
Nicaraguan Spanish
Encyclopedia
Nicaraguan Spanish is geographically defined as the form of Spanish spoken in the country of Nicaragua
Nicaragua
Nicaragua is the largest country in the Central American American isthmus, bordered by Honduras to the north and Costa Rica to the south. The country is situated between 11 and 14 degrees north of the Equator in the Northern Hemisphere, which places it entirely within the tropics. The Pacific Ocean...
in Central America
Central America
Central America is the central geographic region of the Americas. It is the southernmost, isthmian portion of the North American continent, which connects with South America on the southeast. When considered part of the unified continental model, it is considered a subcontinent...
. Affectionately, Nicaraguan Spanish is often called Nicañol.
The Spanish dialect in Nicaragua shares many similarities to that of its neighbors in the region, but it has its stark differences in pronunciation and usage. Such differences are also noticed within the geographic confinements of the country.
Nicaragua is the Central American country that uses voseo
Voseo
Voseo is the use of the second person singular pronoun vos in many dialects of Spanish. In dialects that have it, it is used either instead of tú, or alongside it....
Spanish as its written and spoken form with the strongest frequency, similar to that of Argentina
Argentina
Argentina , officially the Argentine Republic , is the second largest country in South America by land area, after Brazil. It is constituted as a federation of 23 provinces and an autonomous city, Buenos Aires...
and other countries in the Río de la Plata
Río de la Plata
The Río de la Plata —sometimes rendered River Plate in British English and the Commonwealth, and occasionally rendered [La] Plata River in other English-speaking countries—is the river and estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay River and the Paraná River on the border between Argentina and...
region. The pronunciation of Nicaraguan Spanish with other voseo forms, such as Rioplatense Spanish
Rioplatense Spanish
Rioplatense Spanish or River Plate Spanish is a dialectal variant of the Spanish language spoken mainly in the areas in and around the Río de la Plata basin of Argentina and Uruguay, and also in Rio Grande do Sul, although features of the dialect are shared with the varieties of Spanish spoken...
, however, is not similar despite sharing many grammatical similarities. Vos is used frequently in colloquial and familiar settings, but many Nicaraguans understand tuteo. The use of "vos" can be heard in television programs and can be seen in written form in publications.
In the North Atlantic Autonomous Region and the South Atlantic Autonomous Region of the Atlantic Coast, language and pronunciation is fused with native and creole dialects such as Miskito
Miskito language
Miskito is a Misumalpan language spoken by the Miskito people in northeastern Nicaragua, especially in the North Atlantic Autonomous Region, and in eastern Honduras....
, Rama
Rama language
Rama is one of the indigenous languages of the Chibchan family spoken by the Rama people on the island of Rama Cay and south of lake Bluefields on the Atlantic Coast of Nicaragua. Other indigenous languages of this region include Miskito and Sumu . Rama is one of the northernmost languages of the...
, Sumo
Sumo language
Sumo is the collective name for a group of Misumalpan languages spoken in Nicaragua and Honduras. Hale & Salamanca classifies the Sumu languages into a northern Mayangna, composed of the Twahka and Panamahka dialects, and southern Ulwa...
, Miskito Coastal Creole
Miskito Coastal Creole
Mískito Coast Creole or Nicaragua Creole English is a language spoken in Nicaragua based on English. Its approximately 30,000 speakers are found along the Mosquito Coast of the Caribbean Sea. The language is nearly identical to Belizean Creole , and similar to all Central American Creoles...
, Jamaican Patois, Garifuna
Garifuna language
Garifuna is an Arawakan language spoken in Honduras, Guatemala, and Belize by the Garifuna people. The language is also spoken to a lesser extent in Nicaragua's Mosquito Coast. Historically it was referred to as Carib or Black Carib and Igñeri by Europeans. Garifuna has a vocabulary split between...
and Rama Cay Creole
Rama Cay Creole
Rama Cay Creole is a Creole language spoken by some 8-900 people on the island of Rama Cay in eastern Nicaragua. It is based on Miskito Coast Creole with additional elements of the Chibchan language Rama and purportedly some elements of English spoken with a German accent...
.
Origins
Nicaraguan Spanish has many indigenous influences and several distinguishing characteristics. Until the 19th century, a hybrid form of Nahuat-Spanish was the common language of Nicaragua. Today Nahuat, MangueMangue
the word Mangue can refer to several things:*The Mangue Bit, a Brazilian music style.*The Mangue language, an extinct Oto-Manguean language of Nicaragua.*The Mangue people, who spoke the language....
and Mayan
Mayan languages
The Mayan languages form a language family spoken in Mesoamerica and northern Central America. Mayan languages are spoken by at least 6 million indigenous Maya, primarily in Guatemala, Mexico, Belize and Honduras...
words, along with their respective syntax
Syntax
In linguistics, syntax is the study of the principles and rules for constructing phrases and sentences in natural languages....
