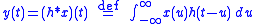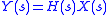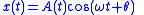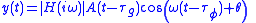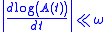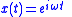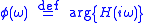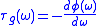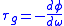Group delay and phase delay
Encyclopedia
Group delay is a measure of the time delay of the amplitude envelopes
of the various sinusoidal components
of a signal through a device under test
, and is a function of frequency for each component. Phase delay is a similar measure of the time delay of the phase, instead of the delay of the amplitude envelope, of each sinusoidal component.
All frequency components of a signal are delayed when passed through a device such as an amplifier, a loudspeaker, or propagating through space or a medium, such as air. This signal delay will be different for the various frequencies unless the device has the property of being linear phase
. The delay variation means that signals consisting of multiple frequency components will suffer distortion because these components are not delayed by the same amount of time at the output of the device. This changes the shape of the signal in addition to any constant delay or scale change. A sufficiently large delay variation can cause problems such as poor fidelity
in audio or intersymbol interference
(ISI) in the demodulation
of digital information from an analog
carrier signal
. High speed modem
s use adaptive equalizer
s to compensate for non-constant group delay.
, with respect to frequency, the phase response
versus frequency of the device under test (DUT). The group delay is a measure of the slope of the phase response at any given frequency. The variations in group delay cause signal distortion, just as deviations from linear phase cause distortion.
In LTI system theory
, control theory
, and in digital
or analog
signal processing
, the relationship between the input signal,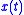 , to output signal,
, to output signal, 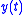 , of an LTI system is governed by the convolution
, of an LTI system is governed by the convolution
operation:
Or, in the frequency domain
,
where
and
Here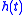 is the time-domain impulse response
is the time-domain impulse response
of the LTI system and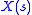 ,
, 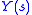 ,
, 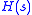 , are the Laplace transforms of the input
, are the Laplace transforms of the input 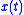 , output
, output 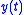 , and impulse response
, and impulse response 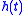 , respectively.
, respectively. 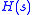 is called the transfer function
is called the transfer function
of the LTI system and, as does the impulse response,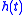 , fully defines the input-output characteristics of the LTI system.
, fully defines the input-output characteristics of the LTI system.
When such a system is driven by a quasi-sinusoidal signal, (a sinusoid with a slowly changing amplitude envelope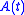 , relative to the rate of change of phase,
, relative to the rate of change of phase, 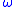 , of the sinusoid),
, of the sinusoid),
the output of such an LTI system is very well approximated as
if
and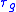 and
and 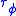 , the group delay and phase delay respectively, are equal to the expressions below (and potentially are functions of angular frequency
, the group delay and phase delay respectively, are equal to the expressions below (and potentially are functions of angular frequency
ω). In a linear phase
system (with non-inverting gain), both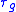 and
and 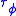 are constant and equal to the same overall delay of the system and the unwrapped phase shift
are constant and equal to the same overall delay of the system and the unwrapped phase shift
of the system is negative with magnitude increasing linearly with frequency ω.
It can be shown that for an LTI system with transfer function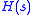 driven by a complex sinusoid
driven by a complex sinusoid
of unit amplitude,
the output is
Envelope detector
An envelope detector is an electronic circuit that takes a high-frequency signal as input and provides an output which is the "envelope" of the original signal. The capacitor in the circuit stores up charge on the rising edge, and releases it slowly through the resistor when the signal falls...
of the various sinusoidal components
Fourier series
In mathematics, a Fourier series decomposes periodic functions or periodic signals into the sum of a set of simple oscillating functions, namely sines and cosines...
of a signal through a device under test
Device under test
Device under test , also known as unit under test , is a term commonly used to refer to a manufactured product undergoing testing.-In semiconductor testing:...
, and is a function of frequency for each component. Phase delay is a similar measure of the time delay of the phase, instead of the delay of the amplitude envelope, of each sinusoidal component.
All frequency components of a signal are delayed when passed through a device such as an amplifier, a loudspeaker, or propagating through space or a medium, such as air. This signal delay will be different for the various frequencies unless the device has the property of being linear phase
Linear phase
Linear phase is a property of a filter, where the phase response of the filter is a linear function of frequency, excluding the possibility of wraps at \pm\pi. In a causal system, perfect linear phase can be achieved with a discrete-time FIR filter...
