
Creatine
Encyclopedia
Creatine is a nitrogen
ous organic acid
that occurs naturally in vertebrate
s and helps to supply energy
to all cells in the body, primarily muscle
. This is achieved by increasing the formation of Adenosine triphosphate
(ATP). Creatine was identified in 1832 when Michel Eugène Chevreul
discovered it as a component of skeletal muscle
, which he later named creatine after the Greek
word for meat, κρέας (kreas). In solution, creatine is in equilibrium with creatinine
.
Creatine is not an essential nutrient, as it is manufactured in the human body from L-arginine, glycine
, and L-methionine.
In humans and animals, approximately half of stored creatine originates from food (mainly from meat
). A study, involving 18 vegetarians and 24 non-vegetarians, on the effect of creatine in vegetarians showed that total creatine was significantly lower than in non-vegetarians. Since vegetables do not represent the primary source of creatine, vegetarians can be expected to show lower levels of directly derived muscle creatine. However, the subjects happened to show the same levels after using supplements. Given the fact that creatine can be synthesized from the above mentioned amino acids, protein sources rich in these amino acids can be expected to provide adequate capability of native biosynthesis in the human body.
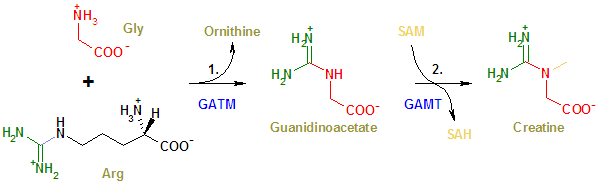
The enzyme
GATM (L-arginine
:glycine
amidinotransferase (AGAT
), EC 2.1.4.1) is a mitochondrial enzyme
responsible for catalyzing the first rate-limiting step of creatine biosynthesis, and is primarily expressed in the kidneys and pancreas
.
The second enzyme in the pathway (GAMT, guanidinoacetate N-methyltransferase, EC:2.1.1.2) is primarily expressed in the liver and pancreas.
Genetic deficiencies in the creatine biosynthetic pathway lead to various severe neurological defects.
(PCr) through a reversible reaction with the enzyme creatine kinase
(CK). In skeletal muscle, PCr concentrations may reach 20-35 mM or more. Additionally, in most muscles, the ATP regeneration capacity of CK is very high and is therefore not a limiting factor. Although the cellular concentrations of ATP are small, changes are difficult to detect because ATP is continuously and efficiently replenished from the large pools of PCr and CK. Creatine has the ability to increase muscle stores of PCr, potentially increasing the muscle’s ability to resynthesize ATP from ADP to meet increased energy demands. For a review of the creatine kinase system and the pleiotropic actions of creatine and creatine supplementation see .
are sometimes used by athletes, bodybuilders, wrestlers, sprinters and others who wish to gain muscle mass, typically consuming 2 to 3 times the amount that could be obtained from a very-high-protein diet. A survey of long-term use gives the creatine content of several foods. The Mayo Clinic
states that creatine has been associated with asthmatic symptoms and warns against consumption by persons with known allergies.
While there was once some concern that creatine supplementation could affect hydration status and heat tolerance and lead to muscle cramping and diarrhea, recent studies have shown these concerns to be unfounded.
There are reports of kidney damage with creatine use, such as interstitial nephritis; patients with kidney disease should avoid use of this supplement. In similar manner, liver function may be altered, and caution is advised in those with underlying liver disease although studies have shown little or no adverse impact on kidney or liver function from oral creatine supplementation. In 2004 the European Food Safety Authority
(EFSA) published a record which stated that oral long-term intake of 3g pure creatine per day is risk-free. The reports of damage to the kidneys by creatine supplementation have been scientifically refuted.
Long-term administration of large quantities of creatine is reported to increase the production of formaldehyde, which has the potential to cause serious unwanted side-effects. However, this risk is largely theoretical because urinary excretion of formaldehyde, even under heavy creatine supplementation, does not exceed normal limits.
Extensive research over the last decade has shown that oral creatine supplementation at a rate of 5 to 20 grams per day appears to be very safe and largely devoid of adverse side-effects, while at the same time effectively improving the physiological response to resistance exercise, increasing the maximal force production of muscles in both men and women.
