Bessel filter
Encyclopedia
In electronics
and signal processing
, a Bessel filter is a type of linear filter
with a maximally flat group delay
(maximally linear phase response
). Bessel filters are often used in audio crossover
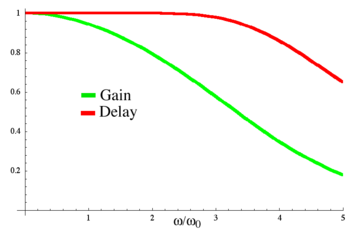
systems. Analog Bessel filters are characterized by almost constant group delay across the entire passband, thus preserving the wave shape of filtered signals in the passband.
The filter's name is a reference to Friedrich Bessel
, a German mathematician (1784–1846), who developed the mathematical theory on which the filter is based. The filters are also called Bessel–Thomson filters in recognition of W. E. Thomson, who worked out how to apply Bessel functions to filter design.
 A Bessel low-pass filter
A Bessel low-pass filter
is characterized by its transfer function
:

where is a reverse Bessel polynomial from which the filter gets its name and
is a reverse Bessel polynomial from which the filter gets its name and  is a frequency chosen to give the desired cut-off frequency. The filter has a low-frequency group delay of
is a frequency chosen to give the desired cut-off frequency. The filter has a low-frequency group delay of  .
.
whose denominator is a reverse Bessel polynomial, such as the following:





The reverse Bessel polynomials are given by:

where

, normalized to have unit group delay, is

The roots of the denominator polynomial, the filter's poles, include a real pole at , and a complex-conjugate pair
of poles at , plotted above. The numerator 15 is chosen to give a gain of 1 at DC
(at s = 0).
The gain is then

The phase is

The group delay
is

The Taylor series
expansion of the group delay is

Note that the two terms in ω2 and ω4 are zero, resulting in a very flat group delay at . This is the greatest number of terms that can be set to zero, since there are a total of four coefficients in the third order Bessel polynomial, requiring four equations in order to be defined. One equation specifies that the gain be unity at and a second specifies that the gain be zero at , leaving two equations to specify two terms in the series expansion to be zero. This is a general property of the group delay for a Bessel filter of order n: the first terms in the series expansion of the group delay will be zero, thus maximizing the flatness of the group delay at .
Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
and signal processing
Signal processing
Signal processing is an area of systems engineering, electrical engineering and applied mathematics that deals with operations on or analysis of signals, in either discrete or continuous time...
, a Bessel filter is a type of linear filter
Linear filter
Linear filters in the time domain process time-varying input signals to produce output signals, subject to the constraint of linearity.This results from systems composed solely of components classified as having a linear response....
with a maximally flat group delay
Group delay
Group delay is a measure of the time delay of the amplitude envelopes of the various sinusoidal components of a signal through a device under test, and is a function of frequency for each component...
(maximally linear phase response
Phase response
In signal processing and electrical engineering, phase response is the relationship between the phase of a sinusoidal input and the output signal passing through any device that accepts input and produces an output signal, such as an amplifier or a filter....
). Bessel filters are often used in audio crossover
Audio crossover
Audio crossovers are a class of electronic filter used in audio applications. Most individual loudspeaker drivers are incapable of covering the entire audio spectrum from low frequencies to high frequencies with acceptable relative volume and lack of distortion so most hi-fi speaker systems use a...
systems. Analog Bessel filters are characterized by almost constant group delay across the entire passband, thus preserving the wave shape of filtered signals in the passband.
The filter's name is a reference to Friedrich Bessel
Friedrich Bessel
-References:* John Frederick William Herschel, A brief notice of the life, researches, and discoveries of Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel, London: Barclay, 1847 -External links:...
, a German mathematician (1784–1846), who developed the mathematical theory on which the filter is based. The filters are also called Bessel–Thomson filters in recognition of W. E. Thomson, who worked out how to apply Bessel functions to filter design.
The transfer function

