
Niqqud
Encyclopedia
| style="margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto; border-style:none"> | ||
Cantillation
Cantillation is the ritual chanting of readings from the Hebrew Bible in synagogue services. The chants are written and notated in accordance with the special signs or marks printed in the Masoretic text of the Hebrew Bible to complement the letters and vowel points...
, geresh
Geresh
Geresh is a sign in Hebrew writing. It has two meanings.#An apostrophe-like sign placed after a letter :...
,
gershayim
Gershayim
Gershayim , also occasionally grashayim , names two distinct typographical marks in the Hebrew language. The name literally means "double geresh".-Punctuation mark:...
|-
| colspan="2" align="center" style="background:white;height:50px"|
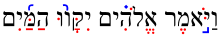
|-
| colspan="2" style="width:250px;background:white" |
"Let the waters be collected".
Letters in black, niqqud in red, cantillation
Cantillation
Cantillation is the ritual chanting of readings from the Hebrew Bible in synagogue services. The chants are written and notated in accordance with the special signs or marks printed in the Masoretic text of the Hebrew Bible to complement the letters and vowel points...
in blue
In Hebrew
Hebrew language
Hebrew is a Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Culturally, is it considered by Jews and other religious groups as the language of the Jewish people, though other Jewish languages had originated among diaspora Jews, and the Hebrew language is also used by non-Jewish groups, such...
orthography
Orthography
The orthography of a language specifies a standardized way of using a specific writing system to write the language. Where more than one writing system is used for a language, for example Kurdish, Uyghur, Serbian or Inuktitut, there can be more than one orthography...
, niqqud or nikkud ( or ) is a system of diacritic
Diacritic
A diacritic is a glyph added to a letter, or basic glyph. The term derives from the Greek διακριτικός . Diacritic is both an adjective and a noun, whereas diacritical is only an adjective. Some diacritical marks, such as the acute and grave are often called accents...
al signs used to represent vowels or distinguish between alternative pronunciations of letters of the Hebrew alphabet
Hebrew alphabet
The Hebrew alphabet , known variously by scholars as the Jewish script, square script, block script, or more historically, the Assyrian script, is used in the writing of the Hebrew language, as well as other Jewish languages, most notably Yiddish, Ladino, and Judeo-Arabic. There have been two...
. Several such diacritical systems were developed in the Early Middle Ages. The most widespread system, and the only one still used to a significant degree today, was created by the Masoretes
Masoretes
The Masoretes were groups of mostly Karaite scribes and scholars working between the 7th and 11th centuries, based primarily in present-day Israel in the cities of Tiberias and Jerusalem, as well as in Iraq...
of Tiberias in the second half of the first millennium in the Land of Israel
Land of Israel
The Land of Israel is the Biblical name for the territory roughly corresponding to the area encompassed by the Southern Levant, also known as Canaan and Palestine, Promised Land and Holy Land. The belief that the area is a God-given homeland of the Jewish people is based on the narrative of the...
(see Masoretic Text
Masoretic Text
The Masoretic Text is the authoritative Hebrew text of the Jewish Bible and is regarded as Judaism's official version of the Tanakh. While the Masoretic Text defines the books of the Jewish canon, it also defines the precise letter-text of these biblical books, with their vocalization and...
, Tiberian Hebrew
Tiberian Hebrew
Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization...
). Text written with niqqud is called ktiv menuqad
Ktiv menuqad
Ktiv menuqad is text in Hebrew supplemented with niqqud diacritics. In modern Israeli orthography niqqud is seldom used, except in specialised texts such as dictionaries, poetry, or texts for children or for new immigrants....
.
Niqqud marks are small compared to consonants, so they can be added without retranscribing texts whose writers did not anticipate them.
In modern Israeli orthography niqqud is seldom used, except in specialised texts such as dictionaries, poetry, or texts for children or for new immigrants. For purposes of disambiguation, a system of spelling without niqqud, known in Hebrew as ktiv maleh , literally "full spelling", has developed. This was formally standardised in the Rules for Spelling without Niqqud (כללי הכתיב חסר הניקוד) enacted by the
Academy of the Hebrew Language
Academy of the Hebrew Language
The Academy of the Hebrew Language was established by the Israeli government in 1953 as the "supreme institution for scholarship on the Hebrew language."-History:...
in 1996.
