
French wine
Encyclopedia



France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, in quantities between 50 and 60 million hectolitres per year, or 7–8 billion bottles. France has the world's second-largest total vineyard area, behind Spain
Spanish wine
Spanish wines are wines produced in the southwestern European country of Spain. Located on the Iberian Peninsula, Spain has over 2.9 million acres planted—making it the most widely planted wine producing nation but it is the third largest producer of wine in the world, the largest...
, and is in the position of being the world's largest wine producer losing it once (in 2008) to Italy
Italian wine
Italian wine is wine produced in Italy, a country which is home to some of the oldest wine-producing regions in the world. Italy is the world's largest wine producer, responsible for approximately one-fifth of world wine production in 2005. Italian wine is exported largely around the world and has...
. French wine traces its history to the 6th century BC, with many of France's regions dating their wine-making history to Roman
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
times. The wines produced today range from expensive high-end wines sold internationally, to more modest wines usually only seen within France.
Two concepts central to higher end French wines are the notion of "terroir
Terroir
Terroir comes from the word terre "land". It was originally a French term in wine, coffee and tea used to denote the special characteristics that the geography, geology and climate of a certain place bestowed upon particular varieties...
", which links the style of the wines to the specific locations where the grapes are grown and the wine is made, and the Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée
Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée
Appellation d’origine contrôlée , which translates as "controlled designation of origin", is the French certification granted to certain French geographical indications for wines, cheeses, butters, and other agricultural products, all under the auspices of the government bureau Institut National...
(AOC) system. Appellation rules closely define which grape varieties and winemaking practices are approved for classification in each of France's several hundred geographically defined appellations, which can cover entire regions, individual villages or even specific vineyards.
France is the source of many grape varieties (such as Cabernet Sauvignon
Cabernet Sauvignon
Cabernet Sauvignon is one of the world's most widely recognized red wine grape varieties. It is grown in nearly every major wine producing country among a diverse spectrum of climates from Canada's Okanagan Valley to Lebanon's Beqaa Valley...
, Chardonnay
Chardonnay
Chardonnay is a green-skinned grape variety used to make white wine. It is originated from the Burgundy wine region of eastern France but is now grown wherever wine is produced, from England to New Zealand...
, Pinot Noir
Pinot Noir
Pinot noir is a black wine grape variety of the species Vitis vinifera. The name may also refer to wines created predominantly from Pinot noir grapes...
, Sauvignon Blanc
Sauvignon blanc
Sauvignon Blanc is a green-skinned grape variety which originates from the Bordeaux region of France. The grape most likely gets its name from the French word sauvage and blanc due to its early origins as an indigenous grape in South West France., a possible descendant of savagnin...
, and Syrah) that are now planted throughout the world, as well as wine-making practices and styles of wine that have been adopted in other producing countries. Although some producers have benefited in recent years from rising prices and increased demand for some of the prestige wines from Burgundy
Burgundy wine
Burgundy wine is wine made in the Burgundy region in eastern France, in the valleys and slopes west of the Saône River, a tributary of the Rhône. The most famous wines produced here - those commonly referred to as "Burgundies" - are red wines made from Pinot Noir grapes or white wines made from...
and Bordeaux
Bordeaux wine
A Bordeaux wine is any wine produced in the Bordeaux region of France. Average vintages produce over 700 million bottles of Bordeaux wine, ranging from large quantities of everyday table wine, to some of the most expensive and prestigious wines in the world...
, the French wine industry as a whole has been influenced by a decline in domestic consumption as well as growing competition from both the New World
New World wine
New World wines are those wines produced outside the traditional wine-growing areas of Europe, in particular from Argentina, Australia, Canada, Chile, New Zealand, South Africa and the United States.-Early wines in the Americas:...
and other European countries.
History
French wine originated in the 6th century BC, with the colonization of Southern GaulGaul
Gaul was a region of Western Europe during the Iron Age and Roman era, encompassing present day France, Luxembourg and Belgium, most of Switzerland, the western part of Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the left bank of the Rhine. The Gauls were the speakers of...
by Greek
Greeks
The Greeks, also known as the Hellenes , are a nation and ethnic group native to Greece, Cyprus and neighboring regions. They also form a significant diaspora, with Greek communities established around the world....
settlers. Viticulture
Viticulture
Viticulture is the science, production and study of grapes which deals with the series of events that occur in the vineyard. When the grapes are used for winemaking, it is also known as viniculture...
soon flourished with the founding of the Greek colony of Marseille
Marseille
Marseille , known in antiquity as Massalia , is the second largest city in France, after Paris, with a population of 852,395 within its administrative limits on a land area of . The urban area of Marseille extends beyond the city limits with a population of over 1,420,000 on an area of...
. The Roman Empire licensed regions in the south to produce wines. St. Martin of Tours (316–397) was actively engaged in both spreading Christianity and planting vineyard
Vineyard
A vineyard is a plantation of grape-bearing vines, grown mainly for winemaking, but also raisins, table grapes and non-alcoholic grape juice...
s. During the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
, monks maintained vineyards and, more importantly, conserved wine-making knowledge and skills during that often turbulent period. Monasteries had the resources, security, and motivation to produce a steady supply of wine both for celebrating mass and generating income. During this time, the best vineyards were owned by the monasteries and their wine was considered to be superior. Over time the nobility developed extensive vineyards. However, the French Revolution
French Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
led to the confiscation of many of the vineyards owned by the Church and others.
The advance of the French wine industry stopped abruptly as first Mildew
Mildew
Mildew refers to certain kinds of molds or fungi.In Old English, it meant honeydew , and later came to mean mildew in the modern sense of mold or fungus....
and then Phylloxera
Phylloxera
Grape phylloxera ; originally described in France as Phylloxera vastatrix; equated to the previously described Daktulosphaira vitifoliae, Phylloxera vitifoliae; commonly just called phylloxera is a pest of commercial grapevines worldwide, originally native to eastern North America...
spread throughout the country, indeed across all of Europe, leaving vineyards desolate. Then came an economic downturn in Europe followed by two world wars, and the French wine industry didn't fully recover for decades. Meanwhile competition had arrived and threatened the treasured French "brands" such as Champagne and Bordeaux. This resulted in the establishment in 1935 of the Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée
Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée
Appellation d’origine contrôlée , which translates as "controlled designation of origin", is the French certification granted to certain French geographical indications for wines, cheeses, butters, and other agricultural products, all under the auspices of the government bureau Institut National...
to protect French interests. Large investments, the economic upturn following World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
and a new generation of Vignerons yielded results in the 1970s and the following decades, creating the modern French wines we know today.
Quality levels and appellation system
In 1935 numerous laws were passed to control the quality of French wine. They established the Appellation d'Origine ContrôléeAppellation d'Origine Contrôlée
Appellation d’origine contrôlée , which translates as "controlled designation of origin", is the French certification granted to certain French geographical indications for wines, cheeses, butters, and other agricultural products, all under the auspices of the government bureau Institut National...
system, which is governed by a powerful oversight board (Institut National des Appellations d'Origine
Institut National des Appellations d'Origine
The Institut National des Appellations d'Origine is the French organization charged with regulating French agricultural products with Protected Designations of Origin . Controlled by the French government, it forms part of the Ministry of Agriculture...