Low-pass filter
A low-pass filter is an electronic filter that passes low-frequency signals but attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The actual amount of attenuation for each frequency varies from filter to filter. It is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble cut filter...
is characterized by its transfer function
Transfer function
A transfer function is a mathematical representation, in terms of spatial or temporal frequency, of the relation between the input and output of a linear time-invariant system. With optical imaging devices, for example, it is the Fourier transform of the point spread function i.e...
:

where
 is a reverse Bessel polynomial from which the filter gets its name and
is a reverse Bessel polynomial from which the filter gets its name and  is a frequency chosen to give the desired cut-off frequency. The filter has a low-frequency group delay of
is a frequency chosen to give the desired cut-off frequency. The filter has a low-frequency group delay of  .
.Bessel polynomials
The transfer function of the Bessel filter is a rational functionRational function
In mathematics, a rational function is any function which can be written as the ratio of two polynomial functions. Neither the coefficients of the polynomials nor the values taken by the function are necessarily rational.-Definitions:...
whose denominator is a reverse Bessel polynomial, such as the following:





The reverse Bessel polynomials are given by:

where

Example
The transfer function for a third-order (three-pole) Bessel low-pass filterLow-pass filter
A low-pass filter is an electronic filter that passes low-frequency signals but attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The actual amount of attenuation for each frequency varies from filter to filter. It is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble cut filter...
, normalized to have unit group delay, is

The roots of the denominator polynomial, the filter's poles, include a real pole at , and a complex-conjugate pair
Complex conjugate
In mathematics, complex conjugates are a pair of complex numbers, both having the same real part, but with imaginary parts of equal magnitude and opposite signs...
of poles at , plotted above. The numerator 15 is chosen to give a gain of 1 at DC
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
(at s = 0).
The gain is then

The phase is

The group delay
Group delay
Group delay is a measure of the time delay of the amplitude envelopes of the various sinusoidal components of a signal through a device under test, and is a function of frequency for each component...
is

The Taylor series
Taylor series
In mathematics, a Taylor series is a representation of a function as an infinite sum of terms that are calculated from the values of the function's derivatives at a single point....
expansion of the group delay is

Note that the two terms in ω2 and ω4 are zero, resulting in a very flat group delay at . This is the greatest number of terms that can be set to zero, since there are a total of four coefficients in the third order Bessel polynomial, requiring four equations in order to be defined. One equation specifies that the gain be unity at and a second specifies that the gain be zero at , leaving two equations to specify two terms in the series expansion to be zero. This is a general property of the group delay for a Bessel filter of order n: the first terms in the series expansion of the group delay will be zero, thus maximizing the flatness of the group delay at .
See also
- Butterworth filterButterworth filterThe Butterworth filter is a type of signal processing filter designed to have as flat a frequency response as possible in the passband so that it is also termed a maximally flat magnitude filter...
- Comb filterComb filterIn signal processing, a comb filter adds a delayed version of a signal to itself, causing constructive and destructive interference. The frequency response of a comb filter consists of a series of regularly spaced spikes, giving the appearance of a comb....
- Chebyshev filterChebyshev filterChebyshev filters are analog or digital filters having a steeper roll-off and more passband ripple or stopband ripple than Butterworth filters...
- Elliptic filterElliptic filterAn elliptic filter is a signal processing filter with equalized ripple behavior in both the passband and the stopband...
- Bessel functionBessel functionIn mathematics, Bessel functions, first defined by the mathematician Daniel Bernoulli and generalized by Friedrich Bessel, are canonical solutions y of Bessel's differential equation:...
- Group delay and phase delayGroup delay and phase delayGroup delay is a measure of the time delay of the amplitude envelopes of the various sinusoidal components of a signal through a device under test, and is a function of frequency for each component...
External links
- http://www.filter-solutions.com/bessel.html
- http://www.rane.com/note147.html
- http://www.crbond.com/papers/bsf.pdf
- http://www-k.ext.ti.com/SRVS/Data/ti/KnowledgeBases/analog/document/faqs/bes.htm

