA also notes that it "results in higher figures than found in many comparable economies."
The measure has been reported by Statistics Canada since the 1960s. They were reported only in their "pre-tax" form until 2000, at which point Statistics Canada started to publish both pre and after-tax LICO rates. After-tax LICO rates have been retroactively calculated back to 1986. The measure is intended to represent an income threshold below which a family will likely devote a larger share of its income on the necessities of food shelter and clothing than the average family. As of 2008, 9.4% of Canadians are in a family whose income is below the after-tax low-income cut-off.
There are 7 family sizes and 5 community sizes, resulting in 35 total LICO groups, each one evaluated on a pre and after-tax basis (70 calculations in total). The LICO is currently set at 63% of the average family income within each group. This stems from the 1992 Family Expenditures Survey, which showed the average family spent 43% of its after-tax income on food, shelter and clothing, plus Statistics Canada added an additional 20% margin.
Statistics Canada
prefers using the after-tax LICO over the pre-tax LICO "to draw conclusions about [families] overall economic well-being"; however, the pre-tax measures are needed depending on the study being conducted because some sources of data, such as the census, contain only pre-tax income information. It can also be useful to know the pre-tax income profile of groups before the effects of progressive tax rates.
It is considered an especially useful measure for international comparisons, and is popular with anti-poverty groups and some foreign governments (e.g., Ireland
). It results in a higher measure of poverty compared to other measures. In 2006, it was estimated to be 19.6% for children on an after-tax basis.
or inequality of wealth distribution. It is defined as a ratio
with values between 0 and 1: the numerator is the area between the Lorenz curve
of the distribution and the uniform distribution line; the denominator is the area under the uniform distribution line. Thus, a low Gini coefficient indicates more equal income or wealth distribution, while a high Gini coefficient indicates more unequal distribution. 0 corresponds to perfect equality (everyone having exactly the same income) and 1 corresponds to perfect inequality (where one person has all the income, while everyone else has zero income). The Gini coefficient requires that no one have a negative net income or wealth.
Serious consideration of the Gini coefficient for public policy implications is rare in Canada. Discussion of income inequality in the Canadian media generally implies that income inequality should be continually reduced as an objective, whereas international economists evaluating Gini coefficients generally focus on the idea of targeting an optimal range for the Gini coefficient. Some researchers have suggested the optimal Gini coefficient range is about .25-.40 (Wolfgang Kitterer, 2006, More Growth through Redistribution?). As of 2004, the Gini coefficient for Canada was estimated to be 0.315 on an after-tax basis.
strategies, following the examples set by the European Union, Ireland and the United Kingdom. Newfoundland & Labrador, Nova Scotia, Quebec, Ontario and Manitoba are all developing provincial strategies. Quebec and Manitoba have enshrined their efforts in legislation. Newfoundland & Labrador has established a provincial ministry. Ontario has set a cabinet roundtable to address child poverty, as per the Liberal's campaign promise.
Because of these moves, each province is exploring the development of a measurement tool to track any progress made on reducing poverty, such as the use of a Deprivation Index.
is highly progressive. This can be seen by comparing the 2005 pre-tax low-income cut-off rate of 15.3% with the after-tax rate of only 10.8%. It is also evident in the Gini coefficient, which was estimated to be 0.428 on a pre-tax basis but only 0.315 on an after-tax basis.
. There is also an extensive mandatory Employment Insurance program designed to assist workers who have become unemployed to lessen the chance of them falling into poverty.
In addition to government transfers, there are number of other publicly funded services and social programs that benefit those with low-incomes like Medicare
, Public education
for grade school; subsidized post-secondary education, Subsidized housing, and Employment equity programs
, which often target various groups of people who are deemed to be susceptible to having low-incomes.
, the responsibility for enacting and enforcing labour law
s including minimum wages in Canada rests with the ten provinces, the three territories also having been granted this power by virtue of federal legislation. This means that each province and territory has its own minimum wage. The lowest general minimum wage currently in force as of October 1, 2011 is that of British Columbia
($
8.75/hour), the highest is that of Nunavut
($
11/hour). Some provinces allow lower wages to be paid to liquor servers and other tip earners, and/or to inexperienced employees.
