.gif)
Human development (biology)
Encyclopedia
Human development is the process of growing
to maturity. In biological terms, this entails growth from a one-celled zygote
to an adult human being.
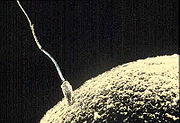 Development begins with fertilization, the process by which the male gamete
Development begins with fertilization, the process by which the male gamete
, the sperm cell
, and the female gamete, the egg
, fuse to produce a zygote. In pregnancy the 3 stages are commonly referred as Z.E.F. - meaning Zygote, Embryo, Fetus.
In medicine, the beginning of pregnancy is the instant a sperm cell enters an ovum and forms a viable zygote
. Recently, in western medicine, pregnancy is defined as beginning when a zygote becomes implanted in a woman's uterus
. This occurs when the zygote then becomes embedded into the endometrium
(lining of the uterus) where it forms a placenta
, for the purpose of receiving essential nutrients through the uterus
wall. The umbilical cord
in an unborn child helps get the nutrients to the child and helps get rid of the waste from the child. Before the placenta is developed the blastocyst receives its nutrients from the yolk sac, which is contained within the blastocyst.
The zygote undergoes rapid cell divisions with no significant growth (a process known as cleavage
) and cellular differentiation
, leading to development of an embryo
.
Childbirth
is the process in which the baby is born. Age is defined relative to this event in most cultures.
Also sometimes used are terms that specify one's age in numbers, such as:
Note: the Tanner stages can be used to approximately judge a child's age based on physical development.
Growing
Growing may refer to:* Growth* Growing , a noise band currently based in Brooklyn, New York* Growing , a 2007 album by the instrumental rock band Sleeping People...
to maturity. In biological terms, this entails growth from a one-celled zygote
Zygote
A zygote , or zygocyte, is the initial cell formed when two gamete cells are joined by means of sexual reproduction. In multicellular organisms, it is the earliest developmental stage of the embryo...
to an adult human being.
Biological development

Gamete
A gamete is a cell that fuses with another cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually...
, the sperm cell
Spermatozoon
A spermatozoon is a motile sperm cell, or moving form of the haploid cell that is the male gamete. A spermatozoon joins an ovum to form a zygote...
, and the female gamete, the egg
Egg (biology)
An egg is an organic vessel in which an embryo first begins to develop. In most birds, reptiles, insects, molluscs, fish, and monotremes, an egg is the zygote, resulting from fertilization of the ovum, which is expelled from the body and permitted to develop outside the body until the developing...
, fuse to produce a zygote. In pregnancy the 3 stages are commonly referred as Z.E.F. - meaning Zygote, Embryo, Fetus.
In medicine, the beginning of pregnancy is the instant a sperm cell enters an ovum and forms a viable zygote
Zygote
A zygote , or zygocyte, is the initial cell formed when two gamete cells are joined by means of sexual reproduction. In multicellular organisms, it is the earliest developmental stage of the embryo...
. Recently, in western medicine, pregnancy is defined as beginning when a zygote becomes implanted in a woman's uterus
Uterus
The uterus or womb is a major female hormone-responsive reproductive sex organ of most mammals including humans. One end, the cervix, opens into the vagina, while the other is connected to one or both fallopian tubes, depending on the species...
. This occurs when the zygote then becomes embedded into the endometrium
Endometrium
-Function:The endometrium is the innermost glandular layer and functions as a lining for the uterus, preventing adhesions between the opposed walls of the myometrium, thereby maintaining the patency of the uterine cavity. During the menstrual cycle or estrous cycle, the endometrium grows to a...
(lining of the uterus) where it forms a placenta
Placenta
The placenta is an organ that connects the developing fetus to the uterine wall to allow nutrient uptake, waste elimination, and gas exchange via the mother's blood supply. "True" placentas are a defining characteristic of eutherian or "placental" mammals, but are also found in some snakes and...
, for the purpose of receiving essential nutrients through the uterus
Uterus
The uterus or womb is a major female hormone-responsive reproductive sex organ of most mammals including humans. One end, the cervix, opens into the vagina, while the other is connected to one or both fallopian tubes, depending on the species...
wall. The umbilical cord
Umbilical cord
In placental mammals, the umbilical cord is the connecting cord from the developing embryo or fetus to the placenta...
in an unborn child helps get the nutrients to the child and helps get rid of the waste from the child. Before the placenta is developed the blastocyst receives its nutrients from the yolk sac, which is contained within the blastocyst.
The zygote undergoes rapid cell divisions with no significant growth (a process known as cleavage
Cleavage (embryo)
In embryology, cleavage is the division of cells in the early embryo. The zygotes of many species undergo rapid cell cycles with no significant growth, producing a cluster of cells the same size as the original zygote. The different cells derived from cleavage are called blastomeres and form a...
