In vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy
Encyclopedia
In vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) is a specialised technique associated to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), also known as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, is a non-invasive analytical technique that has been used to study metabolic changes in brain tumors, strokes, seizure disorders, Alzheimer's disease, depression and other diseases affecting the brain. It has also been used to study the metabolism of other organs such as muscles. In the case of muscles, NMR is used to measure the intramyocellular lipid content (IMCL).
and researchers to obtain biochemical
information about the tissues
of the human body
in a non-invasive way (without the need for a biopsy
), whereas MRI only gives them information about the structure of the body (the distribution of water and fat).
For example, whereas MRI can tell doctors where a tumour (cancer
) is located within a patient's body, MRS can, in theory, tell them how aggressive (malignant) the tumour is.
MRS equipment can be tuned (just like a radio
receiver) to pick up signals from different chemical nuclei within the body. The most common nuclei to be studied are proton
s (hydrogen
), phosphorus
, carbon
, sodium
and fluorine
.
The types of biochemicals (metabolites
) which can be studied include choline
-containing compounds (which are used to make cell
membranes), creatine
(a chemical involved in energy metabolism
), inositol
and glucose
(both sugar
s), N-acetyl aspartate (a chemical associated with the myelin
sheaths of nerve cell
fibres), and alanine
and lactate
which are elevated in some tumor
s.
At present MRS is mainly used as a tool by scientist
s (e.g. medical physicists
and biochemists
) for medical research projects, but it is becoming clear that it also has the ability to give doctors
useful clinic
al information which can be helpful in diagnosis and treatment of disease.
MRS is currently used to investigate a number of disease
s in the human body
, most notably cancer
(in brain
, breast
and prostate
), epilepsy
, Alzheimer's Disease
, Parkinson's disease
and Huntington's Chorea. MRS has been used to diagnose pituitary tuberculosis.
) showing a brain tumour (meningioma
) at the bottom right. The red box shows the volume of interest from which chemical information was obtained by MRS (a cube with 2 cm sides which produces a square when intersecting the 5 mm thick slice of the MRI scan).
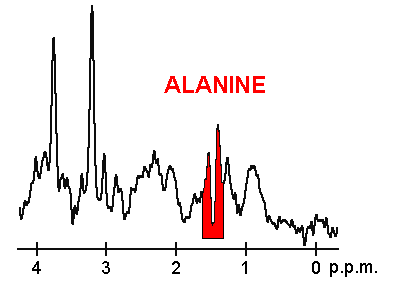
The proton
MRS spectrum
from this tumour is also shown (as acquired with a 1.5 tesla
whole-body MRI scanner). The horizontal axis
is NMR frequency
(or chemical shift
in parts per million, p.p.m., relative to a reference chemical
at 0 p.p.m. rather than in the absolute units of hertz
) and the vertical axis is signal strength (in arbitrary units).
Each biochemical, or metabolite, has a different peak in the spectrum which appears at a known frequency. The peaks corresponding to the amino acid alanine
, are highlighted in red (at 1.4 p.p.m). This is an example of the kind of biochemical information which can help doctors to make their diagnosis
. Other metabolites of note are choline
(3.2 p.p.m.) and creatine
(3.0 p.p.m.).
Both of the above images are kindly provided by The University of Hull
Centre for Magnetic Resonance Investigations
(http://www.hull.ac.uk/mri).
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), also known as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, is a non-invasive analytical technique that has been used to study metabolic changes in brain tumors, strokes, seizure disorders, Alzheimer's disease, depression and other diseases affecting the brain. It has also been used to study the metabolism of other organs such as muscles. In the case of muscles, NMR is used to measure the intramyocellular lipid content (IMCL).
Uses
MRS allows doctorsPhysician
A physician is a health care provider who practices the profession of medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring human health through the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, injury and other physical and mental impairments...
and researchers to obtain biochemical
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
information about the tissues
Tissue (biology)
Tissue is a cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete organism. A tissue is an ensemble of cells, not necessarily identical, but from the same origin, that together carry out a specific function. These are called tissues because of their identical functioning...
of the human body
Human body
The human body is the entire structure of a human organism, and consists of a head, neck, torso, two arms and two legs.By the time the human reaches adulthood, the body consists of close to 100 trillion cells, the basic unit of life...
in a non-invasive way (without the need for a biopsy
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test involving sampling of cells or tissues for examination. It is the medical removal of tissue from a living subject to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist, and can also be analyzed chemically...
), whereas MRI only gives them information about the structure of the body (the distribution of water and fat).
For example, whereas MRI can tell doctors where a tumour (cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
) is located within a patient's body, MRS can, in theory, tell them how aggressive (malignant) the tumour is.
