
Military budget of the United States
Encyclopedia
The military budget
is that portion of the United States
discretionary federal budget
that is allocated to the Department of Defense
, or more broadly, the portion of the budget that goes to any defense-related expenditures. This military budget
pays the salaries, training, and health care of uniformed and civilian personnel, maintains arms, equipment and facilities, funds operations, and develops and buys new equipment. The budget funds all branches of the U.S. military: Army
, Navy
, Air Force
, Marine Corps
and Coast Guard
.
When the budget was signed into law on October 28, 2009, the final size of the Department of Defense's budget was $680 billion, $16 billion more than President Obama had requested. An additional $37 billion supplemental bill to support the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan was expected to pass in the spring of 2010, but has been delayed by the House of Representatives after passing the Senate.
and Afghanistan
were largely funded through supplementary spending bills outside the Federal Budget, so they are not included in the military budget figures listed below. Starting in the fiscal year 2010 budget however, the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan are categorized as "Overseas Contingency Operations" and included in the budget.
By the end of 2008, the U.S. had spent approximately $900 billion in direct costs on the Iraq and Afghanistan Wars. Indirect costs such as interest on the additional debt and incremental costs of caring for the more than 33,000 wounded borne by the Veterans Administration
are additional. Some experts estimate these indirect costs will eventually exceed the direct costs.
for fiscal year 2010, including the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan, is:
budget, Veterans Affairs
, the Treasury Department's payments in pensions to military retirees and widows and their families, interest on debt incurred in past wars, or State Department financing of foreign arms sales and militarily-related development assistance. Neither does it include defense spending that is not military in nature, such as the Department of Homeland Security
, counter-terrorism spending by the FBI, and intelligence-gathering spending by NASA
.
was unable to provide an audit opinion on the 2010 financial statements of the US Government because of 'widespread material internal control weaknesses, significant uncertainties, and other limitations'. The GAO cited as the principal obstacle to its provision of an audit opinion 'serious financial management problems at the Department of Defense that made its financial statements unauditable'.
In FY 2010 six out of thirty-three DoD reporting entities received unqualified audit opinions.
Chief Financial Officer
and Under Secretary of Defense
Robert F. Hale
acknowledged enterprise-wide problems with systems and processes, while the DoD's Inspector General
reported 'material internal control weaknesses ... that affect the safeguarding of assets, proper use of funds, and impair the prevention and identification of fraud, waste, and abuse'. Further management discussion in the FY 2010 DoD Financial Report states 'it is not feasible to deploy a vast number of accountants to manually reconcile our books' and concludes that 'although the financial statements are not auditable for FY 2010, the Department's financial managers are meeting warfighter needs'.
has increased since 2001 and in 2007 payments for contractor services exceeded investments in equipment for the armed forces for the first time. In the 2010 budget the support service contractors will be reduced from the current 39 percent of the workforce down to the pre-2001 level of 26 percent.
 The U.S. Department of Defense budget accounted in fiscal year 2010 for about 19% of the United States federal budgeted expenditures and 28% of estimated tax revenues. Including non-DOD expenditures, defense spending was approximately 28–38% of budgeted expenditures and 42–57% of estimated tax revenues. According to the Congressional Budget Office
The U.S. Department of Defense budget accounted in fiscal year 2010 for about 19% of the United States federal budgeted expenditures and 28% of estimated tax revenues. Including non-DOD expenditures, defense spending was approximately 28–38% of budgeted expenditures and 42–57% of estimated tax revenues. According to the Congressional Budget Office
, defense spending grew 9% annually on average from fiscal year 2000–2009.
Because of constitutional
limitations, military funding is appropriated in a discretionary spending
account. (Such accounts permit government planners to have more flexibility to change spending each year, as opposed to mandatory spending
accounts that mandate spending on programs in accordance with the law, outside of the budgetary process.) In recent years, discretionary spending as a whole has amounted to about one-third of total federal outlays. Military spending's share of discretionary spending was 50.5% in 2003, and has risen steadily ever since.