, can be found in everyday speech. The Nicaraguan accent dates back to the 16th century in Andalusia
Andalusia
Andalusia is the most populous and the second largest in area of the autonomous communities of Spain. The Andalusian autonomous community is officially recognised as a nationality of Spain. The territory is divided into eight provinces: Huelva, Seville, Cádiz, Córdoba, Málaga, Jaén, Granada and...
. Andalusia's profound influence on speech could be found in other areas, particularly Cuba
Cuba
The Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
, the Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic is a nation on the island of La Hispaniola, part of the Greater Antilles archipelago in the Caribbean region. The western third of the island is occupied by the nation of Haiti, making Hispaniola one of two Caribbean islands that are shared by two countries...
and the Caribbean/coastal regions of Venezuela
Venezuela
Venezuela , officially called the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela , is a tropical country on the northern coast of South America. It borders Colombia to the west, Guyana to the east, and Brazil to the south...
, Colombia
Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia , is a unitary constitutional republic comprising thirty-two departments. The country is located in northwestern South America, bordered to the east by Venezuela and Brazil; to the south by Ecuador and Peru; to the north by the Caribbean Sea; to the...
, Panama
Panama
Panama , officially the Republic of Panama , is the southernmost country of Central America. Situated on the isthmus connecting North and South America, it is bordered by Costa Rica to the northwest, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. The...
, Honduras
Honduras
Honduras is a republic in Central America. It was previously known as Spanish Honduras to differentiate it from British Honduras, which became the modern-day state of Belize...
and Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico , officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico , is an unincorporated territory of the United States, located in the northeastern Caribbean, east of the Dominican Republic and west of both the United States Virgin Islands and the British Virgin Islands.Puerto Rico comprises an...
. Nicaragua's relative isolation from Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
and, to an extent, other nations, fostered the development of the Nicaraguan accent, which did not change in the same ways that the Andalusian or Latin American accents did.
Characteristics
In Spanish, few words end in plosives. However, many such words are borrowed from English. In Nicaragua, all such stops are usually pronounced like c's. The Costa Rican ice cream shop Pops, with franchises in Central America is pronounced by populations in certain regions as Pocs. Internet is sometimes pronounced Internec; Laptop is pronounced lactoc; and robot pronounced roboc. This is sometimes extended to native Spanish words where such stops are found at the end of a syllable. For example, Aceptar is sometimes pronounced as Acectar.Pronunciation and Variations
Some Nicaraguans pronounce the word vos with a strong s sound at the end. In the central part of the country, regions like BoacoBoaco
Boaco is the capital city and municipality of the Boaco department of Nicaragua. The municipality of Boaco has a population of 56,900 and an area of 1,086.81 km² while the department is 4,177 km2....
pronounce vos without the s sound at the end. The result is vo, similar to vous in French
French language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
and voi in Italian
Italian language
Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia...
. The opposite occurs in regions like the Rio San Juan or Rivas
Rivas (department)
Rivas is a department of the Republic of Nicaragua. It covers an area of 2,155 km² and has a population of 166,900 . The department's capital is the city of Rivas.-Overview:...
, where the S at the end of words is frequently pronounced. Nicaraguans, unlike most Spanish speaking groups, cannot be categorized uniformly in terms of accent and word usage. Although Spanish is spoken uniformly throughout the country, the country faces a phenomenon similar to the Italian dialects of Italy: vocabulary, pronunciation and word use can vary between towns and departments.
If you want more information about learning Spanish while in Nicaragua, contact one of the several Spanish-language schools that operate in the country. A few of the most well-known ones are Viva Spanish School in Managua and Nicaragua Spanish Schools, with school in several locations. Granada also offers SOL Spanish School.
Additional Characteristics
Some other characteristics of Nicaraguan phonology include:- The presence of Seseo and, to a lesser extent, CeceoCeceoIn Spanish dialectology, the terms distinción, seseo and ceceo are used to describe the opposition between dialects that distinguish the phonemes and , and those that exhibit merger of the two sounds into either or .Dialects that distinguish the two sounds, and thus pronounce the words casa...
.
- /s/ at the end of a syllable or before a consonant is pronounced like [h].
- j (/x/), is aspirated; it is soft as the /h/ in English (e.g.: Yahoo).