, INAO). Consequently, France has one of the oldest systems for protected designation of origin
Protected designation of origin
Protected Geographical Status is a legal framework defined in European Union law to protect the names of regional foods. Protected Designation of Origin , Protected Geographical Indication and Traditional Speciality Guaranteed are distinct regimes of geographical indications within the framework...
for wine in the world, and strict laws concerning winemaking and production.
Many other European systems are modelled after it. The word "appellation
Appellation
An appellation is a legally defined and protected geographical indication used to identify where the grapes for a wine were grown; other types of food often have appellations as well...
" has been put to use by other countries, sometimes in a much looser meaning. As European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
wine laws have been modelled after those of the French, this trend is likely to continue with further EU expansion.
French law divides wine into four categories, two falling under the European Union's Table Wine category and two falling under the EU's Quality Wine Produced in a Specific Region (QWPSR) designation. The categories and their shares of the total French production for the 2005 vintage, excluding wine destined for Cognac, Armagnac and other brandies, were:
Table wine:
- Vin de TableTable wineTable wine is a wine term with two different meanings: a wine style; and a quality level within wine classification.In the United States, table wine primarily designates a wine style - ordinary wine which is neither fortified nor sparkling....
(11.7%) – Carries with it only the producer and the designation that it is from France. - Vin de PaysVin de paysVin de pays is a French term meaning "country wine". Vins de pays are a step in the French wine classification which is above the table wine classification, but below the VDQS and Appellation d'origine contrôlée classifications...
(33.9%) – Carries with it a specific region within France (for example Vin de Pays d'Oc from Languedoc-RoussillonLanguedoc-RoussillonLanguedoc-Roussillon is one of the 27 regions of France. It comprises five departments, and borders the other French regions of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur, Rhône-Alpes, Auvergne, Midi-Pyrénées on the one side, and Spain, Andorra and the Mediterranean sea on the other side.-Geography:The region is...
or Vin de Pays de Côtes de GascogneCôtes de GascogneCôtes de Gascogne is a wine-growing district in Gascony producing principally white wine. It is mainly located in the département of the Gers in the French region Midi-Pyrénées, and it belongs to the wine region South West France. The designation Côtes the Gascogne is used for a Vin de Pays ...
from GasconyGasconyGascony is an area of southwest France that was part of the "Province of Guyenne and Gascony" prior to the French Revolution. The region is vaguely defined and the distinction between Guyenne and Gascony is unclear; sometimes they are considered to overlap, and sometimes Gascony is considered a...
), and subject to less restrictive regulations than AOC wines. For instance, it allows producers to distinguish wines that are made using grape varieties or procedures other than those required by the AOC rules, without having to use the simple and commercially non-viable table wine classification. In order to maintain a distinction from Vin de Table, the producers have to submit the wine for analysis and tasting, and the wines have to be made from certain varieties or blends.
QWPSR:
- Vin Délimité de Qualité Supérieure (VDQS, 0.9%) – Less strict than AOC, usually used for smaller areas or as a "waiting room" for potential AOCs. This category will be abolished at the end of 2011.
- Appellation d'Origine ContrôléeAppellation d'Origine ContrôléeAppellation d’origine contrôlée , which translates as "controlled designation of origin", is the French certification granted to certain French geographical indications for wines, cheeses, butters, and other agricultural products, all under the auspices of the government bureau Institut National...
(AOC, 53.4%) – Wine from a particular area with many other restrictions, including grape varieties and winemaking methods.
The total French production for the 2005 vintage was 43.9 million hl (plus an additional 9.4 million hl destined for various brandies), of which 28.3% was white and 71.7% was red or rosé. The proportion of white wine is slightly higher for the higher categories, with 34.3% of the AOC wine being white.
In years with less favourable vintage conditions than 2005, the proportion of AOC wine tends to be a little lower. The proportion of Vin de table has decreased considerably over the last decades, while the proportion of AOC has increased somewhat and Vin de Pays has increased considerably.
In 2005 there were 472 different wine AOCs in France.
Reforms
The wine classification system of France has been under overhaul since 2006, with a new system to be fully introduced by 2012. The new system consists of three categories rather than four, since there will be no category corresponding to VDQS from 2012. The new categories are:- Vin de FranceVin de FranceVin de France is a designation for table wine from France that has been in use since 2010, when it started to replace the former Vin de Table category. Vins de France may indicate grape variety and vintage on the label, but are not labelled by region or appellation, only as coming from France...
, a table wine category basically replacing Vin de Table, but allowing grape variety and vintage to be indicated on the label. - Indication Géographique Protégée (IGP), an intermediate category basically replacing Vin de Pays.
- Appellation d'Origine Protégée (AOP), the highest category basically replacing AOC wines.
The largest changes will be in the Vin de France category, and to VDQS wines, which either need to qualify as AOP wines or be downgraded to an IGP category. For the former AOC wines, the move to AOP will only mean minor changes to the terminology of the label, while the actual names of the appellations themselves will remain unchanged.
While no new wines will be marketed under the old designations from 2012, bottles already in the distribution chain will not be relabelled.
Wine styles, grape varieties and terroir
All common styles of wine – red, rosé, white (dry, semi-sweet and sweet), sparklingSparkling wine
Sparkling wine is a wine with significant levels of carbon dioxide in it making it fizzy. The carbon dioxide may result from natural fermentation, either in a bottle, as with the méthode champenoise, in a large tank designed to withstand the pressures involved , or as a result of carbon dioxide...
and fortified
Fortified wine
Fortified wine is wine to which a distilled beverage has been added. Fortified wine is distinguished from spirits made from wine in that spirits are produced by means of distillation, while fortified wine is simply wine that has had a spirit added to it...
– are produced in France. In most of these styles, the French production ranges from cheap and simple versions to some of the world's most famous and expensive examples. An exception is French fortified wines, which tend to be relatively unknown outside France.
In many respects, French wines have more of a regional than a national identity, as evidenced by different grape varieties, production methods and different classification systems in the various regions. Quality levels and prices vary enormously, and some wines are made for immediate consumption while other are meant for long-time cellaring.
If there is one thing that most French wines have in common, it is that most styles have developed as wines meant to accompany food, be it a quick baguette
Baguette
A baguette is "a long thin loaf of French bread" that is commonly made from basic lean dough...
, a simple bistro
Bistro
A bistro, sometimes spelled bistrot, is, in its original Parisian incarnation, a small restaurant serving moderately priced simple meals in a modest setting. Bistros are defined mostly by the foods they serve. Home cooking with robust earthy dishes, and slow-cooked foods like cassoulet are typical...
meal, or a full-fledged multi-course menu. Since the French tradition is to serve wine with food, wines have seldom been developed or styled as "bar wines" for drinking on their own, or to impress in tastings when young.