For FY 2010, Department of Defense spending amounts to 4.7% of GDP. Because the U.S. GDP has risen over time, the military budget can rise in absolute terms while shrinking as a percentage of the GDP. For example, the Department of Defense budget is slated to be $664 billion in 2010 (including the cost of operations in Iraq and Afghanistan previously funded through supplementary budget legislation), higher than at any other point in American history, but still 1.1–1.4% lower as a percentage of GDP than the amount spent on defense during the peak of Cold-War military spending in the late 1980s. Admiral Mike Mullen, Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
, has called four percent an "absolute floor". This calculation does not take into account some other defense-related non-DOD spending, such as Veterans Affairs, Homeland Security, and interest paid on debt incurred in past wars, which has increased even as a percentage of the national GDP.
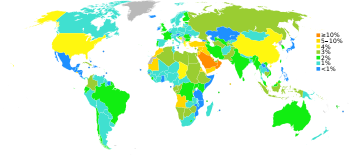 The 2009 U.S. military budget accounts for approximately 40% of global arms spending and is over six times larger than the military budget of China
The 2009 U.S. military budget accounts for approximately 40% of global arms spending and is over six times larger than the military budget of China
(compared at the nominal US dollar / Renminbi
rate, not the PPP
rate). The United States and its close allies are responsible for two-thirds to three-quarters of the world's military spending (of which, in turn, the U.S. is responsible for the majority).
In 2005, the United States spent 4.06% of its GDP on its military (considering only basic Department of Defense budget spending), more than France's 2.6% and less than Saudi Arabia
's 10%.information 2006 This is historically low for the United States since it peaked in 1944 at 37.8% of GDP (it reached the lowest point of 3.0% in 1999–2001). Even during the peak of the Vietnam War
the percentage reached a high of 9.4% in 1968. Countries like Canada and Germany spend only 1.4% of GDP on their military.
, D-Mass., called for a reduction in the defense budget: "The math is compelling: if we do not make reductions approximating 25 percent of the military budget starting fairly soon, it will be impossible to continue to fund an adequate level of domestic activity even with a repeal of Bush's tax cuts for the very wealthy. I am working with a variety of thoughtful analysts to show how we can make very substantial cuts in the military budget without in any way diminishing the security we need...[American] well-being is far more endangered by a proposal for substantial reductions in Medicare, Social Security or other important domestic areas than it would be by canceling weapons systems that have no justification from any threat we are likely to face."
Republican historian Robert Kagan
has argued that 2009 is not the time to cut defense spending, relating such spending to jobs and support for allies: "A reduction in defense spending this year would unnerve American allies and undercut efforts to gain greater cooperation. There is already a sense around the world...that the United States is in terminal decline. Many fear that the economic crisis will cause the United States to pull back from overseas commitments. The announcement of a defense cutback would be taken by the world as evidence that the American retreat has begun."
Secretary of Defense
Robert Gates
wrote in 2009 that the U.S. should adjust its priorities and spending to address the changing nature of threats in the world: "What all these potential adversaries—from terrorist cells to rogue nations to rising powers—have in common is that they have learned that it is unwise to confront the United States directly on conventional military terms. The United States cannot take its current dominance for granted and needs to invest in the programs, platforms, and personnel that will ensure that dominance's persistence. But it is also important to keep some perspective. As much as the U.S. Navy has shrunk since the end of the Cold War, for example, in terms of tonnage, its battle fleet is still larger than the next 13 navies combined—and 11 of those 13 navies are U.S. allies or partners." Secretary Gates announced some of his budget recommendations in April 2009.
The Congressional Research Service
has noted a discrepancy between a budget that is declining as a percentage of GDP while the responsibilities of the DoD have not decreased and additional pressures on the defense budget have arisen due to broader missions in the post-9/11 world, dramatic increases in personnel and operating costs, and new requirements resulting from wartime lessons in the Iraq War and Operation Enduring Freedom.
Military budget
A military budget of an entity, most often a nation or a state, is the budget and financial resources dedicated to raising and maintaining armed forces for that entity. Military budgets reflect how much an entity perceives the likelihood of threats against it, or the amount of aggression it wishes...
is that portion of the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
discretionary federal budget
United States federal budget
The Budget of the United States Government is the President's proposal to the U.S. Congress which recommends funding levels for the next fiscal year, beginning October 1. Congressional decisions are governed by rules and legislation regarding the federal budget process...
that is allocated to the Department of Defense
United States Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense is the U.S...