. The delay variation means that signals consisting of multiple frequency components will suffer distortion because these components are not delayed by the same amount of time at the output of the device. This changes the shape of the signal in addition to any constant delay or scale change. A sufficiently large delay variation can cause problems such as poor fidelity
High fidelity
High fidelity—or hi-fi—reproduction is a term used by home stereo listeners and home audio enthusiasts to refer to high-quality reproduction of sound or images, to distinguish it from the poorer quality sound produced by inexpensive audio equipment...
in audio or intersymbol interference
Intersymbol interference
In telecommunication, intersymbol interference is a form of distortion of a signal in which one symbol interferes with subsequent symbols. This is an unwanted phenomenon as the previous symbols have similar effect as noise, thus making the communication less reliable...
(ISI) in the demodulation
Demodulation
Demodulation is the act of extracting the original information-bearing signal from a modulated carrier wave.A demodulator is an electronic circuit that is used to recover the information content from the modulated carrier wave.These terms are traditionally used in connection with radio receivers,...
of digital information from an analog
Analog signal
An analog or analogue signal is any continuous signal for which the time varying feature of the signal is a representation of some other time varying quantity, i.e., analogous to another time varying signal. It differs from a digital signal in terms of small fluctuations in the signal which are...
carrier signal
Carrier wave
In telecommunications, a carrier wave or carrier is a waveform that is modulated with an input signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave is usually a much higher frequency than the input signal...
. High speed modem
Modem
A modem is a device that modulates an analog carrier signal to encode digital information, and also demodulates such a carrier signal to decode the transmitted information. The goal is to produce a signal that can be transmitted easily and decoded to reproduce the original digital data...
s use adaptive equalizer
Adaptive equalizer
An adaptive equalizer is an equalizer that automatically adapts to time-varying properties of the communication channel. It is frequently used with coherent modulations such as phase shift keying, mitigating the effects of multipath propagation and Doppler spreading.Many adaptation strategies exist...
s to compensate for non-constant group delay.
Introduction
Group delay is a useful measure of time distortion, and is calculated by differentiatingDerivative
In calculus, a branch of mathematics, the derivative is a measure of how a function changes as its input changes. Loosely speaking, a derivative can be thought of as how much one quantity is changing in response to changes in some other quantity; for example, the derivative of the position of a...
, with respect to frequency, the phase response
Phase response
In signal processing and electrical engineering, phase response is the relationship between the phase of a sinusoidal input and the output signal passing through any device that accepts input and produces an output signal, such as an amplifier or a filter....
versus frequency of the device under test (DUT). The group delay is a measure of the slope of the phase response at any given frequency. The variations in group delay cause signal distortion, just as deviations from linear phase cause distortion.
In LTI system theory
LTI system theory
Linear time-invariant system theory, commonly known as LTI system theory, comes from applied mathematics and has direct applications in NMR spectroscopy, seismology, circuits, signal processing, control theory, and other technical areas. It investigates the response of a linear and time-invariant...
, control theory
Control theory
Control theory is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering and mathematics that deals with the behavior of dynamical systems. The desired output of a system is called the reference...
, and in digital
Digital signal processing
Digital signal processing is concerned with the representation of discrete time signals by a sequence of numbers or symbols and the processing of these signals. Digital signal processing and analog signal processing are subfields of signal processing...
or analog
Analog signal processing
Analog signal processing is any signal processing conducted on analog signals by analog means. "Analog" indicates something that is mathematically represented as a set of continuous values. This differs from "digital" which uses a series of discrete quantities to represent signal...
signal processing
Signal processing
Signal processing is an area of systems engineering, electrical engineering and applied mathematics that deals with operations on or analysis of signals, in either discrete or continuous time...
, the relationship between the input signal,
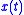 , to output signal,
, to output signal, 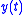 , of an LTI system is governed by the convolution
, of an LTI system is governed by the convolutionConvolution
In mathematics and, in particular, functional analysis, convolution is a mathematical operation on two functions f and g, producing a third function that is typically viewed as a modified version of one of the original functions. Convolution is similar to cross-correlation...
operation:
Or, in the frequency domain
Frequency domain
In electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, frequency domain is a term used to describe the domain for analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency, rather than time....
