
Ocean Surface Topography Mission
Encyclopedia


Earth observation satellite
Earth observation satellites are satellites specifically designed to observe Earth from orbit, similar to reconnaissance satellites but intended for non-military uses such as environmental monitoring, meteorology, map making etc....
mission that continues the sea surface
Sea level
Mean sea level is a measure of the average height of the ocean's surface ; used as a standard in reckoning land elevation...
height measurements begun in 1992 by the joint NASA
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
/CNES TOPEX/Poseidon mission
TOPEX/Poseidon
Launched in 1992, TOPEX/Poseidon was a joint satellite mission between NASA, the U.S. space agency, and CNES, the French space agency, to map ocean surface topography. The first major oceanographic research vessel to sail into space, TOPEX/Poseidon helped revolutionize oceanography by proving the...
and followed by the NASA/CNES Jason-1 mission
Jason 1
Jason-1 is a satellite oceanography mission to monitor global ocean circulation, study the ties between the ocean and the atmosphere, improve global climate forecasts and predictions, and monitor events such as El Niño and ocean eddies....
launched in 2001.
Like its two predecessors, OSTM/Jason-2 uses high-precision ocean altimetry to measure the distance between the satellite and the ocean surface to within a few centimeters. These very accurate observations of variations in sea surface height—also known as ocean topography—provide information about global sea level
Sea level
Mean sea level is a measure of the average height of the ocean's surface ; used as a standard in reckoning land elevation...
, the speed and direction of ocean current
Ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of ocean water generated by the forces acting upon this mean flow, such as breaking waves, wind, Coriolis effect, cabbeling, temperature and salinity differences and tides caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun...
s, and heat stored in the ocean.
Jason-2 was built by Thales Alenia Space
Thales Alenia Space
Thales Alenia Space is an aerospace company born after the Thales Group bought the participation of Alcatel in the two joint-ventures between Alcatel and Finmeccanica, Alcatel Alenia Space and Telespazio.-History:...
using a Proteus
Proteus
In Greek mythology, Proteus is an early sea-god, one of several deities whom Homer calls the "Old Man of the Sea", whose name suggests the "first" , as protogonos is the "primordial" or the "firstborn". He became the son of Poseidon in the Olympian theogony In Greek mythology, Proteus (Πρωτεύς)...
platform, under a contract from CNES, as well as the main Jason-2 instrument, the Poseidon-3 altimeter (successor to the Poseidon and Poseidon 2 altimeter on-board TOPEX/Poseidon and Jason-1)
Scientists consider the 15-plus-year climate
Climate
Climate encompasses the statistics of temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, rainfall, atmospheric particle count and other meteorological elemental measurements in a given region over long periods...
data record that this mission will extend critical understanding how ocean circulation is linked to global climate change
Climate change
Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions or the distribution of events around that average...
.
OSTM/Jason-2 was launched at 07:46 UTC on June 20, 2008, from Space Launch Complex 2W
Vandenberg AFB Space Launch Complex 2
Space Launch Complex 2 is an active rocket launch site at Vandenberg Air Force Base, in California, USA. It consists of two launch pads. The East pad , which has been demolished, was used for Delta, Thor-Agena and Thorad launches between 1966 and 1972...
at the Vandenberg Air Force Base
Vandenberg Air Force Base
Vandenberg Air Force Base is a United States Air Force Base, located approximately northwest of Lompoc, California. It is under the jurisdiction of the 30th Space Wing, Air Force Space Command ....
in California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
, USA
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, by a Delta II
Delta II
Delta II was an American space launch system, originally designed and built by McDonnell Douglas. Delta II is part of the Delta rocket family and was in service from 1989 until November 1, 2011...
7320 rocket. The spacecraft separated from the rocket 55 minutes later.