- Intervocalic /b/, /d/, and /g/ show no sign of reduction, and are much more pronounced than in most dialects.
- There is no confusion between /l/ and /r/, as in the Caribbean.
- /s/, /z/ and in some cases /c/ (as in cerrar) are pronounced as [s].
- /m/ at the end of a word (at times) is pronounced as [n]
Second person singular pronouns
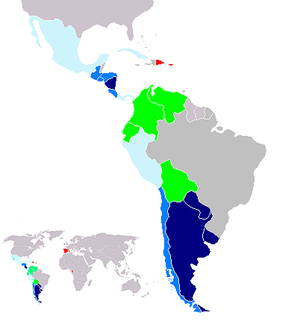
Vos
"Vos" is the dominant second person singular pronoun used by many speakers in familiar or informal contexts. VoseoVoseo
Voseo is the use of the second person singular pronoun vos in many dialects of Spanish. In dialects that have it, it is used either instead of tú, or alongside it....
is most commonly used among people in the same age group in addressing one another. It is common to hear young children address each other with "vos." The phenomenon also occurs among adults who address one another in familiar or informal contexts. "Vos" is also used by adults in addressing children or juveniles. However, the relationship does not re-occur when children address adults. Children address adults with "usted;" regardless of age, status or context.
Conjugations with the Vos Pronoun
See VoseoThe conjugations with the vos second person form vary in comparison with its tuteo counterpart.
Affirmative Imperative
See Voseo Affirmative ImperativeThe use of the imperative in Nicaraguan Spanish is emphatic, with particular emphasis on the final letter of a given verb. The emphasis also removes the need for additional words that establish a given command. For example, ¡Ven aca! or ¡Ven aquí! becomes ¡Vení!
Usted
"Usted" is the formal second person singular pronoun in Nicaraguan Spanish. "Usted" is used in addressing foreigners formally, for acquaintances, and in business settings. Unlike neighboring Costa RicaCosta Rica
Costa Rica , officially the Republic of Costa Rica is a multilingual, multiethnic and multicultural country in Central America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, Panama to the southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the west and the Caribbean Sea to the east....
, "usted" is not the dominant second person pronoun for addressing a person.
Tú
"Tú" is hardly used in Nicaraguan Spanish. The use of tú is limited strictly to foreigners. It is used in addressing foreigners familiarly and when writing correspondence to foreigners (again in familiar contexts).Vocabulary
Certain words are present in Nicaraguan Spanish that may not be immediately recognizable to non-Nicaraguans:- Pinolero/a; Nica; Nicoya: colloquial terms for a Nicaraguan.
- Chavalo/a: usually referring to an adolescent or young man/woman.
- Cachipil: a lot of something. (usually in terms of quantity.)
- Mae/Maje: depending on context, it can be used to refer to a friend, a third person in a familiar manner, or can be colloquially used to refer to a moronMoron (psychology)Moron is a term once used in psychology to denote mild mental retardation. The term was closely tied with the American eugenics movement. Once the term became popularized, it fell out of use by the psychological community, as it was used more commonly as an insult than as a psychological...
. - Caite: form of leather shoe typically worn and made by campesinos.
- Chochada: something unimportant; nonsense, usually made as a comment in regards to someone's words.
- Salvaje: colloquially used to refer to something awesome.
- Rejio: used to refer to something very good.
- Boludo: lazy.
- Gaseosa: soft drinkSoft drinkA soft drink is a non-alcoholic beverage that typically contains water , a sweetener, and a flavoring agent...
. - Pulperia: grocery storeGrocery storeA grocery store is a store that retails food. A grocer, the owner of a grocery store, stocks different kinds of foods from assorted places and cultures, and sells these "groceries" to customers. Large grocery stores that stock products other than food, such as clothing or household items, are...
. - Ideay: a common phrase used when someone is surprised.
- Pofi; Pana: friend.
- Pegue: workplace.
- Chayul; Zancudo: mosquitoMosquitoMosquitoes are members of a family of nematocerid flies: the Culicidae . The word Mosquito is from the Spanish and Portuguese for little fly...
. - Tuani: something very nice or pleasing, usually used when expressing positive attitudes toward an article of clothing.
See also
- Spanish language in the Americas
- Central American SpanishCentral American SpanishCentral American Spanish is the general name of the Spanish language dialects spoken in Central America...
- Seseo
- VoseoVoseoVoseo is the use of the second person singular pronoun vos in many dialects of Spanish. In dialects that have it, it is used either instead of tú, or alongside it....