Although listed here under assistance, some theories suggest that minimum wage laws are a net detriment to low-income people as a whole, because they reduce the attractiveness of hiring low-skilled staff (see Minimum wage#Debate over consequences).
s, and other forms aid for low-income Canadians. Some of the most prominent charities and religious organizations in Canada providing direct assistance to the poor include the Canadian Red Cross
, the Salvation Army
, and United Way of Canada
. Governments are a significant contributor to charities in Canada, most notably through tax deductions.
organizations exist in Canada to assist the poor in fighting for their civil liberties. These groups (such as the Ontario Coalition Against Poverty
in Toronto, the Downtown Eastside Residents Association
in Vancouver, and the Ottawa Panhandlers' Union
in Ottawa) generally organize at a grassroots
level, bringing the poor together in solidarity to struggle for better conditions.
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
remains prevalent with some segments of society. The measurement of poverty
Poverty
Poverty is the lack of a certain amount of material possessions or money. Absolute poverty or destitution is inability to afford basic human needs, which commonly includes clean and fresh water, nutrition, health care, education, clothing and shelter. About 1.7 billion people are estimated to live...
has been a challenge as there is no official government measure. There is an ongoing debate in Canada about whether a relative measure of poverty, or absolute measure of poverty, is more valid. The new 2011 book Poverty in Canada: Implications for Health and Quality of Life provides an overview of the Canadian scene.http://www.cspi.org/books/poverty_canada
Currently, an income inequality measure known low income cut-off published by Statistics Canada
Statistics Canada
Statistics Canada is the Canadian federal government agency commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and culture. Its headquarters is in Ottawa....
is frequently used as a poverty rate and is 10.8% as of 2005. It is used by statistics collators like the Central Intelligence Agency
Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency is a civilian intelligence agency of the United States government. It is an executive agency and reports directly to the Director of National Intelligence, responsible for providing national security intelligence assessment to senior United States policymakers...
in lieu of an official measure, noting that a relative measure results in a higher poverty figure than an absolute one. The Fraser Institute, a conservative think-tank, alleges that the federal Canadian government exaggerates poverty rates, and publishes their own measure, known as the basic needs poverty measure. According to this measure, poverty has declined significantly over the past 60 years and is 4.9% as of 2004. Statistics Canada has refused to endorse any metric as a measure of poverty, including the low-income cut off it publishes, without a mandate to do so from the federal government.
Some elements that work towards reducing poverty in Canada include Canada's strong economic growth, government transfers to persons of $164 billion per annum as of 2008, universal medical
Medicare (Canada)
Medicare is the unofficial name for Canada's publicly funded universal health insurance system. The formal terminology for the insurance system is provided by the Canada Health Act and the health insurance legislation of the individual provinces and territories.Under the terms of the Canada Health...
and public education
Public education
State schools, also known in the United States and Canada as public schools,In much of the Commonwealth, including Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, and the United Kingdom, the terms 'public education', 'public school' and 'independent school' are used for private schools, that is, schools...
systems, a progressive income tax system
Income taxes in Canada
Income taxes in Canada constitute the majority of the annual revenues of the Government of Canada, and of the governments of the Provinces of Canada...
, and minimum wage
Minimum wage
A minimum wage is the lowest hourly, daily or monthly remuneration that employers may legally pay to workers. Equivalently, it is the lowest wage at which workers may sell their labour. Although minimum wage laws are in effect in a great many jurisdictions, there are differences of opinion about...
laws in each of the provinces and territories of Canada
Provinces and territories of Canada
The provinces and territories of Canada combine to make up the world's second-largest country by area. There are ten provinces and three territories...
.
In recent times, after a spike in poverty and low-income rates around the 1996 recession, relative poverty has continued to decline. Certain groups experience higher low-income rates. These include children , families with single-parent mothers, aboriginals, the mentally ill, the physically handicapped, recent immigrants, and students.
History of poverty in Canada
Canada's history is marked by identified periods of growthEconomic growth
In economics, economic growth is defined as the increasing capacity of the economy to satisfy the wants of goods and services of the members of society. Economic growth is enabled by increases in productivity, which lowers the inputs for a given amount of output. Lowered costs increase demand...
and recession
Recession
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction, a general slowdown in economic activity. During recessions, many macroeconomic indicators vary in a similar way...
, and an evolving response of government intervention to assist low-income Canadians.
Reflecting the practice in the British Isles
British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands off the northwest coast of continental Europe that include the islands of Great Britain and Ireland and over six thousand smaller isles. There are two sovereign states located on the islands: the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and...