, or more broadly, the portion of the budget that goes to any defense-related expenditures. This military budget
Military budget
A military budget of an entity, most often a nation or a state, is the budget and financial resources dedicated to raising and maintaining armed forces for that entity. Military budgets reflect how much an entity perceives the likelihood of threats against it, or the amount of aggression it wishes...
pays the salaries, training, and health care of uniformed and civilian personnel, maintains arms, equipment and facilities, funds operations, and develops and buys new equipment. The budget funds all branches of the U.S. military: Army
United States Army
The United States Army is the main branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for land-based military operations. It is the largest and oldest established branch of the U.S. military, and is one of seven U.S. uniformed services...
, Navy
United States Navy
The United States Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the seven uniformed services of the United States. The U.S. Navy is the largest in the world; its battle fleet tonnage is greater than that of the next 13 largest navies combined. The U.S...
, Air Force
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force is the aerial warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the American uniformed services. Initially part of the United States Army, the USAF was formed as a separate branch of the military on September 18, 1947 under the National Security Act of...
, Marine Corps
United States Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps is a branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for providing power projection from the sea, using the mobility of the United States Navy to deliver combined-arms task forces rapidly. It is one of seven uniformed services of the United States...
and Coast Guard
United States Coast Guard
The United States Coast Guard is a branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the seven U.S. uniformed services. The Coast Guard is a maritime, military, multi-mission service unique among the military branches for having a maritime law enforcement mission and a federal regulatory agency...
.
Budget for 2010
For the 2010 fiscal year, the president's base budget of the Department of spending on "overseas contingency operations" brings the sum to $663.84 billion.When the budget was signed into law on October 28, 2009, the final size of the Department of Defense's budget was $680 billion, $16 billion more than President Obama had requested. An additional $37 billion supplemental bill to support the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan was expected to pass in the spring of 2010, but has been delayed by the House of Representatives after passing the Senate.
Emergency and supplemental spending
The recent invasions of IraqIraq
Iraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
and Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
were largely funded through supplementary spending bills outside the Federal Budget, so they are not included in the military budget figures listed below. Starting in the fiscal year 2010 budget however, the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan are categorized as "Overseas Contingency Operations" and included in the budget.
By the end of 2008, the U.S. had spent approximately $900 billion in direct costs on the Iraq and Afghanistan Wars. Indirect costs such as interest on the additional debt and incremental costs of caring for the more than 33,000 wounded borne by the Veterans Administration
United States Department of Veterans Affairs
The United States Department of Veterans Affairs is a government-run military veteran benefit system with Cabinet-level status. It is the United States government’s second largest department, after the United States Department of Defense...
are additional. Some experts estimate these indirect costs will eventually exceed the direct costs.
By title
The federally budgeted (see below) military expenditure of the United States Department of DefenseUnited States Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense is the U.S...
for fiscal year 2010, including the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan, is:
| Components | Funding | Change, 2009 to 2010 |
| Operations and maintenance | $283.3 billion | +4.2% |
| Military Personnel | $154.2 billion | +5.0% |
| Procurement | $140.1 billion | −1.8% |
| Research, Development, Testing & Evaluation | $79.1 billion | +1.3% |
| Military Construction | $23.9 billion | +19.0% |
| Family Housing | $3.1 billion | −20.2% |
| Total Spending | $685.1 billion | +3.0% |
By entity
| Entity | 2010 Budget request | Percentage of Total | Notes |
| Army United States Department of the Army The Department of the Army is one of the three military departments within the Department of Defense of the United States of America. The Department of the Army is the Federal Government agency which the United States Army is organized within, and it is led by the Secretary of the Army who has... |
$243.9 billion | 31.8% | |
| Navy United States Department of the Navy The Department of the Navy of the United States of America was established by an Act of Congress on 30 April 1798, to provide a government organizational structure to the United States Navy and, from 1834 onwards, for the United States Marine Corps, and when directed by the President, of the... |
$149.9 billion | 23.4% | excluding Marine Corps |