MRS equipment can be tuned (just like a radio
Radio
Radio is the transmission of signals through free space by modulation of electromagnetic waves with frequencies below those of visible light. Electromagnetic radiation travels by means of oscillating electromagnetic fields that pass through the air and the vacuum of space...
receiver) to pick up signals from different chemical nuclei within the body. The most common nuclei to be studied are proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
s (hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
), phosphorus
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks...
, carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
, sodium
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal and is a member of the alkali metals; its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists in numerous minerals, most commonly as sodium chloride...
and fluorine
Fluorine
Fluorine is the chemical element with atomic number 9, represented by the symbol F. It is the lightest element of the halogen column of the periodic table and has a single stable isotope, fluorine-19. At standard pressure and temperature, fluorine is a pale yellow gas composed of diatomic...
.
The types of biochemicals (metabolites
Metabolomics
Metabolomics is the scientific study of chemical processes involving metabolites. Specifically, metabolomics is the "systematic study of the unique chemical fingerprints that specific cellular processes leave behind", the study of their small-molecule metabolite profiles...
) which can be studied include choline
Choline
Choline is a water-soluble essential nutrient. It is usually grouped within the B-complex vitamins. Choline generally refers to the various quaternary ammonium salts containing the N,N,N-trimethylethanolammonium cation....
-containing compounds (which are used to make cell
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
membranes), creatine
Creatine
Creatine is a nitrogenous organic acid that occurs naturally in vertebrates and helps to supply energy to all cells in the body, primarily muscle. This is achieved by increasing the formation of Adenosine triphosphate...
(a chemical involved in energy metabolism
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
), inositol
Inositol
Inositol or cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol is a chemical compound with formula 6126 or 6, a sixfold alcohol of cyclohexane. It exists in nine possible stereoisomers, of which the most prominent form, widely occurring in nature, is cis-1,2,3,5-trans-4,6-cyclohexanehexol, or myo-inositol...
and glucose
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
(both sugar
Sugar
Sugar is a class of edible crystalline carbohydrates, mainly sucrose, lactose, and fructose, characterized by a sweet flavor.Sucrose in its refined form primarily comes from sugar cane and sugar beet...
s), N-acetyl aspartate (a chemical associated with the myelin
Myelin
Myelin is a dielectric material that forms a layer, the myelin sheath, usually around only the axon of a neuron. It is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system. Myelin is an outgrowth of a type of glial cell. The production of the myelin sheath is called myelination...
sheaths of nerve cell
Axon
An axon is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body or soma....
fibres), and alanine
Alanine
Alanine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula CH3CHCOOH. The L-isomer is one of the 20 amino acids encoded by the genetic code. Its codons are GCU, GCC, GCA, and GCG. It is classified as a nonpolar amino acid...
and lactate
Lactic acid
Lactic acid, also known as milk acid, is a chemical compound that plays a role in various biochemical processes and was first isolated in 1780 by the Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele. Lactic acid is a carboxylic acid with the chemical formula C3H6O3...
which are elevated in some tumor
Tumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
s.
At present MRS is mainly used as a tool by scientist
Scientist
A scientist in a broad sense is one engaging in a systematic activity to acquire knowledge. In a more restricted sense, a scientist is an individual who uses the scientific method. The person may be an expert in one or more areas of science. This article focuses on the more restricted use of the word...
s (e.g. medical physicists
Medical physics
Medical physics is the application of physics to medicine. It generally concerns physics as applied to medical imaging and radiotherapy, although a medical physicist may also work in many other areas of healthcare...
and biochemists
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
) for medical research projects, but it is becoming clear that it also has the ability to give doctors
Physician
A physician is a health care provider who practices the profession of medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring human health through the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, injury and other physical and mental impairments...
useful clinic
Clinic
A clinic is a health care facility that is primarily devoted to the care of outpatients...
al information which can be helpful in diagnosis and treatment of disease.
MRS is currently used to investigate a number of disease
Disease
A disease is an abnormal condition affecting the body of an organism. It is often construed to be a medical condition associated with specific symptoms and signs. It may be caused by external factors, such as infectious disease, or it may be caused by internal dysfunctions, such as autoimmune...
s in the human body
Human body
The human body is the entire structure of a human organism, and consists of a head, neck, torso, two arms and two legs.By the time the human reaches adulthood, the body consists of close to 100 trillion cells, the basic unit of life...
, most notably cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
(in brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
, breast
Breast
The breast is the upper ventral region of the torso of a primate, in left and right sides, which in a female contains the mammary gland that secretes milk used to feed infants.Both men and women develop breasts from the same embryological tissues...
and prostate
Prostate
The prostate is a compound tubuloalveolar exocrine gland of the male reproductive system in most mammals....
), epilepsy
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a common chronic neurological disorder characterized by seizures. These seizures are transient signs and/or symptoms of abnormal, excessive or hypersynchronous neuronal activity in the brain.About 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy, and nearly two out of every three new cases...
, Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease also known in medical literature as Alzheimer disease is the most common form of dementia. There is no cure for the disease, which worsens as it progresses, and eventually leads to death...
, Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease is a degenerative disorder of the central nervous system...
and Huntington's Chorea. MRS has been used to diagnose pituitary tuberculosis.
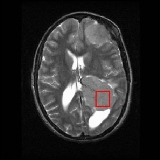
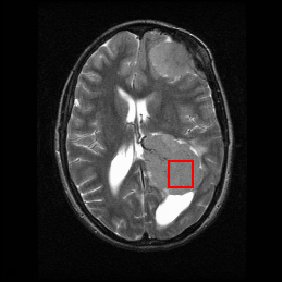
Example
Shown below is an MRI brain scan (in the axial plane, that is slicing from front-to-back and side-to-side through the headHead
In anatomy, the head of an animal is the rostral part that usually comprises the brain, eyes, ears, nose and mouth . Some very simple animals may not have a head, but many bilaterally symmetric forms do....
) showing a brain tumour (meningioma
Meningioma
The word meningioma was first used by Harvey Cushing in 1922 to describe a tumor originating from the meninges, the membranous layers surrounding the CNS ....
) at the bottom right. The red box shows the volume of interest from which chemical information was obtained by MRS (a cube with 2 cm sides which produces a square when intersecting the 5 mm thick slice of the MRI scan).
The proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
MRS spectrum
Spectrum
A spectrum is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary infinitely within a continuum. The word saw its first scientific use within the field of optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light when separated using a prism; it has since been applied by...
from this tumour is also shown (as acquired with a 1.5 tesla
Tesla (unit)
The tesla is the SI derived unit of magnetic field B . One tesla is equal to one weber per square meter, and it was defined in 1960 in honour of the inventor, physicist, and electrical engineer Nikola Tesla...
whole-body MRI scanner). The horizontal axis
Cartesian coordinate system
A Cartesian coordinate system specifies each point uniquely in a plane by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances from the point to two fixed perpendicular directed lines, measured in the same unit of length...
is NMR frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
(or chemical shift
Chemical shift
In nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, the chemical shift is the resonant frequency of a nucleus relative to a standard. Often the position and number of chemical shifts are diagnostic of the structure of a molecule...
in parts per million, p.p.m., relative to a reference chemical
Chemical shift
In nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, the chemical shift is the resonant frequency of a nucleus relative to a standard. Often the position and number of chemical shifts are diagnostic of the structure of a molecule...
at 0 p.p.m. rather than in the absolute units of hertz
Hertz
The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
) and the vertical axis is signal strength (in arbitrary units).
Each biochemical, or metabolite, has a different peak in the spectrum which appears at a known frequency. The peaks corresponding to the amino acid alanine
Alanine
Alanine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula CH3CHCOOH. The L-isomer is one of the 20 amino acids encoded by the genetic code. Its codons are GCU, GCC, GCA, and GCG. It is classified as a nonpolar amino acid...
, are highlighted in red (at 1.4 p.p.m). This is an example of the kind of biochemical information which can help doctors to make their diagnosis
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of anything. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines with variations in the use of logics, analytics, and experience to determine the cause and effect relationships...
. Other metabolites of note are choline
Choline
Choline is a water-soluble essential nutrient. It is usually grouped within the B-complex vitamins. Choline generally refers to the various quaternary ammonium salts containing the N,N,N-trimethylethanolammonium cation....
(3.2 p.p.m.) and creatine
Creatine
Creatine is a nitrogenous organic acid that occurs naturally in vertebrates and helps to supply energy to all cells in the body, primarily muscle. This is achieved by increasing the formation of Adenosine triphosphate...
(3.0 p.p.m.).


Both of the above images are kindly provided by The University of Hull
University of Hull
The University of Hull, known informally as Hull University, is an English university, founded in 1927, located in Hull, a city in the East Riding of Yorkshire...
Centre for Magnetic Resonance Investigations
Centre for Magnetic Resonance Investigations
The Kingston Upon Hull Centre for Magnetic Resonance Investigations , which opened in 1992, is a magnetic resonance imaging centre located in the city of Kingston upon Hull in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England, UK...
(http://www.hull.ac.uk/mri).
See also
- Magnetic resonance imagingMagnetic resonance imagingMagnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
- NMRNMRNMR may refer to:Applications of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance:* Nuclear magnetic resonance* NMR spectroscopy* Solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance* Protein nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy* Proton NMR* Carbon-13 NMR...
- NMR SpectroscopyNMR spectroscopyNuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy, is a research technique that exploits the magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei to determine physical and chemical properties of atoms or the molecules in which they are contained...
- Magnetization transferMagnetization transferMagnetization transfer , as commonly used in biomedical MRI, refers to the transfer of longitudinal magnetization from the hydrogen nuclei of water that have restricted motion to the hydrogen nuclei of water that moves with many degrees of freedom...

