
Mitchella repens
Encyclopedia
Mitchella repens , or Partridge Berry, or Squaw Vine, is the best known plant in the genus Mitchella
.
It is a creeping prostrate herbaceous
woody
shrub, occurring in North America
and Japan
, and belonging to the madder family (Rubiaceae
).
adjective repens "creeping". Common names for Mitchella repens include partridge berry (or partridgeberry), squaw berry (or squaw berry), two-eyed berry, running fox, and Noon kie oo nah yeah (in the Mohawk language).
, no taller than 6 cm tall with creeping stems 15 to 30 cm long. The evergreen, dark green, shiny leaves
are ovate to cordate in shape. The leaves have a pale yellow midrib. The petioles are short, and the leaves are paired oppositely on the stems. Adventitious roots may grow at the node
s; and rooting stems may branch and root repeatedly, producing loose spreading mats.
The small, trumpet-shaped, axillary flowers are produced in pairs, and each flower pair arises from one common calyx
which is covered with fine hairs. Each flower has four white petals, one pistil, and four stamen
s. Partridge Berry is a distylous taxa. The plants have either flowers with long pistils and short stamens (long-styled flowers, called the pin), or have short pistils and long stamens (short-styled flowers, called the thrum). The two style morphs are genetically determined, so the pollen from one morph does not fertilize the other morph, resulting in a form of heteromorphic self-incompatibility.
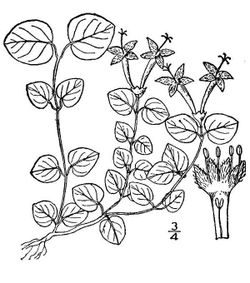
 The ovaries
The ovaries
of the twin flowers fuse, so that there were two flowers for each berry. The two bright red spots on each berry are vestiges of this process. The fruit ripens between July and October, and may persist through the winter. The fruit is a drupe
containing up to eight seeds. The fruits are never abundant. They may be part of the diets of several birds, such as Ruffed Grouse
, Sharp-tailed Grouse
, Northern Bobwhite, and Wild turkey
. They are also consumed by fox
es, White-footed mice, and skunk
s. The foliage is occasionally consumed by White-tailed deer.
The common reproduction is vegetative, with plants forming spreading colonies.
, from south Eastern Canada south to Florida and Texas, and to Guatemala
. It is found growing in dry or moist woods, along stream banks and on sandy slopes.
Mitchella
Mitchella is a small genus from the family Rubiaceae, native to the Americas and eastern Asia.The genus Mitchella L., was named by Carl Linnaeus after his friend John Mitchell , an English physician who lived in America and gave Linnaeus much valuable information on American flora.It consists of a...
.
It is a creeping prostrate herbaceous
Herbaceous
A herbaceous plant is a plant that has leaves and stems that die down at the end of the growing season to the soil level. They have no persistent woody stem above ground...
woody
Woody plant
A woody plant is a plant that uses wood as its structural tissue. These are typically perennial plants whose stems and larger roots are reinforced with wood produced adjacent to the vascular tissues. The main stem, larger branches, and roots of these plants are usually covered by a layer of...
shrub, occurring in North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
and Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
, and belonging to the madder family (Rubiaceae
Rubiaceae
The Rubiaceae is a family of flowering plants, variously called the coffee family, madder family, or bedstraw family. The group contains many commonly known plants, including the economically important coffee , quinine , and gambier , and the horticulturally valuable madder , west indian jasmine ,...
).
Taxonomy
Mitchella repens is one of the many species first described by Carl Linnaeus. Its species name is the LatinLatin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
adjective repens "creeping". Common names for Mitchella repens include partridge berry (or partridgeberry), squaw berry (or squaw berry), two-eyed berry, running fox, and Noon kie oo nah yeah (in the Mohawk language).
Description
Partridge Berry is an evergreen plant growing as a non-climbing vineVine
A vine in the narrowest sense is the grapevine , but more generally it can refer to any plant with a growth habit of trailing or scandent, that is to say climbing, stems or runners...