| Marine Corps United States Marine Corps The United States Marine Corps is a branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for providing power projection from the sea, using the mobility of the United States Navy to deliver combined-arms task forces rapidly. It is one of seven uniformed services of the United States... |
$29.0 billion | 4% | Total Budget taken allotted from Department of Navy |
| Air Force | $170.6 billion | 22% | |
| Defense Intelligence | $50 billion | 7% | Because of classified nature, budget is an estimate and may not be the actual figure |
| Defense Wide Joint Activities | $118.7 billion | 15.5% |
Programs spending more than $1.5 billion
The Department of Defense's FY 2011 $137.5 billion procurement and $77.2 billion RDT&E budget requests included several programs with more than $1.5 billion.| Program | 2011 Budget request | Change, 2010 to 2011 |
| F-35 Joint Strike Fighter | $11.4 billion | |
| Ballistic Missile Defense (Aegis Aegis Ballistic Missile Defense System The Aegis Ballistic Missile Defense System is a United States Department of Defense Missile Defense Agency program developed to provide defense against ballistic missiles. It is part of the United States national missile defense strategy... , THAAD Terminal High Altitude Area Defense Terminal High Altitude Area Defense , formerly Theater High Altitude Area Defense, is a United States Army system to shoot down short, medium, and intermediate ballistic missiles in their terminal phase using a hit-to-kill approach. The missile carries no warhead but relies on the kinetic energy... , PAC-3) |
$9.9 billion | |
| Virginia class submarine Virginia class submarine The Virginia class is a class of nuclear-powered fast attack submarines in service with the United States Navy. The submarines are designed for a broad spectrum of open-ocean and littoral missions... |
$5.4 billion | |
| Brigade Combat Team Modernization BCT Modernization The Brigade combat team Modernization is the United States Army's principal modernization program for Brigade combat teams from 2009 to the present... |
$3.2 billion | |
| DDG 51 Aegis-class Destroyer Arleigh Burke class destroyer The Arleigh Burke class of guided missile destroyers is the United States Navy's first class of destroyer built around the Aegis combat system and the SPY-1D multi-function phased array radar. The class is named for Admiral Arleigh "31-Knot" Burke, the most famous American destroyer officer of... |
$3.0 billion | |
| P–8A Poseidon | $2.9 billion | −1.6% |
| V-22 Osprey V-22 Osprey The Bell Boeing V-22 Osprey is an American multi-mission, military, tiltrotor aircraft with both a vertical takeoff and landing , and short takeoff and landing capability... |
$2.8 billion | −6.5% |
| Carrier Replacement Program | $2.7 billion | |
| F/A-18E/F Hornet F/A-18E/F Super Hornet The Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet is a twin-engine carrier-based multirole fighter aircraft. The F/A-18E single-seat variant and F/A-18F tandem-seat variant are larger and more advanced derivatives of the F/A-18C and D Hornet. The Super Hornet has an internal 20 mm gun and can carry air-to-air... |
$2.0 billion | |
| Predator and Reaper Unmanned Aerial System | $1.9 billion | |
| Littoral combat ship Littoral combat ship A Littoral Combat Ship is a type of relatively small surface vessel intended for operations in the littoral zone . It is "envisioned to be a networked, agile, stealthy surface combatant capable of defeating anti-access and asymmetric threats in the littorals." Two ship classes are the first... |
$1.8 billion | |
| CVN Refueling and Complex Overhaul | $1.7 billion | −6.0% |
| Chemical Demilitarization | $1.6 billion | −7.0% |
| RQ-4 Global Hawk | $1.5 billion | |
| Space-Based Infrared System Space-Based Infrared System The Space-Based Infrared System is a consolidated system intended to meet the United States' infrared space surveillance needs through the first two to three decades of the 21st century... |
$1.5 billion |
Other defense-related expenditures
This does not include many military-related items that are outside of the Defense Department budget, such as nuclear weapons research, maintenance, cleanup, and production, which is in the Department of EnergyNational Nuclear Security Administration
The United States National Nuclear Security Administration is part of the United States Department of Energy. It works to improve national security through the military application of nuclear energy...
budget, Veterans Affairs
United States Department of Veterans Affairs
The United States Department of Veterans Affairs is a government-run military veteran benefit system with Cabinet-level status. It is the United States government’s second largest department, after the United States Department of Defense...
, the Treasury Department's payments in pensions to military retirees and widows and their families, interest on debt incurred in past wars, or State Department financing of foreign arms sales and militarily-related development assistance. Neither does it include defense spending that is not military in nature, such as the Department of Homeland Security
United States Department of Homeland Security
The United States Department of Homeland Security is a cabinet department of the United States federal government, created in response to the September 11 attacks, and with the primary responsibilities of protecting the territory of the United States and protectorates from and responding to...
, counter-terrorism spending by the FBI, and intelligence-gathering spending by NASA
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
.