Grape varieties
Numerous grape varieties are cultivated in France, including both internationally well-known and obscure local varieties. In fact, most of the so-called "international varieties" are of French origin, or became known and spread because of their cultivation in France. Since French appellation rules generally restrict wines from each region, district or appellation to a small number of allowed grape varieties, there are in principle no varieties that are commonly planted throughout all of France.Most varieties of grape are primarily associated with a certain region, such as Cabernet Sauvignon in Bordeaux and Syrah in Rhône, although there are some varieties that are found in two or more regions, such as Chardonnay in Bourgogne (including Chablis) and Champagne, and Sauvignon Blanc in Loire and Bordeaux. As an example of the rules, although climatic conditions would appear to be favourable, no Cabernet Sauvignon wines are produced in Rhône, Riesling wines in Loire, or Chardonnay wines in Bordeaux. (If such wines were produced, they would have to be declassified to Vin de Pays or French table wine. They would not be allowed to display any appellation name or even region of origin.)
Traditionally, many French wines have been blended from several grape varieties. Varietal
Varietal
"Varietal" describes wines made primarily from a single named grape variety, and which typically displays the name of that variety on the wine label. Examples of grape varieties commonly used in varietal wines are Cabernet Sauvignon, Chardonnay and Merlot...
white wines have been, and are still, more common than varietal red wines.
At the 2007 harvest, the most common grape varieties were the following:
| Common grape varieties in France (2007 situation, all varieties over 1 000 ha) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variety | Colour | Area (%) | Area (hectares) |
| 1. Merlot Merlot Merlot is a darkly blue-coloured wine grape, that is used as both a blending grape and for varietal wines. The name Merlot is thought to derive from the Old French word for young blackbird, merlot, a diminutive of merle, the blackbird , probably from the color of the grape. Merlot-based wines... |
red | 13.6% | 116 715 |
| 2. Grenache Grenache Grenache is one of the most widely planted red wine grape varieties in the world. It ripens late, so it needs hot, dry conditions such as those found in Spain, the south of France, and California's San Joaquin Valley. It is generally spicy, berry-flavored and soft on the palate with a relatively... |
red | 11.3% | 97 171 |
| 3. Ugni Blanc | white | 9.7% | 83 173 |
| 4. Syrah | red | 8.1% | 69 891 |
| 5. Carignan | red | 6.9% | 59 210 |
| 6. Cabernet Sauvignon Cabernet Sauvignon Cabernet Sauvignon is one of the world's most widely recognized red wine grape varieties. It is grown in nearly every major wine producing country among a diverse spectrum of climates from Canada's Okanagan Valley to Lebanon's Beqaa Valley... |
red | 6.7% | 57 913 |
| 7. Chardonnay Chardonnay Chardonnay is a green-skinned grape variety used to make white wine. It is originated from the Burgundy wine region of eastern France but is now grown wherever wine is produced, from England to New Zealand... |
white | 5.1% | 43 887 |
| 8. Cabernet Franc Cabernet Franc Cabernet Franc is one of the major black grape varieties worldwide. It is principally grown for blending with Cabernet Sauvignon and Merlot in the Bordeaux style, but can also be vinified alone - as in the Loire's Chinon... |
red | 4.4% | 37 508 |
| 9. Gamay Gamay Gamay is a purple-colored grape variety used to make red wines, most notably grown in Beaujolais and in the Loire Valley around Tours. Its full name is Gamay Noir à Jus Blanc. It is a very old cultivar, mentioned as long ago as the 15th century... |
red | 3.7% | 31 771 |
| 10. Pinot Noir Pinot Noir Pinot noir is a black wine grape variety of the species Vitis vinifera. The name may also refer to wines created predominantly from Pinot noir grapes... |
red | 3.4% | 29 576 |
| 11. Sauvignon Blanc Sauvignon blanc Sauvignon Blanc is a green-skinned grape variety which originates from the Bordeaux region of France. The grape most likely gets its name from the French word sauvage and blanc due to its early origins as an indigenous grape in South West France., a possible descendant of savagnin... |
white | 3.0% | 26 062 |
| 12. Cinsaut Cinsaut Cinsaut or Cinsault is a red wine grape, whose heat tolerance and productivity make it important in Languedoc-Roussillon and the former French colonies of Algeria and Morocco... |
red | 2.6% | 22 239 |
| 13. Melon de Bourgogne Melon de Bourgogne Melon de Bourgogne or Melon is a variety of white grape grown primarily in the Loire Valley region of France. It is also grown in North America. It is best known through its use in the white wine Muscadet.... |
white | 1.4% | 12 483 |
| 14. Sémillon Sémillon Sémillon is a golden-skinned grape used to make dry and sweet white wines, most notably in France and Australia.-History:The origin of the Sémillon grape is hard to determine. It is known that it first arrived in Australia in the early 19th century and by the 1820s the grape covered over 90 percent... |
white | 1.4% | 11 864 |
| 15. Pinot Meunier Pinot meunier Pinot Meunier, , also known as Meunier or Black Riesling, is a variety of black wine grape most noted for being one of the three main grapes used in the production of champagne... |
red | 1.3% | 11 335 |
| 16. Chenin Blanc Chenin Blanc Chenin blanc , is a white wine grape variety from the Loire valley of France. Its high acidity means it can be used to make everything from sparkling wines to well-balanced dessert wines, although it can produce very bland, neutral wines if the vine's natural vigor is not controlled... |
white | 1.1% | 9 756 |
| 17. Mourvèdre Mourvèdre Mourvèdre , Mataró or Monastrell is wine grape variety used to make both strong, dark red wines and rosés. It is an international variety grown in many regions around the world.... |
red | 1.1% | 9 494 |
| 18. Colombard Colombard Colombard is an early fruiting white variety of wine grape, better known as French Colombard in North America. It is possibly the offspring of Gouais Blanc and Chenin Blanc.... |
white | 0.9% | 7 710 |
| 19. Muscat Blanc à Petits Grains Muscat Blanc à Petits Grains Muscat Blanc à Petits Grains is a white wine grape that is a member of the Muscat family of Vitis vinifera. Its name comes from its characteristic small berry size and tight clusters... |
white | 0.9% | 7 634 |
| 20. Malbec Malbec Malbec is a purple grape variety used in making red wine. The grapes tend to have an inky dark color and robust tannins, and are long known as one of the six grapes allowed in the blend of red Bordeaux wine. The French plantations of Malbec are now found primarily in Cahors in the South West... |
red | 0.8% | 6 291 |
| 21. Alicante Bouschet Alicante Bouschet Alicante Bouschet or Alicante Henri Bouschet is a wine grape variety that has been widely cultivated since 1866. It is a cross of Petit Bouschet and Grenache. Alicante is a teinturier, a grape with red flesh. It is one of the few teinturier grapes that belong to the Vitis vinifera species... |
red | 0.7% | 5 680 |
| 22. Grenache Blanc Grenache Blanc Grenache blanc is a variety of white wine grape that is related to the red grape Grenache. It is mostly found in Rhône wine blends and in northeast Spain. Its wines are characterized by high alcohol and low acidity, with citrus and or herbaceous notes. Its vigor can lead to overproduction and... |
white | 0.6% | 5 097 |
| 23. Viognier Viognier Viognier is a white wine grape. It is the only permitted grape for the French wine Condrieu in the Rhone valley.-History:The origin of the Viognier grape is unknown. Viognier is presumed to be an ancient grape, possibly originating in Dalmatia and then brought to Rhône by the Romans. One legend... |
white | 0.5% | 4 111 |
| 24. Muscat de Hambourg | red | 0.4% | 3 605 |
