
Moving parts
Encyclopedia

Machine
A machine manages power to accomplish a task, examples include, a mechanical system, a computing system, an electronic system, and a molecular machine. In common usage, the meaning is that of a device having parts that perform or assist in performing any type of work...
are those parts of it that move. Machines comprise both moving (or movable) and fixed parts. The moving parts have controlled and constrained motions.
Moving parts do not include any moving fluids, such as fuel
Fuel
Fuel is any material that stores energy that can later be extracted to perform mechanical work in a controlled manner. Most fuels used by humans undergo combustion, a redox reaction in which a combustible substance releases energy after it ignites and reacts with the oxygen in the air...
, coolant
Coolant
A coolant is a fluid which flows through a device to prevent its overheating, transferring the heat produced by the device to other devices that use or dissipate it. An ideal coolant has high thermal capacity, low viscosity, is low-cost, non-toxic, and chemically inert, neither causing nor...
or hydraulic fluid
Hydraulic fluid
Hydraulic fluids, also called hydraulic liquids, are the medium by which power is transferred in hydraulic machinery. Common hydraulic fluids are based on mineral oil or water...
. Moving parts also do not include any mechanical lock
Lock (device)
A lock is a mechanical or electronic fastening device that is released by a physical object or secret information , or combination of more than one of these....
s, switch
Switch
In electronics, a switch is an electrical component that can break an electrical circuit, interrupting the current or diverting it from one conductor to another....
es, nuts
Nut (hardware)
A nut is a type of hardware fastener with a threaded hole. Nuts are almost always used opposite a mating bolt to fasten a stack of parts together. The two partners are kept together by a combination of their threads' friction, a slight stretch of the bolt, and compression of the parts...
and bolts
Screw
A screw, or bolt, is a type of fastener characterized by a helical ridge, known as an external thread or just thread, wrapped around a cylinder. Some screw threads are designed to mate with a complementary thread, known as an internal thread, often in the form of a nut or an object that has the...
, screw caps for bottles (the cap used to cover a water bottle
Water bottle
A water bottle is a container used to hold water for consumption. This allows an individual to transport or carry the bottled water from one place to another. A water bottle is usually made of plastic, glass, or metal, and so most can be recycled. Water bottles can be single use, returnable, or...
when not in use) etc.
Mechanical efficiency and wear
The amount of moving parts in a machine is a factor in its mechanical efficiencyMechanical efficiency
Mechanical efficiency measures the effectiveness of a machine in transforming the energy and power that is input to the device into an output force and movement...
. The greater the number of moving parts, the greater the amount of energy lost to heat by friction
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and/or material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:...
between those parts. In a modern automobile engine, for example, roughly 7% of the total power
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
obtained from burning the engine's fuel is lost to friction between the engine's moving parts.
Conversely, the fewer the number of moving parts, the greater the efficiency. Machines with no moving parts at all can be very efficient. An electrical transformer, for example, has no moving parts, and its mechanical efficiency is generally above the 90% mark. (The remaining power losses in a transformer are from other causes, including loss to electrical resistance in the copper windings and hysteresis
Hysteresis
Hysteresis is the dependence of a system not just on its current environment but also on its past. This dependence arises because the system can be in more than one internal state. To predict its future evolution, either its internal state or its history must be known. If a given input alternately...
loss and eddy current
Eddy current
Eddy currents are electric currents induced in conductors when a conductor is exposed to a changing magnetic field; due to relative motion of the field source and conductor or due to variations of the field with time. This can cause a circulating flow of electrons, or current, within the body of...
loss in the iron core.)
Two means are used for overcoming the efficiency losses caused by friction between moving parts. First, moving parts are lubricated
Lubrication
Lubrication is the process, or technique employed to reduce wear of one or both surfaces in close proximity, and moving relative to each another, by interposing a substance called lubricant between the surfaces to carry or to help carry the load between the opposing surfaces. The interposed...
. Second, the moving parts of a machine are designed so that they have a small amount of contact with one another. The latter, in its turn, comprises two approaches. A machine can be reduced in size, thereby quite simply reducing the areas of the moving parts that rub against one another; and the designs of the individual components can be modified, changing their shapes and structures to reduce or avoid contact with one another.
Lubrication also reduces wear
Wear
In materials science, wear is erosion or sideways displacement of material from its "derivative" and original position on a solid surface performed by the action of another surface....
