
Lateral mark
Encyclopedia
Buoy
A buoy is a floating device that can have many different purposes. It can be anchored or allowed to drift. The word, of Old French or Middle Dutch origin, is now most commonly in UK English, although some orthoepists have traditionally prescribed the pronunciation...
, lateral post or lateral mark, as defined by the International Association of Lighthouse Authorities
International Association of Lighthouse Authorities
The International Association of Marine Aids to Navigation and Lighthouse Authorities is a non-profit organization founded in 1957 to collect and provide nautical expertise and advice.-Background:...
, is a sea mark
Sea mark
A sea mark, also seamark and navigation mark, is a form of aid to navigation and pilotage aid which identifies the approximate position of a maritime channel, hazard and administrative area to allow boats, ships and seaplanes to navigate safely....
used in maritime pilotage
Pilotage
Pilotage is the use of fixed visual references on the ground or sea by means of sight or radar to guide oneself to a destination, sometimes with the help of a map or nautical chart. People use pilotage for activities such as guiding vessels and aircraft, hiking and Scuba diving...
to indicate the edge of a channel
Channel (geography)
In physical geography, a channel is the physical confine of a river, slough or ocean strait consisting of a bed and banks.A channel is also the natural or human-made deeper course through a reef, sand bar, bay, or any shallow body of water...
.
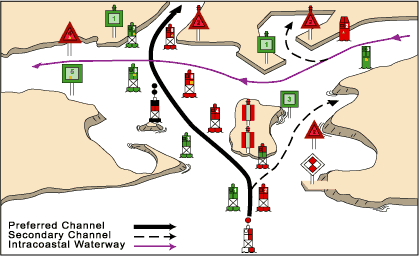
Each mark indicates the edge of the safe water channel in terms of port (left-hand) or starboard (right-hand). These directions are relative to the direction of buoyage; this is usually a nominally upstream
Source (river or stream)
The source or headwaters of a river or stream is the place from which the water in the river or stream originates.-Definition:There is no universally agreed upon definition for determining a stream's source...
direction. In a river, the direction of buoyage is towards the river's source; in a harbour, the direction of buoyage is into the harbour from the sea. Where there may be doubt, it will be labelled on the appropriate chart
Nautical chart
A nautical chart is a graphic representation of a maritime area and adjacent coastal regions. Depending on the scale of the chart, it may show depths of water and heights of land , natural features of the seabed, details of the coastline, navigational hazards, locations of natural and man-made aids...
. Often the cardinal mark
Cardinal mark
A cardinal mark is a sea mark used in maritime pilotage to indicate the position of a hazard and the direction of safe water....
system is used instead, when confusion about the direction would be common.
A vessel heading in the direction of buoyage (eg into a harbour) and wishing to keep in the main channel should:
- keep port marks to its port (left), and
- keep starboard marks to its right.
IALA System
Marks are distinguished by their colour, being red or green, and shape.For historical reasons, two different schemes are in use worldwide, differing in their use of colour.
Previously there had been 30 different buoyage systems, prior to IALA introducing the rationalised system. In 1980 on a conference convened by IALA, they agreed to adopt the rules of a new combined system, which combined the previous two systems (A and B) into one system, with two regions (A and B).
The IALA defines them as Region A and Region B:
- Region A comprises nations in EuropeEuropeEurope is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, AustraliaAustraliaAustralia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
, New ZealandNew ZealandNew Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
, parts of AfricaAfricaAfrica is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
and most of AsiaAsiaAsia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
other than the Philippines, Japan and Korea.
- Region B comprises nations in North AmericaNorth AmericaNorth America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
, Central AmericaCentral AmericaCentral America is the central geographic region of the Americas. It is the southernmost, isthmian portion of the North American continent, which connects with South America on the southeast. When considered part of the unified continental model, it is considered a subcontinent...
and South AmericaSouth AmericaSouth America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
, the PhilippinesPhilippinesThe Philippines , officially known as the Republic of the Philippines , is a country in Southeast Asia in the western Pacific Ocean. To its north across the Luzon Strait lies Taiwan. West across the South China Sea sits Vietnam...
, JapanJapanJapan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
and KoreaKoreaKorea ) is an East Asian geographic region that is currently divided into two separate sovereign states — North Korea and South Korea. Located on the Korean Peninsula, Korea is bordered by the People's Republic of China to the northwest, Russia to the northeast, and is separated from Japan to the...
.
Region A
- port marks are red and may have a red flashing light of any rhythm.
- starboard marks are green and may have a green flashing light of any rhythm.
(Port) (Left) (Red) ______________________ (Starboard) (Right) (Green)
Region B
- port marks are green and may have a green flashing light of any rhythm.
- starboard marks are red and may have a red flashing light of any rhythm.
(Port) (Left) (Green) ____________________ (Starboard) (Right) (Red)
Both regions
- port marks are square or have a flat top
- starboard marks are conical (or present a triangular shape) or have a pointed top.
The shape is an important feature, as colours cannot be distinguished in some light conditions, or by persons with red-green colour blindness. Marks may also carry unique markings of letters and numbers; these may be used to identify the mark as one indicated on a nautical chart
Nautical chart
A nautical chart is a graphic representation of a maritime area and adjacent coastal regions. Depending on the scale of the chart, it may show depths of water and heights of land , natural features of the seabed, details of the coastline, navigational hazards, locations of natural and man-made aids...
. Likewise, a mark's light may flash in a distinctive sequence for the same purpose.
Also defined in the lateral mark systems is a bifurcation mark, which has both red and green horizontal bands, one over the other. This mark indicates that a "preferred" channel (often, a deep channel suitable for heavy commercial traffic) lies to one side, and a secondary channel on the other. Vessels wishing to use the preferred channel observe the top colour of the mark, and vessels wishing to use the secondary channel observe the bottom colour.
In Region A only, the phrase "Is there any red port left?" (referring to the red colour of the fortified wine "port") may be used as a mnemonic, indicating that a red mark must be kept on the left when "returning" to (i.e, entering) a harbour or river.
In Region B only, the phrase "red right returning" may be used as a mnemonic, indicating that a red mark must be kept on the right when returning to (i.e., entering) a harbour or river.
External links
- A web site of Transport Canada, showing lateral buoys in Region B.