| 25. Riesling Riesling Riesling is a white grape variety which originated in the Rhine region of Germany. Riesling is an aromatic grape variety displaying flowery, almost perfumed, aromas as well as high acidity. It is used to make dry, semi-sweet, sweet and sparkling white wines. Riesling wines are usually varietally... |
white | 0.4% | 3 480 |
| 26. Vermentino Vermentino Vermentino is a late-ripening white grape variety, primarily found in Italian wine. It is widely planted in Sardinia, in Liguria primarily under the name Pigato, to some extent in Corsica, in Piedmont under the name Favorita, and in increasing amounts in Languedoc-Roussillon. The leaves are dark... |
white | 0.4% | 3 453 |
| 27. Aramon Aramon (grape) Aramon or Aramon Noir is a variety of red wine grape grown primarily in Languedoc-Roussillon in southern France. Between the late 19th century and the 1960s, it was France's most grown grape variety, but plantings of Aramon have been in continuous decline since the mid-20th century... |
red | 0.4% | 3 304 |
| 28. Gewurztraminer Gewürztraminer Gewürztraminer is an aromatic wine grape variety that performs best in cooler climates. It is sometimes referred to colloquially as Gewürz, and in French it is written '... |
pink | 0.4% | 3 040 |
| 29. Tannat Tannat Tannat is a red wine grape, historically grown in South West France in the Madiran AOC and is now one of the most prominent grapes in Uruguay, where it is considered the "national grape". It is also grown in Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Peru, and in Italy's Puglia region where it is used as a... |
red | 0.3% | 3 001 |
| 30. Gros Manseng Gros Manseng Gros Manseng is a white wine grape variety that is grown primarily in South West France, and is part of the Manseng family. It produces dry wines in the Jurançon and Béarn regions of Southwest France... |
white | 0.3% | 2 877 |
| 31. Macabeu | white | 0.3% | 2 778 |
| 32. Muscat d'Alexandrie | white | 0.3% | 2 679 |
| 33. Pinot Gris Pinot Gris Pinot gris is a white wine grape variety of the species Vitis vinifera. Thought to be a mutant clone of the Pinot noir grape, it normally has a grayish-blue fruit, accounting for its name but the grape can have a brownish pink to black and even white appearance... |
grey | 0.3% | 2 582 |
| 34. Clairette | white | 0.3% | 2 505 |
| 35. Caladoc Caladoc Caladoc is a red French wine grape variety planted primarily in the southern wine regions such as the Languedoc. The grape is a crossing of Grenache and Malbec created by Paul Truel in 1958 at Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique .... |
red | 0.3% | 2 449 |
| 36. Grolleau Grolleau (grape) Grolleau or Grolleau Noir is a red French wine grape variety grown primarily in the Loire Valley of France. The name is derived from the French word grolle, meaning "crow" and is said to reflect the deep black berries of the Grolleau vine... |
red | 0.3% | 2 363 |
| 37. Auxerrois Blanc Auxerrois Blanc Auxerrois Blanc or Auxerrois Blanc de Laquenexy is a white wine grape that is important in Alsace, and is also grown in Germany and Luxembourg. It is a full sibling of Chardonnay that is often blended with the similar Pinot Blanc.-History:... |
white | 0.3% | 2 330 |
| 38. Marselan Marselan Marselan is a French wine grape that is a cross between Cabernet Sauvignon and Grenache. It was first bred in 1961 near the French town of Marseillan. The vine is grown mostly in the Languedoc region with some plantings on Northern Coast of California. The grape produces a medium body red wine.... |
red | 0.3% | 2 255 |
| 39. Mauzac Mauzac (grape) Mauzac or Mauzac Blanc a white variety of grape used for wine, of the species Vitis vinifera. It is mainly grown in the Gaillac and Limoux regions in the southwest of France. Total French plantations of Mauzac stood at in the year 2000.... |
white | 0.2% | 2 077 |
| 40. Aligoté Aligoté Aligoté is a white grape used to make dry white wines in the Burgundy region of France, and which also has significant plantings in much of Eastern Europe including Romania, Russia, Ukraine, Moldova and Bulgaria. With , it was the 22nd most planted vine variety in the world in 2004... |
white | 0.2% | 1 946 |
| 41. Folle Blanche Folle Blanche Folle Blanche was the traditional grape variety of the Cognac and Armagnac regions of France. It is also known as Picpoule as well as Gros Plant and Enrageat Blanc... |
white | 0.2% | 1 848 |
| 42. Grenache Gris | grey | 0.2% | 1 756 |
| 43. Chasselas Chasselas Chasselas or Chasselas Blanc is a wine grape variety grown in Switzerland, France, Germany, Portugal, Baja Norte, Mexico, Hungary and New Zealand.Theories of its origin vary. Pierre Galet believes it is a native Swiss variety.... |
white | 0.2% | 1 676 |
| 44. Nielluccio Nielluccio Nielluccio is a red French wine grape variety that is widely planted on Corsica. It is the principal grape variety used in the production of the Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée AOC red wine Patrimonio, where it must by law make up 95% of the blend. An early budding vine, Nielluccio produces wines... |
red | 0.2% | 1 647 |
| 45. Fer Fer Fer is a red French wine grape variety that is grown primarily in South West France and is most notable for its role in the Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée wines of Gaillac, Marcillac and Béarn but can also be found as minor component in the wines of Madiran, Cabardès and Bergerac... |
red | 0.2% | 1 634 |
| 46. Muscadelle Muscadelle Muscadelle is a white wine grape variety. It has a simple aroma of grape juice and raisins like grapes of the Muscat family of grapes, but it is unrelated.... |
white | 0.2% | 1 618 |
| 47. Terret Blanc | white | 0.2% | 1 586 |
| 48. Sylvaner | white | 0.2% | 1 447 |
| 49. Piquepoul Blanc | white | 0.2% | 1 426 |
| 50. Villard Noir Villard Noir Villard grapes are French wine hybrid grape created by French horticulturalist Bertille Seyve and his father-in-law Victor Villard . They include the dark skin Villard noir and the white-wine variety Villard blanc with both being members of the Seyve-Villard grape family... |
red | 0.2% | 1 399 |
| 51. Marsanne | white | 0.2% | 1 326 |
| 52. Négrette Négrette Négrette is a dark red wine grape grown primarily in South West France in the region between Albi and Toulouse. It is a direct descendant of Mavro rootstock, a grape variety cultivated extensively on the island of Cyprus.-Wine regions:... |
red | 0.2% | 1 319 |
| 53. Roussanne Roussanne Roussanne is a white wine grape grown originally in the Rhône wine region in France, where it is often blended with Marsanne. It is the only other white variety, besides Marsanne, allowed in the northern Rhône appellations of Crozes-Hermitage AOC, Hermitage AOC and Saint-Joseph AOC... |
white | 0.2% | 1 307 |
| 54. Pinot Blanc Pinot Blanc Pinot blanc is a white wine grape. It is a point genetic mutation of Pinot noir. Pinot noir is genetically unstable and will occasionally experience a point mutation in which a vine bears all black fruit except for one cane which produced white fruit.... |
white | 0.2% | 1 304 |
| 55. Plantet Plantet Plantet is a red wine grape variety that was one of the hybrid grape created by French physician and grape breeder Albert Seibel. While the exact parentage of the grape is unknown, the most popular theories has it as a cross of two Seibel grapes, Seibel 867 x Seibel 2524 with another theory... |
white | 0.1% | 1 170 |
| 56. Jacquère Jacquère Jacquère is a variety of white grape found primarily in the Savoy wine region of France. It is a high-yielding vine variety which is used to produce lightly scented, rather neutral dry white wine, such as Vin de Savoie. Jacquère is the grape used in Apremont wines and is the usual wine paired with... |
white | 0.1% | 1 052 |
| All white varieties | 30.1% | 259 130 | |
| All red, pink and grey varieties | 69.9% | 601 945 | |
| Grand total | 100.0% | 861 075 | |
Terroir

The concept of Terroir, which refers to the unique combination of natural factors associated with any particular vineyard
Vineyard
A vineyard is a plantation of grape-bearing vines, grown mainly for winemaking, but also raisins, table grapes and non-alcoholic grape juice...