After the "loading dose" period (1–2 weeks, 12-24 g a day), it is no longer necessary to maintain a consistently high serum level of creatine. As with most supplements, each person has their own genetic "preset" amount of creatine they can hold. The rest is eliminated out of the body as waste. Creatine is consumed by the body fairly quickly, and if one wishes to maintain the high concentration of creatine, Post-loading dose, 2-5 g daily is the standard amount to intake.
s. Creatine supplementation has been, and continues to be, investigated as a possible therapeutic approach for the treatment of muscular, neuromuscular, neurological and neurodegenerative diseases (arthritis
, congestive heart failure
, Parkinson's disease
, disuse atrophy, gyrate atrophy, McArdle's disease, Huntington's disease
, miscellaneous neuromuscular diseases, mitochondrial disease
s, muscular dystrophy
, and neuroprotection
).
A study demonstrated that creatine is twice as effective as the prescription drug riluzole
in extending the lives of mice with the degenerative neural disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
(ALS
, or Lou Gehrig's disease
). The neuroprotective effects of creatine in the mouse model of ALS may be due either to an increased availability of energy to injured nerve cells or to a blocking of the chemical pathway that leads to cell death. A similarly promising result has been obtained in prolonging the life of transgenic mice affected by Huntington's disease. Creatine treatment lessened brain atrophy and the formation of intranuclear inclusions, attenuated reductions in striatal N-acetylaspartate, and delayed the development of hyperglycemia
.
, Raven's Progressive Matrices
, and the backward digit span test from the WAIS
. The treatment group was able to repeat longer sequences of numbers from memory and had higher overall IQ scores than the control group. The researchers concluded that "supplementation with creatine significantly increased intelligence compared with placebo." A subsequent study found that creatine supplements improved cognitive ability in the elderly. A study on young adults (0.03 g/kg/day for six weeks, e.g., 2 g/day for a 70 kilograms (154.3 lb) individual) failed to find any improvements.
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
ous organic acid
Organic acid
An organic acid is an organic compound with acidic properties. The most common organic acids are the carboxylic acids, whose acidity is associated with their carboxyl group –COOH. Sulfonic acids, containing the group –SO2OH, are relatively stronger acids. The relative stability of the conjugate...
that occurs naturally in vertebrate
Vertebrate
Vertebrates are animals that are members of the subphylum Vertebrata . Vertebrates are the largest group of chordates, with currently about 58,000 species described. Vertebrates include the jawless fishes, bony fishes, sharks and rays, amphibians, reptiles, mammals, and birds...
s and helps to supply energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
to all cells in the body, primarily muscle
Muscle
Muscle is a contractile tissue of animals and is derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments that move past each other and change the size of the cell. They are classified as skeletal, cardiac, or smooth muscles. Their function is to...
. This is achieved by increasing the formation of Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
(ATP). Creatine was identified in 1832 when Michel Eugène Chevreul
Michel Eugène Chevreul
Michel Eugène Chevreul was a French chemist whose work with fatty acids led to early applications in the fields of art and science. He is credited with the discovery of margaric acid and designing an early form of soap made from animal fats and salt...
discovered it as a component of skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscle is a form of striated muscle tissue existing under control of the somatic nervous system- i.e. it is voluntarily controlled. It is one of three major muscle types, the others being cardiac and smooth muscle...
, which he later named creatine after the Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
word for meat, κρέας (kreas). In solution, creatine is in equilibrium with creatinine
Creatinine
Creatinine is a break-down product of creatine phosphate in muscle, and is usually produced at a fairly constant rate by the body...
.
Biosynthesis
Creatine is naturally produced in the human body from amino acids primarily in the kidney and liver. It is transported in the blood for use by muscles. Approximately 95% of the human body's total creatine is located in skeletal muscle.Creatine is not an essential nutrient, as it is manufactured in the human body from L-arginine, glycine
Glycine
Glycine is an organic compound with the formula NH2CH2COOH. Having a hydrogen substituent as its 'side chain', glycine is the smallest of the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. Its codons are GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG cf. the genetic code.Glycine is a colourless, sweet-tasting crystalline solid...
, and L-methionine.