Among those who do not speak Hebrew, niqqud are the sometimes unnamed focus of controversy regarding the interpretation of those written with the Tetragrammaton
Tetragrammaton
The term Tetragrammaton refers to the name of the God of Israel YHWH used in the Hebrew Bible.-Hebrew Bible:...
—written as in Hebrew
Hebrew language
Hebrew is a Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Culturally, is it considered by Jews and other religious groups as the language of the Jewish people, though other Jewish languages had originated among diaspora Jews, and the Hebrew language is also used by non-Jewish groups, such...
. The interpretation affects discussion of the authentic ancient pronunciation of the name whose other conventional English forms are "Jehovah
Jehovah
Jehovah is an anglicized representation of Hebrew , a vocalization of the Tetragrammaton , the proper name of the God of Israel in the Hebrew Bible....
" and "Yahweh
Yahweh
Yahweh is the name of God in the Bible, the God of Abraham, Isaac, Jacob, Jews and Christians.The word Yahweh is a modern scholarly convention for the Hebrew , transcribed into Roman letters as YHWH and known as the Tetragrammaton, for which the original pronunciation is unknown...
".
Demonstration
This table uses the consonants , or , where appropriate, to demonstrate where the niqqud is placed in relation to the consonant it is pronounced after. Any other consonants shown are actually part of the vowel. Note that there is some variation among different traditions in exactly how some vowel points are pronounced. The table below shows how most Israelis would pronounce them, but the classic Ashkenazi pronunciation, for example, differs in several respects.- This demonstration is known to work in Internet ExplorerInternet ExplorerWindows Internet Explorer is a series of graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft and included as part of the Microsoft Windows line of operating systems, starting in 1995. It was first released as part of the add-on package Plus! for Windows 95 that year...
and MozillaMozillaMozilla is a term used in a number of ways in relation to the Mozilla.org project and the Mozilla Foundation, their defunct commercial predecessor Netscape Communications Corporation, and their related application software....
browsersWeb browserA web browser is a software application for retrieving, presenting, and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web. An information resource is identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier and may be a web page, image, video, or other piece of content...
in at least some circumstances, but in most other WindowsMicrosoft WindowsMicrosoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
browsers the niqqud do not properly combine with the consonants. It works very well when "dir=rtl" is added in the HTML source. This is because, currently, the Windows text display engine does not combine the niqqud automatically. Except as noted, the vowel pointings should appear directly beneath the consonants and the accompanying "vowel letter" consonants for the mālê (long) forms appear after.
- Note concerning IPA: the transcription symbols are linked to the articles about the sounds they represent. The diacriticDiacriticA diacritic is a glyph added to a letter, or basic glyph. The term derives from the Greek διακριτικός . Diacritic is both an adjective and a noun, whereas diacritical is only an adjective. Some diacritical marks, such as the acute and grave are often called accents...
˘ (breveBreveA breve is a diacritical mark ˘, shaped like the bottom half of a circle. It resembles the caron , but is rounded, while the caron has a sharp tip...
) indicates a short vowelLength (phonetics)In phonetics, length or quantity is a feature of sounds that are distinctively longer than other sounds. There are long vowels as well as long consonants .Many languages do not have distinctive length...
; the triangular colon symbol ː indicates that the vowel is longLength (phonetics)In phonetics, length or quantity is a feature of sounds that are distinctively longer than other sounds. There are long vowels as well as long consonants .Many languages do not have distinctive length...
.