Audit of Implementation of Budget for 2010
The US Government Accountability OfficeGovernment Accountability Office
The Government Accountability Office is the audit, evaluation, and investigative arm of the United States Congress. It is located in the legislative branch of the United States government.-History:...
was unable to provide an audit opinion on the 2010 financial statements of the US Government because of 'widespread material internal control weaknesses, significant uncertainties, and other limitations'. The GAO cited as the principal obstacle to its provision of an audit opinion 'serious financial management problems at the Department of Defense that made its financial statements unauditable'.
In FY 2010 six out of thirty-three DoD reporting entities received unqualified audit opinions.
Chief Financial Officer
Chief financial officer
The chief financial officer or Chief financial and operating officer is a corporate officer primarily responsible for managing the financial risks of the corporation. This officer is also responsible for financial planning and record-keeping, as well as financial reporting to higher management...
and Under Secretary of Defense
Under Secretary of Defense (Comptroller)
The Under Secretary of Defense is the Chief Financial Officer of the United States Department of Defense. The responsibilities of the Department of Defense's Chief Financial Officer include developing and implementing Department of Defense-wide financial policy, financial management systems, and...
Robert F. Hale
Robert F. Hale
Robert F. Hale is the United States Under Secretary of Defense and former Assistant Secretary of the Air Force . Hale has over thirty years of experience as a professional financial manager serving in a wide range of national defense related roles...
acknowledged enterprise-wide problems with systems and processes, while the DoD's Inspector General
Office of the Inspector General, U.S. Department of Defense
The Department of Defense Inspector General is an independent, objective agency that provides oversight related to the programs and operations of the Department of Defense...
reported 'material internal control weaknesses ... that affect the safeguarding of assets, proper use of funds, and impair the prevention and identification of fraud, waste, and abuse'. Further management discussion in the FY 2010 DoD Financial Report states 'it is not feasible to deploy a vast number of accountants to manually reconcile our books' and concludes that 'although the financial statements are not auditable for FY 2010, the Department's financial managers are meeting warfighter needs'.
Budget Breakdown for 2012
| Defense-related expenditure | 2012 Budget request & Mandatory spending | Calculation |
| DOD spending | $707.5 billion | Base budget + "Overseas Contingency Operations" |
| FBI counter-terrorism | $2.7 billion | At least one-third FBI budget. |
| International Affairs | $5.6–$63.0 billion | At minimum, foreign arms sales. At most, entire State budget |
| Energy Department, defense-related | $21.8 billion | |
| Veterans Affairs | $70.0 billion | |
| Homeland Security | $46.9 billion | |
| NASA, satellites | $3.5–$8.7 billion | Between 20% and 50% of NASA's total budget |
| Veterans pensions | $54.6 billion | |
| Other defense-related mandatory spending | $8.2 billion | |
| Interest on debt incurred in past wars | $109.1–$431.5 billion | Between 23% and 91% of total interest |
| Total Spending | $1.030–$1.415 trillion |
Support service contractors
The role of support service contractorsPrivate military company
A private military company or provides military and security services. These combatants are commonly known as mercenaries, though modern-day PMCs refer to their staff as security contractors, private military contractors or private security contractors, and refer to themselves as private military...
has increased since 2001 and in 2007 payments for contractor services exceeded investments in equipment for the armed forces for the first time. In the 2010 budget the support service contractors will be reduced from the current 39 percent of the workforce down to the pre-2001 level of 26 percent.
Military budget and total US federal spending
World War II commenced a new era of permanency in the United States defense budget. With the advent of the Cold War, the United States began to maintain a standing army and a permanent state of readiness for war that permanently elevated national defense expenditures. At the conclusion of his second term, President Eisenhower, wrote:Our military organization today bears little relation to that known by any of my predecessors in peacetime, or indeed by the fighting men of World War II or Korea.
Until the latest of our world conflicts, the United States had no armaments industry. American makers of plowshares could, with time and as required, make swords as well. But now we can no longer risk emergency improvisation of national defense; we have been compelled to create a permanent armaments industry of vast proportions. Added to this, three and a half million men and women are directly engaged in the defense establishment. We annually spend on military security more than the net income of all United States corporations. This conjunction of an immense military establishment and a large arms industry is new in the American experience. The total influence -- economic, political, even spiritual -- is felt in every city, every State house, every office of the Federal government. We recognize the imperative need for this development. Yet we must not fail to comprehend its grave implications. Our toil, resources and livelihood are all involved; so is the very structure of our society. In the councils of government, we must guard against the acquisition of unwarranted influence, whether sought or unsought, by the military industrial complex. The potential for the disastrous rise of misplaced power exists and will persist. We must never let the weight of this combination endanger our liberties or democratic processes. We should take nothing for granted. Only an alert and knowledgeable citizenry can compel the proper meshing of the huge industrial and military machinery of defense with our peaceful methods and goals, so that security and liberty may prosper together.