, organized assistance to the poor was largely the realm of churches. In the early 20th century, the Catholic Encyclopedia
Catholic Encyclopedia
The Catholic Encyclopedia, also referred to as the Old Catholic Encyclopedia and the Original Catholic Encyclopedia, is an English-language encyclopedia published in the United States. The first volume appeared in March 1907 and the last three volumes appeared in 1912, followed by a master index...
reported that there were eighty-seven hospitals in Canada under the control and direction of various Catholic religious communities.
After the Great Depression
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression in the decade preceding World War II. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations, but in most countries it started in about 1929 and lasted until the late 1930s or early 1940s...
, Bennett and Mackenzie King spurred the first stages of Canada's welfare state, and the size and role of the government began to grow immensely over the next decades. Many social programs developed during this time designed to increase the Canadian citizen's quality of life.
At the end of the Sixties, Statistics Canada
Statistics Canada
Statistics Canada is the Canadian federal government agency commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and culture. Its headquarters is in Ottawa....
estimated that the number of Canadians living in poverty (using measurements drawn up by Jenny Podoluk) had fallen from about 25% of the population in 1961 to about 18% in 1969.
In recent years, newly arrived immigrants have higher than average low-income rates, although each immigrant arrival cohort year experiences a declining low-income rate over time.
Measures of poverty in Canada
Canada has no official poverty measure because Statistics Canada has stated that unless politicians express a social consensus on the definition of poverty, there will be no measure because they feel that it is not Statistics Canada's role to determine what constitutes a necessity. There is a debate on whether an absolute or relative measure is more useful. An absolute measure of poverty can provide insight on deprivation, or the inability to provide for basic needs, while a relative measure of poverty encompasses the issues of social exclusion and inequality.Some researchers and governments instead use multiple measures to measure the depth and extent of poverty in Canada.
Basic needs poverty measure

Poverty threshold
The poverty threshold, or poverty line, is the minimum level of income deemed necessary to achieve an adequate standard of living in a given country...
measure. It was developed in 1992 under the auspices of the conservative and libertarian Fraser Institute by economist Chris Sarlo. According to the latest update "the basic-needs approach is partly absolute (the list [of necessities] is limited to items required for long-term physical well-being) and partly relative, reflecting the standards that apply in the individual's own society at the present time."
The measure is based on various data sources including Statistics Canada's databases (for example Survey of Household Spending) and CMHC housing information to determine the cost of a list of household necessities (food
Food
Food is any substance consumed to provide nutritional support for the body. It is usually of plant or animal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals...
, shelter, clothing
Clothing
Clothing refers to any covering for the human body that is worn. The wearing of clothing is exclusively a human characteristic and is a feature of nearly all human societies...
, health care
Health care
Health care is the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in humans. Health care is delivered by practitioners in medicine, chiropractic, dentistry, nursing, pharmacy, allied health, and other care providers...
, personal care
Hygiene
Hygiene refers to the set of practices perceived by a community to be associated with the preservation of health and healthy living. While in modern medical sciences there is a set of standards of hygiene recommended for different situations, what is considered hygienic or not can vary between...
, essential furnishings
Furniture
Furniture is the mass noun for the movable objects intended to support various human activities such as seating and sleeping in beds, to hold objects at a convenient height for work using horizontal surfaces above the ground, or to store things...
, transportation and communication
Communication
Communication is the activity of conveying meaningful information. Communication requires a sender, a message, and an intended recipient, although the receiver need not be present or aware of the sender's intent to communicate at the time of communication; thus communication can occur across vast...
, laundry
Laundry
Laundry is a noun that refers to the act of washing clothing and linens, the place where that washing is done, and/or that which needs to be, is being, or has been laundered...
, home insurance
Home insurance
Home insurance, also commonly called hazard insurance or homeowner's insurance , is the type of property insurance that covers private homes...
, and miscellaneous) for various communities across Canada and then, based on family size, determines how many households have insufficient income to afford those necessities. Before 2004, the determination of the poverty rate was based on pre-tax income inclusive of government social program income such as welfare, employment insurance, and old-age pensions. Taxes were not particularly relevant as households at or beneath the poverty rate would pay little or no income tax. More recently, the after-tax incomes have been used as the indicator of household well-being. Like most measures, it is based on reported income and is therefore subject to error related to unreported employment
Unreported employment
Unreported employment, often referred to colloquially as working or being paid under the table or cash-in-hand, is employment that is not reported as required by law to the appropriate local, state or provincial, or national government agency. This is often done by the employer or the employee in...
and the underground economy
Underground economy
A black market or underground economy is a market in goods or services which operates outside the formal one supported by established state power. Typically the totality of such activity is referred to with the definite article as a complement to the official economies, by market for such goods and...