, is important to French vignerons. It includes such factors as soil
Soil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
, underlying rock, altitude, slope
Slope
In mathematics, the slope or gradient of a line describes its steepness, incline, or grade. A higher slope value indicates a steeper incline....
of hill or terrain, orientation toward the sun
Aspect (geography)
In physical geography, aspect generally refers to the horizontal direction to which a mountain slope faces. For example, a slope on the eastern edge of the Rockies toward the Great Plains is described as having an easterly aspect...
, and microclimate (typical rain, winds, humidity, temperature variations, etc.). Even in the same area, no two vineyards have exactly the same terroir, thus being the base of the Appellation d'origine contrôlée
Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée
Appellation d’origine contrôlée , which translates as "controlled designation of origin", is the French certification granted to certain French geographical indications for wines, cheeses, butters, and other agricultural products, all under the auspices of the government bureau Institut National...
(AOC) system that has been model for appellation
Appellation
An appellation is a legally defined and protected geographical indication used to identify where the grapes for a wine were grown; other types of food often have appellations as well...
and wine laws across the globe. In other words: when the same grape variety is planted in different regions, it can produce wines that are significantly different from each other. In France the concept of terroir manifests itself most extremely in the Burgundy region.
The amount of influence and the scope that falls under the description of terroir has been a controversial topic in the wine industry.
Labelling practices

Alsace wine
Alsace wine or Alsatian wine is produced in the Alsace region in France and is primarily white. These wines, which for historical reasons have a strong Germanic influence, are produced under three different Appellations d'Origine Contrôlées : Alsace AOC for white, rosé and red wines, Alsace Grand...
, France had no tradition of labelling wines with details of the grape varieties used. Since New World wines made the names of individual grape varieties familiar to international consumers in the late 20th century, more French wineries started to use varietal labelling. In general, varietal labelling is most common for the Vin de Pays category, although some AOC wines now also display varietal names. For most AOC wines, if grape varieties are mentioned, they will be in small print on a back label.
Labels will also indicate where the wine was bottled, which can be an indication as to the quality level of the wine, and whether it was bottled by a single producer, or more anonymously and in larger quantities:
- "Mis en bouteille ..."
- "... au château, au domaine, à la propriété": these have a similar meaning, and indicate the wine was "estate bottled", on the same property on which it was grown or at a cooperativeWinemaking cooperativeA winemaking cooperative is an agricultural cooperative which is involved in winemaking, and which in similarity to other cooperatives is owned by its members...
(within the boundary of the appellation) of which that property is a member. - "... par ..." the wine was bottled by the concern whose name follows. This may be the producing vineyard or it may not.
- "... dans la région de production": the wine was not bottled at the vineyard but by a larger business at its warehouse; this warehouse was within the same winemaking region of France as the appellation, but not necessarily within the boundary of the appellation itself. If a chateau or domaine is named, it may well not exist as a real vineyard, and the wine may be an assemblage from the grapes or the wines of several producers.
- "... dans nos chais, dans nos caves": the wine was bottled by the business named on the label.
- "... au château, au domaine, à la propriété": these have a similar meaning, and indicate the wine was "estate bottled", on the same property on which it was grown or at a cooperative
- "Vigneron indépendantVignerons indépendants de FranceThe Vignerons indépendants de France is a viticultural trade association based in Paris that promotes and assists small and independent winemakers within France, similar to the British Society of Independent Brewers. Members may use the association's logo on their products...
" is a special mark adopted by some independent wine-makers, to distinguish them from larger corporate winemaking operations and symbolize a return to the basics of the craft of wine-making. Bottles from these independent makers carry a special logo usually printed on the foil cap covering the cork.
If varietal names are displayed, common EU rules apply:
- If a single varietal name is used, the wine must be made from a minimum of 85% of this variety.
- If two or more varietal names are used, only the displayed varieties are allowed.
- If two or more varietal names are used, they must generally appear in descending order.
Wine regions of France
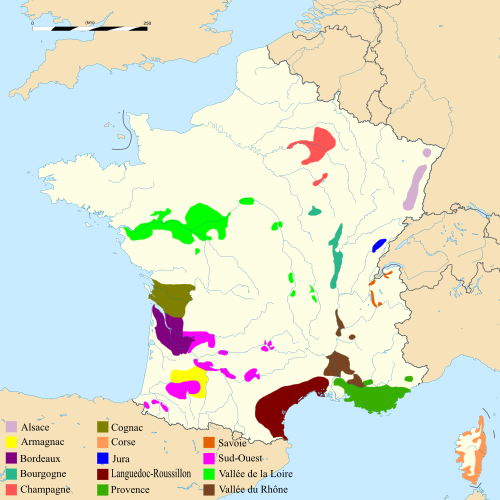
Alsace
AlsaceAlsace wine
Alsace wine or Alsatian wine is produced in the Alsace region in France and is primarily white. These wines, which for historical reasons have a strong Germanic influence, are produced under three different Appellations d'Origine Contrôlées : Alsace AOC for white, rosé and red wines, Alsace Grand...
is primarily a white-wine region, though some red, rosé, sparkling and sweet wines are also produced. It is situated in eastern France on the river Rhine and borders Germany, a country with which it shares many grape varieties as well as a long tradition of varietal labelling. Grapes grown in Alsace include Riesling
Riesling
Riesling is a white grape variety which originated in the Rhine region of Germany. Riesling is an aromatic grape variety displaying flowery, almost perfumed, aromas as well as high acidity. It is used to make dry, semi-sweet, sweet and sparkling white wines. Riesling wines are usually varietally...
, Gewurztraminer
Gewürztraminer
Gewürztraminer is an aromatic wine grape variety that performs best in cooler climates. It is sometimes referred to colloquially as Gewürz, and in French it is written '...
, Pinot Gris
Pinot Gris
Pinot gris is a white wine grape variety of the species Vitis vinifera. Thought to be a mutant clone of the Pinot noir grape, it normally has a grayish-blue fruit, accounting for its name but the grape can have a brownish pink to black and even white appearance...
, Pinot Blanc
Pinot Blanc
Pinot blanc is a white wine grape. It is a point genetic mutation of Pinot noir. Pinot noir is genetically unstable and will occasionally experience a point mutation in which a vine bears all black fruit except for one cane which produced white fruit....