In humans and animals, approximately half of stored creatine originates from food (mainly from meat
Meat
Meat is animal flesh that is used as food. Most often, this means the skeletal muscle and associated fat and other tissues, but it may also describe other edible tissues such as organs and offal...
). A study, involving 18 vegetarians and 24 non-vegetarians, on the effect of creatine in vegetarians showed that total creatine was significantly lower than in non-vegetarians. Since vegetables do not represent the primary source of creatine, vegetarians can be expected to show lower levels of directly derived muscle creatine. However, the subjects happened to show the same levels after using supplements. Given the fact that creatine can be synthesized from the above mentioned amino acids, protein sources rich in these amino acids can be expected to provide adequate capability of native biosynthesis in the human body.
The enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
GATM (L-arginine
Arginine
Arginine is an α-amino acid. The L-form is one of the 20 most common natural amino acids. At the level of molecular genetics, in the structure of the messenger ribonucleic acid mRNA, CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG, AGA, and AGG, are the triplets of nucleotide bases or codons that codify for arginine during...
:glycine
Glycine
Glycine is an organic compound with the formula NH2CH2COOH. Having a hydrogen substituent as its 'side chain', glycine is the smallest of the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. Its codons are GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG cf. the genetic code.Glycine is a colourless, sweet-tasting crystalline solid...
amidinotransferase (AGAT
Arginine:glycine amidinotransferase
L-Arginine:glycine amidinotransferase is the enzyme that catalyses the transfer of an amidino group from L-arginine to glycine. The products are L-ornithine and glycocyamine, also known as guanidinoacetate, the immediate precursor of creatine. Creatine and its phosphorylated form play a central...
), EC 2.1.4.1) is a mitochondrial enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
responsible for catalyzing the first rate-limiting step of creatine biosynthesis, and is primarily expressed in the kidneys and pancreas
Pancreas
The pancreas is a gland organ in the digestive and endocrine system of vertebrates. It is both an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin, as well as a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist...
.
The second enzyme in the pathway (GAMT, guanidinoacetate N-methyltransferase, EC:2.1.1.2) is primarily expressed in the liver and pancreas.
Genetic deficiencies in the creatine biosynthetic pathway lead to various severe neurological defects.

The phosphocreatine system
Creatine, synthesized in the liver and kidney, is transported through the blood and taken up by tissues with high energy demands, such as the brain and skeletal muscle, through an active transport system. The concentration of ATP in skeletal muscle is usually 2-5 mM, which would result in a muscle contraction of only a few seconds. Fortunately, during times of increased energy demands, the phosphagen (or ATP/PCr) system rapidly resynthesizes ATP from ADP with the use of phosphocreatinePhosphocreatine
Phosphocreatine, also known as creatine phosphate or PCr , is a phosphorylated creatine molecule that serves as a rapidly mobilizable reserve of high-energy phosphates in skeletal muscle and brain.-Chemistry:...
(PCr) through a reversible reaction with the enzyme creatine kinase
Creatine kinase
Creatine kinase , also known as creatine phosphokinase or phospho-creatine kinase , is an enzyme expressed by various tissues and cell types. CK catalyses the conversion of creatine and consumes adenosine triphosphate to create phosphocreatine and adenosine diphosphate...
(CK). In skeletal muscle, PCr concentrations may reach 20-35 mM or more. Additionally, in most muscles, the ATP regeneration capacity of CK is very high and is therefore not a limiting factor. Although the cellular concentrations of ATP are small, changes are difficult to detect because ATP is continuously and efficiently replenished from the large pools of PCr and CK. Creatine has the ability to increase muscle stores of PCr, potentially increasing the muscle’s ability to resynthesize ATP from ADP to meet increased energy demands. For a review of the creatine kinase system and the pleiotropic actions of creatine and creatine supplementation see .
Use as food supplement
Creatine supplementsCreatine supplements
Creatine supplements are athletic aids used to increase high-intensity athletic performance. Though researchers have known of the use of creatine as an energy source by skeletal muscles since the beginning of the 20th century, they were popularized as a performance-enhancing supplement in...
are sometimes used by athletes, bodybuilders, wrestlers, sprinters and others who wish to gain muscle mass, typically consuming 2 to 3 times the amount that could be obtained from a very-high-protein diet. A survey of long-term use gives the creatine content of several foods. The Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic is a not-for-profit medical practice and medical research group specializing in treating difficult patients . Patients are referred to Mayo Clinic from across the U.S. and the world, and it is known for innovative and effective treatments. Mayo Clinic is known for being at the top of...
states that creatine has been associated with asthmatic symptoms and warns against consumption by persons with known allergies.