.
The measure is based on various sources of historical income data. The basic needs poverty rate has fallen dramatically over the past 51 years, and as of 2004, was 4.9%, representing 1.6 million Canadians.
Market basket measure
The Government of Canada's Department of Human Resources and Skills Development CanadaHuman Resources and Skills Development Canada
The Department of Human Resources and Skills Development , operating under the FIP applied title Human Resources and Skills Development Canada , is the department of the Government of Canada responsible for developing, managing and delivering a variety of social programs and services...
constructed their own absolute measure through the creation the Market Basket Measure (MBM) in 2003. The MBM costs a broader range of essential goods and services than the Fraser Institute measure. MBM thresholds take into account community size, location and household and composition, estimating the disposable income required to meet basic needs. Forty eight Canadian communities have been included in the measure.
The government of Newfoundland and Labrador are now developing a market basket measure which is more granular, costing out a set of basic goods in over 400 communities in the province.
Relative poverty measures
Relative poverty measures, the most prominent being income distribution measures, also known as income inequality metrics, reveal information about disparities of income within a population. So, for instance, if a society becomes richer, even those in the bottom income bands may see their incomes rise as well. A measure which accounts for this rise is known as a "relative measure of poverty." Each measure has its own strengths and weaknesses.In lieu of an official poverty measure, the LICO is regarded as a poverty measure by various groups. It has been referred to as "the most accepted measure" of poverty. Internationally, the Low Income Measure and the Gini coefficient are a prominent income distribution metrics.
Low-income cut-off (LICO)

Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency is a civilian intelligence agency of the United States government. It is an executive agency and reports directly to the Director of National Intelligence, responsible for providing national security intelligence assessment to senior United States policymakers...
in lieu of an official measure, although the CIA also notes that it "results in higher figures than found in many comparable economies."
The measure has been reported by Statistics Canada since the 1960s. They were reported only in their "pre-tax" form until 2000, at which point Statistics Canada started to publish both pre and after-tax LICO rates. After-tax LICO rates have been retroactively calculated back to 1986. The measure is intended to represent an income threshold below which a family will likely devote a larger share of its income on the necessities of food shelter and clothing than the average family. As of 2008, 9.4% of Canadians are in a family whose income is below the after-tax low-income cut-off.
There are 7 family sizes and 5 community sizes, resulting in 35 total LICO groups, each one evaluated on a pre and after-tax basis (70 calculations in total). The LICO is currently set at 63% of the average family income within each group. This stems from the 1992 Family Expenditures Survey, which showed the average family spent 43% of its after-tax income on food, shelter and clothing, plus Statistics Canada added an additional 20% margin.
Statistics Canada
Statistics Canada
Statistics Canada is the Canadian federal government agency commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and culture. Its headquarters is in Ottawa....
prefers using the after-tax LICO over the pre-tax LICO "to draw conclusions about [families] overall economic well-being"; however, the pre-tax measures are needed depending on the study being conducted because some sources of data, such as the census, contain only pre-tax income information. It can also be useful to know the pre-tax income profile of groups before the effects of progressive tax rates.
Low Income Measure
The Low Income Measure is a purer measure of relative income. It is defined as 50% of median income, adjusted for family size. In effect, this measure indicates the percentage or number of people in the bottom income quartile.It is considered an especially useful measure for international comparisons, and is popular with anti-poverty groups and some foreign governments (e.g., Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
). It results in a higher measure of poverty compared to other measures. In 2006, it was estimated to be 19.6% for children on an after-tax basis.
Gini coefficient
The Gini coefficient is a measure of statistical dispersion most prominently used as a measure of inequality of income distributionIncome inequality metrics
The concept of inequality is distinct from that of poverty and fairness. Income inequality metrics or income distribution metrics are used by social scientists to measure the distribution of income, and economic inequality among the participants in a particular economy, such as that of a specific...
or inequality of wealth distribution. It is defined as a ratio
Ratio
In mathematics, a ratio is a relationship between two numbers of the same kind , usually expressed as "a to b" or a:b, sometimes expressed arithmetically as a dimensionless quotient of the two which explicitly indicates how many times the first number contains the second In mathematics, a ratio is...
with values between 0 and 1: the numerator is the area between the Lorenz curve
Lorenz curve
In economics, the Lorenz curve is a graphical representation of the cumulative distribution function of the empirical probability distribution of wealth; it is a graph showing the proportion of the distribution assumed by the bottom y% of the values...
of the distribution and the uniform distribution line; the denominator is the area under the uniform distribution line. Thus, a low Gini coefficient indicates more equal income or wealth distribution, while a high Gini coefficient indicates more unequal distribution. 0 corresponds to perfect equality (everyone having exactly the same income) and 1 corresponds to perfect inequality (where one person has all the income, while everyone else has zero income). The Gini coefficient requires that no one have a negative net income or wealth.