Congressional Budget Office
The Congressional Budget Office is a federal agency within the legislative branch of the United States government that provides economic data to Congress....
, defense spending grew 9% annually on average from fiscal year 2000–2009.
Because of constitutional
United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It is the framework for the organization of the United States government and for the relationship of the federal government with the states, citizens, and all people within the United States.The first three...
limitations, military funding is appropriated in a discretionary spending
Discretionary spending
Discretionary spending is a spending category through which governments can spend through an appropriations act. This spending is optional as part of fiscal policy, in contrast to entitlement programs for which funding is mandatory....
account. (Such accounts permit government planners to have more flexibility to change spending each year, as opposed to mandatory spending
Mandatory spending
In economics, mandatory spending is spending on certain programs that is required by existing law.In the United States, mandatory spending refers to budget authority and ensuing outlays provided in laws other than appropriations acts, including annually appropriated entitlements...
accounts that mandate spending on programs in accordance with the law, outside of the budgetary process.) In recent years, discretionary spending as a whole has amounted to about one-third of total federal outlays. Military spending's share of discretionary spending was 50.5% in 2003, and has risen steadily ever since.
For FY 2010, Department of Defense spending amounts to 4.7% of GDP. Because the U.S. GDP has risen over time, the military budget can rise in absolute terms while shrinking as a percentage of the GDP. For example, the Department of Defense budget is slated to be $664 billion in 2010 (including the cost of operations in Iraq and Afghanistan previously funded through supplementary budget legislation), higher than at any other point in American history, but still 1.1–1.4% lower as a percentage of GDP than the amount spent on defense during the peak of Cold-War military spending in the late 1980s. Admiral Mike Mullen, Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
The Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff is by law the highest ranking military officer in the United States Armed Forces, and is the principal military adviser to the President of the United States, the National Security Council, the Homeland Security Council and the Secretary of Defense...
, has called four percent an "absolute floor". This calculation does not take into account some other defense-related non-DOD spending, such as Veterans Affairs, Homeland Security, and interest paid on debt incurred in past wars, which has increased even as a percentage of the national GDP.
Comparison with other countries

Military budget of the People's Republic of China
The military budget of the People's Republic of China is the portion of the overall budget of China that is allocated for the funding of the military of the People's Republic of China...
(compared at the nominal US dollar / Renminbi
Renminbi
The Renminbi is the official currency of the People's Republic of China . Renminbi is legal tender in mainland China, but not in Hong Kong or Macau. It is issued by the People's Bank of China, the monetary authority of the PRC...
rate, not the PPP
Purchasing power parity
In economics, purchasing power parity is a condition between countries where an amount of money has the same purchasing power in different countries. The prices of the goods between the countries would only reflect the exchange rates...
rate). The United States and its close allies are responsible for two-thirds to three-quarters of the world's military spending (of which, in turn, the U.S. is responsible for the majority).
In 2005, the United States spent 4.06% of its GDP on its military (considering only basic Department of Defense budget spending), more than France's 2.6% and less than Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia , commonly known in British English as Saudi Arabia and in Arabic as as-Sa‘ūdiyyah , is the largest state in Western Asia by land area, constituting the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and the second-largest in the Arab World...
's 10%.information 2006 This is historically low for the United States since it peaked in 1944 at 37.8% of GDP (it reached the lowest point of 3.0% in 1999–2001). Even during the peak of the Vietnam War
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War was a Cold War-era military conflict that occurred in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. This war followed the First Indochina War and was fought between North Vietnam, supported by its communist allies, and the government of...
the percentage reached a high of 9.4% in 1968. Countries like Canada and Germany spend only 1.4% of GDP on their military.
Recent commentary on military budget
In February 2009, Congressman Barney FrankBarney Frank
Barney Frank is the U.S. Representative for . A member of the Democratic Party, he is the former chairman of the House Financial Services Committee and is considered the most prominent gay politician in the United States.Born and raised in New Jersey, Frank graduated from Harvard College and...