, Pinot Noir
Pinot Noir
Pinot noir is a black wine grape variety of the species Vitis vinifera. The name may also refer to wines created predominantly from Pinot noir grapes...
, and Muscat
Muscat (grape and wine)
The Muscat variety of grapes of the species Vitis vinifera is widely grown for wine, raisins and table grapes. Their color ranges from white to near black. Muscat almost always has a pronounced sweet floral aroma. Muscat grapes are grown around the world...
.
Bordeaux
BordeauxBordeaux wine
A Bordeaux wine is any wine produced in the Bordeaux region of France. Average vintages produce over 700 million bottles of Bordeaux wine, ranging from large quantities of everyday table wine, to some of the most expensive and prestigious wines in the world...
is a large region on the Atlantic coast, which has a long history of exporting its wines overseas. This is primarily a red wine region, famous for the wines Château Lafite-Rothschild
Château Lafite-Rothschild
Château Lafite Rothschild is a wine estate in France, owned by members of the Rothschild family since the 19th century. The name Lafite comes from the Gascon term "la hite" meaning "small hill"....
, Château Latour
Château Latour
Château Latour is a French wine estate, rated as a First Growth under the 1855 Bordeaux Classification. Latour lies at the very southeastern tip of the commune of Pauillac in the Médoc region to the north-west of Bordeaux, at its border with Saint-Julien, and only a few hundred metres from the...
, Château Mouton-Rothschild, Château Margaux
Château Margaux
Château Margaux, archaically La Mothe de Margaux, is a wine estate of Bordeaux wine, and was one of four wines to achieve Premier cru status in the Bordeaux Classification of 1855. The estate's best wines are very expensive...
and Château Haut-Brion
Château Haut-Brion
Château Haut-Brion is a French wine, rated a Premier Cru Classé , produced in the Gironde region. It differs from the other wines on the list in its geographic location in the north of the wine-growing region of Graves...
from the Médoc
Médoc
The Médoc is a region of France, well known as a wine growing region, located in the département of Gironde, on the left bank of the Gironde estuary, north of Bordeaux. Its name comes from Medullicus, or "country of the Medulli", the local Celtic tribe...
sub-region; Château Cheval Blanc
Château Cheval Blanc
Château Cheval Blanc , is a wine producer in Saint-Émilion in the Bordeaux wine region of France. Its wine is one of only two to receive the highest rank of Premier Grand Cru Classé status in the Classification of Saint-Émilion wine of 1955, along with Château Ausone.The estate's second wine is...
and Château Ausone
Château Ausone
Château Ausone is a Bordeaux wine from Saint-Émilion appellation, one of only two wines, along with Château Cheval Blanc, to be ranked Premier Grand Cru Classé in the Classification of Saint-Émilion wine...
in Saint-Émilion
Saint-Émilion AOC
Saint-Émilion is an Appellation d'origine contrôlée for wine in the Bordeaux wine region of France, where it is situated in the Libourne subregion on the right bank of the Dordogne...
; and Château Pétrus
Château Pétrus
Pétrus is a Bordeaux wine estate located in the Pomerol appellation near its eastern border to Saint-Émilion. An estate of limited size, it produces a limited production red wine almost entirely from Merlot grapes, on occasion with small amounts of Cabernet Franc, and produces no second wine...
and Château Le Pin
Château Le Pin
Château Le Pin, or simply Le Pin, is an unclassed Bordeaux wine from the appellation Pomerol. The unusually small estate is located on the Right Bank of France’s Gironde estuary in the commune of Pomerol near the hamlet of Catusseau, and its wine is periodically one of the world's most expensive...
in Pomerol
Pomerol
Pomerol is a commune in the Gironde department in Aquitaine in southwestern France.It is located near Bordeaux.-Population:-Wine:The mostly small-sized producers in this area of about produce red wines. As in the neighbouring appellation of Saint-Émilion, the predominant grape variety is Merlot,...
. The red wines produced are usually blended, from Cabernet Sauvignon
Cabernet Sauvignon
Cabernet Sauvignon is one of the world's most widely recognized red wine grape varieties. It is grown in nearly every major wine producing country among a diverse spectrum of climates from Canada's Okanagan Valley to Lebanon's Beqaa Valley...
, Merlot
Merlot
Merlot is a darkly blue-coloured wine grape, that is used as both a blending grape and for varietal wines. The name Merlot is thought to derive from the Old French word for young blackbird, merlot, a diminutive of merle, the blackbird , probably from the color of the grape. Merlot-based wines...
and sometimes Cabernet Franc
Cabernet Franc
Cabernet Franc is one of the major black grape varieties worldwide. It is principally grown for blending with Cabernet Sauvignon and Merlot in the Bordeaux style, but can also be vinified alone - as in the Loire's Chinon...
. Bordeaux also makes dry and sweet white wines, including some of the world's most famous sweet wines from the Sauternes
Sauternes (wine)
Sauternes is a French sweet wine from the Sauternais region of the Graves section in Bordeaux. Sauternes is made from Sémillon, Sauvignon Blanc, and Muscadelle grapes that have been affected by Botrytis cinerea, also known as noble rot. This causes the grapes to become partially raisined,...
appellation, such as Château d'Yquem
Château d'Yquem
Château d'Yquem is a Premier Cru Supérieur wine from the Sauternes, Gironde region in the southern part of the Bordeaux vineyards known as Graves. In the Bordeaux Wine Official Classification of 1855, Château d'Yquem was the only Sauternes given this rating, indicating its perceived superiority...
.
Burgundy
BurgundyBurgundy wine
Burgundy wine is wine made in the Burgundy region in eastern France, in the valleys and slopes west of the Saône River, a tributary of the Rhône. The most famous wines produced here - those commonly referred to as "Burgundies" - are red wines made from Pinot Noir grapes or white wines made from...
or Bourgogne in eastern France is a region where red and white wines are equally important. Probably more terroir-conscious than any other region, Burgundy is divided into the largest number of appellations of any French region. The top wines from Burgundy's heartland in Côte d'Or
Côte d'Or (escarpment)
The Côte d'Or is a limestone escarpment in Burgundy, France that lends its name to the department which was formed around it...
command high prices.
The Burgundy region is divided in four main parts:
- The Cote de NuitsCôte de NuitsThe Côte de Nuits is a French wine region located in the northern part of the Côte d'Or, the limestone ridge that is at the heart of the Burgundy wine region. It extends from Dijon to just south of Nuits-Saint-Georges, which gives its name to the district and is the regional center...
(from Marsannay-La-Cote down to Nuits-Saint-Georges) - The Cote de BeauneCôte de BeauneThe Côte de Beaune area is the southern part of the Côte d'Or, the limestone ridge that is home to the great names of Burgundy wine. The Côte de Beaune starts between Nuits-Saint-Georges and Beaune, and extends southwards for about 25 km to the River Dheune...
(from north of Beaune to Santenay) - The Cote ChalonnaiseCôte ChalonnaiseCôte Chalonnaise is a subregion of the Burgundy wine region of France. Côte Chalonnaise lies to the south of the Côte d'Or continuing the same geology southward. It is still in the main area of Burgundy wine production but it includes no Grand cru vineyards...