, as does the use of suitable materials. As moving parts wear out, this can affect the precision of the machine. Designers thus have to design moving parts with this factor in mind, ensuring that if precision over the lifetime of the machine is paramount, that wear is accounted for and, if possible, minimized. (A simple example of this is the design of a simple single-wheel wheelbarrow
Wheelbarrow
A wheelbarrow is a small hand-propelled vehicle, usually with just one wheel, designed to be pushed and guided by a single person using two handles to the rear, or by a sail to push the ancient wheelbarrow by wind. The term "wheelbarrow" is made of two words: "wheel" and "barrow." "Barrow" is a...
. A design where the axle
Axle
An axle is a central shaft for a rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to its surroundings, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearings or bushings are provided at the mounting points where the axle...
is fixed to the barrow arms and the wheel rotates around it is prone to wear which quickly causes wobble, whereas a rotating axle that is attached to the wheel and that rotates upon bearing
Bearing (mechanical)
A bearing is a device to allow constrained relative motion between two or more parts, typically rotation or linear movement. Bearings may be classified broadly according to the motions they allow and according to their principle of operation as well as by the directions of applied loads they can...
s in the arms does not start to wobble as the axle wears through the arms.)
The scientific and engineering discipline that deals with the lubrication, friction, and wear of moving parts is tribology
Tribology
Tribology is the science and engineering of interacting surfaces in relative motion. It includes the study and application of the principles of friction, lubrication and wear...
, an interdisciplinary field that encompasses materials science
Materials science
Materials science is an interdisciplinary field applying the properties of matter to various areas of science and engineering. This scientific field investigates the relationship between the structure of materials at atomic or molecular scales and their macroscopic properties. It incorporates...
, mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is a discipline of engineering that applies the principles of physics and materials science for analysis, design, manufacturing, and maintenance of mechanical systems. It is the branch of engineering that involves the production and usage of heat and mechanical power for the...
, chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, and mechanics
Mechanics
Mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the behavior of physical bodies when subjected to forces or displacements, and the subsequent effects of the bodies on their environment....
.
Failure
As mentioned, wear is a concern for moving parts in a machine. Other concerns that lead to failure include corrosionCorrosion
Corrosion is the disintegration of an engineered material into its constituent atoms due to chemical reactions with its surroundings. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metals in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen...
, erosion
Erosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
, thermal stress and heat generation, vibration
Vibration
Vibration refers to mechanical oscillations about an equilibrium point. The oscillations may be periodic such as the motion of a pendulum or random such as the movement of a tire on a gravel road.Vibration is occasionally "desirable"...
, fatigue loading, and cavitation
Cavitation
Cavitation is the formation and then immediate implosion of cavities in a liquidi.e. small liquid-free zones that are the consequence of forces acting upon the liquid...
.
Fatigue is related to large inertial forces, and is affected by the type of motion that a moving part has. A moving part that has a uniform rotation motion is subject to less fatigue than a moving part that oscillates back and forth. Vibration leads to failure when the forcing frequency of the machine's operation hits a resonant frequency of one or more moving parts, such as rotating shafts. Designers avoid this by calculating the natural frequencies of the parts at design time, and altering the parts to limit or eliminate such resonance. Yet further factors that can lead to failure of moving parts include failures in the cooling and lubrication systems of a machine.
One final, particular, factor related to failure of moving parts is kinetic energy. The sudden release of the kinetic energy of the moving parts of a machine causes overstress failures if a moving part is impeded in its motion by a foreign object, such as stone caught on the blades of a fan or propellor, or even the proverbial "spanner
Wrench
A wrench or spanner is a tool used to provide grip and mechanical advantage in applying torque to turn objects—usually rotary fasteners, such as nuts and bolts—or keep them from turning....
/monkey wrench
Monkey wrench
The monkey wrench is an adjustable wrench, a later American development of eighteenth century English coach wrenches. It was popular in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries but is now used only for heavier tasks, having been mostly replaced by the lighter and sleeker shifting adjustable or...
in the works". (See foreign object damage
Foreign object damage
Foreign Object Debris is a substance, debris or article alien to a vehicle or system which would potentially cause damage.Foreign Object Damage is any damage attributed to a foreign object that can be expressed in physical or economic terms that may or may not degrade the product's required...
for further discussion of this.)
Kinetic energy of the moving parts of a machine
The kinetic energyKinetic energy
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion.It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes...
of a machine is the sum of the kinetic energies of its individual moving parts. A machine with moving parts can, mathematically, be treated as a connected system of bodies, whose kinetic energies are simply summed. The individual kinetic energies are determined from the kinetic energies of the moving parts' translation
Translation (physics)
In physics, translation is movement that changes the position of an object, as opposed to rotation. For example, according to Whittaker:...
s and rotation
Rotation
A rotation is a circular movement of an object around a center of rotation. A three-dimensional object rotates always around an imaginary line called a rotation axis. If the axis is within the body, and passes through its center of mass the body is said to rotate upon itself, or spin. A rotation...
s about their axes.