) and cellular differentiation
Cellular differentiation
In developmental biology, cellular differentiation is the process by which a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell type. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as the organism changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of...
, leading to development of an embryo
Embryo
An embryo is a multicellular diploid eukaryote in its earliest stage of development, from the time of first cell division until birth, hatching, or germination...
.
Childbirth
Childbirth
Childbirth is the culmination of a human pregnancy or gestation period with the birth of one or more newborn infants from a woman's uterus...
is the process in which the baby is born. Age is defined relative to this event in most cultures.
Physical stages of human life
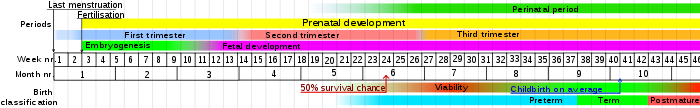
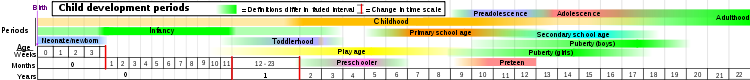
There are no universal definitions for terms of age-related physical development stages, but following are some approximate age ranges:
- Prenatal (fertilization - birth)
- EmbryoHuman embryogenesisHuman embryology is the study of human development during the first eight weeks from gametogenesis pre-conception through fertilization up to and including the 8th week after implantation of the zygote in the uterus...
- (fertilization - 8 weeks of gestational phase)- ZygoteZygoteA zygote , or zygocyte, is the initial cell formed when two gamete cells are joined by means of sexual reproduction. In multicellular organisms, it is the earliest developmental stage of the embryo...
, the point of conception, fertilization - BlastocystBlastocystThe blastocyst is a structure formed in the early embryogenesis of mammals, after the formation of the morula. It is a specifically mammalian example of a blastula. It possesses an inner cell mass , or embryoblast, which subsequently forms the embryo, and an outer layer of cells, or trophoblast,...
the period between conception and embryonic stages - EmbryoEmbryoAn embryo is a multicellular diploid eukaryote in its earliest stage of development, from the time of first cell division until birth, hatching, or germination...
; the embryonic period starts at three weeks and continues until the end of the 8th week of pregnancy
- Zygote
- FetusFetusA fetus is a developing mammal or other viviparous vertebrate after the embryonic stage and before birth.In humans, the fetal stage of prenatal development starts at the beginning of the 11th week in gestational age, which is the 9th week after fertilization.-Etymology and spelling variations:The...
(8 weeks of gestational phase - birth)
- Embryo

- ChildChildBiologically, a child is generally a human between the stages of birth and puberty. Some vernacular definitions of a child include the fetus, as being an unborn child. The legal definition of "child" generally refers to a minor, otherwise known as a person younger than the age of majority...
(ChildbirthChildbirthChildbirth is the culmination of a human pregnancy or gestation period with the birth of one or more newborn infants from a woman's uterus...
)(0 - 12)- Neonate (newborn) (0 – 30 days)
- InfantInfantA newborn or baby is the very young offspring of a human or other mammal. A newborn is an infant who is within hours, days, or up to a few weeks from birth. In medical contexts, newborn or neonate refers to an infant in the first 28 days after birth...
(baby) (1 month - 12 months) - ToddlerToddlerA toddler is a young child, usually defined as being between the ages of one and three. Registered nurse, midwife and author, Robin Barker, states 'Any time from eight months onwards your baby will begin to realise he is a separate person from you...
(1 – 3 years) - Play age (4–5 years)
- Primary school age (also called prepubescence) (4-12)
- Elementary schoolElementary schoolAn elementary school or primary school is an institution where children receive the first stage of compulsory education known as elementary or primary education. Elementary school is the preferred term in some countries, particularly those in North America, where the terms grade school and grammar...
age (also called middle childhood) (4-9) - Preadolescence (preteen, or late childhood. The child in this and the previous phase are called schoolchild (schoolboy or schoolgirl), when still of primary school age.) (10 – 12 years)
- Elementary school
- AdolescenceAdolescenceAdolescence is a transitional stage of physical and mental human development generally occurring between puberty and legal adulthood , but largely characterized as beginning and ending with the teenage stage...
and pubertyPubertyPuberty is the process of physical changes by which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of reproduction, as initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads; the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a boy...
(13 – 19 years)- Peripuberty (8-10 until 15-17)
- AdultAdultAn adult is a human being or living organism that is of relatively mature age, typically associated with sexual maturity and the attainment of reproductive age....