It is now in a 1336 km (830.2 mi) circular, non-sun-synchronous orbit
Orbit
In physics, an orbit is the gravitationally curved path of an object around a point in space, for example the orbit of a planet around the center of a star system, such as the Solar System...
at an inclination of 66 degrees to Earth's equator, allowing it to monitor 95 percent of Earth's ice-free ocean every 10 days. Jason-1 has been moved to the opposite side of Earth and now flies over the same region of the ocean that Jason-2 flew over five days earlier. Jason-1's ground tracks fall mid-way between those of Jason-2, which are about 315 kilometres (195.7 mi) apart at the equator. This interleaved tandem mission provides twice the number of measurements of the ocean's surface, bringing smaller features such as ocean eddies into view. The tandem mission also helps pave the way for a future ocean altimeter mission that would collect much more detailed data with its single instrument than the two Jason satellites now do together.
With OSTM/Jason-2, ocean altimetry makes the transition from research into operational mode. Responsibility for collecting these measurements moves from the space agencies to the world’s weather and climate forecasting agencies, which use them for short-range, seasonal, and long-range weather and climate forecasting.
Science objectives
- Extend the time series of ocean surface topography measurements beyond TOPEX/Poseidon and Jason-1 to accomplish two decades of observations
- Provide a minimum of three years of global ocean surface topography measurement
- Determine the variability of ocean circulation at decadal time scales from combined data record of TOPEX/Poseidon and Jason-1
- Improve the measure of the time-averaged ocean circulation
- Improve the measure of global sea-level change
- Improve open ocean tide models
Ocean altimetry
Spaceborne radar altimeters have proven to be superb tools for mapping ocean-surface topography, the hills and valleys of the sea surface. These instruments send a microwave pulse to the ocean’s surface and time how long it takes to return. A microwave radiometerMicrowave radiometer
A microwave radiometer is a radiometer that measures energy emitted at sub-millimetre-to-centimetre wavelengths known as microwaves. Their primary application has been onboard spacecraft measuring atmospheric and terrestrial radiation, and they are mostly used for meteorological or oceanographic...
corrects any delay that may be caused by water vapor
Water vapor
Water vapor or water vapour , also aqueous vapor, is the gas phase of water. It is one state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from the sublimation of ice. Under typical atmospheric conditions, water vapor is continuously...
in the atmosphere
Atmosphere
An atmosphere is a layer of gases that may surround a material body of sufficient mass, and that is held in place by the gravity of the body. An atmosphere may be retained for a longer duration, if the gravity is high and the atmosphere's temperature is low...
. Other corrections are also required to account for the influence of electrons in the ionosphere
Ionosphere
The ionosphere is a part of the upper atmosphere, comprising portions of the mesosphere, thermosphere and exosphere, distinguished because it is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important part in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere...
and the dry air mass of the atmosphere. Combining these data with the precise location of the spacecraft makes it possible to determine sea-surface height to within a few centimetres (about one inch). The strength and shape of the returning signal also provides information on wind speed and the height of ocean waves. These data are used in ocean models to calculate the speed and direction of ocean current
Ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of ocean water generated by the forces acting upon this mean flow, such as breaking waves, wind, Coriolis effect, cabbeling, temperature and salinity differences and tides caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun...
s and the amount and location of heat stored in the ocean, which, in turn, reveals global climate variations.
Atomic clock synchronization
Another payload aboard Jason-2 is the T2L2 (Time Transfer by Laser Link) instrument. T2L2 is used to synchronize atomic clocks at ground stations, and to calibrate the on-board clock of the Jason-2 DORIS instrument. On 6 November 2008 CNESCNES
The is the French government space agency . Established under President Charles de Gaulle in 1961, its headquarters are located in central Paris and it is under the supervision of the French Ministries of Defence and Research...
reported the T2L2 instrument was working well.
Joint effort
OSTM/Jason-2 is a joint effort by four organizations. The mission participants are:- National Oceanic and Atmospheric AdministrationNational Oceanic and Atmospheric AdministrationThe National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration , pronounced , like "noah", is a scientific agency within the United States Department of Commerce focused on the conditions of the oceans and the atmosphere...