| Symbol | Type | Common name | Alternate names | Scientific name | Hebrew | IPA | Transliteration Transliteration Transliteration is a subset of the science of hermeneutics. It is a form of translation, and is the practice of converting a text from one script into another... |
Comments | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Israeli | Sh'va | sheva | e or Ø Zero (linguistics) A zero, in linguistics, is a constituent needed in an analysis but not realized in speech. This implies that there is a lack of an element where a theory would expect one. It is usually written with the symbol "", in Unicode .There are several kind of zeros.... |
ə, e, ', or nothing | In modern Hebrew, shva represents either /e/ or Ø Zero (linguistics) A zero, in linguistics, is a constituent needed in an analysis but not realized in speech. This implies that there is a lack of an element where a theory would expect one. It is usually written with the symbol "", in Unicode .There are several kind of zeros.... , regardless of its traditional classification as (שווא נח) or shva na (שווא נע), see the following table for examples:
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
ɐ ɛ e i ɔ o u |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Reduced segol | hataf segol | e | e | – | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
ɛ | ĕ | ‒ | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Reduced patach | hataf patah | a | a | – | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
ɐ | ă | – | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Reduced kamatz | hataf kamats | o | o | – | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
ɔ | ŏ | – | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Hiriq | hiriq | i | i | Usually promoted to Hiriq Malei in Israeli writing for the sake of disambiguation. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
i or iː) | i or í | – | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Hiriq malei | hiriq yod | i | i | – | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
iː | î | – | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Zeire | tsere, tzeirei | e | e | – | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
eː | ē | – | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Zeire malei | tsere yod, tzeirei yod | e | e | More commonly ei (IPA [ei]). | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
eː | ê | – | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Segol | segol | e | e | – | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
ɛ or ɛː | e or é | – | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Segol malei | segol yod | e | e | With succeeding yod, it is more commonly ei (IPA [e̞i]) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
ɛː | ệ | – | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Patach | patah | a | a | before the letter, and not behind. Thus, style='font-family: Narkisim, David, Times New Roman, Miriam Fixed, Gisha, Microsoft Sans Serif, serif; font-size:146%;' lang="he" xml:lang="he">נֹחַ (Noah) is pronounced /ˈno.ax/. This only occurs at the ends of words and only with patach and ח, ע, and הּ (that is, ה with a dot (mappiq) in it). This is sometimes called a patach g'nuvah, or "stolen" patach (more formally, "furtive patach"), since the sound "steals" an imaginary epenthetic consonant to make the extra syllable. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
ɐ or ː | a or á | – | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Patach malei | patah yod | a | a | – | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
ɐ | ậ | – | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Kamatz gadol | kamats | a | a | – | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
ɔː | ā | – | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Kamatz malei | kamats he | a | a | comm | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
ɔː | â | – | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Kamatz katan | kamats hatuf | o | o | Usually promoted to Holam Malei in Israeli writing for the sake of disambiguation. Also, not to be confused with Hataf Kamatz. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
ɔ | – | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Holam | holam | o | o | Usually promoted to Holam Malei in Israeli writing for the sake of disambiguation. The holam is written above the consonant on the left corner, or slightly to the left of (i.e., after) it at the top. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
oː | ō | comm | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Holam malei | holam male | o | o | The holam is written in the normal position relative to the main consonant (above and slightly to the left), which places it directly over the vav Waw (letter) Waw is the sixth letter of the Northwest Semitic family of scripts, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew, Syriac, and Arabic .... . |
||||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
oː | ô | – | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Kubutz | kubuts | u | u | Usually promoted to Shuruk in Israeli writing for the sake of disambiguation. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
u or uː | u or ú | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Shuruk | shuruk | u | u | The shuruk is written after the consonant it applies to (the consonant after which the vowel /u/ is pronounced). The dot in the shuruk is identical to a dagesh, thus shuruq and vav with a dagesh are indistinguishable. (see below). | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
uː | û | – | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Dagesh | dagesh | varied | varied | Not a vowel, "dagesh" refers to two distinct grammatical entities:
For most letters the dagesh is written within the glyph, near the middle if possible, but the exact position varies from letter to letter (some letters do not have an open area in the middle, and in these cases it is written usually beside the letter, as with yod). The guttural consonants (אהחע) and resh (ר) are not marked with a dagesh, although the letter he (ה) (and rarely א) may appear with a mappiq (which is written the same way as dagesh) at the end of a word to indicate that the letter does not signify a vowel but is consonantal. To the resulting form, there can still be added a niqqud diacritic designating a vowel. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Rafe | rafe | Not used in Hebrew. Still occasionally seen in Yiddish (actually more often as the spelling becomes more standardized, embracing YIVO YIVO YIVO, , established in 1925 in Wilno, Poland as the Yidisher Visnshaftlekher Institut , or Yiddish Scientific Institute, is a source for orthography, lexicography, and other studies related to the Yiddish language... rules) to distinguish פּ /p/ from פֿ /f/ (note that this letter is always pronounced [f] when in the final position, with the exception of loanword Loanword A loanword is a word borrowed from a donor language and incorporated into a recipient language. By contrast, a calque or loan translation is a related concept where the meaning or idiom is borrowed rather than the lexical item itself. The word loanword is itself a calque of the German Lehnwort,... s—שׁוֹפּ—, foreign names—פִילִיפּ— and some slang Slang Slang is the use of informal words and expressions that are not considered standard in the speaker's language or dialect but are considered more acceptable when used socially. Slang is often to be found in areas of the lexicon that refer to things considered taboo... —חָרַפּ). Some ancient manuscripts have a dagesh or a rafe on nearly every letter. It is also used to indicate that a letter like ה or א is silent. In the particularly strange case of the Ten Commandments Ten Commandments The Ten Commandments, also known as the Decalogue , are a set of biblical principles relating to ethics and worship, which play a fundamental role in Judaism and most forms of Christianity. They include instructions to worship only God and to keep the Sabbath, and prohibitions against idolatry,... , which have two different traditions for their Cantillation Cantillation Cantillation is the ritual chanting of readings from the Hebrew Bible in synagogue services. The chants are written and notated in accordance with the special signs or marks printed in the Masoretic text of the Hebrew Bible to complement the letters and vowel points... s which many texts write together, there are cases of a single letter with both a dagesh and a rafe, if it is hard in one reading and soft in the other. |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
Niqqud, but not a vowel. Used as an "anti-dagesh", to show that a בגדכפת Begadkefat Begadkefat is the name given to a phenomenon of spirantization affecting most plosive consonants of Biblical Hebrew and Aramaic when they are preceded by a vowel and not geminated... letter is soft and not hard, or (sometimes) that a consonant is single and not double, or that a letter like ה or א is completely silent |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Shin dot | shin dot | , or , "right Shin" | ʃ | š/sh | Niqqud, but not a vowel (except when inadequate typefaces merge the holam of a letter before the shin with the shin dot). The dot for shin is written over the right (first) branch of the letter. It is usually transcribed "sh". | |||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Israeli | Sin dot | sin dot | , , "left Sin" | s | ś/s | Niqqud, but not a vowel (except when inadequate typefaces merge the holam of the sin with the sin dot). The dot for sin is written over the left (third) branch of the letter | |||||||||||||||||
| Tiberian Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
Some linguistic evidence indicates that it was originally IPA [ɬ], though poetry and acrostics show that it has been pronounced /s/ since quite ancient times). | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Keyboard
For the Hebrew letters there is a standardized Hebrew keyboardHebrew keyboard
A Hebrew keyboard comes in two different keyboard layouts. Most Hebrew keyboards are bilingual having both Hebrew and English, as English letters are necessary for URLs and Email addresses...
. But when it comes to niqqud, different computer systems and programs provide for adding the signs in different ways.
Using the Hebrew keyboard layout in Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
the typist can enter niqqud by pressing CapsLock, putting the cursor after the consonant letter and then pressing Shift and one of the following keys. In GTK+ Linux systems niqqud can be entered by pressing ctrl+shift+u followed by the appropriate 4 digit Unicode.
Using the Hebrew keyboard layout in Mac OS X
Mac OS X
Mac OS X is a series of Unix-based operating systems and graphical user interfaces developed, marketed, and sold by Apple Inc. Since 2002, has been included with all new Macintosh computer systems...
, the typist can enter niqqud by pressing the Option key together with a number on the top row of the keyboard. Other combinations like sofit and hataf can also be entered by pressing either the Shift key and a number, or by pressing the Shift key, Option key, and a number at the same time.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Notes:
- [1] The letter "O" represents whatever Hebrew letter is used.
- [2] For sin-dot and shin-dot, the letter "ש" (sin/shin) is used since they can only be used with that letter.
- [3] The dagesh, mappiq, and shuruk are different; however, they look the same and (hence) are input the same way (all 3 of them.)
- [4] For shuruk, the letter "ו" (vav) is used since it can only be used with that letter.
See also
- The ArabicArabic languageArabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
equivalent, harakatHarakatThe Arabic script has numerous diacritics, including ijam ⟨⟩ , and tashkil ⟨⟩...
. - Hebrew diacriticsHebrew diacriticsHebrew orthography includes several types of diacritics:* a set of mostly optional ancillary glyphs known as niqqud in Hebrew, which are used either to represent vowels or to distinguish between alternate pronunciations of several letters of the Hebrew alphabet ;* geresh and gershayim, two...
- Q're perpetuum
- Dagesh
- Hebrew spellingHebrew spellingThere are several systems of Hebrew spelling that are used. The Hebrew alphabet contains 22 letters, all of which are primarily consonants. This is because the Hebrew script is an abjad, that is, its letters indicate consonant, not vowels, nor syllables...
- Tiberian HebrewTiberian HebrewTiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization...


 [2]
[2]