, D-Mass., called for a reduction in the defense budget: "The math is compelling: if we do not make reductions approximating 25 percent of the military budget starting fairly soon, it will be impossible to continue to fund an adequate level of domestic activity even with a repeal of Bush's tax cuts for the very wealthy. I am working with a variety of thoughtful analysts to show how we can make very substantial cuts in the military budget without in any way diminishing the security we need...[American] well-being is far more endangered by a proposal for substantial reductions in Medicare, Social Security or other important domestic areas than it would be by canceling weapons systems that have no justification from any threat we are likely to face."
Republican historian Robert Kagan
Robert Kagan
Robert Kagan is an American historian and foreign policy commentator.-Early life and education:Kagan graduated from Yale University in 1980 where he was tapped by Skull and Bones, studied history, and founded the Yale Political Monthly. He later earned an MPP from the John F...
has argued that 2009 is not the time to cut defense spending, relating such spending to jobs and support for allies: "A reduction in defense spending this year would unnerve American allies and undercut efforts to gain greater cooperation. There is already a sense around the world...that the United States is in terminal decline. Many fear that the economic crisis will cause the United States to pull back from overseas commitments. The announcement of a defense cutback would be taken by the world as evidence that the American retreat has begun."
Secretary of Defense
United States Secretary of Defense
The Secretary of Defense is the head and chief executive officer of the Department of Defense of the United States of America. This position corresponds to what is generally known as a Defense Minister in other countries...
Robert Gates
Robert Gates
Dr. Robert Michael Gates is a retired civil servant and university president who served as the 22nd United States Secretary of Defense from 2006 to 2011. Prior to this, Gates served for 26 years in the Central Intelligence Agency and the National Security Council, and under President George H. W....
wrote in 2009 that the U.S. should adjust its priorities and spending to address the changing nature of threats in the world: "What all these potential adversaries—from terrorist cells to rogue nations to rising powers—have in common is that they have learned that it is unwise to confront the United States directly on conventional military terms. The United States cannot take its current dominance for granted and needs to invest in the programs, platforms, and personnel that will ensure that dominance's persistence. But it is also important to keep some perspective. As much as the U.S. Navy has shrunk since the end of the Cold War, for example, in terms of tonnage, its battle fleet is still larger than the next 13 navies combined—and 11 of those 13 navies are U.S. allies or partners." Secretary Gates announced some of his budget recommendations in April 2009.
The Congressional Research Service
Congressional Research Service
The Congressional Research Service , known as "Congress's think tank", is the public policy research arm of the United States Congress. As a legislative branch agency within the Library of Congress, CRS works exclusively and directly for Members of Congress, their Committees and staff on a...
has noted a discrepancy between a budget that is declining as a percentage of GDP while the responsibilities of the DoD have not decreased and additional pressures on the defense budget have arisen due to broader missions in the post-9/11 world, dramatic increases in personnel and operating costs, and new requirements resulting from wartime lessons in the Iraq War and Operation Enduring Freedom.
See also
- United States military aidUnited States military aidThe United States government first recognized the usefulness of foreign aid as a tool of diplomacy in World War II. It was believed that it would promote liberal capitalist models of development in other countries and that it would enhance national security....
- United States Foreign Military FinancingUnited States Foreign Military FinancingThe Foreign Military Financing program provides grants and loans to help countries purchase weapons and defense equipment produced in the United States as well as acquiring defense services and military training. FMF funds purchases are made through the Foreign Military Sales program, which...
- Foreign Military SalesForeign Military SalesThe U.S. Department of Defense's Foreign Military Sales program facilitates sales of U.S. arms, defense equipment, defense services, and military training to foreign governments...
- Foreign policy of the United States
- Overseas expansion of the United States
- Overseas interventions of the United StatesOverseas interventions of the United StatesThe United States has been involved in a number of overseas interventions throughout its history.- Before the Cold War :The Barbary Wars of the 18th and early 19th centuries were the first was waged by the United States outside it's boundaries after the War of Independence...
- List of United States military history events
- List of United States military bases
- List of countries and federations by military expenditures
- List of countries by size of armed forces
External links
- "Office of the Under Secretary of Defense (Comptroller)" Annual Department of Defense budget materials.