(NOAA) - National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)
- France’s Centre National d’Études SpatialesCNESThe is the French government space agency . Established under President Charles de Gaulle in 1961, its headquarters are located in central Paris and it is under the supervision of the French Ministries of Defence and Research...
(CNES) - European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological SatellitesEuropean Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological SatellitesEUMETSAT is an intergovernmental organisation created through an international convention agreed by a current total of 26 European Member States: Austria, Belgium, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Romania, Italy, Latvia, Luxembourg, the...
(EUMETSAT)
CNES provided the spacecraft, NASA and CNES jointly provided the payload instruments and NASA's Launch Services Program at the Kennedy Space Center
Kennedy Space Center
The John F. Kennedy Space Center is the NASA installation that has been the launch site for every United States human space flight since 1968. Although such flights are currently on hiatus, KSC continues to manage and operate unmanned rocket launch facilities for America's civilian space program...
was responsible for the launch management and countdown operations. After completing the on-orbit commissioning of the spacecraft, CNES handed over operation and control of the spacecraft to NOAA in October 2008.
CNES will process, distribute and archive the research-quality data products that will become available in 2009. EUMETSAT will process and distribute operational data received by its ground station to users in Europe and will archive the data. NOAA will process and distribute operational data received by its ground stations to non-European users and archive that data along with the CNES data products. NOAA and EUMETSAT will generate the near-real-time products and distribute them to users.
NASA will evaluate the performance of its instruments: the advanced microwave radiometer, the Global Positioning System payload, and the laser retroreflector assembly. In addition, NASA and CNES will validate scientific data products. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory
Jet Propulsion Laboratory
Jet Propulsion Laboratory is a federally funded research and development center and NASA field center located in the San Gabriel Valley area of Los Angeles County, California, United States. The facility is headquartered in the city of Pasadena on the border of La Cañada Flintridge and Pasadena...
in Pasadena, California, manages the mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate
Science Mission Directorate
The Science Mission Directorate of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration engages the United States’ science community, sponsors scientific research, and develops and deploys satellites and probes in collaboration with NASA’s partners around the world to answer fundamental questions...
in Washington.
Prior similar missions
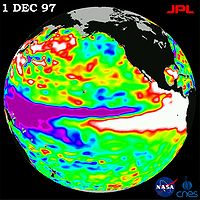
TOPEX/Poseidon
Launched in 1992, TOPEX/Poseidon was a joint satellite mission between NASA, the U.S. space agency, and CNES, the French space agency, to map ocean surface topography. The first major oceanographic research vessel to sail into space, TOPEX/Poseidon helped revolutionize oceanography by proving the...
and Jason-1 have led to major advances in the science of physical oceanography
Physical oceanography
Physical oceanography is the study of physical conditions and physical processes within the ocean, especially the motions and physical properties of ocean waters.Physical oceanography is one of several sub-domains into which oceanography is divided...
and in climate studies. Their 15-year data record of ocean surface topography has provided the first opportunity to observe and understand the global change of ocean circulation and sea level. The results have improved the understanding of the role of the ocean in climate change and improved weather and climate predictions. Data from these missions are used to improve ocean models, forecast hurricane intensity, and identify and track large ocean/atmosphere phenomena such as El Niño and La Niña. The data are also used every day in applications as diverse as routing ships, improving the safety and efficiency of offshore industry operations, managing fisheries and tracking marine mammals.