, no taller than 6 cm tall with creeping stems 15 to 30 cm long. The evergreen, dark green, shiny leaves
Leaf
A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant, as defined in botanical terms, and in particular in plant morphology. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves as a feature of plants....
are ovate to cordate in shape. The leaves have a pale yellow midrib. The petioles are short, and the leaves are paired oppositely on the stems. Adventitious roots may grow at the node
Plant stem
A stem is one of two main structural axes of a vascular plant. The stem is normally divided into nodes and internodes, the nodes hold buds which grow into one or more leaves, inflorescence , conifer cones, roots, other stems etc. The internodes distance one node from another...
s; and rooting stems may branch and root repeatedly, producing loose spreading mats.
The small, trumpet-shaped, axillary flowers are produced in pairs, and each flower pair arises from one common calyx
Sepal
A sepal is a part of the flower of angiosperms . Collectively the sepals form the calyx, which is the outermost whorl of parts that form a flower. Usually green, sepals have the typical function of protecting the petals when the flower is in bud...
which is covered with fine hairs. Each flower has four white petals, one pistil, and four stamen
Stamen
The stamen is the pollen producing reproductive organ of a flower...
s. Partridge Berry is a distylous taxa. The plants have either flowers with long pistils and short stamens (long-styled flowers, called the pin), or have short pistils and long stamens (short-styled flowers, called the thrum). The two style morphs are genetically determined, so the pollen from one morph does not fertilize the other morph, resulting in a form of heteromorphic self-incompatibility.


Ovary (plants)
In the flowering plants, an ovary is a part of the female reproductive organ of the flower or gynoecium. Specifically, it is the part of the pistil which holds the ovule and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals...
of the twin flowers fuse, so that there were two flowers for each berry. The two bright red spots on each berry are vestiges of this process. The fruit ripens between July and October, and may persist through the winter. The fruit is a drupe
Drupe
In botany, a drupe is a fruit in which an outer fleshy part surrounds a shell of hardened endocarp with a seed inside. These fruits develop from a single carpel, and mostly from flowers with superior ovaries...
containing up to eight seeds. The fruits are never abundant. They may be part of the diets of several birds, such as Ruffed Grouse
Ruffed Grouse
The Ruffed Grouse is a medium-sized grouse occurring in forests from the Appalachian Mountains across Canada to Alaska. It is non-migratory.The Ruffed Grouse is frequently referred to as a "partridge"...
, Sharp-tailed Grouse
Sharp-tailed Grouse
The Sharp-tailed Grouse, Tympanuchus phasianellus , is a medium-sized prairie grouse. It is also known as the sharptail, and is known as "fire grouse" or "fire bird" by Native American Indians due to their reliance on brush fires to keep their habitat open.-Taxonomy:The Greater Prairie-chicken,...
, Northern Bobwhite, and Wild turkey
Wild Turkey
The Wild Turkey is native to North America and is the heaviest member of the Galliformes. It is the same species as the domestic turkey, which derives from the South Mexican subspecies of wild turkey .Adult wild turkeys have long reddish-yellow to grayish-green...
. They are also consumed by fox
Fox
Fox is a common name for many species of omnivorous mammals belonging to the Canidae family. Foxes are small to medium-sized canids , characterized by possessing a long narrow snout, and a bushy tail .Members of about 37 species are referred to as foxes, of which only 12 species actually belong to...
es, White-footed mice, and skunk
Skunk
Skunks are mammals best known for their ability to secrete a liquid with a strong, foul odor. General appearance varies from species to species, from black-and-white to brown or cream colored. Skunks belong to the family Mephitidae and to the order Carnivora...
s. The foliage is occasionally consumed by White-tailed deer.
The common reproduction is vegetative, with plants forming spreading colonies.
Distribution and habitat
The species is dispersed throughout eastern North AmericaNorth America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
, from south Eastern Canada south to Florida and Texas, and to Guatemala
Guatemala
Guatemala is a country in Central America bordered by Mexico to the north and west, the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, Belize to the northeast, the Caribbean to the east, and Honduras and El Salvador to the southeast...
. It is found growing in dry or moist woods, along stream banks and on sandy slopes.