While there was once some concern that creatine supplementation could affect hydration status and heat tolerance and lead to muscle cramping and diarrhea, recent studies have shown these concerns to be unfounded.
There are reports of kidney damage with creatine use, such as interstitial nephritis; patients with kidney disease should avoid use of this supplement. In similar manner, liver function may be altered, and caution is advised in those with underlying liver disease although studies have shown little or no adverse impact on kidney or liver function from oral creatine supplementation. In 2004 the European Food Safety Authority
European Food Safety Authority
The European Food Safety Authority is an agency of the European Union that provides independent scientific advice and communication on existing and emerging risks associated with the food chain, created by European Regulation 178/2002....
(EFSA) published a record which stated that oral long-term intake of 3g pure creatine per day is risk-free. The reports of damage to the kidneys by creatine supplementation have been scientifically refuted.
Long-term administration of large quantities of creatine is reported to increase the production of formaldehyde, which has the potential to cause serious unwanted side-effects. However, this risk is largely theoretical because urinary excretion of formaldehyde, even under heavy creatine supplementation, does not exceed normal limits.
Extensive research over the last decade has shown that oral creatine supplementation at a rate of 5 to 20 grams per day appears to be very safe and largely devoid of adverse side-effects, while at the same time effectively improving the physiological response to resistance exercise, increasing the maximal force production of muscles in both men and women.
Pharmacokinetics
Endogenous serum or plasma creatine concentrations in healthy adults are normally in a range of 2–12 mg/L. A single 5 g (5000 mg) oral dose in healthy adults results in a peak plasma creatine level of approximately 120 mg/L at 1–2 hours post-ingestion. Creatine has a fairly short elimination half-life, averaging just less than 3 hours, so to maintain an elevated plasma level it would be necessary to take small oral doses every 3–6 hours throughout the day.After the "loading dose" period (1–2 weeks, 12-24 g a day), it is no longer necessary to maintain a consistently high serum level of creatine. As with most supplements, each person has their own genetic "preset" amount of creatine they can hold. The rest is eliminated out of the body as waste. Creatine is consumed by the body fairly quickly, and if one wishes to maintain the high concentration of creatine, Post-loading dose, 2-5 g daily is the standard amount to intake.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Creatine cannot be recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding due to a lack of scientific information. Pasteurized cow's milk contains higher levels of creatine than human milk.Treatment of diseases
Creatine has been demonstrated to cause modest increases in strength in people with a variety of neuromuscular disorderNeuromuscular disease
Neuromuscular disease is a very broad term that encompasses many diseases and ailments that either directly, via intrinsic muscle pathology, or indirectly, via nerve pathology, impair the functioning of the muscles....
s. Creatine supplementation has been, and continues to be, investigated as a possible therapeutic approach for the treatment of muscular, neuromuscular, neurological and neurodegenerative diseases (arthritis
Arthritis
Arthritis is a form of joint disorder that involves inflammation of one or more joints....
, congestive heart failure
Congestive heart failure
Heart failure often called congestive heart failure is generally defined as the inability of the heart to supply sufficient blood flow to meet the needs of the body. Heart failure can cause a number of symptoms including shortness of breath, leg swelling, and exercise intolerance. The condition...
, Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease is a degenerative disorder of the central nervous system...
, disuse atrophy, gyrate atrophy, McArdle's disease, Huntington's disease
Huntington's disease
Huntington's disease, chorea, or disorder , is a neurodegenerative genetic disorder that affects muscle coordination and leads to cognitive decline and dementia. It typically becomes noticeable in middle age. HD is the most common genetic cause of abnormal involuntary writhing movements called chorea...