Some of the areas in which TOPEX/Poseidon and Jason 1-have made major contributions, and to which OSTM/Jason-2 will continue to add, are:
- Ocean Variability
The missions revealed the surprising variability of the ocean, how much it changes from season
Season
A season is a division of the year, marked by changes in weather, ecology, and hours of daylight.Seasons result from the yearly revolution of the Earth around the Sun and the tilt of the Earth's axis relative to the plane of revolution...
to season, year to year, decade to decade and on even longer time scales. They ended the traditional notion of a quasi-steady, large-scale pattern of global ocean circulation by proving that the ocean is changing rapidly on all scales, from huge features such as El Nino and La Nina, which can cover the entire equatorial Pacific, to tiny eddies swirling off the large Gulf Stream
Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension towards Europe, the North Atlantic Drift, is a powerful, warm, and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates at the tip of Florida, and follows the eastern coastlines of the United States and Newfoundland before crossing the Atlantic Ocean...
in the Atlantic.
- Sea Level Change
Measurements by TOPEX/Poseidon and Jason-1 show that mean sea level has been rising by about three millimeters (.12 inches) a year since 1993. This is about twice the estimates from tide gauges for the previous century, indicating a possible recent acceleration in the rate of sea level rise.
The data record from these altimetry missions has given scientists important insights into how global sea level is affected by natural climate variability, as well as by human activities.
- Planetary Waves
TOPEX/Poseidon and Jason-1 made clear the importance of planetary-scale waves
Ocean surface wave
In fluid dynamics, wind waves or, more precisely, wind-generated waves are surface waves that occur on the free surface of oceans, seas, lakes, rivers, and canals or even on small puddles and ponds. They usually result from the wind blowing over a vast enough stretch of fluid surface. Waves in the...
, such as Rossby
Rossby wave
Atmospheric Rossby waves are giant meanders in high-altitude winds that are a major influence on weather.They are not to be confused with oceanic Rossby waves, which move along the thermocline: that is, the boundary between the warm upper layer of the ocean and the cold deeper part of the...
and Kelvin wave
Kelvin wave
A Kelvin wave is a wave in the ocean or atmosphere that balances the Earth's Coriolis force against a topographic boundary such as a coastline, or a waveguide such as the equator. A feature of a Kelvin wave is that it is non-dispersive, i.e., the phase speed of the wave crests is equal to the...
s. No one had realized how widespread these waves are. Thousands of kilometers wide, these waves are driven by wind
Wind
Wind is the flow of gases on a large scale. On Earth, wind consists of the bulk movement of air. In outer space, solar wind is the movement of gases or charged particles from the sun through space, while planetary wind is the outgassing of light chemical elements from a planet's atmosphere into space...
under the influence of Earth’s rotation and are important mechanisms for transmitting climate signals across the large ocean basins. At high latitudes, they travel twice as fast as scientists believed previously, showing the ocean responds much more quickly to climate changes than was known before these missions.
- Ocean Tides
The precise measurements of TOPEX/Poseidon’s and Jason-1 have brought knowledge of ocean tide
Tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the moon and the sun and the rotation of the Earth....
s to an unprecedented level. The change of water level due to tidal motion in the deep ocean is known everywhere on the globe to within 2.5 centimeters (one inch). This new knowledge has revised notions about how tides dissipate. Instead of losing all their energy over shallow seas near the coasts, as previously believed, about one third of tidal energy is actually lost to the deep ocean. There, the energy is consumed by mixing water of different properties
Mixed layer
The oceanic or limnological mixed layer is a layer in which active turbulence has homogenized some range of depths. The surface mixed layer is a layer where this turbulence is generated by winds, cooling, or processes such as evaporation or sea ice formation which result in an increase in salinity...
, a fundamental mechanism in the physics governing the general circulation of the ocean.
- Ocean Models
TOPEX/Poseidon and Jason-1 observations provided the first global data for improving the performance of the numerical ocean models that are a key component of climate prediction models.
Data use and benefits
The mission's first validated data products in support of improved weather, climate and ocean forecasts are now being distributed to the public within a few hours of observation. Beginning in 2009, other data products for climate research will be available a few days to a few weeks after observations are taken by the satellite.Altimetry data have a wide variety of uses from basic scientific research on climate to ship routing. Applications include:
- Climate researchClimatologyClimatology is the study of climate, scientifically defined as weather conditions averaged over a period of time, and is a branch of the atmospheric sciences...