- The MaconnaisMâconnaisThe Mâconnais district lies in the south of the Burgundy wine region in France, west of the River Saône. It takes its name from the town of Mâcon. It is best known as a source of good value white wines made from the Chardonnay grape; the wines from Pouilly-Fuissé are particularly sought-after....
Two parts of Burgundy that are sometimes considered as separate regions are:
- BeaujolaisBeaujolaisBeaujolais is a French Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée wine generally made of the Gamay grape which has a thin skin and is low in tannins. Like most AOC wines they are not labeled varietally. Whites from the region, which make up only 1% of its production, are made mostly with Chardonnay grapes...
in the south, close to the Rhône Valley region, where mostly red wines are made in a fruity style that is usually consumed young. "Beaujolais Nouveau" is the only wine that can be legally consumed in the year of its production (Third week end of November) - Chablis, halfway between Côte d'Or and Paris, where white wines are produced on chalky soil giving a more crisp and steely style than the rest of Burgundy.
There are two main grape varieties used in Burgundy – Chardonnay for white wines, and Pinot Noir for red. White wines are also sometimes made from Aligoté, and other grape varieties will also be found occasionally.
Champagne
Champagne, situated in eastern France, close to Belgium and LuxembourgLuxembourg
Luxembourg , officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg , is a landlocked country in western Europe, bordered by Belgium, France, and Germany. It has two principal regions: the Oesling in the North as part of the Ardennes massif, and the Gutland in the south...
, is the coldest of France's major wine regions and home to its major sparkling wine. Champagne wines can be both white and rosé. A small amount of still wine is produced in Champagne (as AOC Coteaux Champenois) of which some can be red wine.
Corsica
CorsicaCorsica wine
Corsica wine is wine made on the Mediterranean island of Corsica. Located 90km west of Italy, 170km southeast of France and 11km north of the island of Sardinia, the island is a territorial collectivity of France, but many of the region's winemaking traditions and its grape varieties are Italian in...
is an island in the Mediterranean the wines of which are primarily consumed on the island itself. It has nine AOC regions and an island-wide vin de pays designation and is still developing its production methods as well as its regional style.
Jura
JuraJura wine
Jura wine, is French wine produced in the Jura département. Located between Burgundy and Switzerland, this cool climate wine region produces wines with some similarity to Burgundy and Swiss wine. Jura wines are distinctive and unusual wines, the most famous being vin jaune, which is made by a...
, a small region in the mountains close to Switzerland where some unique wine styles, notably Vin Jaune and Vin de Paille, are produced. The region covers six appellations and is related to Burgundy through its extensive use of the Burgundian grapes Chardonnay and Pinot Noir, though other varieties are used. It also shares cool climate with Burgundy.
Languedoc-Roussillon
Languedoc-RoussillonLanguedoc wine
Languedoc - Roussillon wine, including the vin de pays labeled Vin de Pays d'Oc, is produced in southern France. While "Languedoc" can refer to a specific historic region of France and Northern Catalonia, usage since the 20th century has primarily referred to the northern part of the...
is the largest region in terms of vineyard surface, and the region in which much of France's cheap bulk wines have been produced. While still the source of much of France's and Europe's overproduction, the so-called "wine lake
Wine lake
The wine lake refers to the continuing supply surplus of wine produced in the European Union. A major contributor to that glut is the Languedoc-Roussillon, which produces over one-third of the grapes grown in France. In 2007 it was reported that for the previous several vintages, European...
", Languedoc-Roussillon is also the home of some innovative producers who combine traditional French wine and international styles while using lessons from the New World
New World
The New World is one of the names used for the Western Hemisphere, specifically America and sometimes Oceania . The term originated in the late 15th century, when America had been recently discovered by European explorers, expanding the geographical horizon of the people of the European middle...
. Much Languedoc-Roussillon wine is sold as Vin de Pays d'Oc.
Loire
Loire valleyLoire Valley (wine)
The Loire Valley wine region includes the French wine regions situated along the Loire River from the Muscadet region near the city of Nantes on the Atlantic coast to the region of Sancerre and Pouilly-Fumé just southeast of the city of Orléans in north central France. In between are the regions of...
is a primarily white-wine region that stretches over a long distance along the Loire River in central and western France, and where grape varieties and wine styles vary along the river. Four sub-regions are situated along the river:
- Upper Loire is known for its Sauvignon BlancSauvignon blancSauvignon Blanc is a green-skinned grape variety which originates from the Bordeaux region of France. The grape most likely gets its name from the French word sauvage and blanc due to its early origins as an indigenous grape in South West France., a possible descendant of savagnin...
, producing wines such as Sancerre AOC, but also consisting of several VDQS areas; - TouraineTouraineThe Touraine is one of the traditional provinces of France. Its capital was Tours. During the political reorganization of French territory in 1790, the Touraine was divided between the departments of Indre-et-Loire, :Loir-et-Cher and Indre.-Geography:...
produces cold climate-styled white wines (dry, sweet or sparkling) from Chenin BlancChenin BlancChenin blanc , is a white wine grape variety from the Loire valley of France. Its high acidity means it can be used to make everything from sparkling wines to well-balanced dessert wines, although it can produce very bland, neutral wines if the vine's natural vigor is not controlled...
in Vouvray AOC and red wines from Cabernet FrancCabernet FrancCabernet Franc is one of the major black grape varieties worldwide. It is principally grown for blending with Cabernet Sauvignon and Merlot in the Bordeaux style, but can also be vinified alone - as in the Loire's Chinon...
in Bourgueil AOC and Chinon AOC; - Anjou-Saumur is similar to the Tourain wines with respect to varieties, but the dry Savennières AOC and sweet Coteaux du Layon AOC are often more powerful than their upstream neighbours. Saumur AOC and Saumur-Champigny AOC provides reds; and
- Pays Nantais is situated closest to the Atlantic, and Muscadet AOC produces white wines from the Melon de BourgogneMelon de BourgogneMelon de Bourgogne or Melon is a variety of white grape grown primarily in the Loire Valley region of France. It is also grown in North America. It is best known through its use in the white wine Muscadet....
grape.
Provence
ProvenceProvence wine
Provence wine comes from the French wine-producing region of Provence in southeast France. The Romans called the area nostra provincia , giving the region its name...
, in the south-east and close to the Mediterranean. It is perhaps the warmest wine region of France and produces mainly rosé and red wine. It covers eight major appellations led by the Provence flagship, Bandol. Some Provence wine can be compared with the Southern Rhône wines as they share both grapes and, to some degree, style and climate. Provence also has a classification of its most prestigious estates, much like Bordeaux.
Rhône
Rhone Valley, primarily a red-wine region in south-eastern France, along the Rhône RiverRhône River
The Rhone is one of the major rivers of Europe, rising in Switzerland and running from there through southeastern France. At Arles, near its mouth on the Mediterranean Sea, the river divides into two branches, known as the Great Rhone and the Little Rhone...
. The styles and varietal composition of northern and southern Rhône differ, but both parts compete with Bordeaux as traditional producers of red wines.
Savoy
SavoySavoy wine
Savoy or, in French, Savoie is a wine region situated in the Savoy region in eastern France, and is sometimes referred to as the country of the Allobroges.The Savoy landscape is distinctly alpine...
or Savoie, primarily a white-wine region in the Alps close to Switzerland, where many grapes unique to this region are cultivated.