(20+ years)- Early adulthoodYoung adult (psychology)A young adult, according to Erik Erikson's stages of human development, is generally a person between the age of 20 - 40, whereas an adolescent is a person between the age of 13 - 19, although definitions and opinions vary. The young adult stage in human development precedes middle adulthood. A...
(20 – 39 years) - Middle adulthoodMiddle ageMiddle age is the period of age beyond young adulthood but before the onset of old age. Various attempts have been made to define this age, which is around the third quarter of the average life span of human beings....
(40 – 59 years) - Advanced adulthoodOld ageOld age consists of ages nearing or surpassing the average life span of human beings, and thus the end of the human life cycle...
/Senior citizenSenior citizenSenior citizen is a common polite designation for an elderly person in both UK and US English, and it implies or means that the person is retired. This in turn implies or in fact means that the person is over the retirement age, which varies according to country. Synonyms include pensioner in UK...
(60+ years)
- Early adulthood
- DeathDeathDeath is the permanent termination of the biological functions that sustain a living organism. Phenomena which commonly bring about death include old age, predation, malnutrition, disease, and accidents or trauma resulting in terminal injury....
(occurs at various ages, depending on person)- DecompositionDecompositionDecomposition is the process by which organic material is broken down into simpler forms of matter. The process is essential for recycling the finite matter that occupies physical space in the biome. Bodies of living organisms begin to decompose shortly after death...
(breakdown of the body after death)
- Decomposition
Also sometimes used are terms that specify one's age in numbers, such as:
- Child (0-12)
- Teenager (13-19)
- Twentysomething (20-29)
- Thirtysomething (30-39)
- Fortysomething (40-49) (formerly also Quadragenarian, rarely used since 1980)
- Quinquagenarian (50-59)
- Sexagenarian (60-69)
- Septuagenarian (70-79)
- Octogenarian (80-89)
- Nonagenarian (90-99)
- CentenarianCentenarianA centenarian is a person who is or lives beyond the age of 100 years. Because current average life expectancies across the world are less than 100, the term is invariably associated with longevity. Much rarer, a supercentenarian is a person who has lived to the age of 110 or more, something only...
(100-109) - SupercentenarianSupercentenarianA supercentenarian is someone who has reached the age of 110 years. This age is achieved by about one in a thousand centenarians....
(110+)
Physical development milestones
- Ability to lift and control the orientation of the head
- Crawling begins
- WalkingWalkingWalking is one of the main gaits of locomotion among legged animals, and is typically slower than running and other gaits. Walking is defined by an 'inverted pendulum' gait in which the body vaults over the stiff limb or limbs with each step...
begins - Speech begins
- VoiceHuman voiceThe human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal folds for talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, etc. Its frequency ranges from about 60 to 7000 Hz. The human voice is specifically that part of human sound production in which the vocal folds are the primary...
lowers in pitch (especially noticeable in boys) - Pubic hairPubic hairPubic hair is hair in the frontal genital area, the crotch, and sometimes at the top of the inside of the legs; these areas form the pubic region....
appears - Genitals and reproductive organs mature
- Menstrual cycleMenstrual cycleThe menstrual cycle is the scientific term for the physiological changes that can occur in fertile women for the purpose of sexual reproduction. This article focuses on the human menstrual cycle....
begins (females) - Body hair and facial hairFacial hairFacial hair is a secondary sex characteristic of human males. Men often start developing facial hair in the later years of puberty or adolescence, approximately between 17–20 years of age, and most do not finish developing a fully adult beard until their early 20s or even later...
appears
Note: the Tanner stages can be used to approximately judge a child's age based on physical development.
See also
- AuxologyAuxologyAuxology, sometimes called Auxanology , is a meta-term covering the study of all aspects of human physical growth...
- Child developmentChild developmentChild development stages describe theoretical milestones of child development. Many stage models of development have been proposed, used as working concepts and in some cases asserted as nativist theories....
- Developmental biologyDevelopmental biologyDevelopmental biology is the study of the process by which organisms grow and develop. Modern developmental biology studies the genetic control of cell growth, differentiation and "morphogenesis", which is the process that gives rise to tissues, organs and anatomy.- Related fields of study...
- EmbryogenesisEmbryogenesisEmbryogenesis is the process by which the embryo is formed and develops, until it develops into a fetus.Embryogenesis starts with the fertilization of the ovum by sperm. The fertilized ovum is referred to as a zygote...
- Life-history theory
- Mammalian embryogenesisMammalian embryogenesisMammalian embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation during early prenatal development which leads to the development of a mammalian embryo.-Difference from human embryogenesis:...
- Memory developmentMemory developmentThe development of memory in children becomes evident within the first 2 to 3 years of a child's life as they show considerable advances in declarative memory...