Serious consideration of the Gini coefficient for public policy implications is rare in Canada. Discussion of income inequality in the Canadian media generally implies that income inequality should be continually reduced as an objective, whereas international economists evaluating Gini coefficients generally focus on the idea of targeting an optimal range for the Gini coefficient. Some researchers have suggested the optimal Gini coefficient range is about .25-.40 (Wolfgang Kitterer, 2006, More Growth through Redistribution?). As of 2004, the Gini coefficient for Canada was estimated to be 0.315 on an after-tax basis.
Poverty Reduction
Several Canadian provinces are introducing poverty reductionPoverty reduction
Poverty is the state of human beings who are poor. That is, they have little or no material means of surviving—little or no food, shelter, clothes, healthcare, education, and other physical means of living and improving one's life....
strategies, following the examples set by the European Union, Ireland and the United Kingdom. Newfoundland & Labrador, Nova Scotia, Quebec, Ontario and Manitoba are all developing provincial strategies. Quebec and Manitoba have enshrined their efforts in legislation. Newfoundland & Labrador has established a provincial ministry. Ontario has set a cabinet roundtable to address child poverty, as per the Liberal's campaign promise.
Because of these moves, each province is exploring the development of a measurement tool to track any progress made on reducing poverty, such as the use of a Deprivation Index.
Reduced tax burden
The Canadian income tax systemIncome taxes in Canada
Income taxes in Canada constitute the majority of the annual revenues of the Government of Canada, and of the governments of the Provinces of Canada...
is highly progressive. This can be seen by comparing the 2005 pre-tax low-income cut-off rate of 15.3% with the after-tax rate of only 10.8%. It is also evident in the Gini coefficient, which was estimated to be 0.428 on a pre-tax basis but only 0.315 on an after-tax basis.
Social programs
Canada has a wide range of government transfers to persons, which totaled $164 billion in 2008. Some of the transfers designed to assist low-income people in Canada include Welfare and Old age securityOld Age Security
The Old Age Security pension is a taxable monthly social security payment available to most Canadians 65 years of age or older. As of July, 2011, the basic amount is C$533.70 per month. At tax time, recipients with 2010 incomes over C$67,668 must pay back a portion of their Old Age Security at a...
. There is also an extensive mandatory Employment Insurance program designed to assist workers who have become unemployed to lessen the chance of them falling into poverty.
In addition to government transfers, there are number of other publicly funded services and social programs that benefit those with low-incomes like Medicare
Medicare (Canada)
Medicare is the unofficial name for Canada's publicly funded universal health insurance system. The formal terminology for the insurance system is provided by the Canada Health Act and the health insurance legislation of the individual provinces and territories.Under the terms of the Canada Health...
, Public education
Public education
State schools, also known in the United States and Canada as public schools,In much of the Commonwealth, including Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, and the United Kingdom, the terms 'public education', 'public school' and 'independent school' are used for private schools, that is, schools...
for grade school; subsidized post-secondary education, Subsidized housing, and Employment equity programs
Employment equity (Canada)
Employment equity, as defined in Canadian law by the Employment Equity Act, requires employers to engage in proactive employment practices to increase the representation of four designated groups: women, people with disabilities, Aboriginal peoples, and visible minorities...
, which often target various groups of people who are deemed to be susceptible to having low-incomes.
Working income tax benefit
Introduced in 2007 to encourage low income people to keep working rather than quit to rely on certain social programs that could be more profitable, a tax credit of $500 is given to all individuals earning between $3,000 and $9,500 per year. The benefit is transitioned to zero at $12,833. Those with spouses or another dependent can claim the higher $1,000 amount if combined they earn between $8,000 and $14,500, after which it declines to zero at $21,166.Child credits
Low-income Canadians are eligible for the Canada Child Tax Benefit (a federal benefit), and provincial child tax credits or benefits and Québec family allowances. For example, Ontario pays a benefit scheduled to grow to $180 per month by 2011 for a family earnings less than $20,000 with two children. These credits are not taxed (see Income taxes in Canada#Income not taxed).Minimum wage laws
Under the Constitution of CanadaConstitution of Canada
The Constitution of Canada is the supreme law in Canada; the country's constitution is an amalgamation of codified acts and uncodified traditions and conventions. It outlines Canada's system of government, as well as the civil rights of all Canadian citizens and those in Canada...