: Altimetry data are incorporated into computer models to understand and predict changes in the distribution of heat in ocean, a key element of climate.
- El Niño and La NiñaLa NiñaLa Niña is a coupled ocean-atmosphere phenomenon that is the counterpart of El Niño as part of the broader El Niño-Southern Oscillation climate pattern. During a period of La Niña, the sea surface temperature across the equatorial Eastern Central Pacific Ocean will be lower than normal by 3–5 °C...
forecasting: Understanding the pattern and effects of climate cycles such as El Niño helps predict and mitigate the disastrous effects of floods and drought.

- Tropical cycloneTropical cycloneA tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
forecasting: Altimeter data and satellite ocean wind data are incorporated into atmospheric models for hurricane season forecasting and individual storm severity.
- Ship routingShipping routeA shipping route is a trade route used by merchant ships.Early routes usually were coastal in nature as navigators had to rely on the coastal landmarks...
: Maps of currents, eddies, and vector winds are used in commercial shipping and recreational yachting to optimize routes.
- Offshore industriesOil platformAn oil platform, also referred to as an offshore platform or, somewhat incorrectly, oil rig, is a lаrge structure with facilities to drill wells, to extract and process oil and natural gas, and to temporarily store product until it can be brought to shore for refining and marketing...
: Cable-laying vessels and offshore oil operations require accurate knowledge of ocean circulation patterns, to minimize impacts from strong currents.
- Marine mammal research: Sperm whaleSperm WhaleThe sperm whale, Physeter macrocephalus, is a marine mammal species, order Cetacea, a toothed whale having the largest brain of any animal. The name comes from the milky-white waxy substance, spermaceti, found in the animal's head. The sperm whale is the only living member of genus Physeter...
s, fur sealFur sealFur seals are any of nine species of pinnipeds in the Otariidae family. One species, the northern fur seal inhabits the North Pacific, while seven species in the Arctocephalus genus are found primarily in the Southern hemisphere...
s, and other marine mammals can be tracked, and therefore studied, around ocean eddies where nutrients and plankton are abundant.
- Fisheries managementFisheries managementFisheries management draws on fisheries science in order to find ways to protect fishery resources so sustainable exploitation is possible. Modern fisheries management is often referred to as a governmental system of appropriate management rules based on defined objectives and a mix of management...
: Satellite data identify ocean eddies which bring an increase in organisms that comprise the marine food web, attracting fish and fishermen.
- Coral reefCoral reefCoral reefs are underwater structures made from calcium carbonate secreted by corals. Coral reefs are colonies of tiny living animals found in marine waters that contain few nutrients. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, which in turn consist of polyps that cluster in groups. The polyps...
research: Remotely sensed data are used to monitor and assess coral reefCoral reefCoral reefs are underwater structures made from calcium carbonate secreted by corals. Coral reefs are colonies of tiny living animals found in marine waters that contain few nutrients. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, which in turn consist of polyps that cluster in groups. The polyps...
ecosystems, which are sensitive to changes in ocean temperature.
- Marine debrisMarine debrisMarine debris, also known as marine litter, is human created waste that has deliberately or accidentally become afloat in a lake, sea, ocean or waterway. Oceanic debris tends to accumulate at the centre of gyres and on coastlines, frequently washing aground, when it is known as beach litter or...
tracking: Altimetry can help locate hazardous materials such as floating and partially submerged fishing netFishing netA fishing net or fishnet is a net that is used for fishing. Fishing nets are meshes usually formed by knotting a relatively thin thread. Modern nets are usually made of artificial polyamides like nylon, although nets of organic polyamides such as wool or silk thread were common until recently and...
s, timber, and ship debris.