,
where
and
-
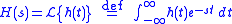 .
.
Here
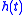 is the time-domain impulse response
is the time-domain impulse responseImpulse response
In signal processing, the impulse response, or impulse response function , of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an impulse. More generally, an impulse response refers to the reaction of any dynamic system in response to some external change...
of the LTI system and
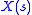 ,
, 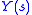 ,
, 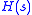 , are the Laplace transforms of the input
, are the Laplace transforms of the input 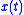 , output
, output 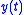 , and impulse response
, and impulse response 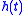 , respectively.
, respectively. 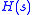 is called the transfer function
is called the transfer functionTransfer function
A transfer function is a mathematical representation, in terms of spatial or temporal frequency, of the relation between the input and output of a linear time-invariant system. With optical imaging devices, for example, it is the Fourier transform of the point spread function i.e...
of the LTI system and, as does the impulse response,
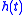 , fully defines the input-output characteristics of the LTI system.
, fully defines the input-output characteristics of the LTI system.When such a system is driven by a quasi-sinusoidal signal, (a sinusoid with a slowly changing amplitude envelope
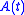 , relative to the rate of change of phase,
, relative to the rate of change of phase,  , of the sinusoid),
, of the sinusoid),the output of such an LTI system is very well approximated as
if
and
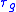 and
and 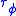 , the group delay and phase delay respectively, are equal to the expressions below (and potentially are functions of angular frequency
, the group delay and phase delay respectively, are equal to the expressions below (and potentially are functions of angular frequencyAngular frequency
In physics, angular frequency ω is a scalar measure of rotation rate. Angular frequency is the magnitude of the vector quantity angular velocity...
ω). In a linear phase
Linear phase
Linear phase is a property of a filter, where the phase response of the filter is a linear function of frequency, excluding the possibility of wraps at \pm\pi. In a causal system, perfect linear phase can be achieved with a discrete-time FIR filter...
system (with non-inverting gain), both
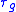 and
and 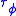 are constant and equal to the same overall delay of the system and the unwrapped phase shift
are constant and equal to the same overall delay of the system and the unwrapped phase shiftPhase (waves)
Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
of the system is negative with magnitude increasing linearly with frequency ω.
It can be shown that for an LTI system with transfer function
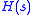 driven by a complex sinusoid
driven by a complex sinusoidPhasor
Phasor is a phase vector representing a sine wave.Phasor may also be:* Phasor , a stereo music, sound and speech synthesizer for the Apple II computer* Phasor measurement unit, a device that measures phasors on an electricity grid...
of unit amplitude,
the output is
-
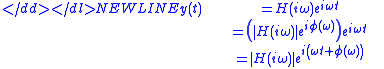
where the phase shift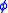 is
is
Additionally, it can be shown that the group delay,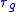 , and phase delay,
, and phase delay, 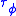 , are related to the phase shift
, are related to the phase shift 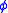 as
as
-
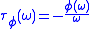 .
.
Group delay in optics
In physicsPhysicsPhysics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, and in particular in opticsOpticsOptics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
, the term group delay has the following meanings:
- 1. The rate of change of the total phase shift with respect to angular frequencyAngular frequencyIn physics, angular frequency ω is a scalar measure of rotation rate. Angular frequency is the magnitude of the vector quantity angular velocity...
, - through a device or transmission mediumTransmission mediumA transmission medium is a material substance that can propagate energy waves...
, where is the total phase shift in radians, and
is the total phase shift in radians, and 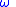 is the angular frequencyAngular frequencyIn physics, angular frequency ω is a scalar measure of rotation rate. Angular frequency is the magnitude of the vector quantity angular velocity...
is the angular frequencyAngular frequencyIn physics, angular frequency ω is a scalar measure of rotation rate. Angular frequency is the magnitude of the vector quantity angular velocity...
in radianRadianRadian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius. The radian is the standard unit of angular measure, used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly a SI supplementary unit, but this category was abolished in 1995 and the radian is now considered a SI derived unit...
s per unit time, equal to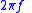 , where
, where 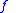 is the frequencyFrequencyFrequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
is the frequencyFrequencyFrequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
(hertzHertzThe hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
if group delay is measured in seconds).