, the responsibility for enacting and enforcing labour law
Labour law
Labour law is the body of laws, administrative rulings, and precedents which address the legal rights of, and restrictions on, working people and their organizations. As such, it mediates many aspects of the relationship between trade unions, employers and employees...
s including minimum wages in Canada rests with the ten provinces, the three territories also having been granted this power by virtue of federal legislation. This means that each province and territory has its own minimum wage. The lowest general minimum wage currently in force as of October 1, 2011 is that of British Columbia
British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost of Canada's provinces and is known for its natural beauty, as reflected in its Latin motto, Splendor sine occasu . Its name was chosen by Queen Victoria in 1858...
($
Canadian dollar
The Canadian dollar is the currency of Canada. As of 2007, the Canadian dollar is the 7th most traded currency in the world. It is abbreviated with the dollar sign $, or C$ to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies...
8.75/hour), the highest is that of Nunavut
Nunavut
Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993...
($
Canadian dollar
The Canadian dollar is the currency of Canada. As of 2007, the Canadian dollar is the 7th most traded currency in the world. It is abbreviated with the dollar sign $, or C$ to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies...
11/hour). Some provinces allow lower wages to be paid to liquor servers and other tip earners, and/or to inexperienced employees.
Although listed here under assistance, some theories suggest that minimum wage laws are a net detriment to low-income people as a whole, because they reduce the attractiveness of hiring low-skilled staff (see Minimum wage#Debate over consequences).
Private Charity
A number of non-denominational and religious organizations operate homeless shelters, food bankFood bank
A food bank or foodbank is a non-profit, charitable organization that distributes mostly donated food to a wide variety of agencies that in turn feed the hungry. The largest sources of food are for-profit growers, manufacturers, distributors and retailers who in the normal course of business have...
s, and other forms aid for low-income Canadians. Some of the most prominent charities and religious organizations in Canada providing direct assistance to the poor include the Canadian Red Cross
Canadian Red Cross
The Canadian Red Cross Society is a Canadian humanitarian charitable organization and one of 186 national Red Cross and Red Crescent societies....
, the Salvation Army
Salvation Army
The Salvation Army is a Protestant Christian church known for its thrift stores and charity work. It is an international movement that currently works in over a hundred countries....
, and United Way of Canada
United Way of Canada
United Way of Canada is the national organization for the 117 autonomous, volunteer-based United Ways across Canada. United Way campaigns raise money for local groups that address community issues and problems, and the national organization provides leadership, services and coordination to the...
. Governments are a significant contributor to charities in Canada, most notably through tax deductions.
Advocacy Groups
A number of direct actionDirect action
Direct action is activity undertaken by individuals, groups, or governments to achieve political, economic, or social goals outside of normal social/political channels. This can include nonviolent and violent activities which target persons, groups, or property deemed offensive to the direct action...
organizations exist in Canada to assist the poor in fighting for their civil liberties. These groups (such as the Ontario Coalition Against Poverty
Ontario Coalition Against Poverty
The Ontario Coalition Against Poverty is an anti-poverty group in Ontario, Canada, who promote the interests of the poor and homeless...
in Toronto, the Downtown Eastside Residents Association
Downtown Eastside Residents Association
The Downtown Eastside Residents Association is a non-profit Society in the Downtown Eastside area of Vancouver.The association was founded in 1973 by Bruce Eriksen, Libby Davies, Jean Swanson and other residents of the Downtown Eastside and membership is restricted to those who live within the...
in Vancouver, and the Ottawa Panhandlers' Union
Ottawa Panhandlers' Union
The Ottawa Panhandlers' Union is a union for panhandlers formed in Ottawa, Canada in early 2003. It is a shop of the Industrial Workers of the World , Ottawa-Outaouis General Members Branch...
in Ottawa) generally organize at a grassroots
Grassroots
A grassroots movement is one driven by the politics of a community. The term implies that the creation of the movement and the group supporting it are natural and spontaneous, highlighting the differences between this and a movement that is orchestrated by traditional power structures...
level, bringing the poor together in solidarity to struggle for better conditions.
External links
- Stats & Facts, Canadian Council on Social Development