The kinetic energy of rotation of the moving parts can be determined by noting that every such system of moving parts can be reduced to a collection of connected bodies rotating about an instantaneous axis, which form either a ring or a portion of an ideal ring, of radius
 rotating at
rotating at  revolutions per second
revolutions per secondRevolutions per minute
Revolutions per minute is a measure of the frequency of a rotation. It annotates the number of full rotations completed in one minute around a fixed axis...
. This ideal ring is known as the equivalent fly wheel, whose radius is the radius of gyration. The integral
Integral
Integration is an important concept in mathematics and, together with its inverse, differentiation, is one of the two main operations in calculus...
of the squares of the radii all the portions of the ring with respect to their mass
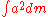 , also expressible if the ring is modelled as a collection of discrete particles as the sum of the products of those mass and the squares of their radii
, also expressible if the ring is modelled as a collection of discrete particles as the sum of the products of those mass and the squares of their radii  is the ring's moment of inertia
is the ring's moment of inertiaMoment of inertia
In classical mechanics, moment of inertia, also called mass moment of inertia, rotational inertia, polar moment of inertia of mass, or the angular mass, is a measure of an object's resistance to changes to its rotation. It is the inertia of a rotating body with respect to its rotation...
, denoted
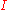 . The rotational kinetic energy of the whole system of moving parts is
. The rotational kinetic energy of the whole system of moving parts is 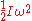 , where
, where 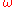 is the angular velocity
is the angular velocityAngular velocity
In physics, the angular velocity is a vector quantity which specifies the angular speed of an object and the axis about which the object is rotating. The SI unit of angular velocity is radians per second, although it may be measured in other units such as degrees per second, revolutions per...
of the moving parts about the same axis as the moment of inertia.
The kinetic energy of translation of the moving parts is
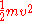 , where
, where 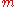 is the total mass and
is the total mass and  is the magnitude of the velocity
is the magnitude of the velocityVelocity
In physics, velocity is speed in a given direction. Speed describes only how fast an object is moving, whereas velocity gives both the speed and direction of the object's motion. To have a constant velocity, an object must have a constant speed and motion in a constant direction. Constant ...
. This gives the formula for the total kinetic energy of the moving parts of a machine as
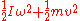 .
.Representing moving parts in engineering diagrams
In technical drawingTechnical drawing
Technical drawing, also known as drafting or draughting, is the act and discipline of composing plans that visually communicate how something functions or has to be constructed.Drafting is the language of industry....
, moving parts are, conventionally, designated by drawing the solid outline of the part in its main or initial position, with an added outline of the part in a secondary, moved, position drawn with a phantom line (a line comprising "dot-dot-dash" sequences of two short and one long line segments) outline. These conventions are enshrined in several standards from the American National Standards Institute
American National Standards Institute
The American National Standards Institute is a private non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organization also coordinates U.S. standards with international...
and the American Society of Mechanical Engineers
American Society of Mechanical Engineers
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers is a professional body, specifically an engineering society, focused on mechanical engineering....
, including ASME Y14.2M published in 1979.
In recent decades, the use of animation
Animation
Animation is the rapid display of a sequence of images of 2-D or 3-D artwork or model positions in order to create an illusion of movement. The effect is an optical illusion of motion due to the phenomenon of persistence of vision, and can be created and demonstrated in several ways...
has become more practical and widespread in technical and engineering diagrams for the illustration of the motions of moving parts. Animation represents moving parts more clearly and enables them and their motions to be more readily visualized. Furthermore, computer aided design tools allow the motions of moving parts to be simulated, allowing machine designers to determine, for example, whether the moving parts in a given design would obstruct one another's motion or collide by simple visual inspection of the (animated) computer model rather than by the designer performing a numerical analysis directly.
See also
- kinetic artKinetic artKinetic art is art that contains moving parts or depends on motion for its effect. The moving parts are generally powered by wind, a motor or the observer. Kinetic art encompasses a wide variety of overlapping techniques and styles.-Kinetic sculpture:...
— sculpture that contains moving parts - movement (clockwork)Movement (clockwork)In horology, a movement is the internal mechanism of a clock or watch, as opposed to the case, which encloses and protects the movement, and the face which displays the time. The term originated with mechanical timepieces, whose movements are made of many moving parts...
— the specific name for the moving parts of a clock or watch