South West France
South West FranceSouth West France (wine region)
South West France or in French Sud-Ouest, is a wine region in France covering several wine-producing areas situated respectively inland from, and south of, the wine region of Bordeaux...
or Sud-Ouest, a somewhat heterogeneous collection of wine areas inland or south of Bordeaux. Some areas produce primarily red wines in a style reminiscent of red Bordeaux, while other produce dry or sweet white wines. Areas within Sud-Ouest include among other:
- BergeracBergerac, DordogneBergerac is a commune and a sub-prefecture of the Dordogne department in southwestern France.-Population:-Economy:The region is primarily known for wine and tobacco...
and other areas of upstream DordogneDordogneDordogne is a départment in south-west France. The départment is located in the region of Aquitaine, between the Loire valley and the High Pyrénées named after the great river Dordogne that runs through it...
; - Areas of upstream GaronneGaronneThe Garonne is a river in southwest France and northern Spain, with a length of .-Source:The Garonne's headwaters are to be found in the Aran Valley in the Pyrenees, though three different locations have been proposed as the true source: the Uelh deth Garona at Plan de Beret , the Ratera-Saboredo...
, including Cahors; - Areas in GasconyGasconyGascony is an area of southwest France that was part of the "Province of Guyenne and Gascony" prior to the French Revolution. The region is vaguely defined and the distinction between Guyenne and Gascony is unclear; sometimes they are considered to overlap, and sometimes Gascony is considered a...
, also home to the production of ArmagnacArmagnac (drink)Armagnac is a distinctive kind of brandy or eau de vie produced in the Armagnac region in Gascony, southwest France. It is distilled from wine usually made from a blend of Armagnac grapes, including Baco 22A, Colombard, and Ugni Blanc, using column stills rather than the pot stills used in the...
, Madiran, Côtes de GascogneCôtes de GascogneCôtes de Gascogne is a wine-growing district in Gascony producing principally white wine. It is mainly located in the département of the Gers in the French region Midi-Pyrénées, and it belongs to the wine region South West France. The designation Côtes the Gascogne is used for a Vin de Pays ...
, Côtes de Saint-MontSaint-MontSaint-Mont is a commune in the Gers department in southwestern France.-Population:-Saint-Mont wine:Wines are produced under the VDQS designation Saint-Mont and the area's vineyards are part of the South West France wine region...
, Pacherenc du Vic-Bilh and TursanTursanTursan is a Vin délimité de qualité supérieure for wine in South West France since 1958 .-Presentation:...
; - BéarnBéarnBéarn is one of the traditional provinces of France, located in the Pyrenees mountains and in the plain at their feet, in southwest France. Along with the three Basque provinces of Soule, Lower Navarre, and Labourd, the principality of Bidache, as well as small parts of Gascony, it forms in the...
, such as Jurançon; and - Basque CountryNorthern Basque CountryThe French Basque Country or Northern Basque Country situated within the western part of the French department of the Pyrénées-Atlantiques constitutes the north-eastern part of the Basque Country....
areas, such as IrouléguyIrouléguy AOCIrouléguy AOC wines come from Lower Navarre in the Northern Basque Country, France and are usually considered as part of the wine region of South West France . They are named after the village of Irouléguy and are the only wines with AOC certification in the Northern Basque Country...
.
There are also several smaller production areas situated outside these major regions. Many of those are VDQS
VDQS
Vin Délimité de Qualité Supérieure , usually abbreviated as VDQS, is the second highest category of French wine, below Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée in rank, but above Vin de pays . VDQS is sometimes written as AOVDQS, with AO standing for Appellation d'Origine...
wines, and some, particularly those in more northern locations, are remnants of production areas that were once larger.
Trends
France has traditionally been the largest consumer of its own wines. However, wine consumption has been dropping in France for 40 years. During the decade of the 1990s, per capita consumption dropped by nearly 20 percent. Therefore, French wine producers must rely increasingly on foreign marketsExport
The term export is derived from the conceptual meaning as to ship the goods and services out of the port of a country. The seller of such goods and services is referred to as an "exporter" who is based in the country of export whereas the overseas based buyer is referred to as an "importer"...
. However, consumption has also been dropping in other potential markets such as Italy, Spain and Portugal.
The result has been a continuing wine glut, often called the wine lake
Wine lake
The wine lake refers to the continuing supply surplus of wine produced in the European Union. A major contributor to that glut is the Languedoc-Roussillon, which produces over one-third of the grapes grown in France. In 2007 it was reported that for the previous several vintages, European...
. This has led to the distillation of wine into industrial alcohol as well as a government program to pay farmers to pull up their grape vines through vine pull schemes
Vine pull schemes
Vine pull schemes are programs whereby grape growers receive a financial incentive to pull up their grape vines, a process known as arrachage in French. A large program of the kind was initiated by the European Union in 1988 to reduce the wine lake glut from overproduction and declining demand...
. A large part of this glut is caused by the re-emergence of Languedoc wine
Languedoc wine
Languedoc - Roussillon wine, including the vin de pays labeled Vin de Pays d'Oc, is produced in southern France. While "Languedoc" can refer to a specific historic region of France and Northern Catalonia, usage since the 20th century has primarily referred to the northern part of the...
.
Immune from these problems has been the market for Champagne as well as the market for the expensive ranked or classified wines. However, these constitute only about five percent of French production.
French regulations in 1979 created simple rules for the then-new category of Vin de pays
Vin de pays
Vin de pays is a French term meaning "country wine". Vins de pays are a step in the French wine classification which is above the table wine classification, but below the VDQS and Appellation d'origine contrôlée classifications...
. The Languedoc-Roussillon
Languedoc-Roussillon
Languedoc-Roussillon is one of the 27 regions of France. It comprises five departments, and borders the other French regions of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur, Rhône-Alpes, Auvergne, Midi-Pyrénées on the one side, and Spain, Andorra and the Mediterranean sea on the other side.-Geography:The region is...
region has taken advantage of its ability to market varietal wines.
Organisations
L'Office national interprofessionnel des vins, abbreviated ONIVINS, is a FrenchEconomy of France
France is the world's fifth largest economy by nominal figures and the ninth largest economy by PPP figures. It is the second largest economy in Europe in nominal figures and third largest economy in Europe in PPP figures...
association of vintner
Vintner
A vintner is a wine merchant. You pronounce it like this In some modern use, in particular in American English, the term is alsoused as a synonym for winemaker....
s.
See also
- List of Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée wines
- List of VDQS wines
- Wine labelWine labelWine labels are important sources of information for consumers since they tell the type and origin of the wine. The label is often the only resource a buyer has for evaluating the wine before purchasing it...
- History of WineHistory of wineThe history of wine spans thousands of years and is closely intertwined with the history of agriculture, cuisine, civilization and humanity itself...
- List of Vins de Primeur
- Old World wineOld World wineOld World wine refers primarily to wine made in Europe but can also include other regions of the Mediterranean basin with long histories of winemaking such as North Africa and the Near East. The phrase is often used in contrast to "New World wine" which refers primarily to wines from New World wine...