- 2. In an optical fiberOptical fiberAn optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
, the transit timeTimeTime is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
required for optical powerPower (physics)In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
, traveling at a given modeTransverse modeA transverse mode of a beam of electromagnetic radiation is a particular electromagnetic field pattern of radiation measured in a plane perpendicular to the propagation direction of the beam...
's group velocityGroup velocityThe group velocity of a wave is the velocity with which the overall shape of the wave's amplitudes — known as the modulation or envelope of the wave — propagates through space....
, to travel a given distance.
- Note: For optical fiber dispersionDispersion (optics)In optics, dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency, or alternatively when the group velocity depends on the frequency.Media having such a property are termed dispersive media...
measurement purposes, the quantity of interest is group delayPropagation delayPropagation delay is a technical term that can have a different meaning depending on the context. It can relate to networking, electronics or physics...
per unit length, which is the reciprocal of the group velocity of a particular mode. The measured group delay of a signal through an optical fiber exhibits a wavelengthWavelengthIn physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
dependence due to the various dispersionDispersion (optics)In optics, dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency, or alternatively when the group velocity depends on the frequency.Media having such a property are termed dispersive media...
mechanisms present in the fiber.
It is often desirable for the group delay to be constant across all frequencies; otherwise there is temporal smearing of the signal. Because group delay is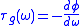 , as defined in (1), it therefore follows that a constant group delay can be achieved if the transfer functionTransfer functionA transfer function is a mathematical representation, in terms of spatial or temporal frequency, of the relation between the input and output of a linear time-invariant system. With optical imaging devices, for example, it is the Fourier transform of the point spread function i.e...
, as defined in (1), it therefore follows that a constant group delay can be achieved if the transfer functionTransfer functionA transfer function is a mathematical representation, in terms of spatial or temporal frequency, of the relation between the input and output of a linear time-invariant system. With optical imaging devices, for example, it is the Fourier transform of the point spread function i.e...
of the device or medium has a linearLinearIn mathematics, a linear map or function f is a function which satisfies the following two properties:* Additivity : f = f + f...
phase response (i.e.,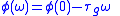 where the group delay
where the group delay 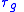 is a constant).
is a constant).
The degree of nonlinearity of the phase indicates the deviation of the group delay from a constant.
Group delay in audio
Group delay has some importance in the audio field and especially in the sound reproduction field. Many components of an audio reproduction chain, notably loudspeakers and multiway loudspeaker crossover networksAudio crossoverAudio crossovers are a class of electronic filter used in audio applications. Most individual loudspeaker drivers are incapable of covering the entire audio spectrum from low frequencies to high frequencies with acceptable relative volume and lack of distortion so most hi-fi speaker systems use a...
, introduce group delay in the audio signal. It is therefore important to know the threshold of audibility of group delay with respect to frequency, especially if the audio chain is supposed to provide high fidelityHigh fidelityHigh fidelity—or hi-fi—reproduction is a term used by home stereo listeners and home audio enthusiasts to refer to high-quality reproduction of sound or images, to distinguish it from the poorer quality sound produced by inexpensive audio equipment...
reproduction. The best thresholds of audibility table has been provided by .
Frequency Threshold 500 Hz HertzThe hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
3.2 ms MillisecondA millisecond is a thousandth of a second.10 milliseconds are called a centisecond....1 kHz 2 ms 2 kHz 1 ms 4 kHz 1.5 ms 8 kHz 2 ms
See also
- Audio system measurementsAudio system measurementsAudio system measurements are made for several purposes. Designers take measurements so that they can specify the performance of a piece of equipment. Maintenance engineers make them to ensure equipment is still working to specification, or to ensure that the cumulative defects of an audio path are...
- Bessel filterBessel filterIn electronics and signal processing, a Bessel filter is a type of linear filter with a maximally flat group delay . Bessel filters are often used in audio crossover systems...
- Eye patternEye patternIn telecommunication, an eye pattern, also known as an eye diagram, is an oscilloscope display in which a digital data signal from a receiver is repetitively sampled and applied to the vertical input, while the data rate is used to trigger the horizontal sweep...
- Group velocityGroup velocityThe group velocity of a wave is the velocity with which the overall shape of the wave's amplitudes — known as the modulation or envelope of the wave — propagates through space....
External links
-