, miscellaneous neuromuscular diseases, mitochondrial disease
Mitochondrial disease
Mitochondrial diseases are a group of disorders caused by dysfunctional mitochondria, the organelles that are the "powerhouses" of the cell. Mitochondria are found in every cell of the human body except red blood cells...
s, muscular dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy is a group of muscle diseases that weaken the musculoskeletal system and hamper locomotion. Muscular dystrophies are characterized by progressive skeletal muscle weakness, defects in muscle proteins, and the death of muscle cells and tissue.In the 1860s, descriptions of boys who...
, and neuroprotection
Neuroprotection
Neuroprotection within the nervous system protects neurons from apoptosis or degeneration, for example following a brain injury or as a result of chronic neurodegenerative diseases....
).
A study demonstrated that creatine is twice as effective as the prescription drug riluzole
Riluzole
Riluzole is a drug used to treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. It delays the onset of ventilator-dependence or tracheostomy in selected patients and may increase survival by approximately 3–5 months....
in extending the lives of mice with the degenerative neural disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis , also referred to as Lou Gehrig's disease, is a form of motor neuron disease caused by the degeneration of upper and lower neurons, located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord and the cortical neurons that provide their efferent input...
(ALS
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis , also referred to as Lou Gehrig's disease, is a form of motor neuron disease caused by the degeneration of upper and lower neurons, located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord and the cortical neurons that provide their efferent input...
, or Lou Gehrig's disease
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis , also referred to as Lou Gehrig's disease, is a form of motor neuron disease caused by the degeneration of upper and lower neurons, located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord and the cortical neurons that provide their efferent input...
). The neuroprotective effects of creatine in the mouse model of ALS may be due either to an increased availability of energy to injured nerve cells or to a blocking of the chemical pathway that leads to cell death. A similarly promising result has been obtained in prolonging the life of transgenic mice affected by Huntington's disease. Creatine treatment lessened brain atrophy and the formation of intranuclear inclusions, attenuated reductions in striatal N-acetylaspartate, and delayed the development of hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia or Hyperglycæmia, or high blood sugar, is a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose circulates in the blood plasma. This is generally a glucose level higher than 13.5mmol/l , but symptoms may not start to become noticeable until even higher values such as 15-20 mmol/l...
.
Cognitive ability
A placebo-controlled double-blind experiment found that a group of subjects composed of vegetarians and vegans who took 5 grams of creatine per day for six weeks showed a significant improvement on two separate tests of fluid intelligenceFluid and crystallized intelligence
In psychology, fluid and crystallized intelligence are factors of general intelligence originally identified by Raymond Cattell...
, Raven's Progressive Matrices
Raven's Progressive Matrices
Raven's Progressive Matrices are non-verbal multiple choice measures of the reasoning component of Spearman's g , which is often referred to as general intelligence. The tests were originally developed by John C. Raven in 1936...
, and the backward digit span test from the WAIS
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale
The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale intelligence quotient tests are the primary clinical instruments used to measure adult and adolescent intelligence. The original WAIS was published in February 1955 by David Wechsler, as a revision of the Wechsler-Bellevue Intelligence Scale...
. The treatment group was able to repeat longer sequences of numbers from memory and had higher overall IQ scores than the control group. The researchers concluded that "supplementation with creatine significantly increased intelligence compared with placebo." A subsequent study found that creatine supplements improved cognitive ability in the elderly. A study on young adults (0.03 g/kg/day for six weeks, e.g., 2 g/day for a 70 kilograms (154.3 lb) individual) failed to find any improvements.
External links
- NCBI Online Mendelian Inheritance In MAN (OMIM) GATM human mutation record
- Creatine Supplementation, Beth Lulinski, QuackwatchQuackwatchQuackwatch is an American non-profit organization founded by Stephen Barrett with the stated aim being to "combat health-related frauds, myths, fads, fallacies, and misconduct" and with a primary focus on providing "quackery-related information that is difficult or impossible to get elsewhere."...
- Creatine 'boosts brain power', BBC News, 12 August 2003
- Creatine: From Muscle to Brain, Peter W. Schutz, The Science Creative Quarterly, 2009
- Creatine Supplementation A primer for athletes
- Creatine during Pregnancy and Protection of Babies against Anoxia A mouse study
- "The creatine kinase system and pleiotropic effects of creatine" in: Amino Acids. 2011 May;40(5):1271-96 A recent Review from May 2011

